GIMP、またはG NU I mage M anipulation P rogramのおかげで、壮大な外観のサムネイルと(P)高品質のロゴ(high-quality logos)を作成することがこれまでになく簡単で手頃な価格になりました。GIMPは、 (GIMP)AdobePhotoshopの代替品(Adobe Photoshop alternative)を探している画像編集者への無料で使用できるオープンソースの回答です。また、非常に初心者向けであり、画像に必要な変更や修正を行うためのヒントやコツが満載の活発なコミュニティがあります。
GIMPには、あらゆる画像を撮影して独自のプロフェッショナルなタッチを追加するためのツールとリソースが豊富に用意されています。ウェブデザイン、グラフィックアーティスト、アマチュア写真家の人は、GIMPが彼らの画像強化のニーズに簡単に対応できる素晴らしいプログラムであることに気付くでしょう。画像加工(image manipulation)の分野で始めたばかりの人にも同じことが言えます。

初心者にとって、特に新しいインターフェースを扱うことになると、GIMPを使用するというあなたの冒険は気が遠くなるように思えるかもしれません。必要な編集が最小限である場合、画像(image shouldn)のトリミングやサイズ変更に沿ったもので、フープをジャンプする必要はありません。時間をかけて基礎と特定のものを探す場所を学ぶことで、 GIMP(GIMP)が大きな投資である理由を理解するのにそれほど時間はかかりません。

GIMPプログラム(GIMP program)をダウンロードしてインストールしたら、インターフェイスの操作を支援しながら基本的な編集を検討し、この記事で使用したようなサムネイルを作成する方法を説明します。また、将来のGIMP(GIMP)プロジェクトの高度なヘルプを見つけるために使用できるいくつかのリソースも提供します。
GIMPをダウンロードしてインストールする(Download and Install GIMP)

- 開発者のWebサイト(developer’s website)に移動し、ダウンロードを選択します。ファイルのダウンロードが開始されます。インストールを試みるまで、数秒待ってください。
- 最近ダウンロードしたファイルを実行します。インストーラーが開いたら、[インストール(Install )]ボタンをクリックして、gimpをデフォルトのフォルダー(default folder)にインストールします。
- インストール設定とアドオンを変更するには、代わりに[カスタマイズ(Customize )]をクリックします。
- 表示されているすべてのインストール手順に従ってください。GIMPが完全にインストールされるまでに数分かかる場合があります。
- インストールが完了したら、GIMPの使用を開始できます。
GIMPの使用:基本を学ぶ(Using GIMP: Learning The Basics)

GIMPを起動し、空白のキャンバスウィンドウ(canvas window)にプルアップして、以下の手順を開始します。各セクションで同じ画像を使用します。
Image Scaling/Resizing
- (Click)「ファイル」タブをクリックし、「開く…」(Open…)(CTRL + O)を選択して画像をインポートします

- 画像が読み込まれたら、[画像]タブをクリックし、ドロップダウンメニューから[画像の拡大縮小]を選択します。(Scale Image)

- 編集を有効にするためのダイアログボックスが表示されます。(dialog box)

- 提供されているオプションを使用して、画像を拡大縮小/サイズ変更します。
- 幅と高さ(width and height)、またはX、Y解像度(Y resolution)で画像を調整します。
- 変更は、ピクセル、パーセント、センチメートルなどで行うことができます。
- 画像を大きくすると、画像のピクセル化が進む可能性があることを理解してください。
- パラメータを調整したら、[スケール(Scale )]をクリックして続行します。
ファイルサイズの縮小(File Size Reduction)
- 「ファイル」タブをクリックし、「名前を付けてエクスポート…(Export As… ) 」を選択します(Shift + CTRL + E)

- ファイルを保存する場所の名前と場所(name and location)を選択します。

- [(Click)ファイルタイプの選択(Select File Type)(拡張子による) ]の横にある[+]をクリックして、ファイルタイプ(file type)のリストを開き、名前を付けて保存します。jpgやpng(jpg or png)などの不可逆ファイルタイプ(file type)が推奨されます。

