サイバー犯罪者が情報を入手できるように、インターネット(Internet)のユーザーを危険にさらすために使用されている方法はたくさんあります。コンピューターが危険にさらされると、サイバー犯罪者はユーザーのデータを好きなように使用できます。このようなイベントは、サイバー犯罪者があなたのIDを使用してローンを組むなどして、あなたを混乱させるID盗難につながる可能性さえあります。(Identity Theft)(Identity Theft)コンピュータを危険にさらす多くの新しい方法の中には –Malvertisingがあります。マルバタイジングとは何か、そしてそれを避けて安全を保つ方法を見てみましょう。
マルバタイジングとは
Malicious + Advertisingという2つの単語が含まれています。これは、ユーザーをフィッシング(Phishing)(Phishing)Webサイトに誘導する悪意のある誤解を招く広告だけではありません。マルバタイジング(Malvertising)とは、広告にカーソルを合わせたりクリックしたりしたときに、コンピュータに短い悪意のあるコードをダウンロードすることで、コンピュータを危険にさらすことです。一部の広告は、Webサイトがバックグラウンドでロードされている間に、悪意のあるコードをコンピューターにダウンロードすることさえあります。このような場合、ユーザーはWebサイトにアクセスするだけで、ドライブバイダウンロード(Drive-by-downloads)(Drive-by-downloads)を介して感染する可能性があります。
サイバー犯罪者は、コンピューターをハッキングする手段として広告を使用しています。これらの広告は本物のように見えるので、ユーザーはWebサイトに移動することを期待してクリックし、そこで広告に関する詳細情報を入手できます。ただし、リダイレクトされる代わりに、クリックアクションにより、小さいが悪意のあるコードがユーザーのコンピューターにダウンロードされます。実際、広告がブラウザによってロードされている場合でも、感染はバックグラウンドでサイレントに発生する可能性があります。これらの広告を配信する広告ネットワークは非常に巨大であるため、悪意のある広告の背後にいる個人または組織を特定することはほぼ不可能です。多くの人気のあるWebサイトも、広告が悪意のあるものであることを知らないため、有害な意図なしにそのような広告を無意識のうちに配信することになります。
マルバタイジングはどのように機能しますか
そのウェブサイトに悪意のある広告を掲載するためにウェブサイトをハッキングする必要はありません。代わりに、犯罪者は広告ネットワークを使用して、何千万ものWebサイトに広告を挿入します。インターネット(Internet)での広告の仕組みを知っていれば、広告が送信されると、精査された後、インターネット(Internet)にプッシュされ、ユーザーがあらゆる種類の情報を入力したキーワードに関連するWebサイトに表示されます。
サイバー犯罪者は、ディスプレイ広告を使用してマルウェアを配布します。攻撃の可能性のあるベクトルには、広告クリエイティブ内に隠された悪意のあるコード(swfファイルなど)、Webページに埋め込まれた実行可能ファイル、またはソフトウェアダウンロードにバンドルされた実行可能ファイルが含まれます。すべてのWebパブリッシャーとWebサイトは、広告のSWF(SWF)(Flash)ファイル、GIFファイル、またはランディングページ内に悪意のあるコードを隠して、ソフトウェアを拡散しようとするマルウェア作成者の潜在的な標的です。
広告主または代理店が感染した広告を提供した場合、あなたのコンピューターと個人情報、およびあなたのサイトの訪問者の情報は深刻な危害にさらされる可能性があります。GoogleのAnti-Malvertising.comWebサイトには、広告発行者とWebサイト所有者が(Google’s Anti-Malvertising.com website)確認し(check out)たいヒントがいくつかあります。
評判の高い広告ネットワークは、禁止されている単語や禁止されている製品などの明らかな要因について広告を精査しますが、コードを適切に精査しなくても、不正行為がすり抜ける可能性があります。このようなシナリオでは、広告ネットワークはさまざまなWebサイトに感染性の広告を表示することにより、何百万ものユーザーを危険にさらします。そして、良いお金の誘惑のために、そのようなマルバタイジングを無視するかもしれない他の広告ネットワークがまだあります。
