すべてのワイヤレスルーター(wireless router)の名前にはACが含まれ、その後に番号が続きます。たとえば、Tenda AC9 AC1200、TP-Link Archer C7 AC1750、NETGEAR Nighthawk XR500 AC2500、またはASUSRT(ASUS RT-AC88U AC3100) -AC88UAC3100と呼ばれるルーターがあります。このACの後に数字が続くとはどういう意味(number mean)ですか?ACに続く数字は、ルーターの速度を示していますか?AC1900ルーターはAC1200(AC1200 router)ルーターよりも高速ですか?理論的には、メーカーはそうだと言っています。実際には、真実は異なります。これが、このAC命名規則が消費者にとってほとんど価値のないマーケティングである理由と、ワイヤレスルーター(wireless router)を購入するときに自分を騙さない方法です。
AC1200 、AC1750(AC1200)、AC1900(AC1750)、AC2900(AC1900)、AC3200(AC2900)、およびその他の同様の命名手段は、ルーターに関して何を意味しますか?(AC3200)
ワイヤレスルーター(wireless router)を購入すると、ACという用語の後に、名前のどこかに数字が表示されます。新しい(Newer)モデルには、AXという用語の後にさらに大きな数字が続く場合があります。ACは、ルーターが(AC means that the router has support for the)802.11ac(またはWi-Fi 5)ワイヤレスネットワーク標準(wireless networking standard)をサポートしていることを意味します。これは、5GHz周波数での高速WiFiネットワーク接続を提供します。(WiFi network)AXは、ルーターが802.11ax(またはWi-Fi 6)ワイヤレスネットワーク標準をサポートしていることを意味します。

(The number that comes after AC or AX represents the maximum THEORETICAL bandwidth)ACまたはAXの後に続く数字は、ルータの最大理論帯域幅を表します。1200は1200Mbpsを意味し(Mbps)、1900は1900 Mbpsを意味し、3200は3200Mbpsを意味し(Mbps)ます。ルーターの名前でAC2300を(AC2300 in the name of a router, it means)読み取る場合は、802.11ac(Wi-Fi 5)規格を使用し、理論上の合計最大帯域幅が2300Mbpsの(a total maximum theoretical bandwidth of 2300 Mbps.)ワイヤレスネットワーク(wireless network)を提供するWiFiルーター(WiFi router)を扱っていることを意味します。
AC3200ルーターが(AC3200 router)3200Mbps(Mbps)で動作するワイヤレスネットワーク(wireless network)を提供していると信じたくなるかもしれません。それは驚くべきことですが、残念ながら、それは誤りです。真実は、この命名規則は購入決定(purchasing decision)を行うのに役立たないということです。これは、ルーターが実際よりも高速であると思わせるためのマーケティング戦術(marketing tactic)にすぎません。
AC1200、AC1750、AC1900などは、ルーターが(AC1900)WiFi信号(WiFi signal)を発信するすべての帯域の合計であり、ルーターの実際の速度ではありません。
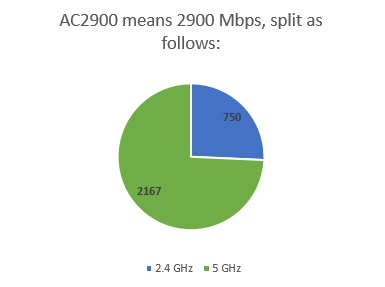
ACまたはAXの命名(AC or AX naming)につながる計算の重要な側面の1つは、ルーターがワイヤレス信号を発信する帯域または周波数の数です。例として、現代的で人気のあるルーターを取り上げましょう:ASUSRT-AC86UAC2900。