- 次に、[エクスポート(Export )]ボタンをクリックして、オプションの新しいウィンドウをポップアップ表示します。

- 保存するものが少ないほど、画像ファイル(image file)のサイズは小さくなります。
- 最小サイズの場合、圧縮レベルが「 (Compression level)9 」に設定されていることを確認してください。
- 保存する画像の要素を決定したら、[エクスポート(Export)]をクリックします。
画像のトリミング(Image Cropping)
- 「ツール」タブに移動し、「Transform Tools > Crop(Shift + C) 」を選択します。

- インターフェイスの左上にあるツールドキュメント(Tool Doc)のアイコンをクリックして、切り抜きツール(Crop Tool)を選択することもできます。

- 次に、マウスの左ボタンを押したまま、最終的な画像として作成する領域にカーソルをドラッグします。
- 落ち着くと、選択したパーツ以外の画像のすべてのパーツが暗くなり、最終的な画像として設定されたパーツはそのまま残ります。

- ボックスの角を使用して、マウスボタン(mouse button)をドラッグして縮小または拡大することにより、領域を調整できます。
- 希望どおりの画像が得られたら、画像を左クリックするか、Enterキーを押すか、 (Enter)Shift + Cを同時に押して選択範囲にトリミングします。

画像の回転(Image Rotation)
この変更では、別の画像をインポートして、現在の画像の上に重ねます。
- 「ファイル」タブで、「レイヤーとして開く」を選択します…(Open As Layers…)(CTRL + ALT + O)

- 画像に追加するレイヤーを選択します。この場合は矢印を使用して、[開く(Open)]をクリックします。
- 現在の画像の上に新しいレイヤーが配置されているのがわかります。レイヤーがどのようにスタックされているかを確認するには、レイヤーウィンドウ(layer window)が右側にあります。
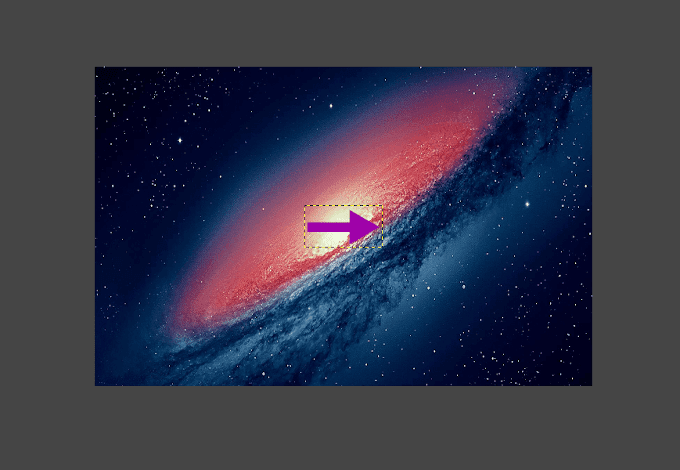

- 新しいレイヤーが強調表示された状態で、変換ツールに戻り、[(Transform Tools)回転(Rotate)]を選択します。回転ツールアイコン(Rotate Tool icon)は、ツールドキュメント(Tool Doc)にもあります。

