すべてのPCの同期を維持するには、インターネット時間を更新することで問題を解決できます。そのためには、最初にNTP(NTP)(ネットワークタイムプロトコル(Network Time Protocol))サーバーを見つける必要があります。
Windowsのコマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt )が表示されます。そして、どこから始めればよいかわからなくても心配しないでください。
この投稿では、ドメインのNTP(NTP)サーバーを見つける方法について必要なことを学びます。

登録して開始
Windows Time Serviceをまだ登録していない場合は、以下のコマンドで登録方法を確認できます。また、コンピュータの時刻をNTP(NTP)サーバーと同期する前に、サービスを開始する必要があります。
まず、コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)を起動します。[管理者として実行]を(Run as administrator)選択します。

次に、次のコマンドを入力してシステムを登録します:w32tm
/register

Enterキーを押すと、登録が成功したかどうかがわかります。

ここで、次のコマンドを発行して起動します。sc start w32time(sc start
w32time)

W32tm / query
Windows Time Serviceが登録されて実行されたので、そこから情報を取得できます。
これを行うには、次のように入力します:w32tm /query を入力し、次のパラメーターと照合します。
/状態
これにより、 WindowsTimeService(Windows Time Service)のステータスが表示されます。

/ status / verbose
これにより、詳細モードが設定され、より多くの情報が表示されます。

/ソース
これにより、タイムソースが表示されます。

/構成
これにより、ランタイムの構成と設定が表示されます。

/ピア
これにより、システムを使用しているユーザーのリストが表示されます。

W32tm / resync
コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt )を使用して、できるだけ早くクロックを再同期することもできます。
このコマンドの各パラメーターについての説明は次のとおりです。
/ computer:<再同期するコンピューターの名前>
これにより、再同期するコンピューターを指定できます。これを空白のままにすると、件名はローカルコンピューターになります。
/ nowait
これにより、再同期の待機時間をなくすことができます。これは、結果が返される前にプロセスが完了するのを待つ必要がないことを意味します。
/柔らかい
これにより、既存のエラーを使用してクロックを再同期できます。もちろん、これはあなたに何の役にも立たないでしょう。ただし、互換性のために提供されている情報を参照できます。

W32tm / config
このコマンドを使用して、システムを構成します。
そのコンポーネントを見てみましょう:
/ manualpeerlist:
これにより、ピアのリストを設定できます。これはIPアドレスのリストです。
空白のままにすることができ、デフォルトでは<peers>に設定されます。
/アップデート
これにより、有効にする必要のある新しい変更があることをサービスに通知できます。
/ localclockdispersion:<秒単位>
これにより、内部(Internal)クロックの精度が構成されます。
/ reliable:<はいまたはいいえ>
これにより、システムが時間の信頼できるソースであるかどうかを指定できます。
/ largephaseoffset:<ミリ秒単位>
これにより、ローカル時間とネットワーク時間に関連する時差を設定できます。

W32tm / dumpreg
レジストリキーに関する情報を取得するには、コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)に移動することもできます。w32tm /dumpregとともに次のように入力します
/ subkey:<key>
これにより、デフォルトキーのサブキーに関連付けられている値が表示されます。
/ computer:<コンピューターの名前>
これにより、指定したコンピューターのクエリレジストリ設定が表示されます。

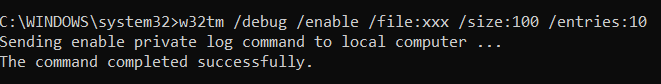
W32tm / debug
コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt )は、コンピューターのプライベートログにアクセスするための場所でもあります。このカテゴリのパラメータについて簡単に説明します。
/enableまたは/disable
これにより、プライベートログを有効(enable )または無効にできます。(disable )このログにアクセスしたいので、有効にするのが方法です。
/ file:<ファイルの名前>
これにより、ファイルの名前を指定できます。以下の例では、ファイルの名前が「xxx」であるとしましょう。
/ size:<ファイルのサイズ>
これにより、ファイルのサイズを指定できます。ここに入力する必要があるのは最大バイト数です。この例では、ファイルのサイズは100バイトです。
/ items:<エントリ数>
これにより、エントリの値を一覧表示できます。このフィールドの有効な数値は0から300の間です。この例では、値は10です。
How to Find NTP Server in a Domain to Sync All PCs
To keep all PCs
synchronized, υpdating the internet time will help you pull it оff. And tо do
that, you need to find the NTP (Network Time Protocol) server first.
Windows’ Command Prompt will get you there. And
if you don’t know where to begin, don’t worry.
In this post,
you’ll learn what you need on how to find the NTP server for the domain.

Register and Start
If you haven’t
registered Windows Time Service yet, the commands below will show you how to do
it. You also need to start the service before you can sync your computer time
with your NTP server.
First up is to
launch the Command Prompt. Choose Run as administrator.

Then enter the
following command to register your system: w32tm
/register

Once you hit
enter, you will find out if the registration was a success.

Now, start things
up by issuing this command: sc start
w32time

W32tm /query
Now that the
Windows Time Service is registered and running, you can get information from
it. You can do this by typing the following: w32tm /query and match it with the following parameters.
/status
This will show
you the status of Windows Time Service.

/status
/verbose
This will set the
verbose mode to show you more information.

/source
This will show
you the time source.

/configuration
This will show
you the run-time’s configuration and settings.

/peers
This will show a
list of people using your system.

W32tm
/resync
You can also use
the Command Prompt to resynchronize
the clock the soonest time possible.
Here’s a
discussion on each parameter of this command:
/computer:<name
of computer to be resynchronized>
This lets you
specify a computer that will be resynchronized. If you leave this blank, the
subject will be the local computer.
/nowait
This lets you
eliminate the wait time for the resynchronization. It means that you will not
have to wait for the process to be completed before the results are returned.
/soft
This lets you
resync the clock using the existing errors. Of course, this wouldn’t do you any
good. But you can refer to the information it provides for compatibility.

W32tm
/config
Use this command
to configure your system.
Let’s look at its
components:
/manualpeerlist:
This lets you set
a list of peers. It’s a list of IP addresses.
You can leave it
blank and by default, it will be set to <peers>.
/update
This allows you
to notify the service that there are new changes that need to take effect.
/localclockdispersion:<in
seconds>
This configures
the Internal clock’s accuracy.
/reliable:<YES
or NO>
This allows you
to specify whether the system is a reliable source for time.
/largephaseoffset:<in
milliseconds>
This lets you set
the time difference involving your local and network time.

W32tm
/dumpreg
To get
information about a registry key, you can also go to the Command Prompt. There, enter the following, along with w32tm /dumpreg
/subkey:<key>
This shows you
the values that are associated with the sub-key of the default key.
/computer:<name
of the computer>
This shows you
the queries registry settings for a specified computer.

W32tm
/debug
The Command Prompt is also where you can
access your computer’s private log. Here’s a short discussion of the parameters
in this category.
/enable
or /disable
This lets you enable or disable the private log. Because you want to access this log,
enabling is the way to go.
/file:<name
of your file>
This lets you
specify the name of your file. In the example below, let’s say the name of our
file is “xxx”.
/size:<size
of your file>
This lets you
specify the size of your file. What you should enter here is the maximum number
of bytes.in the example, the size of our file is 100 bytes.
/entries:<number
of entries>
This allows you
to list down the value for your entries. The valid numbers for this field are
in between 0 to 300. In the example, the value is 10.















