Windowsコンピューターは、 DNSサーバーによってホストされているドメインゾーンのDNSレコードを(DNS)24時間ごと(every 24 hours)に更新します。Windowsコンピューターがドメインから削除された場合、またはDNSサーバー(DNS Server)のDNSレコードを更新できない場合、そのWindowsコンピューターの(Windows)DNSレコードは(DNS)DNSデータベースに残り、古いDNSレコードと見なされます。古いDNSレコードは、手動で削除しない限り、 DNSデータベースに残ります。(DNS)DNSエージング(DNS Aging)とスカベンジング(Scavenging)は古いDNSレコードをすばやく特定し、手動で削除します(quickly identify the stale DNS records and remove them manually)。この投稿では、DNSエージング(DNS Aging)とスカベンジングとは何かについて説明し、 (Scavenging)Windowsサーバーでこの機能を構成/有効化するために必要な手順の概要を説明します。
DNSエージングとは何ですか?
エージングは、古い(Aging)DNSレコードを識別できるようにする機能です。実際には2つの間隔を使用し、両方が経過するとDNSレコードは失効したと見なされます。
これらの間隔は次のとおりです。
- 非更新間隔(Non-Refresh Interval):リソースレコードを更新できない期間です(*)。この期間中に更新を拒否すると、同じ情報を再度複製する必要がないため、複製トラフィックが減少します。
- 更新間隔(Refresh Interval):リソースレコードを更新できる期間です(*)。
(*)リソースレコードの更新は、ホスト名とIPが変更されないDNS動的更新です。(DNS)リソースレコードの登録済みIPを変更するためのDNS動的更新は、更新とは見なされず、非更新間隔(Interval)から除外されます。
DNSスカベンジングとは何ですか?
清掃は、 DNS(DNS)ゾーン内の古いリソースレコードのクリーンアップと削除を可能にする機能です。
古いリソースレコードは、以下でスカベンジングが有効になっている場合にのみ削除されます。
- リソースレコード
- リソースレコードが存在するDNSゾーン(DNS)
- リソースレコードが存在するDNS(DNS)ゾーンのプライマリコピーをホストしている少なくとも1つのDNS
DNSサーバーで有効にすると、定期的に清掃が行われます。古くなったリソースレコードは、 DNS(DNS)スカベンジングの次のサイクルまで存在する可能性があります。
DNSエージング(DNS Aging)とスカベンジングを有効にしないと、次の状況に直面する可能性があります。
- ドメイン(Domain)ゾーンは、不要なDNSレコードを保持します。(DNS)
- 一定期間にわたって、DNSデータベースのサイズは増加します。
- DNSサーバーサービスが(DNS)DNSデータベースを列挙してメモリにロードするのに時間がかかります。
- DNSサーバーが(DNS)DNSクエリに応答するまでに時間がかかります。これは、DNSサーバーが必要な(DNS)DNSレコードを見つけて応答を送信する前に、すべてのDNSレコードを列挙する必要があるためです。
- DNSサーバーは、ネットワーク上に存在しなくなった無効なDNSレコードで応答し、ネットワーク上で名前の解決の問題を引き起こす可能性があります。(DNS)
- 古いDNS(DNS)レコードで同じIPアドレスが使用されている場合、別のWindowsクライアントコンピューターが自身のDNSレコードを登録できない可能性があります。
(Enable)DNSエージング(Configure DNS Aging)とスカベンジングを有効にして構成する
Windowsサーバーで(Windows)DNSエージング(DNS Aging)とスカベンジングを正常に構成/有効化するには、この順序で3つの手順を実行する必要があります。
- サーバーのDNSレコードを確認する(Check Server DNS Records)(非常に重要な最初のステップ)
- DNSゾーンでDNSエージングとスカベンジングを有効にする
- DNSゾーンのプライマリコピーをホストしている少なくとも1つのDNSサーバーで(DNS)DNSスカベンジングを有効にする
詳細な手順を見てみましょう。
1]サーバーのDNSレコードを確認します(Check Server DNS Records)(非常に重要な最初のステップ)
この手順を最初に実行しないと、サーバーのDNSレコードが削除される可能性があるため、この手順は非常に重要です。予防策として、 DNS(DNS)サーバーやレコードもバックアップすることをお勧めします。
清掃はタイムスタンプで機能するため、タイムスタンプのあるDNSレコードはすべて処理され、場合によっては削除されます。したがって、サーバーのDNS(DNS)レコードをチェックし、それらが静的であることを確認することをお勧めします。