このルーターには2つの帯域があり、それぞれに独自の最大理論帯域幅があります。
- 最初の帯域(および最も遅い帯域)は2.4GHzワイヤレス(GHz wireless)帯域です。理論上の最大帯域幅は750Mbps(Mbps)です。
- 2番目の帯域(および最速)は5GHzワイヤレス(GHz wireless)帯域です。理論上の最大帯域幅は2167Mbpsです(Mbps)。
したがって、AC2900は、1つの(AC2900)ワイヤレス帯域または周波数(wireless band or frequency)で得られる最大帯域幅ではなく、使用可能なすべてのワイヤレス帯域または周波数の合計です。取得できる最大速度は、実験室の条件でのみ、最速の帯域(5GHzワイヤレス(GHz wireless)帯域で2167Mbps(Mbps) )の速度です。これについては、この記事の後半で説明します。
さらに理解を深めるために、帯域または周波数に関してワイヤレスルーターがどのように分類されるかを次に示します。
- シングルバンドで、1つのワイヤレス周波数でのみWiFiを送信し(Single-band and emit WiFi only on one wireless frequency)ます。つまり、1つのワイヤレスネットワーク(wireless network)のみを送信します。ほとんどの場合、2.4 GHzの周波数(GHz frequency)で放射し、名前には最大AC1000が含まれています。一部のメーカーは、そのようなルーターの製造を停止しています。それらは信じられないほど低価格ですが、電力が不足しており、フルHD映画(Full HD movie)ストリーミングやオンラインゲームなどに適していない古いワイヤレスネットワーク(wireless network)標準を使用しているため、現代のスマートホームには適していません。
- デュアルバンドで、2つのワイヤレス周波数でWiFiを放射します(Dual-band and emit WiFi on two wireless frequencies:)。2.4GHz(低速ですがカバレッジエリアが広い)と5 GHz(GHz)(高速です(coverage area)がカバレッジ(GHz)エリア(coverage area)が小さい)です。異なる名前の2つのワイヤレスネットワークがブロードキャストされているのがわかります。同じネットワーク名(network name)を使用するように両方の帯域の設定を変更することもできます。最新のルーターの大部分はデュアルバンドです。価格は大きく異なりますが、ほとんどの人が利用できる傾向があります。ただし、 AC命名(AC naming)規則の後の数値が小さいほど、価格が低くなるという観察結果があります。したがって(Therefore)、AC1750ワイヤレス(AC1750 wireless)ルーターは、AC2900ワイヤレス(AC2900 wireless)ルーター。
- トライバンドで、3つのワイヤレス周波数で放射します(Tri-band and emit on three wireless frequencies:)。1つは2.4 GHz周波数(GHz frequency)、2つは5GHz(GHz)周波数です。3つのワイヤレスネットワークがブロードキャストされているのがわかりますが、同じ名前を使用するように設定できます。最も高価な無線ルーターはトライバンドであり、その名前にはAC3200以上が含まれています。最新のルーターの中には、名前にAC5400が含まれているものもあり、5400 (AC5400)Mbpsでワイヤレスネットワークを発信していると思われますが、これは真実とはほど遠いものです。
バンドの数とそれらがAC命名(AC naming)規則にどのように関連しているかを確実に理解するために、最後の例としてTP- LinkArcherC5400X(Archer C5400X)を取り上げましょう。これは、3つの帯域を備えたAC5400ワイヤレス(AC5400 wireless)ルーターであり、次の図のように理論上の最大帯域幅が分割さ(bandwidth split)れています。
- 2.4GHzワイヤレス(GHz wireless)帯域(Mbps)の場合は1000Mbps
- 2つの5GHzワイヤレス(GHz wireless)帯域(Mbps)のそれぞれで2167Mbps

