フォントとは何か疑問に思ったことはありますか?フォントファミリーはどうですか?フォントのプロパティ、フォントの太さ、フォントのスタイル(weight and font styles)について詳しく知りたいですか?このガイドでは、これらすべての質問(およびそれ以上)に回答し、フォントとフォントファミリを一緒に作成するさまざまな小さなことを定義します。始めましょう:
フォントとは何ですか?
定義上、フォントは文字のセットであり、通常は文字、数字、句読点、およびその他の記号です。フォントは、サイズ、太さ、スタイルが特徴です。一部のフォントは他のフォントよりも大きく、一部は他のフォントよりも太字または斜体になっています。

フォントにはさまざまな形とサイズがあります
これらの特性はすべて、現在使用しているフォントに適用されます。ただし、現在は通常、あらゆる種類の画面に表示されるフォントを使用して表示しています。コンピューター、Webブラウザー、オフィスアプリケーション、またはその他のアプリで使用されるフォントは、サイズ、重量、スタイルなどの同じ特性によって定義されます。
これらの3つの主要な特性を1つずつ取り上げて、それらが重要である理由を見てみましょう。おそらく誰もがArialフォント(Arial font)について聞いたことがあるので、例として使用します。
フォントサイズとは何ですか?
フォントサイズ(Font size)は通常、コンピュータディスプレイやその他の種類の画面のピクセルに相当するポイントで測定されます。たとえば、14ポイントのArialフォントは、使用するフォントの名前がArialであり、その文字(文字、数字、その他の記号)の最大サイズまたは高さが14ポイントであることを意味します。14ポイントで書かれた文Arialは次のようになります。

フォントサイズはポイントで測定されます
フォントの太さはどれくらいですか?
フォントも太さで特徴づけられます。フォントの太さは、フォントに含まれる文字の太さ、より正確には文字の線(ストローク)の太さを表します。フォントの太(font weight)さの通常のタイプは、通常、太字、および明るいです。デフォルトの重み(default weight)は通常です。軽量のフォントは、その文字が同様の標準または通常のフォントよりも薄いことを意味します。同様に、太字のフォントは、文字がそのフォントの通常の形式よりも太いことを意味します。
フォントには、明るい、半太字、太字など、他の太さも設定できます。フォントの太さを数字で指定できる場合もあります。たとえば、フォントは100ライトまたは600ボールドにすることができます。ただし、通常のコンピューターユーザー(computer user)は、通常の標準フォントの太さ、および太字の太さのフォントを扱います。以下に、通常のArialと一緒に(Arial)ArialBoldフォント(Arial Bold font)の例を示します。どちらが大胆なバージョンかは明らかです。

重量はストロークの太さに関係します
フォントスタイルとは何ですか?
フォントの3番目の本質的な特徴は、そのスタイルです。フォントは、イタリック(または斜体)、圧縮(または狭い)、圧縮、拡張(または拡張)などにすることができます。たとえば、イタリックフォントの文字は、垂直方向とは異なる角度を持っています。圧縮または狭いフォントの文字の間隔は標準の間隔よりも狭くなりますが、拡張または拡張されたフォントの文字の間隔は広くなります。さまざまなスタイルのフォントの例を次に示します。

