Ubuntuを含むすべてのオペレーティングシステムがクラッシュする可能性があります。Linuxを実行していて問題が発生した場合は、クラッシュから抜け出すのに役立ついくつかの理由と解決策を次に示します。
Ubuntuがハングした場合、最初に試すことはシステムを再起動する(reboot your system)ことです。場合によっては、コールドブートを実行する必要があります。コンピュータの電源を切り、電源を入れ直します。コンピュータを再起動すると、メモリ不足、アプリケーションのクラッシュ、ブラウザのハングなど、多くの問題が解決します。
コンピューター(Make)がクラッシュする直前に行ったことをメモします。特定のアプリケーションの使用中に常に発生する場合は、更新や既知の問題があるかどうかを調べてください。AudacityやOpenShotVideoEditor など、一部のアプリケーションは時々クラッシュすることが知られています。

アプリケーションの問題を解決するには、ソフトウェアを再起動、修復、またはリロードします。または、作成者に通知してください。
Firefoxのアップデートにより、Linuxもフリーズしました。問題が解決するまで、Firefoxの使用を避ける必要があるかもしれません。
アプリケーションが問題を引き起こしていない場合は、ハードドライブの空き容量が不足しているか、ハードウェアに問題がある可能性があります。
この記事では、クラッシュを診断して回復するための次の方法について説明します。
- ハードドライブのスペースを解放する
- あなたの記憶をテストする
- ハードウェア障害
- 断続的なハードウェアの問題
- Xサーバーのクラッシュからの回復
- 別のソースからLinuxを起動する
ハードドライブのスペースを解放する方法(How To Free Up Hard Drive Space)
- ハードドライブの空き容量を確認するには、[スタート](Start)ボタン、 [アクセサリ]、[(Accessories)ディスク(Disks)]の順にクリックします。

Ubuntuには、 (Ubuntu)Windowsのような同じディスククリーンアップツールと組み込みのデフラグ(built-in defrag like Windows)がありません。では、ディスク領域を解放するために何ができるでしょうか。
- ゴミ箱を空にする
- .ISOダウンロードを削除する
- (Remove)不要になった古いカーネルを削除します
- 使用しないゲームやアプリをアンインストールする
- システムクリーナーを使用する
- 定期的にAPTキャッシュをクリーンアップする
- システムを最新の状態に保つ
上記の最後の箇条書きは、直感に反しているように見えるかもしれません。Linuxの更新は、より多くのスペースを占める(Linux)Windowsの更新とは対照的に、スペースを解放します。
低メモリ(Low Memory)

Ubuntuを実行していて、システムがランダムにクラッシュする場合は、メモリが不足している可能性があります。メモリ不足は、インストールしたメモリに収まらないほど多くのアプリケーションまたはデータファイルを開くことによって発生する可能性があります。
それが問題である場合は、一度に多くを開いたり、コンピュータのメモリを増やしたりしないでください。
メモリ不足のもう1つの原因は、RAMの障害です。メモリテストを実行して、RAMメモリが不良かどうかを判断します。
メモリテストを実行する方法(How To Perform a Memory Test)
- システムの電源を入れるか、再起動することから始めます。
- (Bring)キーボードのShift(Shift)キーを押しながら(GRUB)、GRUBメニューを表示します。
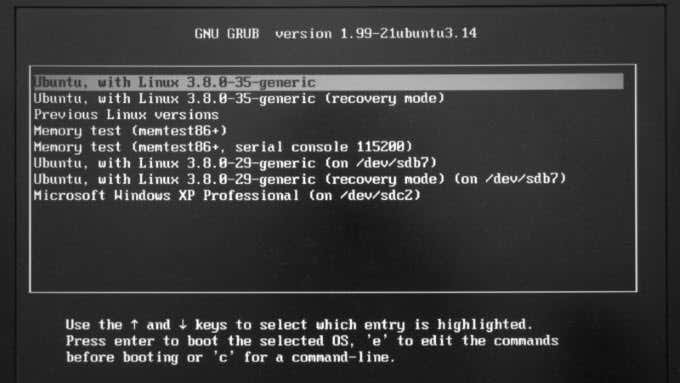
- 矢印キーを使用して、Ubuntumemtest86 (Ubuntu) memtest86+ラベルを見つけます。

