特定の時間にプロセッサの電力がどれだけ使用されているかを知りたいと思ったことはありませんか?または、お気に入りのゲームで使用できる空きRAMがどれだけ残っているでしょうか。ビデオカードの電力はどのくらい使用されていますか?これらはすべて、アプリやゲーム(apps and games)をうまく実行できない重要なシステムリソースです。統計情報とリアルタイム情報を表示する場合は、Windows タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)を使用すると、ユーザーが現在のプロセッサ(CPU)とメモリ使用率を監視したり、(memory utilization)ビデオカード(video card)(GPU)の使用状況を確認したりできることを知っておく必要があります。システムリソース。システムリソースを監視する方法は次のとおりです。
注:(NOTE:)このガイドはWindows10およびWindows8.1用に作成されており、ここで示す機能の一部は、最新バージョンの(Windows 8.1)Windows10でのみ使用できます。
システムリソースを監視できるツールの場所:タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)の[パフォーマンス]タブにアクセスします(Performance tab)
リソース消費量(resource consumption)を確認するには、タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)を起動する必要があります。これを行う方法はたくさんありますが、速度と使いやすさのために、(speed and ease)キーボードショートカット(keyboard shortcut) "Ctrl + Shift + Esc."を使用することをお勧めします。タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)がコンパクトビューで開いた場合は、[詳細]を("More Details")クリックまたはタップ(click or tap)してフルビューに展開します。
次に、[パフォーマンス(Performance)]タブをクリックまたはタップします。下のスクリーンショットのようになります。その外観と内容は、使用しているWindowsのバージョンと使用しているハードウェアによって異なります。
![タスクマネージャの[パフォーマンス]タブ](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-u9fhyQqqwro/YjcZU2UQFSI/AAAAAAAAmsk/fZ3jS0thPj0CGH2tVjPZzB3szxsJPfnZwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCTz9yRBg/s0/AGr88uz0-fIguUcPzLBGVTO177w.png)
タスクマネージャーの[(Task Manager)パフォーマンス(Performance)]タブを使用して、 CPU、GPU、メモリ使用率(memory utilization)などの重要なハードウェアコンポーネントのパフォーマンスを監視する方法を見てみましょう。
1.タスクマネージャー(Manager)を使用すると、ユーザーは現在のプロセッサー使用率を監視できます。(processor utilization)
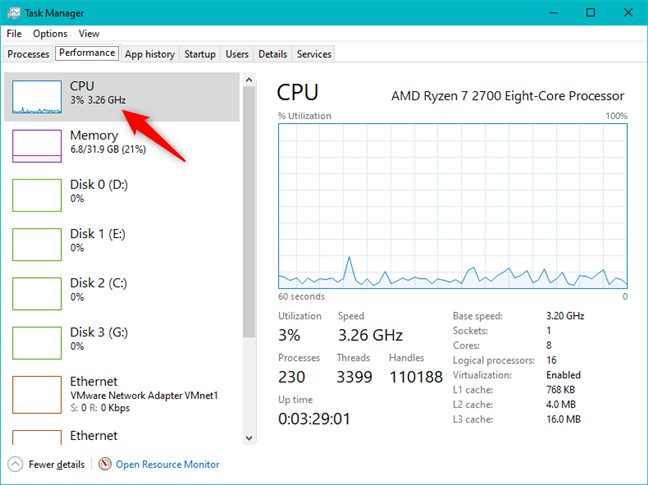
デフォルトでは、タスクマネージャの[(Task Manager)パフォーマンス(Performance)]タブには、最初にCPUの使用状況(プロセッサとも呼ばれます)が表示されます。まだ選択されていない場合は、ウィンドウの左側にあるCPUをクリックまたはタップすることにより、手動で選択できます。
![タスクマネージャの[パフォーマンス]タブのCPUセクション](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-ys3rRVzoabI/YjcN7LYTWRI/AAAAAAAABrM/ooohJK1UK90gqrHJZznmC4cwwpTxTq_lQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxeSqmKu1BtuATYSULyy9OK0vUZJMh4EEreX9rzJid57_Lr5itgoyxzXecCdHil_kcjllNp636SB8ECcTxmI--8us7mIs7_4fcnjy5EcSKFLsehZVlA79dQvMROYqrbbfCkZz25BePPjbkt5vMp0a-Ffrw5A99b5RlKddBRMXeM9g_FOe-xFzRbvRW7TYY6HykLA9PekQsEvOV8jpg0SHFKFaAgGIgHmS8N7Z4b0t8oAyxaq09z-wMB1q859mpaUbsnf4wcrBa-aLiovkCSe0-odM-A-9luIU_P030lCRFTGU9BY0zVaY2-1KUD4qSF0CxrUZ63BI5AN1rY-GLaYkrr6q6sLymszIx_5ReHwutHRLMCol2Y3bqo8_EmWqm1xKORC4FaaCfGnEFVJB_wg7045IZzS73d4lf5GevtJPILvrX6AAn4MdBndWPI54Il_GyriQm-PvgqlWRU8VIZSbskQDSr606f1DhUT0lFbEm55jRTZO5fxh4ah9Me-2zfxCotjHRzCLkIkXarR56jt-M2SgQLbI-FEfyKwUTPXJ4v_RR4iPWc90tJKVi01D3pbDGX5WGBgfwItEcVTJrbT3YKakmk0mweSX3-I0kynawDx1NIRHydgBsBNyU99ZZWyYdyYcFCu2SsV1d5Oa8w3tXckQY/s0/CehB0_FJDnaW6F6NmvzpNsLOV68.png)
ウィンドウ(window and choosing)内の任意の場所を右クリックして["View -> CPU."CPU使用率を表示することもできます。
![タスクマネージャの[パフォーマンス]タブからCPUセクションを開く](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-QdjV1bHSxZ4/YjdbefHgF-I/AAAAAAAAP90/a2exaDuqSDskMLWDiwyi1Hu7z9jfbnvzQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhyU0JW91iiU4HdUNyWpEBsKLTw-6rQ88JJcf3GF8lMk7uR2vURQvSrLKx3HPJ-0bFTSQRDYtFiF0xXMnzMqjkeinj0p4_6R1kO7c7YxY5qQhApZ0W4keaxtQNkUgY3tkRT5-ypFY9VCwWOdWlQjQXqnqqmUhUOHojDHDyRxOdzXgn83uL9cUhyZQAyqoLNXwTuyPI3w7jMVLY_X3G_jMusEXoZHkAYQKZqBgUhPxBxFlPwhH-2DdZDXsVjKZqfavx4quKoI8Dn5vbKBw1fBP2LP-TMONu3R7eOkf34NH9fhPJJ8dtB0a9Nr9Lbun4wsDt2UkPoVWdXK-T5WEyqL8jtJIZzuNmeYS32rgbNJxt2MkVJe0ECNAjwjXY1oCKwCAja-lwWv2MG2WdS5jNcBqq8uNpsf5TXfjQaewupijbNsp_viGHOdMXhU68bv9CYzh3Jg897TZj113lNc9x2yiPm9ZLpb68caNxrHKk6kQvdPMHMRzJzCFsHGdrcsGW8UUQ6Ht3UrJUSKHvNnPH9C-EavJf8LBHVfter4gT7dO0uaIhreDldhomF7fI1DE1HmW7QFlecOcn2MqpmjESsYDZlEqVL_O7bu6l5iDcDGvhsDH0Fhqz9rIOYRCpkWkIV1yugxhdBnKN3LY3H2ntww_uXdkQY/s0/XFfiTcUXgDNcPnLRCU-Zcp99ds4.png)
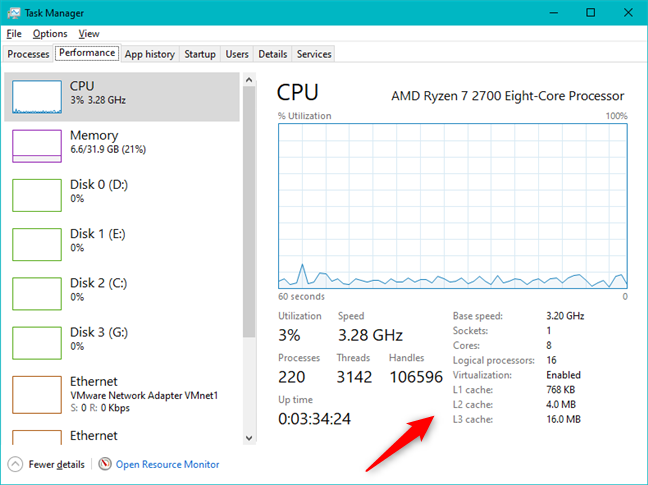
プロセッサを選択すると、ウィンドウの右側に、過去60秒間のCPU使用率のパーセンテージを示すグラフが表示されます。(CPU usage)リソースビューの(resource view)右上隅(right corner)に、タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)にプロセッサの正確なモデルが表示されていることに注意してください。(Notice)

