Firefoxを長い間使用している場合は、時間が経つにつれてFirefoxの速度が低下することに気付いたかもしれません。起動するのに数秒かかるか、ウェブページの読み込みに少し時間がかかるかもしれません。タブを切り替えるのに1秒ほどかかることや、メニューオプション(menu option doesn)がすぐにポップアップしないことに気付くかもしれません。
Firefoxのインストールが遅くなったり、気になる以上にフリーズしたりする場合は、速度を上げるためのさまざまな方法があります。この記事では、 Firefoxを高速かつ効率的(Firefox fast and efficient)に保つために、長年にわたって学んだすべてのヒントとコツを紹介します。オペレーティングシステムとシステム構成(operating system and system configuration)によっては、いくつかの調整により、他の調整よりも多くのブーストが得られる場合があります。
一部の調整では、 about:config(about:config)でブラウザ設定を変更する必要があることに注意してください。私が何について話しているのかわからない場合は、Firefoxでのabout: (Firefox)config構成(config configuration)のバックアップと変更に関する以前の投稿を読んでください。
HTTPキャッシュを有効にする

Firefoxで有効にできる新しいHTTPキャッシュ(HTTP cache)オプションがあります。これは、UIの不具合やその他のさまざまなブラウザのクラッシュを減らすのに役立ちます。about:configを(config and search)開き、次のエントリを検索します。
browser.cache.use_new_backend
それをダブルクリックして、値を0から1に変更します。次に、about: configタブ(config tab)を閉じて、ブラウジングを続行できます。ブラウザやコンピュータ(browser or computer)などを再起動する必要はありません。新しいキャッシュが有効になり、速度が向上し、(speed boost)ブラウジングエクスペリエンス(browsing experience)がよりスムーズになります。
Firefoxを更新する
Firefoxには、 (Firefox)Firefoxのインストール(Firefox installation)で基本的に自動調整を実行する非常に優れた機能があります。ただし、これを実行するのは、それが何をするのかを正確に理解した後でのみです。まず、閲覧履歴、ブックマーク、パスワード、Cookie、Webサイトの自動入力情報、および個人辞書を保持します。
拡張機能とテーマ、Webサイトのアクセス許可、追加された検索エンジン、ダウンロード履歴(download history)、セキュリティ設定、プラグイン設定、ツールバーのカスタマイズ、ユーザースタイル、ソーシャル機能が削除されます。アクセスするには、アドレスバーにabout:supportと入力する必要があります。(about:support)
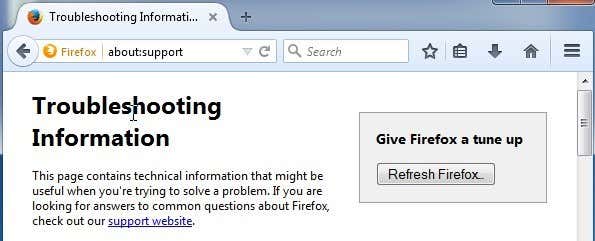
開始するには、右上の[ Firefox(Refresh Firefox)の更新]ボタンをクリックします。私はこの機能を数回使用しましたが、うまく機能します。いくつかのアドオンを再インストールするのには少し時間がかかりますが、そもそも使用したことのないアドオンを取り除くのに役立つことがわかりました。
セーフモードを有効にする
Firefoxには、拡張機能が問題を引き起こしているかどうかを判断するために拡張機能とテーマを無効にするセーフモード(Safe mode)と呼ばれる優れた機能があります。Firefoxはすべて拡張機能に関するものなので、コードの記述が不十分で、多くの悲しみを引き起こす可能性のあるものに間違いなく遭遇するでしょう。
セーフモードでのブラウジングが通常のブラウジングに比べて非常に高速であることがわかった場合は、それが速度低下の原因となる拡張機能であることをほぼ保証できます。メニューアイコン(menu icon)をクリックしてからヘルプアイコンをクリックすると、 (help icon)Firefoxをセーフモードで再起動できます。