レコードを確認するには、DNSコンソールを開き、[タイムスタンプ(Timestamp)]列を確認するために、サーバーを静的に設定する必要があります。そうでない場合は、単にレコードを開き、[古くなったらこのレコードを削除(Delete this record when it becomes stale )する]チェックボックスをオフにします。
それが完了したら、DNSコンソールを更新すると、そのレコードのタイムスタンプが静的に表示されます。(static)
次の手順に進む前に、すべてのサーバーレコードを確認し、静的に変更してください。
2] DNSゾーンでDNS(Enable DNS)エージングとスカベンジングを有効にする
以下をせよ:
- DNS管理ツール(dnsmgmt.msc)を使用して、DNS ゾーンのプロパティに移動し、[(zones)エージング…(Aging…) ]をクリックします 。
- Scavenge stale resource records チェックボックスを有効にし、Non- Refresh間隔(Refresh)とRefresh間隔期間を指定します。
- [ OK]をクリックします。(OK.)
DNSサーバー上のすべての(DNS)DNSゾーンでDNSエージングとスカベンジングをデフォルトで有効にするには、次の手順を実行する必要があります。
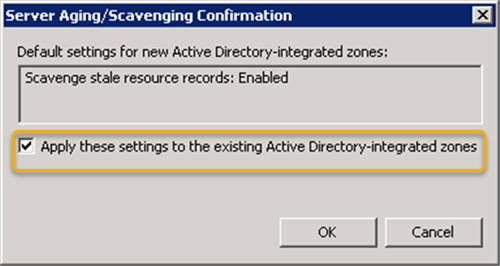
- (Right-click)サーバー名を右クリックし、[Set Aging/Scavenging for All Zones…
- Scavenge stale resource records チェックボックスを有効にし、Non- Refresh間隔(Refresh)とRefresh間隔期間を指定します。
- [ OK]をクリックします。(OK.)
- [これらの設定を既存のActiveDirectory統合ゾーンに適用する(Apply these settings to the existing Active Directory-integrated zones )]チェックボックスをオンにします(これにより、既存のActive Directory統合ゾーンのDNSエージングと清掃が有効になり(Active Directory-integrated)ます(DNS))。
- [ OK]をクリックします。(OK.)
次に、次の最後のステップに進みます。
3] DNSゾーンのプライマリコピーをホストしている少なくとも1つのDNSサーバーで(DNS)DNSスカベンジングを有効にします(Enable DNS)
以下をせよ:
- DNSサーバーのプロパティに移動します。
- [詳細設定 (Advanced )]タブに移動します。
- [古いレコードの自動清掃を有効に(Enable automatic scavenging of stale records )する]チェックボックスをオンにします。
- 完了したら、清掃(Scavenging)期間を指定します(これは、DNSサーバーでの(DNS)清掃(Scavenging)の繰り返し間隔です)。
- [ OK]をクリックします。(OK.)
That’s it! That completes the setup of DNS Aging and Scavenging.
How to Enable & Configure DNS Aging & Scavenging in Windows Server
Windows computers refresh their DNS records in the domain zones hosted by the DNS servers every 24 hours. When a Windows computer is removed from the domain or is not able to update its DNS record in the DNS Server, the DNS record of that Windows computer remains in the DNS database and is considered to be a stale DNS record. The stale DNS records remain in the DNS database unless it’s manually removed. DNS Aging and Scavenging helps to quickly identify the stale DNS records and remove them manually. In this post, we will provide a description of what DNS Aging and Scavenging is, as well as outline the steps required to configure/enable this feature on the Windows server.
