インターネット(Internet)に接続されているデバイスは、スマートデバイスと呼ばれます。インターネット(Internet)に関連するほとんどすべてがスマートデバイス(smart device)として知られています。このコンテキストでは、デバイスをよりスマートにするコード(最小限(SMARTER – )の介入で、または人間の介入なしで動作できるようにする)は、( –)人工知能(Artificial Intelligence)(AI)に基づいていると言えます。他の2つ、つまり機械学習(Machine Learning)(ML)とディープラーニング(Deep Learning)(DL)は、スマートデバイスにより多くの機能をもたらすために構築されたさまざまなタイプのアルゴリズムです。AIとMLとDL(AI vs ML vs DL )の詳細を以下で見て、それらが何をし、どのようにAIに接続されているかを理解しましょう。
MLとDLに関する人工知能とは何ですか
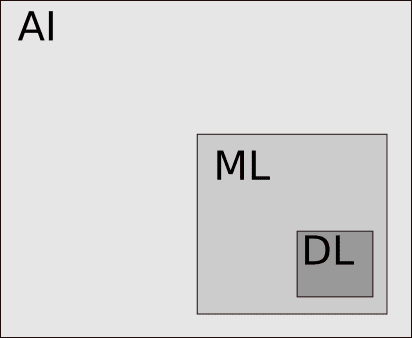
AIは、機械学習(Machine Learning)(ML)プロセスとディープラーニング(Deep Learning)(DL)プロセスのスーパーセットと呼ぶことができます。AIは通常、MLとDLに使用される総称です。ディープラーニング(Deep Learning)もまた、機械学習(Machine Learning)のサブセットです(上の画像を参照)。
機械学習(Machine Learning)はもはやユニバーサルAIの一部ではないと主張する人もいます。彼らは、MLはそれ自体が完全な科学であり、したがって、人工知能(Artificial Intelligence)を参照して呼び出す必要はないと言います。AIはデータで繁栄します:ビッグデータ(Big Data)。消費するデータが多いほど、精度は高くなります。常に正しく予測できるわけではありません。偽旗もあります。AIはこれらの間違いについて自分自身を訓練し、人間の監督の有無にかかわらず、それが行うことになっていることをより良くします。
人工知能は、ほとんどすべての業界に浸透しており、非常に多くの種類の(ビジネス)プロセスやアルゴリズムに影響を与えるため、適切に定義することはできません。人工知能は(Intelligence)データサイエンス(Data Science)(DS:ビッグデータ(Big Data))に基づいており、その別個の部分として機械学習(Machine Learning)が含まれていると言えます。同様に(Likewise)、ディープラーニング(Deep Learning)は機械学習(Machine Learning)の明確な部分です。
IT市場が傾斜しているように、将来はモノのインターネット(IoT)(Internet of Things (IoT))と呼ばれる接続されたスマートデバイスによって支配されるでしょう。スマート(Smart)デバイスとは、直接的または間接的に人工知能を意味します。あなたはすでに日常生活の多くのタスクで人工知能(AI)を使用しています。たとえば、「単語の提案」が上手くいくスマートフォンのキーボードで入力します。あなたが無意識のうちに人工知能(Artificial Intelligence)を扱っている他の例の中には、インターネット(Internet)、オンラインショッピング、そしてもちろん、これまでになくスマートなGmailとOutlookの電子メール受信ボックスで物事を検索しています。
機械学習とは
機械学習(Learning)は人工知能(Artificial Intelligence)の分野であり、その目的は、機械(またはコンピューター、またはソフトウェア)に、プログラミングをあまり行わずに自分自身を学習させ、訓練させることです。このようなデバイスは、パフォーマンスを向上させる方法の学習など、タスクを完了するために人間の方法を適用するため、プログラミングが少なくて済みます。基本的(Basically)に、MLとは、コンピューター/デバイス/ソフトウェアを少しプログラミングし、それ自体で学習できるようにすることを意味します。
機械学習(Machine Learning)を促進する方法はいくつかあります。そのうち、次の3つが広く使用されています。
- 監視あり、
- 教師なし、および
- 強化学習。
機械学習(Machine Learning)における教師あり学習
プログラマーが最初にラベル付けされたデータとすでに処理された回答をマシンに提供するという意味で監視されます。ここで、ラベルとは、データベースまたはスプレッドシートの行名または列名を意味します。そのようなデータの膨大なセットをコンピューターに供給した後、それはさらなるデータセットを分析し、それ自体で結果を提供する準備ができています。それはあなたがそれに供給されたデータを分析する方法をコンピュータに教えたことを意味します。