グラフの下には、現在のCPU使用率と速度に関する詳細情報、および(CPU utilization and speed)仮想化(Virtualization)機能がオンかオフかを問わず、ベース速度、(Base speed,)ソケット(Sockets)とコア(Cores)の数、論理プロセッサ(Logical processors)(スレッド)などのプロセッサの仕様に関する情報があります。、およびその上で使用可能なレベル1、2(Level 1)、および3のキャッシュメモリ(cache memory)の量。
デフォルトでは、PCの各物理プロセッサのグラフが表示されます。それは理にかなっていますが、一部のユーザーが探しているものではない場合があります。プロセッサの使用状況(processor usage)をより詳細に把握するために、グラフを論理プロセッサに分割できます。CPUグラフを右クリックまたは長押しし、[グラフの変更]にカーソルを合わせて、[("Change graph to")論理プロセッサ("Logical processors.")]をクリックまたはタップします。
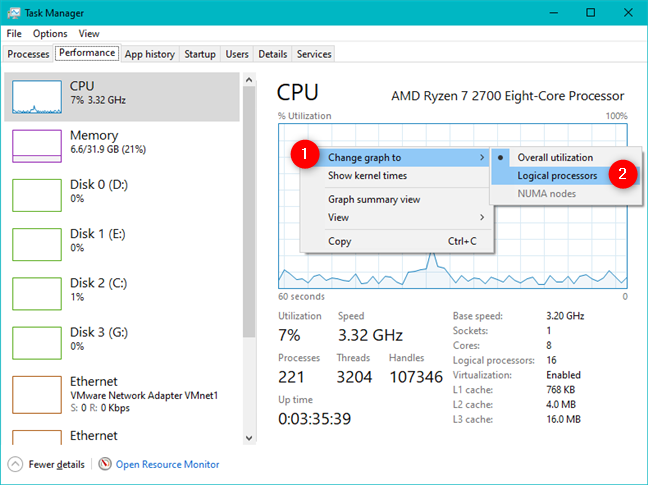
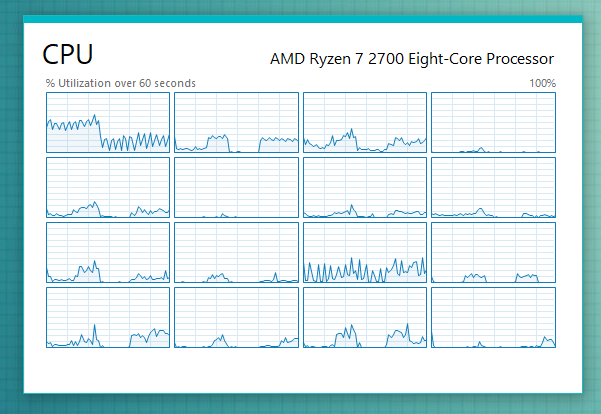
これで、 CPU(CPU)の論理プロセッサごとに小さなグラフが表示されます。AMD Ryzen 7 2700プロセッサの場合、スレッドごとに1つずつ、合計16のグラフが表示されます。コンピュータのプロセッサに応じて、多かれ少なかれ表示される場合があります。

CPUサイクルがどのように割り当てられているかについてさらに詳しい情報が必要な場合は、カーネル時間を表示することを検討してください。これらは、内部システム機能を担当するカーネルによって使用されているCPUサイクルの数と、ユーザープロセスによって使用されている量を示します。(CPU)
カーネル時間を有効にするには、 CPU(CPU)グラフを右クリックまたは長押しして、[カーネル時間を表示]をクリックまたはタップします。("Show kernel times.")

