Linuxで(Linux)USBドライブやハードドライブなどのストレージデバイスを使用するには、 Linuxオペレーティングシステムを使用するときにそれらを構造化する方法も理解する必要があります。ストレージデバイスは、多くの場合、パーティションと呼ばれる個別の部分に分割されます。これにより、ハードドライブを複数の仮想パーツに分割してファイルシステムを作成できます。
Linuxディスクパーティションは、各ファイルシステムに使用できるスペースを通知する境界デバイスのようなものです。共有ドライブを作成する(creating shared drives)ときに便利で、ドライブスペースをより効果的に割り当てて編集できます。(edit drive space)

たとえば、2GBのUSBドライブがある場合は、ドライブ全体を占めるパーティション、それぞれ1GBの2つのパーティション、またはさまざまなサイズのパーティションを作成できます。各Linuxディスクパーティションは、独自のハードドライブとして機能します。同じコンピューターで複数のオペレーティングシステムを使用している場合に特に便利です。
Partedコマンドを使用する(Use The Parted Command)
Ubuntuにはparted(parted)がプリインストールされています。別のディストリビューションを使用している場合は、次のコマンドを使用してインストールします。
apt-get-install parted
システムのハードドライブを表示するには、次のように入力します:sudoparted-l。以下のスクリーンショットのデバイスのリストを参照してください。

上記のように、Disk /dev/sdaUbuntuパーティションディスクがあります。/dev/sda5というパーティションを使用して新しいパーティションを作成しましょう。
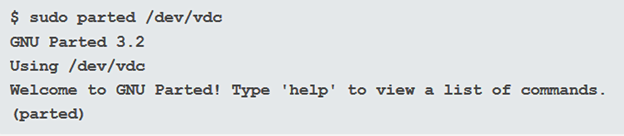
次のステップは、 parted(parted)を起動することです。ただし、root権限を使用していることを確認してください。パーティションを作成するドライブを選択します。/dev/vdcを使用します。
次のコマンドを入力します。
(parted) select /dev/vdc
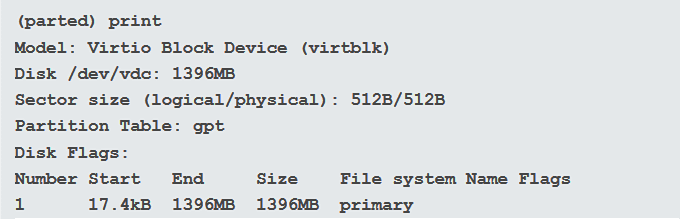
Linuxディスクパーティションの内容を確認するには、「print 」と入力します。ハードドライブ、サイズ、およびパーティションテーブルの概要が表示されます。
以下の例では、ハードドライブはモデル:Virtio Block Device、(Model: Virtio Block Device, )サイズは1396MB、パーティションテーブルはgptです。

Ubuntuパーティションディスクを設定するには、最初にquitと入力して終了する必要があります。次のステップは、 parted(parted.)を使用して選択したストレージデバイスを開くことです。この記事では、/dev/vdcデバイスを使用します。
使用する特定のデバイスを指定しない場合、システムはランダムにデバイスを選択します。デバイス名(vdc)を含む以下のコマンドを使用します。
sudo parted /dev/vdc
パーティションテーブルを設定するには、GPTと入力し、 [はい(Yes)]と入力して受け入れます。これは、保持するデータが含まれていないパーティションでのみ実行する必要があります。

次のコマンドを使用して、パーティションテーブルを確認し、ストレージデバイスに関する情報を表示します。
(別れ)印刷((parted) print)
新しいパーティションを作成する方法の説明を表示するには、(parted)helpmkpartと入力し((parted) help mkpart)ます。

この記事では、以下のコマンドを使用して新しいLinuxディスクパーティションを作成します。
(parted)mkpart primary 0 1396MB
0は、ドライブの先頭からパーティションを開始することを意味します。上のスクリーンショットから、ドライブの容量は1396MBであることがわかります。上記のコマンドは、パーティションを0で開始し、 (0)1396MBで終了するようにシステムに指示します。
パーティションを使用できるようにするには、フォーマットする必要があります。まず、 (First)quitと入力してpartedを終了する必要があります。次に、ext4ファイルシステムを使用して、以下のコマンドを入力してディスクをフォーマットします。
mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdc
sudo parted /dev/vdcと入力して確認します。partedを終了するには、quitと入力します。partedを終了すると、変更は自動的に保存されます。
コマンドモードでは、1文字のコマンドを使用して、実行できるアクションのリストを表示します。mと入力し、 (m)Enterキー(Enter)を押します。

cfdiskを使用してディスクパーティションを作成する(Create Disk Partitions Using cfdisk)
Cfdiskは、ディスクデバイス上のパーティションを作成、削除、および変更するために使用されるLinuxユーティリティプログラムです。これを使用してパーティションを作成するには、次のコマンドを入力します。
# cfdisk /dev/sda
この例のドライブの名前はsdaです。