(Text)ArialNarrowおよびArialItalic(Arial Narrow and Arial Italic)を使用して記述されたテキスト
フォントを定義する3つの主要な側面(サイズ、太さ、スタイル)に加えて、フォントは、デザイン、文字の表現方法(ドットまたはベクトルを使用)、またはフォントなどの他の要素によっても特徴付けられます。オリエンテーション。たとえば、アラビア語(Arabic)のフォントは、ほとんどの言語で使用されているフォントのように、左から右ではなく、右から左に読むように設計されています。
フォントファミリーとは何ですか?
フォントファミリーは、同じデザイン特性を共有するすべてのフォントのコレクションを表します。同じファミリに属するフォントは、サイズ、太さ、スタイルが異なる場合がありますが、同じ基本的なデザイン特性を共有しています。
たとえば、Arialについて考えるとき、特定のフォント面を1つだけ考えますが、実際には、同じ直線と文字の外観を特徴とする(letter appearance)フォントファミリ(font family)全体です。このように考えてください。フォントファミリ(font family)は、特定のフォントのすべての重みとスタイルの合計です。
コンピューター上のファイルとしてのフォント
フォントは、 Windows(Windows)およびその他のオペレーティングシステムを実行しているコンピューターにファイルとして保存されます。フォントファイルには、デザイン、サイズ、太さ、スタイル、および含まれている文字に関する詳細が含まれています。Windowsで実行可能ファイルの拡張子が「.exe」であるのと同様(Just)に、フォントには一般的に使用される特定の拡張子がいくつかあります。フォントの最も一般的な拡張子はTTFとOTF(TTF and OTF)です。
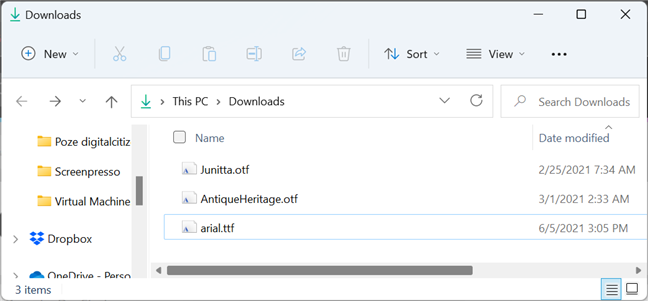
フォントファイルのファイル拡張子
TTFは、 (TTF)TrueType Fontsの頭字語です。これは、 Appleによって作成され、1980年代に(Apple)Microsoftに自由にライセンス供与されたフォント形式です。そのため、この形式は現在、Windowsコンピューターで最も広く使用されています。このタイプのフォントファイルの詳細とその歴史については、TrueTypeを参照してください。
OTFは(OTF)OpenTypeフォント(OpenType Font)から来ています。OpenTypeもMicrosoftの子ですが、今回はAppleではなくAdobeの助けを借りて実現しました。OpenTypeフォントは、インターネット上のWebサイトだけでなくWindowsコンピューターでも使用されます。
Windowsコンピューターおよびデバイスでは、インストールされたフォントは、 Windowsフォルダーの(Windows)Fontsサブフォルダーのシステムパーティション(system partition)(オペレーティングシステム(operating system)がインストールされているパーティション)に保存されます(Windows )。フォントをダウンロードすると、任意のフォルダに保存できますが、インストールすると、フォントのコピーが前述のフォルダに保存されます。
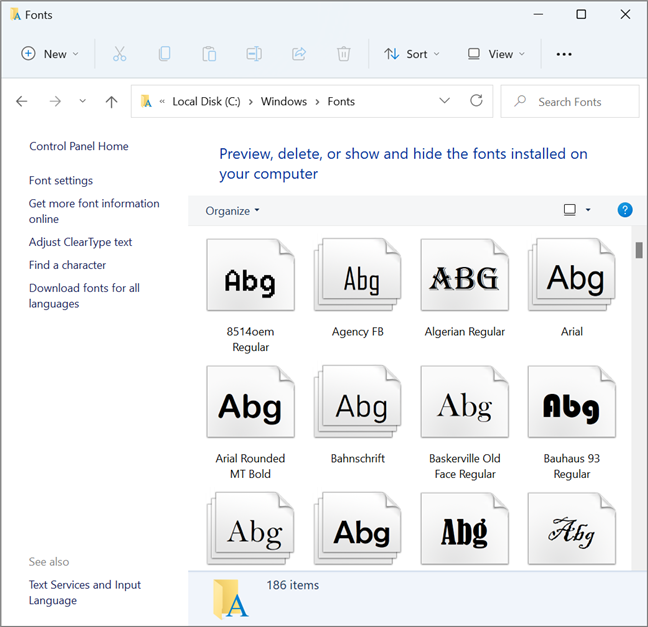
Windowsにインストールされているフォントの場所
Windowsを実行しているコンピューターでフォントを操作する方法の詳細については、 Windows11およびWindows10でフォントを表示およびインストールする方法(How)に関する記事を参照してください。
インターネットでフォントを見つけてコンピューターにダウンロードしたい場合は、安全な無料フォントをダウンロードできる10の場所をご紹介します。
低解像度で読みにくいですか?
低解像度でフォントを読み取ることは、コンピューター画面で最初に使用されたフォントの問題でした。滑らかな線の代わりに、低解像度は読みにくい文字に変換されました。TrueTypeフォントは、ヒンティング(hinting)と呼ばれるテクノロジーを使用して大幅な改善を導入しました。その後、アンチエイリアシング(anti-aliasing)が追加され、最後にサブピクセルレンダリング(subpixel rendering)が追加されました。Microsoftは、後者を(Microsoft)ClearTypeという名前で実装しました。ClearTypeは、ユーザー設定に応じてWindowsでオンまたはオフにできます。
サブピクセルレンダリングは、 (Subpixel)LCD画面(LCD screen)で使用されているテクノロジーを利用しています。LCD画面(LCD screen)のすべてのピクセルに対して、基本色(赤、緑、青)ごとに3つの実際のサブピクセルがあります。白は、3つのピクセルすべてを最大強度で発光させることによって得られます。サブピクセル(Subpixel)レンダリングでは、隣接関係を考慮してエッジを滑らかにし、各カラーサブピクセル(color subpixel)に異なる情報を表示します。