グラフ(graph represent kernel time)の暗い領域はカーネル時間を表し、明るい領域は他のタイプの使用法を表します。

2.タスクマネージャー(Manager)を使用すると、ユーザーは現在のメモリ使用率(memory utilization)(RAM)を監視できます。
特にスローダウン時に注意が必要なもう1つのリソースは、RAM(ランダムアクセスメモリ(Random Access Memory))です。[パフォーマンス(Performance)]タブの左側にあるリソースのリストから[メモリ(Memory)]を選択すると、メモリ使用量(memory usage)を表示できます。
![タスクマネージャの[パフォーマンス]タブの[メモリ]セクション](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-YNr5APHXF4Q/Yjcd6c5fSRI/AAAAAAAAmpg/RF216h7Zq2gXaJYwItZ-C8v1bZq2xIzYACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCTz9yRBg/s0/a3DIkX6rH1TXcZmaqVS2BFhV7Qg.png)
メモリ(Memory)グラフに切り替えるには、ウィンドウ内の任意の場所を右クリックまたは長押しして、"View -> Memory."

[メモリ](Memory)セクションには2つのグラフが表示されます。上のグラフには、直前に使用されたメモリの割合が表示されます。下のグラフは、メモリがどのように割り当てられているかを示しています。下のグラフの各セクションにマウスを合わせると、何が何であるかがわかります。

RAM(RAM usage)の使用量は、次の4つの使用法タイプに分けられます。
- 使用(In Use)中-アプリ、ドライバー、またはWindows自体によって現在使用されているメモリ。
- 変更(Modified)済み-他の目的に使用する前に内容をディスクに書き込む必要があるメモリ。
- スタンバイ(Standby)-キャッシュされたデータと現在使用されていないコードを含むメモリ。
- 空き(Free)-現在使用されておらず、使用できるように解放されているメモリ。
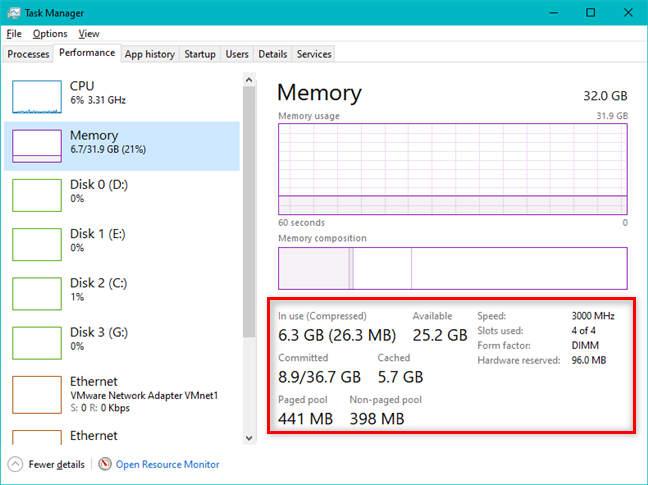
グラフの下には、使用済みメモリ、使用可能なメモリ、速度、使用済みスロットとフォームファクタ、ページングおよび非ページングメモリプールサイズなど、 (memory pool size)RAMに関する詳細情報があります。表示されるメモリプールは、物理メモリに存在することが保証されているか、必要に応じてディスクとの間で交換できます。キャッシュに使用されたメモリの合計とコミットされたメモリの合計も表示されます。表示されるデータの量は、コンピューターのハードウェア構成(hardware configuration)によっても異なります。
3.タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)を使用すると、ユーザーは現在のビデオカードの使用率(video card utilization)(GPU)を監視できます。
2019年5月の(May 2019)更新とFallCreatorsUpdate(Update and Fall Creators Update)を含むWindowsの最新バージョンでは、タスクマネージャーで(Task Manager)GPUの使用状況(GPU usage)を確認することもできます。この機能は、古いバージョンのWindows10にも古いバージョンのWindowsにもありません。
タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)ウィンドウの左側にあるリストからグラフィックカードを選択すると、すべてのグラフィックカードのパフォーマンスを監視できます。デバイスに複数のビデオカード(video card)がインストールされている場合は、それぞれにエントリが必要です。
![タスクマネージャーの[パフォーマンス]タブのGPUセクション](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-qus1RXXClgw/YjdXLv5mwyI/AAAAAAAAxNs/JGqEs2sVA3A-iEO1y-5iUhZq2nGF4FFGACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCe4d2RBg/s0/TsVrEdoapROdE2WkOuJlmo2iffE.png)
監視するビデオカード(video card)を選択すると、ウィンドウの右側にグラフとそのアクティビティに関する情報が表示されます。選択したビデオカード(video card)のタイプに応じて、その電力のどれだけが3D、コピー、ビデオエンコード(3D, Copy, Video Encode)、およびビデオデコード(Video Decode)に費やされているかを示すグラフが表示されます。

デフォルトでは、タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)には4つの異なるグラフのみを表示するのに十分なスペースがあります。ただし、それらの1つを変更して他の機能を監視する場合は、グラフの左上隅にある小さな矢印ボタンをクリックまたはタップして、監視するものを選択できます。そのビデオカード(video card)が提供する実際の機能に応じて、ビデオ処理、レガシーオーバーレイ、セキュリティ、Cuda、VRなど(Video Processing, Legacy Overlay, Security, Cuda, VR,)から選択できます。

4つの機能グラフの下に、タスクマネージャは(Task Manager)ビデオメモリ(video memory)がどのように使用されているかも示します。「共有GPUメモリ使用量」("Shared GPU memory usage")のグラフが必要です。ビデオカード(video card)にも専用メモリがある場合は、「専用GPUメモリ使用量」というグラフも必要です。("Dedicated GPU memory usage.")各グラフの右上隅で、システムで使用可能なビデオメモリの合計量を確認できます。
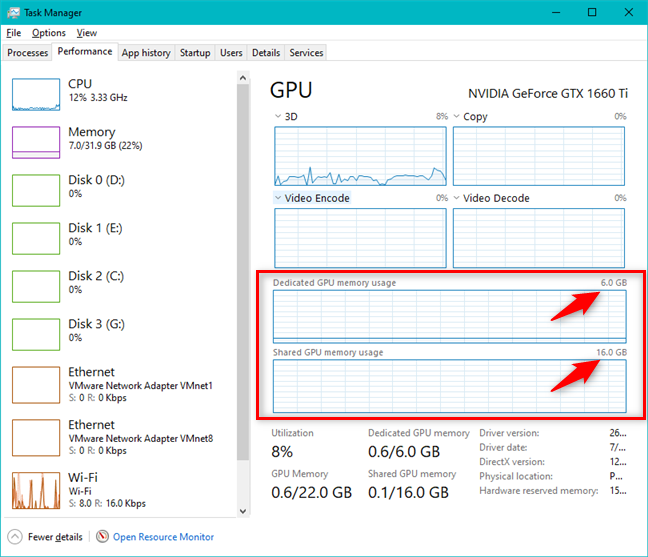
グラフの下には、他にも役立つ情報がたくさんあります。ビデオカードの合計使用(Utilization)率、使用されているGPUメモリの量と使用可能な量、(GPU Memory)専用GPUメモリ、(Dedicated GPU memory,)使用されている共有GPUメモリ(Shared GPU memory)と使用可能な量を確認できます。使用されているドライバーのバージョン、(driver version)ドライバーの日付(driver date)、DirectXのバージョン、(DirectX version)ハードウェアの予約済みメモリ(Hardware reserved memory)の量(ある場合)、およびコンピューター内でビデオカード(video card)が接続されているPCIバス(PCI bus)を示す物理的な場所(Physical location)についての詳細もあります。