次に、 [アドオンを無効にして再起動]を(Restart with Add-ons Disabled)選択し、セーフモードに入ります。

セーフモードでは、ハードウェアアクセラレーションもオフになり、(hardware acceleration)ツールバーとボタンのカスタマイズ(toolbar and button customizations)がリセットされます。Firefoxを通常どおり再起動すると、すべてが通常に戻るため、行ったカスタマイズが失われたとは思わないでください。
また、再起動すると、セーフモードで起動する(Start in Safe Mode)か、 Firefoxを更新(Refresh Firefox)するかを尋ねられます。これは、前述したもう1つのヒントです。

すべてのアドオンを無効にしてから、1つずつ有効にして、Firefoxの速度低下、フリーズ、またはクラッシュ(freeze or crash)の原因となっているアドオンを確認することをお勧めします。Firefoxメニューをクリック(Firefox menu and clicking)し、[アドオン( Add-ons)]をクリックすると、すべてのアドオンとプラグインを表示できます。

無効化または削除するアドオンとプラグインが多いほど、Firefoxの実行速度は速くなります。一部のプラグインは、 Ask to Activateに設定されますが、これは問題ありません。[常にアクティブ化](Always Activate)に設定されているものをすべてチェックし、[アクティブ(Activate)化を要求]に切り替えることができるものを確認します。
メモリ使用量を最小限に抑える
Firefoxには、これらの組み込みのパフォーマンストリックがかなりあります。もう1つは、メモリ使用量(memory usage)を最小限に抑えることです。アドレスバー(address bar)にabout:memoryと入力すると、 Firefoxに関する詳細なメモリ使用量情報を取得できます。
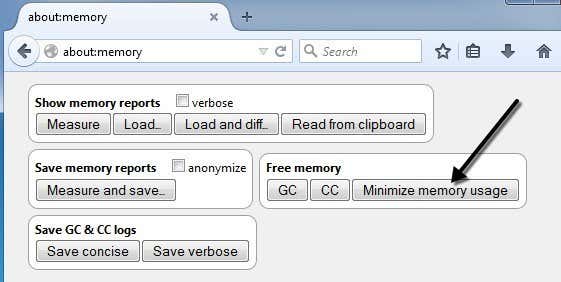
[メモリ使用量の最小化(Minimize memory usage)]というボタンが[空きメモリ(Free Memory)]の下に表示されます。それをクリック(Click)すると、すぐにメモリが解放され、Firefoxの実行速度が向上します。これは、 Firefox(Firefox)で多数のタブを開いていて、最近それらの多くを閉じた場合に使用するのに適したオプションです。これらのタブによって以前に保持されていて、Firefoxによってまだ使用されているメモリはすべて解放されます。
キャッシュの消去
Firefoxを高速化(Firefox faster)するもう1つの簡単な方法は、定期的にキャッシュをクリアすることです。デフォルトでは、FirefoxはアクセスしたほとんどのWebサイトのコンテンツをキャッシュするため、再度アクセスしたときの読み込みが速くなります。短期的には、これはうまく機能し、ブラウジングを高速化しますが、キャッシュが非常に大きくなると、処理速度が低下し始める可能性があります。
Firefoxのメニュー(Firefox menu)をクリックし、[オプション]、[(Options)詳細(Advanced)設定]の順にクリックすると、キャッシュをクリアできる[ネットワーク(Network)]タブが表示されます。
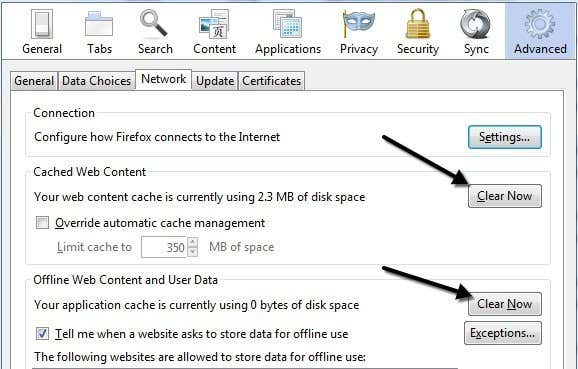
キャッシュを頻繁にクリアすると、ブラウジングが遅くなるため、あまり頻繁にクリアすることはお勧めしません。最善の方法は、数か月ごとにチェックするか、[自動キャッシュ管理を上書きする]チェックボックス(Override automatic cache management box)をオンにして、使用しているハードドライブの種類に応じて値を設定することです。このキャッシュはディスク経由でアクセスされるため、低速のハードドライブを使用している場合はかなり遅くなる可能性があります。
ただし、非常に高速なSSDドライブ(SSD drive)を使用している場合は、キャッシュを使用する方が有利な場合があります。したがって、ハードドライブが遅い場合は小さく(<250 MB)、非常に高速なハードディスクを使用している場合はそのままにしておきます。
Firefoxパイプライン
Firefoxを長い間使用している場合は、おそらく多くのブログでこのハックに遭遇したことがあります。パイプライン処理(Pipelining)は、基本的にFirefoxがサーバーへの複数の接続を開き、理論的にはページの読み込みを高速化する機能です。この設定ではさまざまな結果が得られたため、最初に自分でテストして、有効にしておく価値があるかどうかを確認することをお勧めします。
接続の最大数に設定する値についてはさまざまな見解がありますが、ほとんどのFirefoxの熱狂的なファンからのコンセンサスは8です。パイプラインを有効にするには、config(config and type)に移動 し、フィルターに(filter box)network.http.pipeと入力します。ボックスを開くと、いくつかの設定が表示されます。