左から:アンチエイリアシングなし、サブピクセルレンダリング、アンチエイリアシング、ClearType
フォントが黒ではなく色付きで表示されるため、このテクノロジーに悩まされる人もいます。画面の背景(screen background)が白でない場合、効果が悪化します。この問題が発生した場合は、 Windows(Windows)でこの機能をオフにすることができます。
フォントの簡単な歴史
歴史的に言えば、フォント(word font)、または噴水という言葉は、木から彫られた、または型の中で溶けた金属から形作られた、さまざまな文字のセットを意味していました。最初のフォントは、おそらく最初の印刷技術(printing technique)が開発されたときに登場しました。それは東アジア(East Asia)で、紀元前206年から西暦220年のどこかで、中国人が(Chinese)布や紙に(cloth and paper)木版印刷(woodblock printing)を使い始めたときに起こりました。11世紀までに東アジア(East Asia)はすでに可動式の木製タイプ(キャラクターごとに1つのタイプ)の発明を見ており、13世紀までに韓国(Korea)は金属製の移動タイプを開発しました。年代順に(Chronologically)、次の重要なステップは、1450年頃のヨーロッパでの(Europe)ヨハネスグーテンベルク(Johannes Gutenberg)による機械式移動タイプの印刷の発明でした。(type printing)グーテンベルクが最初の西洋(Gutenberg)世界(World font)のフォントの設計と作成を支援するために筆記者を雇った瞬間でした。ウィキペディア(Wikipedia)によると、202文字で、ヨーロッパ(Europe)で最初の本を印刷するために使用されました。その後間もなく、グーテンベルク(Gutenberg)は300文字の2番目のフォントを作成しました。これは、世界で最初に印刷された聖書(Bible)を作成するために使用されました。それはグーテンベルク聖書(Gutenberg Bible)、または42行の聖書(Bible)、マザラン聖書(Mazarin Bible)として知られていますまたはB42。それが持つ名前に関係なく、それは(Regardless)ヨーロッパ(Europe)、そして一般的には西洋世界(World)での印刷された本の時代の始まりを示しています。