- これにより、画像にレチクルのようなテクスチャを適用しながら、新しいポップアップウィンドウが表示されます。

- 適用する回転角がわかっている場合は、表示されたボックスに値を入力できます。そうでない場合は、 「角度」というラベルの付いたボックスのすぐ下にあるスライドバー(slide bar)を使用するか、マウスの左クリックとドラッグを使用して画像を自分で回転させるかを選択できます。
- 正確な値を使用すると、より正確な結果がより迅速に得られます。
- 結果がお好みになったら、[回転(Rotate)]をクリックします。
サムネイルのデザイン(Designing a Thumbnail)
このセクションでは、GIMPを使用してこの記事のサムネイルを作成した方法を紹介します。このチュートリアルの一部では、 「基本の学習」で(Learning the Basics)使用されるツールの一部を使用します。
始める前に、必要な画像を収集することをお勧めします。サムネイルはシンプルに保たれているため、必要な画像レイヤーは(image layer)Wikipediaから取得したGIMPロゴ(GIMP logo)のみです。
ダウンロードしてコンピュータに保存したら、開始できます。
- 「ファイル」タブを開き、「新規…(New…) 」を選択します(CTRL + N)
- これにより、「新しい画像の作成」ウィンドウが表示され、事前に作成された(Create)テンプレート(Template)から選択するか、画像のサイズを手動で決定できます。
- サムネイルの幅が680ピクセルを超えることはないため、画像サイズ(image size)をそのように設定します。高さは400pxのままにします。
- 寸法を設定したら、[ OK ]をクリックします。
- これで、空白の(白い)キャンバスが表示されます。ツールドキュメントの(Tool Doc)バケット塗りつぶしツール(Bucket Fill Tool)を使用して、背景の色を自由に選択できますが、今のところ、白のままにしておきます。
- 今すぐレイヤーを追加するのが最善です。そうすれば、テキストの追加を開始したら、画像が遮られないように調整できるようになります。(t block)したがって、[ファイル]タブを開き、今度は[レイヤーとして開く]を(Open As Layers…)選択します。これは、(time select) 画像の回転(Image Rotation)中の矢印の場合と同じです。以前にダウンロードしたGIMPロゴ(GIMP logo)を選択し、 [開く(Open)]をクリックします。
- レイヤー画像(layer image)は1200x1200(x 1200)であり、680x400のプライマリ画像には大きすぎます。縮小する必要があります。上記の手順に従う場合は、画像の幅と高さ(image width and height)を200pxに調整します。
- 次に、画像を横にドラッグして、再配置が必要になるまでテキストの邪魔にならないようにします。

- 次はテキストです。ショートカットコマンド(shortcut command)を使用し、キーボードの「T」キーを押してテキストツール(Text Tool)を選択します。次に、画像の白い部分を左クリックして、タイトルの入力を開始します。

- すべて入力したら、テキストを強調表示して(CTRL + A)、使用するフォントを選択します。標準フォントではないBauhaus93フォントを使用しました。GIMPは、 (GIMP)Windowsフォントフォルダ(Windows Font folder)にあるすべてのフォントを取得し、選択したライブラリに追加します。DaFontやGoogleFontsなどのサイトからフォントをダウンロードしてWindowsFontフォルダーに移動することで、フォントを追加できます(Windows Font folder)。
- 次に、レタリングのサイズを調整して、画像にぴったり収まるようにしますが、スペースを取りすぎないようにします。100pxに落ち着きました。
- テキストの調整が完了したら、移動ツールに切り替えることで、(Move Tool)テキストボックス(text box)を必要な場所に移動できます。これは、テキストではない画像の領域をクリックして[ (text and clicking ‘)M ]をクリックすることで簡単に実行できます。
- ウィンドウの右側にあるテキストレイヤー(text layer)を選択して右クリックし、リストから[(list select) アルファ]から[選択]を選択(Alpha to Selection)します。これにより、画像のテキストにアニメーションの境界線が追加されます。
- 次に、レイヤーを追加する必要があります。これを行うには、同じ右側のウィンドウで、[(side window)新しいレイヤー(Create a New Layer)の作成]ボタンを見つけてクリックします。これにより、ウィンドウが開き、新しいレイヤーが作成されます。ここにあるもののほとんどについて心配する必要はありません。これは、より高度なチュートリアル用です。今のところ、[Fill with:]セクション(” section)のドロップダウンに[ Transparency ]が表示されていることを確認し、[ OK ]をクリックします。

- AlphaをSelectionに適用したテキストを反映した新しいレイヤーが作成されます。デフォルトで選択されたレイヤーになります。次に、テキストの周囲に境界線を追加します。
- 「選択」タブをクリックして、「成長(Grow)」を選択します。ポップアップ表示される選択ボックスで、値を「2」に設定し、「OK 」(selection box)を(2)クリック(OK)します。