What is DNS Aging?
Aging is a feature that allows identifying stale DNS records. It actually uses two intervals and a DNS record is considered as stale once both are elapsed.
These intervals are:
- Non-Refresh Interval: It is a period of time during which a resource record cannot be refreshed (*). Refusing the refresh during this period of time reduces the replication traffic as there is no need to replicate the same information again.
- Refresh Interval: It is a period of time during which a resource record could be refreshed (*).
(*) A resource record refresh is a DNS dynamic update where the hostname and IP do not change. A DNS dynamic update to change the registered IP for a resource record is not considered as a refresh and is exempt from the Non-Refresh Interval.
What is DNS Scavenging?
Scavenging is a feature that allows the cleanup and removal of stale resource records in DNS zones.
A stale resource record will be removed only if scavenging is enabled on:
- The resource record
- The DNS zone where the resource record exists
- At least one DNS hosting a primary copy of the DNS zone where the resource record exists
Scavenging occurs on recurring intervals when enabled on a DNS server. A stale resource record can then still exist until the next cycle of DNS scavenging.
If you do not enable DNS Aging and scavenging, you might face the following situations:
- Domain zones will hold the DNS records that are not needed.
- Over a period of time, the DNS database size will be increased.
- It will take more time for the DNS server service to enumerate and load the DNS database in memory.
- It will take more time for the DNS server to respond to a DNS query. This is because the DNS server needs to enumerate all DNS records before it can find the required DNS record and then send a response.
- DNS servers might respond with an invalid DNS record that no longer exists on the network causing naming resolution problems on the network.
- Another Windows client computer might not be able to register its own DNS records if the same IP address is being used by a stale DNS record.
Enable & Configure DNS Aging and Scavenging

To successfully configure/enable DNS Aging and Scavenging on Windows server, you need to follow 3 steps in this order;
- Check Server DNS Records (very important first step)
- Enable DNS aging and scavenging on DNS zones
- Enable DNS scavenging on at least one DNS server hosting primary copies of your DNS zones
Let’s take a look at the steps involved in detail.
1] Check Server DNS Records (very important first step)
This step is crucial because if you don’t follow this step first you could end up deleting server DNS records. As a precaution, you may want to also backup your DNS server and or records.
Scavenging works on timestamps, so any DNS record with a timestamp will get processed and possibly deleted. So it’s recommended you check your server DNS records and make sure they are static.
To check your records open the DNS console and check the Timestamp column, your servers should be set to static. If not, simply open the record then uncheck the Delete this record when it becomes stale box.
Once you have done that, refresh the DNS console the timestamp will now show static for that record.
Check all your server records and change them to static before moving onto the next step.
2] Enable DNS aging and scavenging on DNS zones
Do the following:
- Using DNS administrative tool (dnsmgmt.msc), go to the properties of your DNS zones and then click on Aging…
- Enable Scavenge stale resource records checkbox, specify the Non-Refresh interval, and Refresh interval periods.
- Click OK.
To make DNS aging and scavenging enabled by default for all DNS zones on a DNS server, you need to proceed as follows:
- Right-click on the server name and then click on Set Aging/Scavenging for All Zones…
- Enable Scavenge stale resource records checkbox, specify the Non-Refresh interval, and Refresh interval periods.
- Click OK.
- Check the Apply these settings to the existing Active Directory-integrated zones box (This will enable DNS aging and scavenging for the existing Active Directory-integrated zones).
- Click OK.
Now, proceed with the next and final step.
3] Enable DNS scavenging on at least one DNS server hosting primary copies of your DNS zones
Do the following:
- Go to the properties of your DNS server.
- Go to Advanced tab.
- Check the Enable automatic scavenging of stale records box.
- Once done, specify the Scavenging period (That is the recurring interval for Scavenging on a DNS server).
- Click OK.
That’s it! That completes the setup of DNS Aging and Scavenging.