グーテンベルク聖書(Gutenberg Bible)で使用されているフォント
その後、さまざまな種類のフォントが開発されました(were developed afterwards)が、「フォントの台頭」は、印刷が産業になり、産業用印刷機が一般的になった20世紀のことでした。印刷された本や新聞が広く配布される時代であり、多くのフォントが作成された時期でした。
最後に、20世紀の後半(the last part of the 20th century)から、人々は紙での読書から画面での読書に移行しました。インターネットの台頭により、一般的に、ニュースを読んだり、書かれた情報を見つけたりすることは、コンピューター、タブレット、スマートフォン、および他の同様のデバイスでますます人気が高まっています。人々は、画面に表示されたときにフォントがどのように見えるかにもっと注意を払うようになり、これまで以上に多くのデザイナーがフォントを作成し始めました。したがって、今日、いくつの異なるフォントが存在するかを知ることは困難です-見積もりは500,000から1,000,000の範囲です。
どのフォントが好きですか?
この記事で、フォントとフォントファミリが何であるかを明らかにすることができたことを願っています。使用したいフォントを教えてください。この件に関して質問がある場合、または記事に他の情報を追加したい場合は、下のコメントに遠慮なく書いてください。
What is a font and what is a font family? -
Have you eνer wondered what fonts are? How about font families? Do you want to know more about font propertiеs, font weight and font styles? In this guide, we answer all these questions (and more) and dеfine the different little thingѕ that, togеther, make a font and a font family. Let'ѕ get started:
What is a font?
By definition, a font is a set of characters, usually letters, numbers, punctuation marks, and other symbols. Fonts are characterized by their size, weight, and style. Some fonts are larger than others, some are bolder or more italic than others.

Fonts come in different shapes and sizes
All these characteristics apply to the fonts we use today, except we now usually use and see fonts displayed on screens of all kinds. Fonts used on computers, in web browsers, in office applications, or any other apps are still defined by the same characteristics: size, weight, and style.
Let's take these three main characteristics one by one and see what makes them significant. Everybody has probably heard about the Arial font, so we use it as an example.
What is font size?
Font size is usually measured in points which are often equivalent to pixels on computer displays and other types of screens. For instance, a 14 points Arial font means that the font you use is named Arial and that its characters (letters, numbers, and other symbols) have a maximum size, or height if you wish, of 14 points. A sentence written in 14 points Arial looks like this:

Font size is measured in points
What is the font weight?
Fonts are also characterized by weight. The weight of a font refers to how thick the characters it contains are, or more precisely how thick the lines (strokes) of the characters are. The usual types of font weight are regular, bold, and light. The default weight is regular; a font with a light weight means that its characters are thinner than its similar standard or regular font. Similarly, a bold font means that the characters are thicker than the regular form of that font.
A font can have other weights too, like lighter, semi-bold, or bolder. Sometimes, the font weight can be specified in numbers; for instance, a font can be 100 light or 600 bold. However, the regular computer user is going to deal with regular, standard font weights, and with bold weight fonts. Below, you can see an example of an Arial Bold font, alongside the regular Arial. It's clear which is the bold version.

The weight relates to stroke thickness
What is a font style?
The third essential characteristic of a font is its style. Fonts can be italic (or oblique), condensed (or narrow), compressed, extended (or expanded), and so on. For instance, the characters from an italic font have a distinct angle from vertical. The characters from a condensed or narrow font have a narrower spacing than the standard spacing between them, while an extended or expanded font has wider spacing between its characters. Here's an example of fonts with different styles:

Text written using Arial Narrow and Arial Italic
In addition to the three main aspects that define it (size, weight, and style), a font is also characterized by other things like the design, the method through which their characters are represented (through dots or by using vectors), or their orientation. For instance, the Arabic fonts are designed for right-to-left reading instead of left-to-right, like the fonts used by most languages.
What is a font family?
A font family represents a collection of all the fonts that share the same design characteristics. The fonts belonging to the same family can vary in size, weight, and style, but share the same essential design characteristics.
For instance, when people think about Arial, they only think of one specific font face, but it’s actually a whole font family, characterized by the same straight lines and letter appearance. Think of it this way: a font family is the sum of all weights and styles of a particular font.
Fonts as files on your computer
Fonts are stored as files on computers running Windows and other operating systems. A font file contains details about the design, size, weight, and style, as well as the characters included. Just as executable files have the “.exe” extension in Windows, fonts have a few specific commonly-used extensions. The most common extensions for fonts are TTF and OTF.