WiFiでこのルーターから得られる最大速度は、実験室の条件で、2つの5GHzワイヤレス(GHz wireless)帯域(Mbps)のそれぞれで2167Mbpsです。
AC命名規則が誤解を招く(convention misleading)のはなぜですか?
ワイヤレスルーター(wireless router)の製造元が使用するAC命名規則は、(AC naming)ワイヤレスルーター(wireless router)によってブロードキャストされるすべてのワイヤレス帯域の理論上の最大帯域幅を合計するため、誤解を招く恐れがあります。それが、 AC5400(AC5400)のようなクレイジーな数字になってしまう方法です。実際には、 AC5400(AC5400)ワイヤレスルーター(wireless router)を使用している場合、WiFiで5400 (WiFi)Mbpsを取得することはできません。これは、ネットワークデバイスが一度に接続できるのは一度に1つの帯域のみであり、一度にすべての帯域に接続できるわけではないためです。よりよく理解するために、下の写真を見てください。3つのネットワークデバイス(iPhone、Surface Pro、Xbox One)があり、それぞれが異なる接続に接続されています WiFiバンド(WiFi band)、TP-LinkArcherC5400Xルーター(TP-Link Archer C5400X router)によって利用可能になった3つから。

これらのデバイスが取得する速度は、接続されているワイヤレス(wireless band)帯域の理論上の最大帯域幅よりも大きくなることはありません。したがって、iPhoneは1000 Mbpsを超える速度を取得しませんが、他の2つのデバイスは(Mbps)2167Mbps(Mbps)を超える速度を取得しません。
メーカーのラボで最大ワイヤレス帯域幅はどのように測定されますか?(wireless bandwidth)
先ほど、トライバンドルーターの例を示し、AC5400のような名前は、 (AC5400)5400Mbpsで(Mbps)ワイヤレスネットワーク(wireless network)を提供することを意味するものではないことを説明しました。WiFiで得られる最高速度は2167Mbpsであると想定できます。これは、ルーターが提供する2つの5GHz(GHz)帯域の理論上の最大帯域幅です。(Mbps)残念ながら、これも誤りです。これは、 WiFiなどのネットワーク機器のすべてのメーカーが(ALL)ルーターは、人々の家やアパートのような実際の測定環境を使用しないでください。彼らは、可能な限り最高の速度を主張できるように、専門のラボで測定を行います。合計最大帯域幅を計算するために、ルーターメーカーが行う傾向があるのは次のとおりです。
- 測定は、無線信号を吸収する厚い壁がなく、計算に使用されるルーターとネットワーククライアント間の直接の見通し線を使用してラボで行われます。
- 帯域幅の測定に使用するデバイスを、2〜3メートル(6〜10フィート)の最適な距離に配置します。彼らは、家やアパートの隅、またはルーターから(home or apartment)厚い壁(thick wall)で隔てられた部屋の帯域幅を測定することに関心がありません。
- 多くの場合、それらは互いに接続された2つまたは3つの同一のルーターを使用して、それらの間でデータを転送するときに最大帯域幅を測定します。企業は、ユーザーのように通常のコンピューターやスマートフォンを使用しません。ルーターは、PC、ラップトップ、タブレット、またはスマートフォンに含まれるネットワークカードよりもワイヤレステクノロジーをより適切にサポートしているためです。その結果、たとえばラップトップを使用する場合よりも転送が高速になります。
- メーカーが最大帯域幅の測定にコンピューターを使用する場合、ルーターで使用しているネットワーク標準に最適なプロセッサー、 RAM、および最速のネットワークカード(network card)を備えた高価なハイエンドPCを使用します。ほとんどのユーザーは、同様のハイエンドコンピューターに投資するための同じ予算を持っていません。ASUS PCE-AC88の(ASUS PCE-AC88)ようなハイエンドのワイヤレスネットワークカード(wireless network card)を購入しますか?ほとんどの人はそうしません。
- ネットワーキング企業は、最新の標準とWiFiテクノロジーで動作するように最適化された専用のネットワーキングソフトウェアとドライバーを使用して、(networking software and drivers)ワイヤレス帯域幅(wireless bandwidth)を測定します。多くのコンピューターやデバイスは、多くの場合、古いソフトウェアやオペレーティングシステムを使用していますが、これらは最新のWiFiネットワーク(WiFi networking)テクノロジーではうまく機能しません。多く(Often)の場合、ドライバー、特にほとんどの消費者向けラップトップのネットワークカードのドライバーも古くなっています。
- メーカーは、ルーターによってブロードキャストされるWiFi(WiFi broadcast)に可能な限り少ない数のデバイスを接続して、最大帯域幅を測定します。自宅や職場(home or workplace)では、接続するデバイスよりもはるかに多くのデバイスを同時に接続し、使用可能なワイヤレス帯域幅(wireless bandwidth)をめぐって競合させます。
- ルーターのアンテナを、最大のワイヤレススループット(wireless throughput)を保証する位置に配置します。自宅では、ルーターとそのアンテナを最適ではない方法で配置して、ルーターが邪魔にならないようにしたり、子供が簡単にアクセスできないようにしたりする可能性があります。
- 企業は、ファームウェア設定を最大速度に最適化します。たとえば、一部のWiFiルーターでは、USBポートは、その(USB port)位置とデフォルト設定(positioning and default settings)に応じて、最大ワイヤレススループット(wireless throughput)を低下させる可能性があります。したがって、ネットワーク会社は、ワイヤレス帯域幅(wireless bandwidth)を測定しながら、ファームウェア設定を変更してUSBスループット(USB throughput)を低下させ、干渉を最小限に抑えます。また、リアルタイムのウイルス対策スキャン(antivirus scanning)やペアレンタルコントロールなど、 WiFi速度(WiFi speed)を低下させるセキュリティ機能を無効にする場合もあります。
ACの命名規則と現実の違いはどれくらいですか?
ACの命名(AC naming)規則と実際の速度の違いは、気のめいるように大きくなる可能性があります。また、それらは大きく異なり、多くの場合、ACネーミング(AC naming)で番号が大きいルーターは、番号が小さいルーターよりも必ずしも高速であるとは限りません。より良い視点を与えるために、いくつかの例について説明しましょう。
Tenda AC9のような手頃な価格のAC1200ルーター(AC1200 router)は、通常のWindows 10ラップトップを使用する場合、5GHz帯域(GHz band)で(Mbps)224.09Mbpsの最大ダウンロード速度を提供します。(download speed)その帯域の理論上の最大帯域幅(maximum bandwidth)は867Mbpsです(Mbps)。実際の速度は、宣伝されている最大帯域幅(maximum bandwidth)の2.86分の1です。