通常、80/20の法則を使用して確認されます。膨大な(Huge)データセットがコンピューターに送られ、コンピューターが答えの背後にある論理を学習します。イベントからのデータの80%は、回答とともにコンピューターに送られます。残りの20%は、コンピューターが適切な結果を出すことができるかどうかを確認するための回答なしで供給されます。この20%は、コンピューター(マシン)がどのように学習しているかを確認するためのクロスチェックに使用されます。
教師なし機械学習
教師なし学習は、ラベルが付けられておらず、順序が決まっていないランダムなデータセットがマシンに供給された場合に発生します。マシンは、結果を生成する方法を理解する必要があります。たとえば、さまざまな色のソフトボールを提供する場合、色で分類できる必要があります。したがって、将来、マシンに新しいソフトボールが提示されると、データベースにすでに存在するラベルを持つボールを識別できます。この方法にはトレーニングデータはありません。マシンはそれ自体で学習する必要があります。
強化学習
一連の決定を行うことができるマシンは、このカテゴリに分類されます。次に、報酬システムがあります。マシンがプログラマーの望むことを何でも上手くやれば、報酬がもらえます。マシンは、最大の報酬を切望するようにプログラムされています。そしてそれを得るために、それはさまざまなケースでさまざまなアルゴリズムを考案することによって問題を解決します。つまり、AIコンピューターは試行錯誤の方法を使用して結果を出します。
たとえば、自動運転車の場合、道路上で独自のシナリオを作成する必要があります。機械が外出中の場合、プログラマーはすべての可能性を考えることができないため、プログラマーがすべてのステップをプログラムできる方法はありません。そこで、強化学習(Reinforcement Learning)が登場します。試行錯誤のAIと呼ぶこともできます。
ディープラーニングと機械学習の違い(Machine Learning)
ディープラーニング(Deep Learning)は、より複雑なタスクを対象としています。ディープラーニング(Deep Learning)は機械学習(Machine Learning)のサブセットです。それだけが、機械の学習を助けるより多くの神経ネットワークを含んでいます。人工(Manmade)ニューラルネットワークは新しいものではありません。世界中のラボは、マシンが情報に基づいた意思決定を行えるように、ニューラルネットワークを構築および改善しようとしています。(Labs)定期的に市民権を与えられたサウジアラビア(Saudi)のヒューマノイド、ソフィア(Sophia)について聞いたことがあるはずです。ニューラルネットワークは人間の脳のようなものですが、脳ほど洗練されていません。
教師なし深層学習を提供する優れたネットワークがいくつかあります。ディープラーニング(Deep Learning)は、人間の脳を模倣するより多くのニューラルネットワークであると言えます。それでも、十分なサンプルデータがあれば、ディープラーニング(Deep Learning)アルゴリズムを使用してサンプルデータから詳細を取得できます。たとえば、画像プロセッサDLマシンを使用すると、マシンに尋ねられる質問に応じて感情が変化する人間の顔を簡単に作成できます。
上記は、AI対MI対DLをより簡単な言葉で説明しています。AIとMLは広大な分野であり、開放されつつあり、大きな可能性を秘めています。これが、人工知能(Artificial Intelligence)で機械学習(Machine Learning)とディープラーニング(Deep Learning)を使用することに反対する人がいる理由です。
What are Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Artificial Intelligence
Devices connected to the Internet are called smart devices. Pretty much everything related to the Internеt is known аs a smart device. In this context, the code that makes the devices SMARTER – so that it can work with minimal or without any human intervention – can be said to be based on Artificial Intelligence (AI). The other two, namely: Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL), are different types of algorithms built to bring more capabilities to the smart devices. Let’s see AI vs ML vs DL in detail below to understand what they do and how they are connected to AI.