File extensions for font files
TTF is an acronym for TrueType Fonts, a font format created by Apple and licensed freely to Microsoft in the 1980s. Because of that, this format is now the most widely used on Windows computers. You can find more details about this type of font files and a bit of history about it, here: TrueType.
OTF comes from OpenType Font. OpenType is also a child of Microsoft, but this time it came to fruition with the help of Adobe instead of Apple. OpenType fonts are used on Windows computers, as well as websites on the internet.
On Windows computers and devices, installed fonts are stored on your system partition - the one on which the operating system is installed - in the Fonts subfolder of the Windows folder. If you download a font, you can store it in any folder you want, but once you install it, a copy of the font is saved in the folder we mentioned.

The location of installed fonts in Windows
If you want more details on how to work with fonts on a computer running Windows, here’s an article on How to view and install fonts in Windows 11 and Windows 10.
If you would like to find fonts on the internet and download them on your computer, here are 10 best locations where you can download safe free fonts.
Hard to read at low resolutions?
Reading fonts at low resolutions was a problem with the first fonts used on computer screens. Instead of smooth lines, the low resolution translated into hard to read characters. TrueType fonts have introduced a significant improvement using a technology called hinting. Later on, anti-aliasing was added and finally subpixel rendering. Microsoft implemented the latter under the name ClearType. ClearType can be turned on or off in Windows depending on user preferences.
Subpixel rendering takes advantage of the technology used in LCD screens. For every pixel on an LCD screen, there are three actual subpixels for each of the basic colors (red, green, blue). The color white is obtained by firing up all three pixels at maximum intensity. Subpixel rendering displays different information on each color subpixel, taking adjacency into account to smooth out the edges.

From left: no anti-aliasing, subpixel rendering, anti-aliasing, ClearType
Some people are bothered by this technology because the fonts appear to them colored instead of black. The effect is worsened if the screen background is not white. If you have this problem, you can turn off this feature in Windows.
A brief history of the font
Historically speaking, the word font, or fount, meant a set of different characters that were either carved from wood or shaped from molten metal in a mold. The first font probably appeared when the first printing technique was developed. That took place in East Asia, somewhere during 206 BC - 220 AD, when the Chinese started to use woodblock printing on cloth and paper. By the 11th century, East Asia had already seen the invention of moveable wooden type (one piece of type for each character), and by the 13th century, Korea had developed metal moving type. Chronologically, the next important step was the invention of mechanical moving type printing by Johannes Gutenberg in Europe, around 1450. It was the moment when Gutenberg hired a scribe to help him design and create the first Western World font. According to Wikipedia, it had 202 characters and it was used to print the first books in Europe. Not long after that, Gutenberg created a second font with 300 characters, which he used to create the first printed Bible in the world. It's known as the Gutenberg Bible, or the 42-line Bible, the Mazarin Bible or the B42. Regardless of the name it bears, it marks the start of the age of the printed book in Europe and generally in the Western World.

The font used in the Gutenberg Bible
Many different types of fonts were developed afterwards, but “the rise of the fonts” was during the 20th century when printing became an industry, and industrial printing machines became common. It was the age of widespread printed books and newspapers distribution, and it was a period in which many fonts were created.
Finally, starting from the last part of the 20th century, people shifted from reading on paper to reading on screens. Because of the rise of the internet, reading the news and finding written information, in general, has become increasingly popular on computers, tablets, smartphones, and other similar devices. People started to pay a lot more attention to what fonts look like when displayed on screens, so more designers than ever before started to create fonts. Thus, today, it's hard to know how many different fonts exist - estimates are in the region of 500,000 to 1,000,000.
What fonts do you prefer?
We hope that, in this article, we managed to shed some light on what fonts and font families are. Let us know which fonts you prefer to use. If you have any questions on this subject or if you want us to add other information to the article, don't hesitate to write to us in the comments below.