- この時点で、簡単にするために、レイヤーウィンドウの元のテキストレイヤー(text layer)の横にある目のアイコンをクリックします。(Eye icon)クリックすると目が消え、境界線をバケツで塗りつぶしている間、テキストの表示が非表示になります。

- Click Shift + Bバケット塗りつぶしツール(Bucket Fill Tool)を選択し、メインの色の四角(color square)をクリックして色のオプションを開きます。いくつかのデフォルトオプションから選択するか、独自のオプションを作成できます。1b56ffのHTML表記(HTML notation)で青の色合いに落ち着きました。
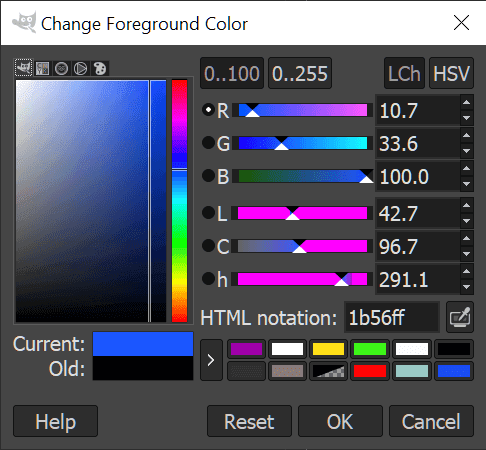
- CSSについて少し知っている場合は、そのボックスのカラーコードを使用できます。
- アニメーション化された境界線でマークされた非表示のテキスト領域にカーソルをドラッグ(Drag)し、左クリックして色で塗りつぶします。

- (Click)目のアイコン(Eye icon)があった領域をクリックして、元のテキストを再表示します。次に、元のテキストをレイヤーウィンドウ(layer window)の色付きのレイヤーの上にドラッグします。
- 一番上のレイヤーを右クリックして、[下にマージ(Merge Down)]を選択します。画像は次のようになります。

- 次に、テキストに少し影を付けます。[(Click)フィルター]タブをクリックし、[Light and Shadow > Drop Shadow (Legacy)…
- ポップアップウィンドウ(pop-up window)で、影のx、yアクセス、半径、および不透明度を選択します。

- サムネイルには、XとYの両方で「 8 」、ぼかし半径で「 (blur radius)20」を選択し、不透明度を「100」に上げました。
- 影の色を変更して、背景で見やすくすることができます。たとえば、背景が黒の場合は、明るい色(brighter color)を選択することをお勧めします。ただし、背景が白なので、黒は問題ありません。
- 画像のずれを防ぐには、[ OK(OK) ]を押す前に[サイズ変更を許可(Allow resizing)する]チェックボックスをオフにします。
- (Merge Down)テキストレイヤー(text layer)の上にドロップシャドウレイヤーを(Drop Shadow layer)マージします。
- 「選択」タブ>なし(None)(Shift + CTRL + A)
- 必須ではありませんが、 GIMPのロゴ(GIMP logo)に影を付けることにしました。そうすることを選択した場合、方向は同じです。それ以外の場合は、GIMPロゴ(GIMP logo)レイヤーを選択して、サムネイル内の目的の位置に移動します。
- 最後に、白い背景が適切でないと感じた場合は、背景レイヤーを強調表示し、(Background layer)バケット塗りつぶしツール(Bucket Fill Tool)を選択して、少し色を追加します。影をかき消さないように、微妙なグレーを選択しました。完成品は次のようになります。

- これで、必要なのは名前を付けてエクスポート(Export As)し、希望の場所に保存することだけです。
GIMPの使用:追加ヘルプ(Using GIMP: Additional Help)