その他の場合、犯罪者は本物の機関を代表していると主張し、広告ネットワークではなくWebサイトに直接クリーンな広告を送信します。後で、彼らは悪意のあるコードを、ウェブサイト上の広告をクリックするユーザーのコンピューターにダウンロードされる広告に添付します。しばらくして、目標が達成されると、犯罪者はコードを削除します。広告は契約期間中そこにとどまります。コードを添付してから削除するまでの間(Between)に、犯罪者は多くのコンピューターをハッキングするため、さまざまなインターネット(Internet)ユーザーに関する多くの情報が手元にあります。彼らはこの情報を好きな目的に使うことができます。
マルバタイジングを回避する方法
(Precaution)マルバタイジングを避けるための唯一の鍵は予防策です。悪意のある広告は、評判の高いWebサイトにも表示される可能性があります。明らかに有望に見える広告がある場合は、単にそれらを避けてください。たとえば、あなたが100人目の訪問者であり、賞品に選ばれたことを示すポップアップは無視してください。お金、贈り物、割引クーポンなどを無料で約束するものは避けてください。ウェブサイトに表示される広告はネットワーク広告主の結果であるため、悪意のあるコードがないか広告を確認するのは広告主の責任です。それらのほとんどは、言語の冒とく的な表現をチェックして広告を公開するだけです。最近では、Google AdSenseネットワークのような評判の高いネットワークがコード全体をチェックしていますが、悪意のある広告が侵入するというまれなケースがまだあります。
クラウドベースのマルバタイジング検出プラットフォームとソリューションがいくつかあり、Webサイトに配信されるオンライン広告の安全性に関する洞察と制御を提供します。大規模なサイト運営者は、このオプションを確認することをお勧めします。ユーザーとして、優れたセキュリティソフトウェアを使用し、安全なブラウジングの習慣を身に付けていることを確認してください。また、オペレーティングシステムと、ブラウザプラグインを含む、インストールされているソフトウェアを常に最新の状態に保つことを忘れないでください。
マルバタイジングの最近の例
DeviantART.comの特定の(Certain)広告は、疑いを持たないユーザーに不要な可能性のあるアプリケーションをインストールするために、ユーザーを(Optimum Installer)OptimumInstallerWeb(DeviantART.com)ページにリダイレクトしていました。ハッカーは、マルウェアを配布するためにClicksorAdNetworkを侵害していました。(Clicksor Ad Network)Blackhole Exploitキットは、ClicksorAdNetworkなど(Clicksor Ad Network)を介して配布されていました。さらに別のごく最近のケースでは、JavaエクスプロイトはJava.comの広告を介して提供されていた、と(Java.com)FoxIT.comは報告しました。
インフォグラフィック(Infographic)このインフォグラフィックは、(Infographic)マルバタイジング(Malvertising)がどのように機能するかを示しています。
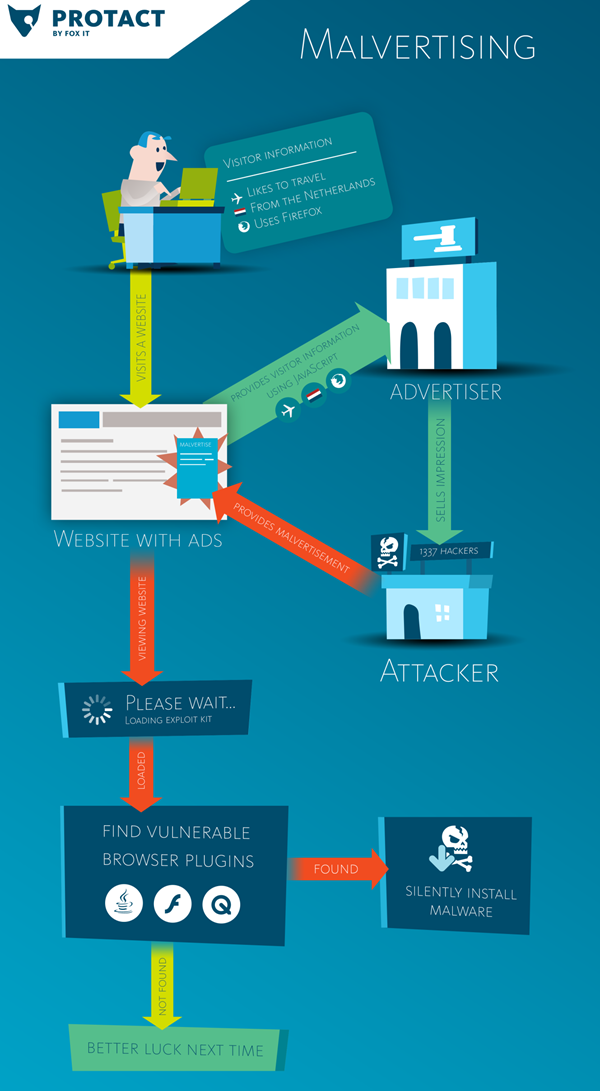
したがって、サイト運営者は、システム内でのマルウェアの拡散を防ぎ、被害を封じ込めるために、強力なスクリーニング方法を備え、マルバタイズメントのインスタンスが見つかったらすぐに行動を起こすような広告ネットワークとエクスチェンジのみを使用することが重要です。発生する可能性があります。
悪い(Bad)、脆弱で安全でないプラグインはしばしば危険にさらされます。したがって、前述したように、優れたセキュリティソフトウェアを使用し、安全なブラウジングの習慣を身に付けていることを確認してください。また、オペレーティングシステムと、ブラウザプラグインを含む、インストールされているソフトウェアを常に最新の状態に保つことを忘れないでください。
Stay safe!