4.タスクマネージャー(Manager)を使用すると、ユーザーは現在のネットワーク使用率(network utilization)(Wi-Fi、イーサネット(Ethernet)、Bluetooth)を監視できます。
ネットワークの使用状況(network usage)を監視するには、まず、監視するネットワークインターフェイスを選択します。これは、 [タスクマネージャーの(Task Manager)パフォーマンス(Performance)]タブの左側にあるリソースリスト(resource list)から実行できます。必要に応じて、[パフォーマンス(Performance)]タブの任意の場所を右クリックまたは長押しして、 ["View -> Network."]を選択することもできます。
![[タスクマネージャーのパフォーマンス]タブの[Wi-Fi]セクション](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-_iF2fBeqnzY/YjcmbnC6k6I/AAAAAAAAFHI/zwHhqwV4Y3oNR5xcBOXqF4X6QLMGfqzaQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxeSqmKu1BtuATYSULyy9OK0vUZJMh4EEreX9rzJid57_Lr5itgoyxzXecCdHil_kcjllNp636SB8ECcTxmI--8us7mIs7_4fcnjy5EcSKFLsehZVlA79dQvMROYqrbbfCkZz25BePPjbkt5vMp0a-Ffrw5A99b5RlKddBRMXeM9g_FOe-xFzRbvRW7TYY6HykLA9PekQsEvOV8jpg0SHFKFaAgGIgHmS8N7Z4b0t8oAyxaq09z-wMB1q859mpaUbsnf4wcrBa-aLiovkCSe0-odM-A-9luIU_P030lCRFTGU9BY0zVaY2-1KUD4qSF0CxrUZ63BI5AN1rY-GLaYkrr6q6sLymszIx_5ReHwutHRLMCol2Y3bqo8_EmWqm1xKORC4FaaCfGnEFVJB_wg7045IZzS73d4lf5GevtJPILvrX6AAn4MdBndWPI54Il_GyriQm-PvgqlWRU8VIZSbskQDSr606f1DhUT0lFbEm55jRTZO5fxh4ah9Me-2zfxCotjHRzCLkIkXarR56jt-M2SgQLbI-FEfyKwUTPXJ4v_RR4iPWc90tJKVi01D3pbDGX5WGBgfwItEcVTJrbT3YKakmk0mweSX3-I0kynawDx1NIRHydgBsBNyU99ZZWyYdyYcFCu2SsV1d5Oa8w4NXckQY/s0/du5QNIMtIzFEDyq-yTUU_wNyyRU.png)
イーサネット接続とWi-Fi接続(Ethernet and Wi-Fi connections)は、仮想マシンまたはBluetoothアダプターに使用する可能性のある仮想(Bluetooth)ネットワークアダプター(network adapter)とともに、別々にリストされています。監視するインターフェイスを選択します。グラフには直前の合計使用量が表示され、下のグラフにはデータの送受信速度(sending and receiving speeds)、接続の種類(connection type)、IPアドレス(IP address)に関する情報が表示されます。また、ウィンドウの左側の各ネットワークアダプター(network adapter)の下にあるリストで、平均の送信速度と受信速度を(send and receive speeds)確認できます。

ネットワークの使用状況(network usage)の詳細については、グラフを(graph and click)右クリックまたは長押しして、[ネットワークの詳細を表示("View network details.")]をクリックまたはタップしてください。

結果のウィンドウには、ネットワークの総使用率(network utilization)、リンク状態と速度、送受信されたバイト数、送受信されたユニキャストおよび非ユニキャストパケットの数など、目の肥えたネットワーク(discerning network)技術者にとって役立つ情報が大量に表示されます。
![[ネットワークの詳細]ウィンドウ](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-6YPft5SwB2k/YjcphqjocYI/AAAAAAAAK08/nTLr6gvjlhwerxnB0xnt06PvQ6Sj4AhegCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxqHo63eC-w2z6yviSn9DYRDJuWMKm_sPX6g-BI1OEFwv6L01SgCY8x7NMPafCADWrqG-5bpVDJ9v1dX5VJUMKLtB4dJOAcVJsEhFbbXtL-XEojuNI5AruC6OEcs4cjQnBRmHxiidG_bT2PUln-JyMDeM9aSWLAKSXNGv7-yc7yQmIvhyUYhbDkEh81nfEAWmrpABM29e2_Sw9E50aw52PTBbSFGr-9f2F_zVQ6X8hhfsueD2Q3TAAeasc4-YpuzFdw2-e8Er4zY_PbIim0s6V3-GMF_pNVuXyk43N0cVPAQ4d5EcEKzOSQZl94Dd4hs_80k2TqFQdbSNhpq9D9NQyskK8FU-cfokIaFU0zhsWLLuGZVsuH1NRNGn4YNiKEV3QCAPqc9kzi1dPCRqXGd--4GOATbeSeKcQVgEuAwUTG5knE2W6mc6eg3LAB05feSMp5RK6QTKY72osxAAWsYKriaD-cjcVT3-YNVM5UanAfvczKJd_aCqsMi7kY2O-rOOq_hTYACxmVLcoKulU2T9PDKqZObOmLUWvpw1LFqfbIcIgdTfhTJx2pOU5yBgXu92TP53dU475DxGW5MnLmd0KwZo4qU3vaO3OQOutgpXWW1yHWLDsgvUWG4wybPqFh4idUvTQRR786lrgNYjAwlKDdkQY/s0/KZLKGm2-ehXEpbSskebxVA9v7Ew.png)
5.タスクマネージャー(Manager)を使用すると、ユーザーは現在のストレージ使用率(storage utilization)(HDDまたはSSD(HDD or SSD))を監視できます。
監視したいもう1つのリソースは、ディスク(Disk)使用量です。タスクマネージャの[(Task Manager)パフォーマンス(Performance)]タブの左側にあるリストで選択すると、アクセスできます。または、必要に応じて、ウィンドウ内のどこかを右クリック(または長押し)して、"View -> Disk."
![タスクマネージャの[パフォーマンス]タブの[ディスク]セクション](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-xcqy5twsPm8/Yjcne0-2jrI/AAAAAAAAFNc/BAxMb4e25tUJmduMerwRKQYFADII-W4hQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxeSqmKu1BtuATYSULyy9OK0vUZJMh4EEreX9rzJid57_Lr5itgoyxzXecCdHil_kcjllNp636SB8ECcTxmI--8us7mIs7_4fcnjy5EcSKFLsehZVlA79dQvMROYqrbbfCkZz25BePPjbkt5vMp0a-Ffrw5A99b5RlKddBRMXeM9g_FOe-xFzRbvRW7TYY6HykLA9PekQsEvOV8jpg0SHFKFaAgGIgHmS8N7Z4b0t8oAyxaq09z-wMB1q859mpaUbsnf4wcrBa-aLiovkCSe0-odM-A-9luIU_P030lCRFTGU9BY0zVaY2-1KUD4qSF0CxrUZ63BI5AN1rY-GLaYkrr6q6sLymszIx_5ReHwutHRLMCol2Y3bqo8_EmWqm1xKORC4FaaCfGnEFVJB_wg7045IZzS73d4lf5GevtJPILvrX6AAn4MdBndWPI54Il_GyriQm-PvgqlWRU8VIZSbskQDSr606f1DhUT0lFbEm55jRTZO5fxh4ah9Me-2zfxCotjHRzCLkIkXarR56jt-M2SgQLbI-FEfyKwUTPXJ4v_RR4iPWc90tJKVi01D3pbDGX5WGBgfwItEcVTJrbT3YKakmk0mweSX3-I0kynawDx1NIRHydgBsBNyU99ZZWyYdyYcFCu2SsV1d5Oa8w4NXckQY/s0/e6cbkW5y-iYGYjPTCRbuSqD-XJc.png)
このセクションでは、ハードドライブまたはソリッドステートドライブのアクティビティを確認できます。上のグラフは過去60秒間のディスク使用量を示し、下のグラフはデータの転送速度を示しています。