- エンターキーを押すと、メモリテストが自動的に実行されます。テストの実行中はブルースクリーンが表示されます。
- エスケープキーを押すまでテストは終了しません。少なくとも1回のフルパスでテストを実行します。問題が非常に断続的に発生する場合は、テストをもっと長く実行してください。
テストでエラーが見つかった場合は、RAMメモリカードの1つを交換する必要があります。
その他のハードウェア障害(Other Hardware Failures)
コンピュータの電源がオフになり、まったくオンにならない(ライトもサウンドもない)場合は、最初にコンセントに電源が入っていることを確認してください。コンセントに電力が供給されている場合に最も可能性の高い原因は、電源装置の不良です。
電源を入れてから30秒以内に電源を切り直そうとすると、ファンが遅いか動かない可能性があります。または、ファンの速度を検出するセンサーが故障している可能性があります。
コンピュータをクラッシュさせる可能性のあるその他のコンポーネントは次のとおりです。
- (Overheating)ファンが遅い、またはまったく回転しないことによる過熱
- ハードドライブのクラッシュ
- 不良電源
- マザーボードまたはCPUの故障
- グラフィックカードの問題
- センサー
ハードドライブの障害を自分でテストすることもできます。一定数のエラーは許容されます。新しいハードドライブでさえ、すでにいくつかのエラーがあります。

独自の修理方法を知っている場合は、故障したコンポーネントを交換してください。それ以外の場合は、コンピューター技術者にマシンの修理を依頼してください。
断続的なハードウェアの問題(Intermittent Hardware Problems)
散発的な問題の最も一般的な原因は、メモリの過熱障害とハードドライブエラーです。
テストで障害のあるコンポーネントが特定されない場合は、問題が見つかるまで一度に1つずつ交換する必要があります。
Xサーバーのクラッシュからの回復(Recovering From an X Server Crash)
Linuxシステムは、クラッシュから回復するための複数の方法を提供します。最も簡単な方法は再起動です。しかし、他の方法があります:
- キーボードショートカットを使用して、Xサーバーを再起動します。
- 仮想コンソールを切り替えます。
- SSH(Kill)を使用してネットワーク経由でXサーバーを強制終了(SSH)します。
- MagicSysRqキーを使用します。
別のソースからLinuxを起動する(Boot Linux From Another Source)
コンピューターの電源がオンになったが、Linuxのロードを拒否した場合はどうなりますか?ハードドライブが不良であるか、オペレーティングシステムファイルが破損している可能性があります。
Ubuntu Live CDまたはUSBを作成した場合は、他のオペレーティングシステムから起動できます。
事前にこれを行う必要があります。または、別のコンピューターでライブブートを行います。
詳細な手順については、「起動可能なLinuxUSB(How to Build Your Own Bootable Linux Live CD)ドライブを作成するためのツール」または「独自の起動可能なLinuxLiveCDを作成する方法」を参照してください。
多くの要因により、システムがクラッシュする可能性があります。解決策は1つではありません。最悪のシナリオでは、上記の提案のいずれも機能しない場合は、新しいコンピューターまたは優れたコンピューター技術者が必要になる場合があります。
Common Reasons for Ubuntu Crashes and How to Recover
Any operating system can crash, including Ubuntu. If you arе running Linux and have a problem, here are a few rеasons and solutions to help you get out of yоur crash.
If Ubuntu hangs, the first thing to try is to reboot your system. Sometimes you might have to do a cold boot. Power your computer off and then bring it back up. Restarting your computer resolves many problems such as low memory, application crashes, and the browser hangs.
Make note of what you did just before the computer crashed. If it always happens while using a specific application, research to find out if there are any updates or known issues. Some applications are known to crash at times, such as Audacity and OpenShot Video Editor.