Linksys EA7500 v2のようなAC1900ワイヤレス(AC1900 wireless)ルーターの理論上の最大帯域幅は、5GHz帯域で(GHz band)1300Mbps(Mbps)です。通常のWindows10ラップトップを使用すると、最大ダウンロード速度(download speed)は539.86Mbpsになります(Mbps)。実際の速度は、宣伝されている最大帯域幅の2.4分の1です。

次に、ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AC2900の(ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AC2900)ような、5GHz(GHz band)帯域の理論上の最大帯域幅(maximum bandwidth)が2167Mbpsの(Mbps)AC2900ワイヤレス(AC2900 wireless)ルーターを見てみましょう。実際には、 ASUS PCE-AC88の(ASUS PCE-AC88)よう(Mbps)な高価なネットワークカード(network card)を使用すると、ルーターが配置されている部屋でのみ、ダウンロード速度(download speed)が701.60Mbpsに達する可能性があります。これは、アドバタイズされた最大帯域幅(maximum bandwidth)の3分の1です。

ASUSBlueCaveのようなAC1900(ASUS Blue Cave)ルーター(AC1900 router)に戻ります。同じ高価なネットワークカード(network card)を使用すると、さらに高速のダウンロード速度(download speed)(741.54 Mbps )が得られました。面白い(fun bit)点は、このルーターの5GHz帯域(GHz band)の理論上の最大帯域幅が1734Mbps(Mbps)であるということです。これは、より高価なAC2900ワイヤレス(AC2900 wireless)ルーターの帯域幅よりも低くなっています。それでも、実際の速度は、宣伝されている最大帯域幅よりも2.33低くなります。