グラフの下には、ドライブがアクティブであった時間の割合、要求に応答する平均速度、平均読み取りおよび書き込み速度、ドライブの容量などの詳細情報があります。

6.システムリソース(system resource)(プロセッサ、グラフィックス、メモリ、ネットワーク、またはストレージ(network or storage))の使用率の概要を表示します
長期間にわたってリソースの使用状況を監視する場合は、タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)ウィンドウに表示される情報の量を最小限に抑えることができます。結局のところ、ウィンドウを最小化すると同時にそれを見ることができません。画面スペースを維持するために、タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)は現在のチャートのみを表示し、他には何も表示しないグラフサマリービューを提供します。試してみるには、監視したいシステムリソースのグラフをダブルクリック(ダブルタップ)してください。(system resource)または、システムリソースグラフ(system resource graph)を右クリックまたは長押ししてから、[グラフの概要ビュー("Graph summary view.")]をクリックまたはタップすることもできます。

結果として得られるウィンドウは小さくなり、雑然としません。これは、プロセッサ(CPU)で得られるものです。
また、これはワイヤレスカードで得られるものです。

他のシステムリソース用に取得するミニグラフは、上記のものと同様です。
7.単一の小さなウィンドウで、すべての重要なシステムリソースの使用率の概要を同時に表示します
すべてのリソースの使用状況をすばやく確認したい場合は、リソースのリストを右クリックまたは長押しして、 [概要ビュー]を("Summary View.")クリックまたはタップします。(click or tap)

タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)ウィンドウが縮小して、各リソースとその総使用量の割合が表示されるため、画面のスペースをあまり占有せずに監視しやすくなります。

最新バージョンのWindows10では、(Windows 10)タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)ウィンドウの左側の列に、デフォルトで各リソース使用量(resource usage)のミニグラフが表示されます。デフォルトでは、概要ビュー(Summary view)にも表示されます。ただし、古いバージョンのWindowsでは(Windows)、デフォルトで表示されない場合があります。その場合は、リストを右クリックまたは長押しし、[グラフを表示]("Show graphs")を選択(list and select) して表示します。

システムリソースの使用に関する情報をコピーして貼り付ける方法
システムのリソースに関する有用な情報をすべて表示する方法がわかったので、一部のデータを記録することをお勧めします。スクリーンショットを撮ることはできますが、最終的には画像しか表示されないため、その情報を処理する必要がある場合は役に立ちません。幸い、必要なデータをコピーして貼り付けることができます。任意のリソース(resource and click)からデータチャートを右クリックまたは長押しして、[コピー(Copy.)]をクリックまたはタップします。

ワードプロセッサまたはスプレッドシートアプリケーション(word processor or spreadsheet application)を開き、プレゼンテーションやレコードに使用できる適切な形式の情報ダンプのデータを貼り付けます。(info dump)

CPU、RAM、GPU、およびその他のシステムリソースの使用状況を確認したいのはなぜですか?
これで、Windows10およびWindows8.1で(Windows 8.1)タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)を使用して、システムのパフォーマンスを監視する方法がわかりました。各リソースのデータチャートは多く(resource share plenty)の情報を共有しており、技術者とホームユーザーの両方が、タスクマネージャーの[(Task Manager)パフォーマンス(Performance)]タブから収集できるデータを高く評価しています。タスクマネージャーは、現在の(Task Manager)CPUとメモリの使用率を監視したり、 (CPU and memory utilization)GPUの使用状況(GPU usage)を確認したりできる優れたツールであることをご存知でしょう。、またはネットワークインターフェイスやストレージドライブなどの他の重要なリソースの使用。このテーマについて質問がある場合は、下にコメントを残すことを躊躇しないでください。
7 ways to keep tabs on your systems' performance with the Task Manager
Have уou ever wanted to know how much of your processor's power is being used аt a particular time? Or maybe how much frеe RAM was left for your favoritе game to use? How about how much of your video card's power is used? All these are essential ѕуstem resourcеs without which apps and games cannot run well. If you want to see statistics aѕ well as reаl-time informatіon, you should know that the Windows Task Manager allows the user to monitor the current processor (CPU) and memory utilization, check the video card (GPU) usage, as well as other system resources. Here's how to keep tabs on your system resources:
NOTE: This guide is created for Windows 10 and Windows 8.1, and some of the features we show are available only in the latest versions of Windows 10.
Where to find the tools that let you monitor the system resources: access the Task Manager's Performance tab
To get a look at resource consumption, you must launch the Task Manager. While there are many methods to do that, for speed and ease we recommend using the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl + Shift + Esc." If the Task Manager opens in its compact view, click or tap on "More Details" to expand to full view.