GIMPを使い始めてから、基本をマスターしたように感じ、より複雑でプロフェッショナルなスタイルの編集に目を向けるまで、そう長くはかからないでしょう。GIMPソフトウェア(GIMP software)の実用的な知識を広げるのに役立つチュートリアルが無数にあります。
公式のGIMPチュートリアルセクション(official GIMP tutorials section)から始めることができますが、私はYouTubeを使用して探しているものを正確に検索することを好みます。
GIMPには、(GIMP)サブレディット、 (subreddit)GIMPフォーラム(GIMP Forums)やGIMPチャット(GIMP Chat)などの非公式ディスカッションプラットフォーム、StackExchangeのグラフィックデザインセクション(Graphic Design section)のタグ付き質問、 (tagged questions)Google Plus GIMPユーザー(GIMP users)グループなどのソーシャルメディアチャネルなど、インターネット全体に広がる大規模なユーザーコミュニティもあります。(user community)
The Beginner’s Guide To Using GIMP
Thanks to GIMP, or the GNU Image Manipulation Program, it’s never been easier and more affordable to create epic looking thumbnails and high-quality logos. GIMP is a free to use, open-source answer to image editors looking for an Adobe Photoshop alternative. It’s also quite beginner friendly and has a thriving community filled with tips and tricks to help produce the alterations and revisions that your image requires.
GIMP provides plenty of tools and resources to take any image and add your own professional touch. Those in web design, graphic artists, and amateur photographers will find that GIMP is a great program that can easily accommodate their image enhancing needs. The same can also be said for those just starting out in image manipulation fields.

For beginners, especially when it comes to dealing with new interfaces, your adventure into using GIMP can seem daunting. When the edits you want are minimal, something along the lines of cropping or resizing an image shouldn’t require that you jump through hoops. By taking the time to learn the foundations and where to look for specific things, it won’t take long to realize why GIMP is a great investment.

Once we’ve downloaded and installed the GIMP program, we’ll look into basic editing, while helping navigating the interface, and walk you through how to create a thumbnail like the one used for this article. We’ll also provide a few resources you can use to find advanced help for future GIMP projects.
Download and Install GIMP

- Navigate to the developer’s website and select your download. The file will begin downloading. Allow a few seconds to pass until attempting to install.
- Run the recently downloaded file. Once the installer opens, click the Install button to have gimp installed to the default folder.
- To change installation settings and add-ons, click Customize instead.
- Follow all installation instructions as they’re presented. It may take several minutes for GIMP to be fully installed.
- After installation is complete, you can begin using GIMP.
Using GIMP: Learning The Basics

Begin the steps below by having GIMP launched and pulled up to a blank canvas window. We’ll use the same image throughout each section.
Image Scaling/Resizing
- Click the “File” tab and import your image by selecting Open… (CTRL + O)

- After the image loads in, click the “Image” tab and select Scale Image from the drop-down menu.

- A dialog box will appear to enable edits.

- Scale/Resize your image using the options provided.
- Adjust the image by width and height or the X, Y resolution.
- Modifications can be made by pixels, percent, centimeters, etc.
- Understand that making the image larger can result in a more pixelated image.
- Once parameters have been adjusted, click Scale to proceed.
File Size Reduction
- Click the “File” tab and select Export As… (Shift + CTRL + E)

- Choose a name and location for where you’d like to save the file.

- Click the ‘+’ next to Select File Type (By Extension) to open a list of file types to save it as. A lossy file type such as jpg or png is preferred.

- Next, click the Export button to have a new window of options pop-up.

- The less things saved, the smaller the size of the image file.
- Ensure that the Compression level is set to ‘9’ for the smallest size.
- Once you’ve decided which elements of the image you’d like saved, click Export.
Image Cropping
- Navigate to the “Tools” tab and select Transform Tools > Crop (Shift + C)

- You can also select the Crop Tool by clicking on its icon in the Tool Doc near the top-left of the interface.

- Next, holding down the left-mouse button, drag your cursor across the area you want to make as your final image.
- Once settled, all parts of the image outside of the part you selected, will darken while the part set as your final image will remain intact.

- You can adjust the area using the corners of the box by either shrinking or expanding them by dragging your mouse button.
- Once you have the image as you’d like it, either left-click it, press Enter, or press Shift + C simultaneously to crop to your selection.