変更する必要のある値は上の画像に示されています。はっきりしない場合は、以下にもリストしました。
network.http.pipelining – true
network.http.pipelining.aggressive – true
network.http.pipelining.maxrequests – 8
network.http.pipelining.ssl – true
その他の設定
Firefoxのブラウジング(Firefox browsing)を高速化する可能性のある、さらにあいまいな設定がいくつかありますが、結果は保証されません。これらをテストして、目立った違いがあるかどうかを確認することをお勧めします。
network.dns.disableIPv6 – true
browser.tabs.animate – false
browser.display.show_image_placeholders – false
うまくいけば、 (Hopefully)Firefoxのインストールは少し速く実行されます。FasterFoxのようなアドオンを使用することはお勧めしません。アドオンは上記で説明した設定を変更するだけであり、 Firefoxを高速化するためにアドオンを追加しても意味がありません。Firefoxを高速化するための独自のヒントがある場合は、コメントでお知らせください。楽しみ!
The Ultimate Guide to Making Firefox Faster
If you’ve been uѕing Firefоx for a long timе, you may have noticed it gettіng slower аs time passed. Maybe it takes a few seconds to start up or takes a bit longer loading webpages. You might start notiсing that it takes a second or so to switch between tabs or that the menυ option doesn’t pop up instantly.
If your installation of Firefox runs slow or freezes more than you’d care for, there are a lot of different ways to speed things up a bit. In this article, I’m going to go through all the tips and tricks I’ve learned over the years to keep Firefox fast and efficient. Depending on your operating system and system configuration, some tweaks might give you more of a boost than others.
Note that some tweaks require changing the browser settings in about:config. If you don’t know what I’m talking about, read my previous post on backing up and modifying the about:config configuration in Firefox.
Enable HTTP Cache

There is a new HTTP cache option that can be enabled in Firefox, which will help reduce UI glitches and various other browser crashes. Open about:config and search for the following entry:
browser.cache.use_new_backend
Double-click on it and change the value from 0 to 1. You can then simply close the about:config tab and continue browsing. There is no need to restart the browser or computer, etc. The new cache will be enabled and you should get a speed boost and a smoother browsing experience.
Refresh Firefox
Firefox has a really cool feature that basically performs an automatic tune up on your Firefox installation. However, you only want to do this after you understand exactly what it does. Firstly, it will keep your browsing history, bookmarks, passwords, cookies, website auto-fill info and personal dictionary.
It will delete extensions and themes, website permissions, added search engines, download history, security settings, plugin settings, toolbar customizations, user styles and social feature. To get to it, you have to type in about:support in the address bar.