Malvertising attacks: Definition, examples, protection, security
There are many methods being used to comрromise users of the Internet so that their infоrmation can be obtained by cуber-criminаls. Once a computer iѕ compromised, the cyber-criminаls can use the user’s data for anything they want. Such events maу even result in Identity Theft, where cyber-criminals use your identity for taking loans, etc. and leave you in a mess. Among the many newer methods of compromising a computer is – Malvertising. Let us take a look at what is malvertising and how to stay safe by avoiding it.
What is Malvertising
Malvertising or Maladvertising contains two words: Malicious + Advertising. This is not just about malicious misleading advertisements that lure users to Phishing websites. Malvertising is about compromising your computer, by downloading a short malicious code on to it, when you hover on or click on an advertisement. Some adverts will even download malicious code to your computer, while the website is still loading in the background. In such cases, by simply visiting a website, users can get infected via Drive-by-downloads.
Cybercriminals are using advertisements as a means to hack into your computers. Since these advertisements look genuine, users click on them expecting to be taken to a website, where they can get more information about the advert. However, instead of being redirected, the click action triggers a download of a small but malicious code to users’ computers. In fact, the infection can even take place silently in the background, even as the ad is being loaded by the browser. Since the ad networks serving these ads are pretty huge, it is nearly impossible to identify the person or organization behind the malicious advertisement. Many popular websites too end up unknowingly serving such adverts without any harmful intent, as they do not know that the adverts are malicious.
How Does Malvertising Work
One does not need to hack a website to place malicious advertisements on that website. Instead, criminals use advertising networks to insert their advertisements on thousands of millions of websites. If you know how advertising on the Internet works, you know that once an ad is submitted, after scrutiny, it is pushed into the Internet where it appears on websites related to the keywords typed by users for any kind of information.
Cyber-criminals use display advertising to distribute malware. Possible vectors of attack include malicious code hidden within an ad creative (such as a swf file), executables embedded on a webpage, or bundled within software downloads. All web publishers and websites are potential targets for malware authors attempting to spread their software by hiding malicious code within an ad’s SWF (Flash) file, GIF file or landing page.
If an advertiser or agency provides you with an infected ad, your computer, and personal information, and that of your site’s visitors, can be exposed to serious harm. Google’s Anti-Malvertising.com website has a few tips ad publishers and website owners may want to check out.
Although reputed advertising networks do scrutinize the ads for the obvious factors, like banned words, prohibited products, etc., without proper scrutiny of the code, malvertisements can slip through! In such a scenario, the ad network places millions of users at risk by displaying infectious advertisements on various websites. And there are yet other ad networks who may even ignore such malvertising, for the lure of good money.
In other cases, criminals claim to represent genuine institutions, submit clean adverts directly to the websites instead of ad networks. Later, they attach malicious code to the advert that is downloaded to computers of users who click on the adverts on websites. After a while, when the target is met, the criminals remove the code. The advert stays there for the contract period. Between attaching and removing the code, the criminals get to hack plenty of computers, and thus, much information about different Internet users is at their hands. They can use this information for any purpose they like.
How To Avoid Malvertising
Precaution is the only key to avoid malvertising. Malicious ads can appear even on reputed websites. If any ad looks overtly promising, simply avoid them. For example, popups saying you are the 100th visitor and are chosen for a prize – ignore it. Avoid anything that promises you the likes of money, gifts, discount coupons, etc. for free. Since the advertisements that appear on the websites are the result of network advertisers, it is up to them to check the advertisements for malicious codes. Most of them just check the language profanity and publish the ads. These days, most reputed networks like the Google AdSense network check the entire code, but there has still been the rare case, where malicious advertisements have crept in.
There are some cloud-based malvertising detection platforms and solutions, which deliver insight about and control over the safety of online ads being served on the websites. Large publishers may want to check this option out. As a user, make sure you have a good security software and inculcate safe browsing habits. And remember to keep your operating system and your installed software, including browser plugins, always updated.
Some recent examples of Malvertising
Certain ads on DeviantART.com were redirecting users to the Optimum Installer web page in order to install Potentially Unwanted Applications on unsuspecting users. Hackers had compromised Clicksor Ad Network to distribute malware. Blackhole Exploit kits were being distributed via the Clicksor Ad Network and others. In yet another very recent case, Java exploits were being served via advertisements on Java.com, reported Fox IT.com.
Infographic This Infographic shows how Malvertising works.

It is therefore important that publishers use only such advertising networks and exchanges that have strong screening methods and who take immediate action, once instances of Malvertisements are found, in order to prevent the spread of malware within their systems, as well as contain the damage which may be caused.
Bad, vulnerable and insecure plugins often get compromised. So as I mentioned earlier, make sure you have a good security software and inculcate safe browsing habits. And remember to keep your operating system and your installed software, including browser plugins, always updated.
Stay safe!