Image Rotation
For this modification, we’re going to import another image to layer atop our current image.
- In the “File” tab, select Open As Layers… (CTRL + ALT + O)

- Select the layer you’d like to add to the image, in this case we’ll be using an arrow, and click Open.
- You’ll see the new layer placed on top of the current image. To see how the layers are stacked, the layer window is located on the right.

- With the new layer highlighted, head back into Transform Tools and choose Rotate. You can also find the Rotate Tool icon in the Tool Doc.

- This will pull up a new pop-up window while applying a reticle-like texture to your image.

- If you know the angle of rotation you want to apply, you can enter the values into the provided boxes. If not, you can choose to use the slide bar just below the box labeled ‘Angle’ or rotate the image yourself using your mouse’s left-click and drag.
- Using the exact values provides more precise results, quicker.
- Once the results are to your liking, click Rotate.
Designing a Thumbnail

In this section, we’re going to show you how we created the thumbnail for this article using GIMP. Portions of this tutorial will use some of the tools used in Learning the Basics.
Before we begin, it’s best to gather up any images you may need. Because the thumbnail has been kept simple, the only image layer it will require is the GIMP logo, acquired via Wikipedia.
Once downloaded and saved to your computer, we can get started.
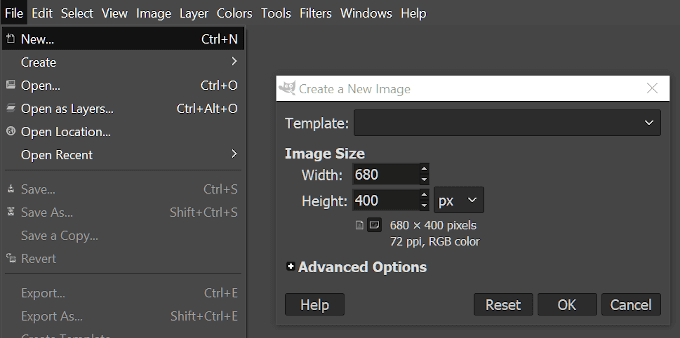
- Open the “File” tab and select New… (CTRL + N)
- This will pull up a “Create a New Image” window where you can select from a pre-created Template or decide on the size of the image manually.

- Our thumbnails are never any larger than 680px width, so we’ll set our image size as such. As for the height, we’ll keep it at 400px.
- Once the dimensions are set, click OK.
- We should now be looking at a blank (white) canvas. You can choose to color the background however you like using the Bucket Fill Tool in the Tool Doc, but for now, we’ll keep it white.
- The best thing to do is add your additional layer now, that way once we begin adding the text, we’ll be able to adjust it so that it doesn’t block out the image. So, open the “File” tab and this time select Open As Layers… just as we did for the arrow during Image Rotation. Select the GIMP logo you downloaded earlier and click Open.
- The layer image is a 1200 x 1200 which is much too large for our primary image at 680 x 400. We’ll need to scale it down. If you follow the instructions illustrated above, adjust the image width and height to 200px.
- We can then drag the image off to the side so that it’s out of the way for our text until we need to reposition it.

- Next comes the text. We’ll use the shortcut command and hit the ‘T’ key on your keyboard to have the Text Tool selected. Now, left-click in the nice white area of the image and begin typing your title.

- Once it’s all typed out, highlight the text (CTRL + A) and select the font you’d like to use. We used the Bauhaus 93 font, which isn’t a standard font. GIMP will take all fonts located in the Windows Font folder and add them to its library of choices. You can add additional fonts by downloading them from sites like DaFont and Google Fonts and moving them over to the Windows Font folder.
- Next, adjust the size of the lettering so that it fits well within the image but doesn’t take up too much room. We settled on 100px.
- Once the text adjustments have been made, you can move the text box around to fit where you need it by swapping to the Move Tool. You can do this easily by clicking on an area of the image that isn’t the text and clicking ‘M’.