このすべてのデータは、ワイヤレスルーター(wireless router)に使用されるAC命名(AC naming)規則が非現実的な見積もりであることを証明しています。これは、次のルーターを選択するときに重要ではありません。他の基準はもっと重要です:ワイヤレスルーター(wireless router)を購入するときに考慮すべき8つのこと(初心者向け)
ワイヤレスルーター(wireless router)から得られる実際の速度を知りたい場合は、購入する前に、オンラインで詳細なレビューを読む必要があります。Digital Citizenのような多くのWebサイトは、ワイヤレスルーターをテストし、高価な(wireless router)実験装置(lab equipment)を使用せずに、通常の日常的な状況で何が得られるかを示すために多くの時間を費やしています。
ワイヤレスルーターに関しては、このAC命名規則をどのように解釈すればよいですか?
ACの命名規則では、ルーターを購入したときに得られるワイヤレスネットワーク(wireless network)の実際の速度はわかりません。この命名規則は、次のような他のことを示しています。
- ルーターが高価か手頃な価格か。(Whether the router is expensive or affordable.)AC1750まで、場合によってはAC1900までのワイヤレスルーターは、ほとんどの人にとって手頃な価格になる傾向があります。AC3200を超えるルーターは常にプレミアムモデルであり、多額の費用がかかります。
- ルーターがシングルバンド、デュアルバンド、トライバンドのいずれであるか:(Whether the router is single band, dual-band or tri-band:)AC1000までのルーターは常にシングルバンドであり、低速の2.4GHz周波数で(GHz frequency)WiFi信号(WiFi signal)を発信します。AC3200(AC1200)までのAC1200ルーターは、 (AC3200)2.4GHz(GHz)と5GHz(GHz)の両方の周波数で信号を発信するデュアルバンドルーターです。AC3200より上の命名規則のルーターは、トライバンド無線ルーターです。
- 入手できる機能:(The features you get:)AC1750までのルーターは手頃な価格である傾向があり、人々が必要とする基本的な機能しか備えていません。上記のルーターは、ウイルス対策保護(antivirus protection)、高度なペアレンタルコントロール、ゲーム指向のサービスなど、ますます高度な機能を提供する傾向があります。
- ハードウェアの強力さ:(How powerful their hardware is:)AC1750までのルーターには、ハードウェアリソースが限られたシングルコアプロセッサが搭載されています。AC3200に移行すると、ルーターにデュアルコアプロセッサとRAMおよびストレージスペース(RAM and storage space)が追加されます。AC5400に近づくと、クアッドコアプロセッサと大量のRAMが搭載されます。覚えておくべき1つのルールは、ルーターのハードウェアが優れているほど、より多くのネットワーククライアントにサービスを提供でき、品質と速度(quality and speed)が向上することです。
結論を要約すると、AC命名(AC naming)規則がどのように使用されているかを思い出せるように、以下の図を作成しました。