Then, click or tap on the Performance tab. It should look more or less like in the screenshot below. Its looks and contents depend on the version of Windows that you use and on the hardware you have.

Let's see how to use the Performance tab from Task Manager to monitor the performance of the essential hardware components such as your CPU, GPU, and memory utilization.
1. Task Manager allows the user to monitor the current processor utilization
By default, the Performance tab of Task Manager first shows you the usage of CPU, otherwise known as the processor. If it is not already selected, you can do so manually by clicking or tapping on CPU on the left side of the window.
You can also choose to view the CPU usage by right-clicking anywhere inside the window and choosing "View -> CPU."

Once you have selected the processor, on the right side of the window, you should see a graph that shows the percentage of the CPU usage during the last 60 seconds. Notice that in the upper right corner of the resource view, Task Manager shows you the exact model of your processor.

Below the graph, there is detailed information about the current CPU utilization and speed, as well as information about your processor's specifications such as its Base speed, number of Sockets and Cores, Logical processors (threads), whether the Virtualization feature is on or off, and the amounts of Level 1, 2, and 3 cache memory available on it.

By default, you get a graph for each physical processor in your PC. It makes sense, but it may not be what some users are looking for: to get a more detailed picture of your processor usage, you can split the graph into logical processors. Right-click or press-and-hold on the CPU graph, hover over "Change graph to" and then click or tap on "Logical processors."

You should now see smaller graphs for each of the CPU's logical processors. For our AMD Ryzen 7 2700 processor, we get 16 charts, one for each of its threads. You may see more or less, depending on your computer's processor.

If you want to see even more information about how CPU cycles are being allotted, you might want to consider showing kernel times. They show how many of your CPU cycles are being used by the kernel, which is responsible for internal system functions, and how much is getting used by user processes.
To enable kernel times, right-click or press-and-hold the CPU graph and click or tap "Show kernel times."

The darker areas of the graph represent kernel time, while the lighter areas represent other types of usage.

2. Task Manager allows the user to monitor the current memory utilization (RAM)
Another resource that you probably want to keep a close eye on, especially during slowdowns, is your RAM (Random Access Memory). You can view memory usage by choosing Memory from the list of resources on the left side of the Performance tab.

To switch to the Memory graph, you can also right-click or press-and-hold anywhere inside the window and go to "View -> Memory."

The Memory section displays two graphs. The top graph displays the percentage of memory used during the last minute. The lower graph shows how memory is allocated. Hover your mouse over each section of the lower graph to see what is what.

The RAM usage is split into four usage types:
- In Use - Memory currently being used by apps, drivers, or Windows itself.
- Modified - Memory whose contents must be written to disk before it can be used for other purposes.
- Standby - Memory that contains cached data and code that is not currently in use.
- Free - Memory that is not currently in use and free for use.
Below the graphs, there's more detailed information about the RAM, including used memory, available memory, its speed, slots used and form factor, paged and nonpaged memory pool size, and so on. The pools of memory that you see are either guaranteed to reside in physical memory or can be swapped back and forth to the disk, as needed. You should also see the total memory used for cache and the total committed memory. The amount of data displayed also depends on your computer's hardware configuration.

3. Task Manager allows the user to monitor the current video card utilization (GPU)
In the last versions of Windows, including the May 2019 Update and Fall Creators Update, the Task Manager also lets you check GPU usage. This feature is not present in older versions of Windows 10, nor older versions of Windows.
You can monitor the performance of all your graphics cards by selecting them from the list on the left of the Task Manager window. If you have more than one video card installed on your device, you should have an entry for each of them.

When you select a video card that you want to monitor, the right side of the window fills up with graphs and information about its activity. Depending on the type of video card you select, you should see graphs for how much of its power is spent on 3D, Copy, Video Encode, and Video Decode.

By default, the Task Manager has enough room to display only four different graphs. However, if you want to change one of them and monitor some other feature, you can click or tap on the small arrow button on the top-left corner of a graph and select what to watch. You can choose from things like Video Processing, Legacy Overlay, Security, Cuda, VR, and so on, depending on the actual features offered by that video card.

Under the four feature graphs, the Task Manager also shows how the video memory is used. You should have a graph for the "Shared GPU memory usage" and, if your video card also has dedicated memory, you should also have one called "Dedicated GPU memory usage." On the top-right corner of each graph, you can find out the total amount of video memory available on your system.

Below the graphs, there's plenty of other useful information. You can see the total Utilization percentage of your video card, the amount of GPU Memory used and the amount available, as well as the Dedicated GPU memory, and the Shared GPU memory used and the amounts available. There are also details about the driver version used, the driver date, DirectX version, the amount of Hardware reserved memory, if any, and the Physical location, which shows you the PCI bus to which the video card is connected inside your computer.

4. Task Manager allows the user to monitor the current network utilization (Wi-Fi, Ethernet, Bluetooth)
To monitor your network usage, first, select which of your network interfaces you want to monitor. You can do that from the resource list on the left side of the Task Manager Performance tab. If you prefer, you can also right-click or press-and-hold anywhere in the Performance tab and choose "View -> Network."

The Ethernet and Wi-Fi connections are listed separately, along with any virtual network adapters you might use for virtual machines or Bluetooth adapters. Choose the interface that you want to monitor. The graph displays the total usage for the last minute, and the chart below shows information about the data sending and receiving speeds, the connection type, and the IP address. You can also see the average send and receive speeds in the list from the left side of the window, under each network adapter.

For a greater level of details about your network usage, right-click or press-and-hold the graph and click or tap on "View network details."

The resulting window displays tons of useful information for the discerning network technician including the total network utilization, link-state and speed, bytes sent/received and the number of unicast and non-unicast packets sent and received.

5. Task Manager allows the user to monitor the current storage utilization (HDD or SSD)
Another resource that you may want to monitor is Disk usage. You can get to it by selecting it in the list from the left of the Performance tab in Task Manager. Or, if you prefer, right-click (or press-and-hold) somewhere inside the window and go to "View -> Disk."