To resolve application issues, restart, repair or reload the software. Or, notify the people who created it.
Firefox updates have also caused Linux to freeze. You may have to avoid using Firefox until they fix the issues.
If an application is not causing your problem, you may be out of room on your hard drive or have a hardware issue.
This article covers the following ways to diagnose and recover from a crash:
- Freeing up hard drive space
- Testing your memory
- Hardware failures
- Intermittent hardware problems
- Recovering from an X Server crash
- Boot Linux from another source
How To Free Up Hard Drive Space
- To find out how much free space you have on your hard drive, click the Start Button, then Accessories, and then Disks.

Ubuntu doesn’t have the same disk clean-up tools and built-in defrag like Windows. So, what can you do to free up some disk space?
- Empty your trash
- Delete .ISO downloads
- Remove old kernels you no longer need
- Uninstall games and apps you don’t use
- Use a system cleaner
- Regularly clean APT Cache
- Keep your system updated
The last bullet point above might seem counterintuitive. Linux updates free up space as opposed to Windows updates that take up more space.
Low Memory

If you are running Ubuntu and your system randomly crashes, you may be running out of memory. Low memory could be caused by opening more applications or data files than will fit in the memory you have installed.
If that is the problem, do not open so much at one time or upgrade to more memory on your computer.
Another cause of low memory is a failing RAM. Run a memory test to determine whether your RAM memory is bad.
How To Perform a Memory Test
- Start by turning on or restarting your system.
- Bring up the GRUB menu by holding down Shift on your keyboard.

- Using the arrow keys, find the Ubuntu memtest86+ label.

- After you press the enter key, the memory test will automatically run. You will see a blue screen while the test is running.
- The test won’t end until you press the escape key. Let the test run for at least one full pass. If your problem is very intermittent, let the test run much longer.
Should the test find any errors, you need to replace one of your RAM memory cards.
Other Hardware Failures
If your computer powers off and will not power on at all (has no lights and no sounds), first check to make sure there is power at the outlet. The most likely cause if you have power at the outlet is a bad power supply.
If it tries to power up and then powers back down within 30 seconds, you may have a slow or non-moving fan. Or the sensor that detects fan speed may be failing.
Other components that can cause your computer to crash are:
- Overheating due to fans being slow or not turning at all
- Hard drive crash
- Bad power supply
- Failing motherboard or CPU
- Graphics card problems
- Sensors
You can also test your hard drive for failures yourself. A certain number of errors are acceptable. Even new hard drives already have some errors.

If you know how to do your own repairs, replace the failing component. Otherwise, have your computer technician repair your machine.
Intermittent Hardware Problems
The most common causes of sporadic problems are overheating memory failures and hard drive errors.
If testing doesn’t identify the failing component, you may have to replace them one at a time until you find the problem.
Recovering From an X Server Crash
Linux systems provide multiple ways to recover from a crash. The easiest way is a reboot. But there are other methods:
- Use a keyboard shortcut to restart the X server.
- Switch virtual consoles.
- Kill the X server over the network using SSH.
- Use the Magic SysRq key.
Boot Linux From Another Source
What if your computer powers on but refuse to load Linux? You could have a bad hard drive, or the operating system files could be corrupted.
If you have made an Ubuntu Live CD or USB, you can boot from that other operating system.
You need to have done this in advance. Or, you make a Live boot on a different computer.
See Tools To Create A Bootable Linux USB Drive or How to Build Your Own Bootable Linux Live CD for detailed instructions.
Many factors can cause your system to crash. There isn’t one solution. In the worst-case scenario, if none of the above suggestions work, you may need a new computer or a good computer technician.