(Are)他に未回答の質問はありますか?
私たちDigitalCitizenは、 (Digital Citizen)ASUS、TP-Link、Netgear、Tenda、D-Link、Linksys、Synologyなどの多くのメーカーの多くのワイヤレスルーターをテストしてきました。この記事は、この分野での長年の作業に基づいて作成されました。この業界の現実を明らかにし、この命名規則とその使用方法について多くのことを知っていただければ幸いです。未回答の質問がある場合は、以下にコメントして話し合いましょう。
What does AC1200, AC1750, AC1900 or more, mean and what's the difference?
All wireless routers have AC in thеir name, fоllowed by a number. For еxample, yоu have routers that are called: Tenda AC9 ΑC1200, TP-Link Archer C7 AC1750, NETGEAR Nighthawk XR500 AC2500, or ASUS RT-AC88U ΑC3100. What doеs this AC followed by a number mean? Does the number following AC tell you hоw fast the router іs? Is an AC1900 router faster than an AC1200 router? In theory, manufacturers say that it is. In reality, the trυth is different. Here is why this AC naming convention is marketing with little value for consumers, and how not to fool yourself when purchasing a wireless router:
What does AC1200, AC1750, AC1900, AC2900, AC3200, and other similar naming means, when it comes to routers?
When you purchase a wireless router, you see the term AC followed by a number, somewhere in its name. Newer models may have the terms AX followed by an even larger number. AC means that the router has support for the 802.11ac (or Wi-Fi 5) wireless networking standard, which offers fast WiFi network connections on the 5GHz frequency. AX means that the router has support for the 802.11ax (or Wi-Fi 6) wireless networking standard.

The number that comes after AC or AX represents the maximum THEORETICAL bandwidth of the router. 1200 means 1200 Mbps, 1900 means 1900 Mbps, 3200 means 3200 Mbps, and so on. When reading AC2300 in the name of a router, it means that you are dealing with a WiFi router that offers a wireless network using the 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) standard, with a total maximum theoretical bandwidth of 2300 Mbps.
You might be tempted to believe that an AC3200 router provides a wireless network that works at 3200 Mbps. That would be amazing, but, unfortunately, it is false. The truth is that this naming convention is not useful for making a purchasing decision. It is just a marketing tactic that tries to make you believe that a router is faster than it really is.
AC1200, AC1750, AC1900 and so on, is a sum of all the bands on which the router emits WiFi signal, not the real speed of the router
One key aspect of the calculation that results in an AC or AX naming is the number of bands or frequencies on which the router emits the wireless signal. Let's take a modern and popular router as an example: ASUS RT-AC86U AC2900.

This router has two bands, each of them with its own maximum theoretical bandwidth:
- The first band (and the slowest) is the 2.4 GHz wireless band. It has a maximum theoretical bandwidth of 750 Mbps.
- The second band (and the fastest) is the 5 GHz wireless band. It has a maximum theoretical bandwidth of 2167 Mbps.
Therefore, AC2900 is not the maximum bandwidth you get on one wireless band or frequency, but the sum of all the available wireless bands or frequencies. The maximum speed you could get is that of the fastest band - 2167 Mbps on the 5 GHz wireless band - only in laboratory conditions, which we are going to explain later in this article.

To give you an even better understanding, here's how wireless routers are categorized when it comes to bands or frequencies:
- Single-band and emit WiFi only on one wireless frequency, meaning that they emit only one wireless network. In most cases, they emit on the 2.4 GHz frequency, and they have up to AC1000 in their name. Some manufacturers have stopped producing such routers. They have incredibly low prices, but are not the right choice for modern smart homes, because they are underpowered, and use an old wireless networking standard that is not suitable for Full HD movie streaming, online gaming, and so on.
- Dual-band and emit WiFi on two wireless frequencies: 2.4 GHz (which is slower but with a larger coverage area) and 5 GHz (which is faster but with a smaller coverage area). You see two wireless networks being broadcast, with different names. You can also change the settings for both bands to use the same network name. The majority of modern routers are dual-band. Their pricing varies a lot, but it tends to be accessible for most people. However, one observation is that the lower the number after the AC naming convention, the lower the price. Therefore, an AC1750 wireless router should be cheaper than an AC2900 wireless router.
- Tri-band and emit on three wireless frequencies: one 2.4 GHz frequency and two 5 GHz frequencies. You see three wireless networks being broadcast, but they can be set to use the same name. The most expensive wireless routers are tri-band, and their names have AC3200 or more in their name. Some of the latest routers even have AC5400 in their name, making you believe that they emit wireless networks at 5400 Mbps, which is far from the truth.
To make sure that you understand the number of bands and how they are related to the AC naming convention, let's take one final example: TP-Link Archer C5400X. It is an AC5400 wireless router with three bands, having their maximum theoretical bandwidth split like in the graphic below:
- 1000 Mbps for the 2.4 GHz wireless band
- 2167 Mbps for each of the two 5 GHz wireless bands