What is Artificial Intelligence with respect to ML & DL

AI can be called a superset of Machine Learning (ML) processes, and Deep Learning (DL) processes. AI usually is an umbrella term that is used for ML and DL. Deep Learning is again, a subset of Machine Learning (see image above).
Some argue that Machine Learning is no more a part of the universal AI. They say ML is a complete science in its own right and thus, need not be called with reference to Artificial Intelligence. AI thrives on data: Big Data. The more data it consumes, the more accurate it is. It is not that it will always predict correctly. There will be false flags as well. The AI trains itself on these mistakes and becomes better at what it is supposed to do – with or without human supervision.
Artificial Intelligence cannot be defined properly as it has penetrated into almost all industries and affects way too many types of (business) processes and algorithms. We can say that Artificial Intelligence is based on Data Science (DS: Big Data) and contains Machine Learning as its distinct part. Likewise, Deep Learning is a distinct part of Machine Learning.
The way the IT market is tilting, the future would be dominated with connected smart devices, called the Internet of Things (IoT). Smart devices mean artificial intelligence: directly or indirectly. You are already using artificial intelligence (AI) in many tasks in your daily life. For example, typing on a smartphone keyboard that keeps on getting better on “words suggestion”. Among other examples where you unknowingly are dealing with Artificial Intelligence are searching for things on the Internet, online shopping, and of course, the ever-smart Gmail and Outlook email inboxes.
What is Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a field of Artificial Intelligence where the aim is to make a machine (or computer, or a software) learn and train itself without much programming. Such devices need less programming as they apply human methods to complete tasks, including learning how to perform better. Basically, ML means programming a computer/device/software a bit and allowing it to learn on its own.
There are several methods to facilitate Machine Learning. Of them, the following three are used extensively:
- Supervised,
- Unsupervised, and
- Reinforcement learning.
Supervised Learning in Machine Learning
Supervised in a sense that programmers first provide the machine with labeled data and already processed answers. Here, labels mean the row or column names in a database or spreadsheet. After feeding huge sets of such data to the computer, it is ready to analyze further data sets and provide results on its own. That means you taught the computer how to analyze the data fed to it.
Usually, it is confirmed using the 80/20 rule. Huge sets of data are fed to a computer that tries and learns the logic behind the answers. 80 percent of data from an event is fed to the computer along with answers. The remaining 20 percent is fed without answers to see if the computer can come up with proper results. This 20 percent is used for cross-checking to see how the computer (machine) is learning.
Unsupervised Machine Learning
Unsupervised Learning happens when the machine is fed with random data sets that are not labeled, and not in order. The machine has to figure out how to produce the results. For example, if you offer it softballs of different colors, it should be able to categorize by colors. Thus, in the future, when the machine is presented with a new softball, it can identify the ball with already present labels in its database. There is no training data in this method. The machine has to learn on its own.
Reinforcement Learning
Machines that can make a sequence of decisions fall into this category. Then there is a reward system. If the machine does good at whatever the programmer wants, it gets a reward. The machine is programmed in a way that it craves maximum rewards. And to get it, it solves problems by devising different algorithms in different cases. That means the AI computer uses trial and error methods to come up with results.
For example, if the machine is a self-driving vehicle, it has to create its own scenarios on road. There is no way a programmer can program every step as he or she can’t think of all the possibilities when the machine is on the road. That is where Reinforcement Learning comes in. You can also call it trial and error AI.
How is Deep Learning different from Machine Learning
Deep Learning is for more complicated tasks. Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning. Only that it contains more neural networks that help the machine in learning. Manmade neural networks are not new. Labs across the world are trying to build and improve neural networks so that the machines can make informed decisions. You must have heard of Sophia, a humanoid in Saudi that was provided regular citizenship. Neural networks are like human brains but not as sophisticated as the brain.
There are some good networks that provide for unsupervised deep learning. You can say that Deep Learning is more neural networks that imitate the human brain. Still, with enough sample data, the Deep Learning algorithms can be used to pick up details from sample data. For example, with an image processor DL machine, it is easier to create human faces with emotions changing according to the questions the machine is asked.
The above explains AI vs MI vs DL in easier language. AI and ML are vast fields – that are just opening up and have tremendous potential. This is the reason some people are against using Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Artificial Intelligence.