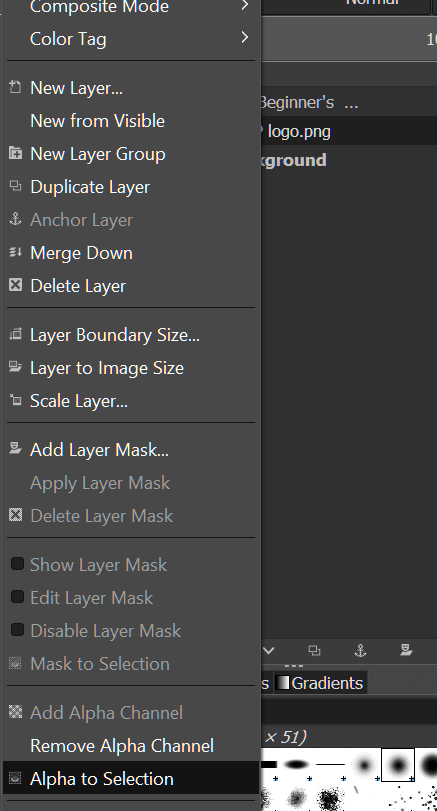
- Select the text layer in the window to the right, right-click it, and from the list select Alpha to Selection. This will add an animated border to the text in the image.

- Next, we’re going to need to add an additional layer. To do this, in the same right side window, locate and click the Create a New Layer button. This will open up the window to create a new layer. Don’t worry about most of what is on here, that’s for a more advanced tutorial. For now, just ensure that the “Fill with:” section has Transparency in the drop-down and click OK.

- A new layer mirroring the text that you had applied Alpha to Selection is created. It should be the selected layer by default. We’re now going to add a border around the text.
- Click the “Select” tab and choose Grow. In the selection box that pops up, set the value to ‘2’ and click OK.

- At this point, to make it easier for you, click the Eye icon next to the original text layer in the layers window. The eye will disappear once clicked, and this will hide the text’s visibility while you bucket fill in the border.

- Click Shift + B to select the Bucket Fill Tool and then click on the main color square to open up color options. You can select from a few default options or create your own. We settled on a shade of blue with the HTML notation of 1b56ff.

- If you happen to know a little about CSS, you can use the color codes in that box.
- Drag your cursor over the invisible text area marked by the animated border, and left-click to fill it with color.

- Click the area where the Eye icon used to be to re-reveal the original text. Then, drag the original text above the colored layer in the layer window.
- Right-click the top most layer and select Merge Down. The image should now look like this:

- Now we’ll add a bit of shadow to the text. Click the “Filters” tab, select Light and Shadow > Drop Shadow (Legacy)…
- In the pop-up window, select the x,y access of the shadow, the radius, and the opacity.

- For the thumbnail we selected ‘8’ in both X and Y, ‘20’ in blur radius, and cranked the opacity to ‘100’.
- You could change the color of the shadow to make it more visible on the backdrop, say for instance if your background was black it would be better to choose a brighter color. However, since our background is white, black is perfectly fine.
- To avoid a shift in the image, uncheck the box marked Allow resizing before pressing OK.
- Merge Down the Drop Shadow layer on top of your text layer.
- “Select” tab > None (Shift + CTRL + A)
- It’s not necessary but we decided to add a shadow to the GIMP logo. If you choose to do so, the directions are the same. Other than that, select the GIMP logo layer and move it into the position you want in the thumbnail.
- At the end, should you feel the white background to not be adequate, you can highlight the Background layer, select the Bucket Fill Tool, and proceed to add a bit of color. We’ve chosen a subtle gray so as not to drown out the shadowing. The finished product should look like this:

- Now, all that’s needed is to Export As and save it to your preferred location.
Using GIMP: Additional Help

It won’t be long once you start using GIMP before you’ll feel like you’ve mastered the basics and look toward more complicated and professional style editing. There are countless tutorials out there to sink your teeth into that can help with expanding your working knowledge of GIMP software.
You can begin in the official GIMP tutorials section but I prefer to search exactly what I’m looking for using YouTube.
GIMP also has a large user community spread across the internet that includes a subreddit, unofficial discussion platforms like GIMP Forums and GIMP Chat, tagged questions in the Graphic Design section of StackExchange, and social media channels like the Google Plus GIMP users group.


