The maximum speed you could get from this router, on WiFi, is 2167 Mbps on each of its two 5 GHz wireless bands, in laboratory conditions.
Why is the AC naming convention misleading?
The AC naming convention used by wireless router manufacturers is misleading, because it sums up the maximum theoretical bandwidth of all the wireless bands that are broadcast by the wireless router. That's how we end-up with crazy numbers like AC5400. In reality, you do not get 5400 Mbps on WiFi, when using an AC5400 wireless router, because network devices can connect to only one band at a time, not all bands at once. To better understand, look at the picture below. There are three network devices (an iPhone, a Surface Pro, and an Xbox One), each connected to a different WiFi band, from the three made available by the TP-Link Archer C5400X router.

The speed these devices get is never bigger than the theoretical maximum bandwidth of the wireless band that they are connected to. Therefore, the iPhone won't get a speed that is higher than 1000 Mbps, while the other two devices won't get a speed that is higher than 2167 Mbps.
How is the maximum wireless bandwidth measured in manufacturer's labs?
Earlier we gave an example of a tri-band router and explained that a naming like AC5400 did not mean that it offers a wireless network at 5400 Mbps. You could assume that the top speed you get on WiFi is 2167 Mbps - the maximum theoretical bandwidth for the two 5 GHz bands offered by the router. Unfortunately, this is also false. This is because ALL manufacturers of networking equipment such as WiFi routers, do not use real-life measuring environments, like people's homes and apartments. They do their measurements in specialized labs so that they can claim the maximum possible speed. Here is what router manufacturers tend to do, to calculate the total maximum bandwidth:
- The measurements are made in labs without thick walls that absorb the wireless signal, and with a direct line of sight between the router and the network clients used to make the calculations.
- They place the devices that they use for measuring the bandwidth at an optimal distance of two to three meters (6 to 10 feet). They have no interest in measuring the bandwidth in the far corner of a home or apartment, or in a room separated from the router by a thick wall.
- Many times, they use two or three identical routers connected to each other to measure the maximum bandwidth when transferring data between them. Companies do not use regular computers or smartphones, like users do, because their routers have better support for wireless technologies than the network cards included in PCs, laptops, tablets or smartphones. As a result, their transfers are faster than when using a laptop, for example.
- When manufacturers use computers for measuring the maximum bandwidth, they use expensive high-end PCs, with the best possible processor, RAM, and the fastest network card for the network standards that they are using on their routers. Most users do not have the same budget to invest in similar high-end computers. Would you buy a high-end wireless network card like ASUS PCE-AC88? Most people would not.
- Networking companies measure the wireless bandwidth using specialized networking software and drivers, that are optimized to work with the latest standards and WiFi technologies. Many computers and devices often use older software and operating systems, that do not work as well with modern WiFi networking technologies. Often, drivers are also outdated, especially those of the network cards on most consumer laptops.
- Manufacturers connect the smallest possible number of devices to the WiFi broadcast by their routers, so that they measure its maximum bandwidth. In your home or workplace, you connect a lot more devices than they do, at the same time, causing them to fight over the available wireless bandwidth.
- They place the router's antennas in a position that guarantees the maximum wireless throughput. In your home, you are likely to place the router and its antennas in a less optimal way, to make sure the router is not in your way or easily reached by children.
- Companies optimize their firmware settings for maximum speed. For example, on some WiFi routers, the USB port, depending on its positioning and default settings, can lower the maximum wireless throughput. Therefore, networking companies change the firmware settings to lower the USB throughput and minimize interference, while measuring the wireless bandwidth. They may also disable security features that reduce the WiFi speed, like real-time antivirus scanning or parental controls.
How big is the difference between AC naming conventions and reality?
The differences between AC naming conventions and the speeds you get in real life can be depressingly high. They also vary wildly, and, many times, routers with high numbers in their AC naming are not necessarily faster than others with lower numbers. To give you a better perspective, let's discuss some examples:
An affordable AC1200 router like Tenda AC9, delivers a maximum download speed of 224.09 Mbps, on the 5 GHz band, when using a regular Windows 10 laptop. Its theoretical maximum bandwidth for that band is of 867 Mbps. The real-life speed you get is 2.86 times lower than its advertised maximum bandwidth.