This section allows you to see the activity of your hard drives or solid-state drives. The top graph displays disk usage over the past 60 seconds, while the bottom graph displays how fast your data is getting transferred.

Below the graphs, there is more information, including the percentage of time your drives have been active, the average speed with which they respond to requests, the average read and write speeds and the drives' capacities.

6. View a summary of the utilization of a system resource (processor, graphics, memory, network or storage)
If you plan to monitor resource usage over an extended period, you may want to minimize the amount of information displayed in the Task Manager window. After all, you cannot minimize the window and watch it at the same time. To preserve screen space, the Task Manager offers a graph summary view that shows only the current charts and nothing else. To try it out, double-click (double-tap) on the graph of the system resource you want to monitor. Alternatively, you can also right-click or press-and-hold on the system resource graph and then click or tap on "Graph summary view."

The resulting window is smaller and less cluttered. This is what you get for the processor (CPU):

Also, this is what you get for a wireless card:

The mini-graphs you get for the other system resources are similar to the ones above.
7. View a summary of the utilization of all the essential system resources at the same time, in a single small window
If you would rather get a quick view of all your resources usage, you can right-click or press-and-hold the list of resources and click or tap "Summary View."

The Task Manager window shrinks down to show you each resource and its percentage of total usage, making it easier to monitor without taking up too much screen real estate.

In the latest versions of Windows 10, the column from the left side of the Task Manager windows shows mini-graphs for each resource usage, by default. They're also shown in the Summary view by default. However, in older versions of Windows, you might not see them by default. If that is the case for you, right-click or press-and-hold the list and select "Show graphs" to display them.

How to copy and paste information about the use of your system resources
Now that you know how to view all that useful information about your system's resources, you may want to record some of the data. While you could take a screenshot, you would only end up with an image, which is not useful if you need to work with that information. Fortunately, you can copy and paste the data that you need. Right-click or press-and-hold on the data chart from any resource and click or tap Copy.

Open a word processor or spreadsheet application and paste the data for a well-formatted info dump that you can use for presentations or records.

Why did you want to check the usage of your CPU, RAM, GPU, and other system resources?
Now you know how to use the Task Manager in Windows 10 and Windows 8.1, to keep tabs on your system's performance. The data charts for each resource share plenty of information, and both techies and home users alike appreciate the data they can gather from the Performance tab of Task Manager. You know that the Task Manager is a neat tool that allows you to monitor the current CPU and memory utilization, as well as check the GPU usage, or the usage of other important resources such as your network interfaces or storage drives. If you have any questions on this subject, do not hesitate to leave a comment below.

![タスクマネージャの[パフォーマンス]タブ](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-u9fhyQqqwro/YjcZU2UQFSI/AAAAAAAAmsk/fZ3jS0thPj0CGH2tVjPZzB3szxsJPfnZwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCTz9yRBg/s0/AGr88uz0-fIguUcPzLBGVTO177w.png)
![タスクマネージャの[パフォーマンス]タブのCPUセクション](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-ys3rRVzoabI/YjcN7LYTWRI/AAAAAAAABrM/ooohJK1UK90gqrHJZznmC4cwwpTxTq_lQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxeSqmKu1BtuATYSULyy9OK0vUZJMh4EEreX9rzJid57_Lr5itgoyxzXecCdHil_kcjllNp636SB8ECcTxmI--8us7mIs7_4fcnjy5EcSKFLsehZVlA79dQvMROYqrbbfCkZz25BePPjbkt5vMp0a-Ffrw5A99b5RlKddBRMXeM9g_FOe-xFzRbvRW7TYY6HykLA9PekQsEvOV8jpg0SHFKFaAgGIgHmS8N7Z4b0t8oAyxaq09z-wMB1q859mpaUbsnf4wcrBa-aLiovkCSe0-odM-A-9luIU_P030lCRFTGU9BY0zVaY2-1KUD4qSF0CxrUZ63BI5AN1rY-GLaYkrr6q6sLymszIx_5ReHwutHRLMCol2Y3bqo8_EmWqm1xKORC4FaaCfGnEFVJB_wg7045IZzS73d4lf5GevtJPILvrX6AAn4MdBndWPI54Il_GyriQm-PvgqlWRU8VIZSbskQDSr606f1DhUT0lFbEm55jRTZO5fxh4ah9Me-2zfxCotjHRzCLkIkXarR56jt-M2SgQLbI-FEfyKwUTPXJ4v_RR4iPWc90tJKVi01D3pbDGX5WGBgfwItEcVTJrbT3YKakmk0mweSX3-I0kynawDx1NIRHydgBsBNyU99ZZWyYdyYcFCu2SsV1d5Oa8w3tXckQY/s0/CehB0_FJDnaW6F6NmvzpNsLOV68.png)
![タスクマネージャの[パフォーマンス]タブからCPUセクションを開く](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-QdjV1bHSxZ4/YjdbefHgF-I/AAAAAAAAP90/a2exaDuqSDskMLWDiwyi1Hu7z9jfbnvzQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhyU0JW91iiU4HdUNyWpEBsKLTw-6rQ88JJcf3GF8lMk7uR2vURQvSrLKx3HPJ-0bFTSQRDYtFiF0xXMnzMqjkeinj0p4_6R1kO7c7YxY5qQhApZ0W4keaxtQNkUgY3tkRT5-ypFY9VCwWOdWlQjQXqnqqmUhUOHojDHDyRxOdzXgn83uL9cUhyZQAyqoLNXwTuyPI3w7jMVLY_X3G_jMusEXoZHkAYQKZqBgUhPxBxFlPwhH-2DdZDXsVjKZqfavx4quKoI8Dn5vbKBw1fBP2LP-TMONu3R7eOkf34NH9fhPJJ8dtB0a9Nr9Lbun4wsDt2UkPoVWdXK-T5WEyqL8jtJIZzuNmeYS32rgbNJxt2MkVJe0ECNAjwjXY1oCKwCAja-lwWv2MG2WdS5jNcBqq8uNpsf5TXfjQaewupijbNsp_viGHOdMXhU68bv9CYzh3Jg897TZj113lNc9x2yiPm9ZLpb68caNxrHKk6kQvdPMHMRzJzCFsHGdrcsGW8UUQ6Ht3UrJUSKHvNnPH9C-EavJf8LBHVfter4gT7dO0uaIhreDldhomF7fI1DE1HmW7QFlecOcn2MqpmjESsYDZlEqVL_O7bu6l5iDcDGvhsDH0Fhqz9rIOYRCpkWkIV1yugxhdBnKN3LY3H2ntww_uXdkQY/s0/XFfiTcUXgDNcPnLRCU-Zcp99ds4.png)