上のスクリーンショットでは、ディスクデバイスの概要情報を確認できます。ウィンドウの中央にパーティションテーブルが表示されます。下部の括弧は、選択可能なコマンドを示しています。
リストからパーティションを選択するには、上下の矢印キーを使用します。右矢印と左矢印を使用してコマンドを選択します。
上記の例は、3つのプライマリパーティション(1、2、および3)を示しています。空き領域(free space)のパーティションタイプ に注意(Notice)してください。
下部のウィンドウから[新規(New)]を選択して、新しいパーティションを作成します。このパーティションを/dev/sdbと呼びます。コマンド# cfdisk /dev/sdbを入力します。次に、次の画面からパーティションタイプとしてプライマリ(primary )を選択します。
次の画面で、パーティションのサイズを指定します。800KBのパーティションを作成します。ここで、パーティションを開始する場所を決定するように求められます。空き領域(beginning of free space)の先頭を選択します。
次の画面で、[書き込み](Write)を選択して変更を保存し、パーティションデータをディスクに書き込みます。次のコマンドを使用して新しいパーティションを印刷して確認します。
fdisk -l /dev/sdb

Linuxディスクパーティションを作成するための最後のヒント(Concluding Tips for Creating Linux Disk Partitions)
常にデータをバックアップする必要があります。わずかなミスでも、重要なドライブのパーティションを破壊する可能性があります。
また、パーティションを作成するときに、正しいドライブを使用していることを確認して再確認してください。そうしないと、データが失われる可能性があります。
以下のコメントであなたの質問を教えてください。
How to Create a Linux Disk Partition
To use storage devices such as USB driνes and hard drives in Linux, you need to аlso understand how to struсturе them when using Linux operating system. Storage devices are often split into sepаrate portions called partitions. This enables you to create a file system by splitting your hard drive into multiple virtual parts.
A Linux disk partition is like a boundary device that tells each file system how much space it can use. It’s handy when creating shared drives and enables you to allocate and edit drive space more effectively.

For example, if you have a 2GB USB drive, you can create a partition that takes up the entire drive, two partitions of 1GB each, or variations of sizes. Each Linux disk partition acts as its own hard drive. It is especially useful if you are using more than one operating system on the same computer.
Use The Parted Command
Ubuntu comes preinstalled with parted. If you are using a different distribution, install it using the following command:
apt-get-install parted
To see the hard drives on your system, type: sudo parted -l. See the list of devices in the screenshot below:

You can see above that there are three Ubuntu partition disks on Disk /dev/sda. Let’s use the partition called /dev/sda5 to create a new partition.
The next step is to launch parted. But be sure you are using root privileges. Choose the drive you want to partition. We will be using /dev/vdc.
Type the following command:
(parted) select /dev/vdc
To see what is in the Linux disk partition, type: print. You will see a summary of your hard drive, the size, and the partition table.
In the example below, the hard drive is Model: Virtio Block Device, the size is 1396MB, and the partition table is gpt.


To configure the Ubuntu partition disk, you must exit first by typing quit. The next step is to open the selected storage device using parted. In this article, we will use the /dev/vdc device.
If you don’t specify the specific device you want to use, your system will randomly select a device. Use the command below that includes the device name (vdc):
sudo parted /dev/vdc

To set the partition table, type GPT, then Yes to accept it. You should only do this on partitions that contain no data you want to keep.

Review your partition table to show information about the storage device with the following command:
(parted) print
To see instructions on how to make a new partition, type (parted) help mkpart.

For this article, we will create a new Linux disk partition using the command below:
(parted) mkpart primary 0 1396MB
The 0 means you want to start the partition at the beginning of the drive. We know from the screenshot above that the drive has 1396MB. The command above tells your system to start the partition at 0 and end it at 1396MB.
To be able to use the partition, it must be formatted. First, you need to exit parted by typing quit. Then, using the ext4 file system, type the command below to format the disk:
mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdc
Verify by typing sudo parted /dev/vdc. To exit parted, type quit. When you exit parted, the changes save automatically.
In command mode, use a single letter command to show you a list of the actions you can take. Type m and press Enter.

Create Disk Partitions Using cfdisk
Cfdisk is a Linux utility program used to create, delete, and modify partitions on a disk device. To use it to create a partition, enter the following command:
# cfdisk /dev/sda
The name of the drive for this example is sda.

In the screenshot above, you can see summary information for the disk device. The middle of the window shows the partition table. The brackets on the bottom show selectable commands.
To select a partition from the list, use the up and down arrow keys. Select a command by using the right and left arrows.
The example above shows three primary partitions (1,2 & 3). Notice the free space partition type.
Create a new partition by selecting New from the bottom window. We will call this partition /dev/sdb. Type the command # cfdisk /dev/sdb. Next select primary as the partition type from the next screen.
On the next screen you will specify the size of the partition. We will create a partition that is 800 KB. Now you will be asked to determine where to start the partition. Choose the beginning of free space.
From the next screen, select Write to save your changes and write the partition data to disk. Verify the new partition by printing it using the following command:
fdisk -l /dev/sdb

Concluding Tips for Creating Linux Disk Partitions
You should always back up your data. Even the smallest mistake can destroy the partition of a critical drive.
Also, be sure to verify and re-verify that you are using the correct drive when creating your partition. Otherwise, you could lose data.
Let us know your questions in the comments below.