Click on the Refresh Firefox button at the top right to get started. I have used this feature a several times and it works great. It does take a bit of time reinstalling a few add-ons, but I’ve found that it helps me get rid of the add-ons I never used in the first place.
Enable Safe Mode
Firefox has a nice feature called Safe mode that disables extensions and themes in order to determine whether an extension is causing problems. Since Firefox is all about extensions, you’ll definitely run into some with poorly written code that can cause a lot of grief.
If you find that browsing in safe mode is super fast compared to normal browsing, then you can almost guarantee that it’s an extension causing the slowdown. You can restart Firefox in safe mode by clicking on the menu icon and then clicking on the help icon.

Now choose Restart with Add-ons Disabled to get into safe mode.

Safe mode will also turn off hardware acceleration and will reset toolbar and button customizations. Everything will go back to normal when you restart Firefox normally so don’t think you’ve lost any customizations you might have made.
Also, when you restart, it’ll ask you to Start in Safe Mode or Refresh Firefox, which is the the other tip I already mentioned above.

It’s best to disable all add-ons and then enable them one by one to see which one is causing Firefox to slow down, freeze or crash. You can see all the add-ons and plugins by clicking on the Firefox menu and clicking on Add-ons.

The more add-ons and plugins you disable or delete, the faster Firefox will run. Some plugins will be set to Ask to Activate, which is ok. You want to check all the ones that are set to Always Activate and see which ones can be switched to Ask to Activate.
Minimize Memory Usage
Firefox has quite a few of these built-in performance tricks and another one is to minimize the memory usage. Go ahead and type in about:memory into the address bar and you can get detailed memory usage information about Firefox.

You’ll see a button under Free Memory called Minimize memory usage. Click on that and it will try to free up memory immediately and therefore make Firefox run faster. This is a good option to use if you had a bunch of tabs open in Firefox and you recently closed out a lot of them. Any memory being previously held by those tabs and still being used by Firefox will be freed.
Clear Cache
Another easy way to make Firefox faster is to periodically clear the cache. By default, Firefox will cache the contents of most websites you visit, so that they load faster when you visit them again. In the short term, this works well and does speed up browsing, however, once the cache becomes very large, it can start to slow things down.
If you click on the Firefox menu, click Options and then click on Advanced, you’ll see a Network tab that lets you clear the cache.

I don’t suggest clearing the cache very often, as that will slow down browsing. The best thing to do is to check every few months or to check the Override automatic cache management box and set the value depending on what type of hard drive you have. Since this cache is accessed via disk, it can be pretty slow if you have a slow hard drive.
However, if you have an extremely fast SSD drive, then using the cache can be more beneficial. So keep it small (<250 MB) if you hard drive is slow and leave it alone if you have a very fast hard disk.
Firefox Pipelining
If you have used Firefox for a long time, you have probably come across this hack on many blogs. Pipelining is a feature that basically lets Firefox open multiple connections to a server, theoretically loading pages faster. I’ve had mixed results with this setting, so it’s best to test it yourself first to see whether it’s worth keeping enabled.
There are different views on what value should be set for the max number of connections, but the consensus from most diehard Firefox fans is 8. In order to enable pipelining, go to about:config and type in network.http.pipe in the filter box and you’ll see several settings.

The values you need to change are shown in the image above. I have also listed them below if it’s not clear.
network.http.pipelining – true
network.http.pipelining.aggressive – true
network.http.pipelining.maxrequests – 8
network.http.pipelining.ssl – true
Other Settings
There are a couple of more obscure settings that could possibly speed up your Firefox browsing, but results are not guaranteed. It’s best to test these and see if there is any noticeable difference.
network.dns.disableIPv6 – true
browser.tabs.animate – false
browser.display.show_image_placeholders – false
Hopefully, your installation of Firefox is running a bit faster. I don’t recommend using add-ons like FasterFox because they only change the settings we have talked about above and adding more add-ons to speed up Firefox just doesn’t make any sense. If you have your own tip for speeding up Firefox, let us know in the comments. Enjoy!