![タスクマネージャの[パフォーマンス]タブの[メモリ]セクション](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-YNr5APHXF4Q/Yjcd6c5fSRI/AAAAAAAAmpg/RF216h7Zq2gXaJYwItZ-C8v1bZq2xIzYACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCTz9yRBg/s0/a3DIkX6rH1TXcZmaqVS2BFhV7Qg.png)



![タスクマネージャーの[パフォーマンス]タブのGPUセクション](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-qus1RXXClgw/YjdXLv5mwyI/AAAAAAAAxNs/JGqEs2sVA3A-iEO1y-5iUhZq2nGF4FFGACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCe4d2RBg/s0/TsVrEdoapROdE2WkOuJlmo2iffE.png)




![[タスクマネージャーのパフォーマンス]タブの[Wi-Fi]セクション](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-_iF2fBeqnzY/YjcmbnC6k6I/AAAAAAAAFHI/zwHhqwV4Y3oNR5xcBOXqF4X6QLMGfqzaQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxeSqmKu1BtuATYSULyy9OK0vUZJMh4EEreX9rzJid57_Lr5itgoyxzXecCdHil_kcjllNp636SB8ECcTxmI--8us7mIs7_4fcnjy5EcSKFLsehZVlA79dQvMROYqrbbfCkZz25BePPjbkt5vMp0a-Ffrw5A99b5RlKddBRMXeM9g_FOe-xFzRbvRW7TYY6HykLA9PekQsEvOV8jpg0SHFKFaAgGIgHmS8N7Z4b0t8oAyxaq09z-wMB1q859mpaUbsnf4wcrBa-aLiovkCSe0-odM-A-9luIU_P030lCRFTGU9BY0zVaY2-1KUD4qSF0CxrUZ63BI5AN1rY-GLaYkrr6q6sLymszIx_5ReHwutHRLMCol2Y3bqo8_EmWqm1xKORC4FaaCfGnEFVJB_wg7045IZzS73d4lf5GevtJPILvrX6AAn4MdBndWPI54Il_GyriQm-PvgqlWRU8VIZSbskQDSr606f1DhUT0lFbEm55jRTZO5fxh4ah9Me-2zfxCotjHRzCLkIkXarR56jt-M2SgQLbI-FEfyKwUTPXJ4v_RR4iPWc90tJKVi01D3pbDGX5WGBgfwItEcVTJrbT3YKakmk0mweSX3-I0kynawDx1NIRHydgBsBNyU99ZZWyYdyYcFCu2SsV1d5Oa8w4NXckQY/s0/du5QNIMtIzFEDyq-yTUU_wNyyRU.png)


![[ネットワークの詳細]ウィンドウ](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-6YPft5SwB2k/YjcphqjocYI/AAAAAAAAK08/nTLr6gvjlhwerxnB0xnt06PvQ6Sj4AhegCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxqHo63eC-w2z6yviSn9DYRDJuWMKm_sPX6g-BI1OEFwv6L01SgCY8x7NMPafCADWrqG-5bpVDJ9v1dX5VJUMKLtB4dJOAcVJsEhFbbXtL-XEojuNI5AruC6OEcs4cjQnBRmHxiidG_bT2PUln-JyMDeM9aSWLAKSXNGv7-yc7yQmIvhyUYhbDkEh81nfEAWmrpABM29e2_Sw9E50aw52PTBbSFGr-9f2F_zVQ6X8hhfsueD2Q3TAAeasc4-YpuzFdw2-e8Er4zY_PbIim0s6V3-GMF_pNVuXyk43N0cVPAQ4d5EcEKzOSQZl94Dd4hs_80k2TqFQdbSNhpq9D9NQyskK8FU-cfokIaFU0zhsWLLuGZVsuH1NRNGn4YNiKEV3QCAPqc9kzi1dPCRqXGd--4GOATbeSeKcQVgEuAwUTG5knE2W6mc6eg3LAB05feSMp5RK6QTKY72osxAAWsYKriaD-cjcVT3-YNVM5UanAfvczKJd_aCqsMi7kY2O-rOOq_hTYACxmVLcoKulU2T9PDKqZObOmLUWvpw1LFqfbIcIgdTfhTJx2pOU5yBgXu92TP53dU475DxGW5MnLmd0KwZo4qU3vaO3OQOutgpXWW1yHWLDsgvUWG4wybPqFh4idUvTQRR786lrgNYjAwlKDdkQY/s0/KZLKGm2-ehXEpbSskebxVA9v7Ew.png)
![タスクマネージャの[パフォーマンス]タブの[ディスク]セクション](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-xcqy5twsPm8/Yjcne0-2jrI/AAAAAAAAFNc/BAxMb4e25tUJmduMerwRKQYFADII-W4hQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxeSqmKu1BtuATYSULyy9OK0vUZJMh4EEreX9rzJid57_Lr5itgoyxzXecCdHil_kcjllNp636SB8ECcTxmI--8us7mIs7_4fcnjy5EcSKFLsehZVlA79dQvMROYqrbbfCkZz25BePPjbkt5vMp0a-Ffrw5A99b5RlKddBRMXeM9g_FOe-xFzRbvRW7TYY6HykLA9PekQsEvOV8jpg0SHFKFaAgGIgHmS8N7Z4b0t8oAyxaq09z-wMB1q859mpaUbsnf4wcrBa-aLiovkCSe0-odM-A-9luIU_P030lCRFTGU9BY0zVaY2-1KUD4qSF0CxrUZ63BI5AN1rY-GLaYkrr6q6sLymszIx_5ReHwutHRLMCol2Y3bqo8_EmWqm1xKORC4FaaCfGnEFVJB_wg7045IZzS73d4lf5GevtJPILvrX6AAn4MdBndWPI54Il_GyriQm-PvgqlWRU8VIZSbskQDSr606f1DhUT0lFbEm55jRTZO5fxh4ah9Me-2zfxCotjHRzCLkIkXarR56jt-M2SgQLbI-FEfyKwUTPXJ4v_RR4iPWc90tJKVi01D3pbDGX5WGBgfwItEcVTJrbT3YKakmk0mweSX3-I0kynawDx1NIRHydgBsBNyU99ZZWyYdyYcFCu2SsV1d5Oa8w4NXckQY/s0/e6cbkW5y-iYGYjPTCRbuSqD-XJc.png)