An AC1900 wireless router like Linksys EA7500 v2 has a maximum theoretical bandwidth of 1300 Mbps for the 5 GHz band. When you use a normal Windows 10 laptop, you get a maximum download speed of 539.86 Mbps. The real-life speed you get is 2.4 times lower than its advertised maximum bandwidth.

Next, let's look at an AC2900 wireless router, like ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AC2900, with a theoretical maximum bandwidth of 2167 Mbps for the 5 GHz band. In real life, you can reach 701.60 Mbps for the download speed, only in the room where the router is placed, using an expensive network card like ASUS PCE-AC88. That's three times lower than its advertised maximum bandwidth.

Getting back to an AC1900 router, like ASUS Blue Cave. With the same expensive network card, it obtained an even higher download speed: 741.54 Mbps. The fun bit is that this router has a maximum theoretical bandwidth of 1734 Mbps for the 5 GHz band, which is lower than that of the more expensive AC2900 wireless router. Even so, the real-life speed is 2.33 lower than its advertised maximum bandwidth.

All this data proves that the AC naming conventions used for wireless routers are unrealistic estimations, that should not matter when you choose your next router. Other criteria are a lot more important: 8 things to consider when buying a wireless router (for beginners)
If you want to know the real-life speed you get from a wireless router, before purchasing it, you should read in-depth reviews online. Many websites, like Digital Citizen, spend a lot of time testing wireless routers and showing what you get in normal, day-to-day situations, without expensive lab equipment.
How should I interpret this AC naming convention, when it comes to wireless routers?
The AC naming convention does not tell you the real-life speed of the wireless network that you get when buying one router or another. This naming convention tells you other things like:
- Whether the router is expensive or affordable. Wireless routers up to AC1750 and sometimes even AC1900, tend to be affordable for most people. Routers above AC3200 are always premium models for which you pay a lot of money.
- Whether the router is single band, dual-band or tri-band: routers up to AC1000 are always single band, and emit their WiFi signal on the slow 2.4 GHz frequency. AC1200 routers up to AC3200 are dual-band routers that emit their signal both on the 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequencies. Routers with a naming convention above AC3200 are tri-band wireless routers.
- The features you get: routers up to AC1750 tend to be affordable, and they only have the basic features people need. Routers above that tend to offer more and more advanced features, like included antivirus protection, advanced parental controls, or gaming-oriented services.
- How powerful their hardware is: routers up to AC1750 have single-core processors, with limited hardware resources. When you go up to AC3200, you get dual-core processors and more RAM and storage space on your router. Going close to AC5400, you get quad-core processors and lots of RAM. One rule to remember is that the better the hardware of your router, the more network clients it can serve, with better quality and speed.
To summarize our conclusions, we created the illustration below, to help you remember how the AC naming convention is used.

Are there any other questions left unanswered?
We at Digital Citizen have tested many wireless routers from many manufacturers: ASUS, TP-Link, Netgear, Tenda, D-Link, Linksys, Synology, and others. This article was made based on years of working in this field. We hope that we clarified the realities of this industry and that you now know a lot more about this naming convention and how it is used. If you have any questions left unanswered, comment below and let's discuss.










