友達がLinux(Linux)についていつも話しているのを聞いたり、WindowsとLinuxのどちらのOSが自分に適して(which OS is better for you, Windows or Linux)いるのか疑問に思っているかもしれません。あなたはそれを試してみたいと思うかもしれませんが、Linuxが好きかどうかは完全にはわかりません。最初に試してみる方法はありますか?幸いなことに、あります。
VirtualBoxを使用して、 Windows10内にLinuxベースのOSをインストールできます。Linux OSを(Linux OS)Windowsと一緒にデュアルブートすることもできますが、数日後にLinux OSを放棄することを選択した場合、VirtualBoxははるかにクリーンな状態を提供します。(VirtualBox)

VirtualBoxを使用してWindows(Windows Using VirtualBox)にLinuxをインストールする方法
この方法を使用して任意のLinuxOSをインストールでき(install any Linux OS)ますが、最も人気があるため、このチュートリアルで はUbuntuを使用します。(Ubuntu)
1.UbuntuのISOをダウンロードします(1. Download the ISO for Ubuntu)
Ubuntu用のISOを(ISO for Ubuntu)ダウンロードすることから始めます。予備の空のディスクやフラッシュドライブがないことを心配する必要はありません。VirtualBoxを使用してUbuntuをインストールし(installing Ubuntu with VirtualBox)ているので、必要なのはISOだけです。
LTS(長期サポート)バージョンを使用するのが理想的です。現在のLTSバージョンはUbuntu20.04.2LTSです(LTS)。

2.VirtualBoxをダウンロードします
PCにVirtualBoxを(VirtualBox)ダウンロード(download)してインストールする必要があります。Windowsパッケージをダウンロードできますが、 LinuxおよびmacOSでも利用できるパッケージがあります。インストールプロセスはそれらの間でわずかに異なる場合があることに注意してください。

インストールを実行し、プロンプトに従います。インストールしたら、UbuntuISOのダウンロードが完了したかどうかを確認します。ある場合は、先に進んで、 Ubuntu用にVirtualBoxを構成できます。
3.Ubuntu用にVirtualBoxを構成します
VirtualBoxを起動すると、次のウェルカム画面が表示されます。[(Click)新規(New)]をクリックして、構成プロセスを開始します。

ダイアログボックスが表示されます。次に、次の手順に従います。
- 仮想マシンに名前(Name)を付けます(例:Ubuntu v20.04.2 LTS ) 。
- (Click)「タイプ(Type )」の横にあるドロップダウンメニューをクリックして、「 Linux 」を選択します。
- Ubuntu(64ビット)またはUbuntu(32ビット)としてバージョン(Version )を選択します。

- 仮想マシンにメモリサイズ(Memory size)を割り当てます。理想的には、PCのRAM(RAM)の約4分の1を割り当てることを選択する必要があります。たとえば、合計16GBのRAMがある場合は、仮想マシンに4GBを割り当てます。
- [次へ(Next )]ボタンを選択します。
また、ハードディスクの一部を仮想マシンに割り当てる必要があります。この部分は、仮想オペレーティングシステム(この場合はUbuntu )にのみアクセスできます。(Ubuntu)選択できるオプションは2つあります。ストレージを使い続けるにつれて大きくなる動的に割り当てられた(Dynamically allocated)ストレージを使用するか、より高速なパフォーマンスを提供する固定サイズの(Fixed-size)ストレージ制限を割り当てることができます。
- 次の画面で、仮想マシン用の新しいハードディスクを作成する必要があります。[今すぐ仮想ハードディスクを作成する(Create a virtual hard disk now)]オプションを選択し、[作成]をクリックします(Create)。
- 次に、仮想ハードディスクに使用するファイルの種類を選択する必要があります。VDI(VirtualBox Disk Image)を選択し、Nextを(Next)選択します。
- [動的に割り当て](Dynamically allocated)を選択し、[次へ(Next)]を選択します。
- 次の画面にデフォルトのVDIストレージの場所とサイズが表示されますが、そのままにして、[(VDI)作成](Create)を選択します。

これで、構成プロセスの最初の部分が完了します。仮想マシンがセットアップされたので、次に進んで、UbuntuISOを仮想マシンに追加しましょう。すでにUbuntu CD/DVDをお持ちの場合は、それをドライブに挿入して、仮想マシンでも使用できます。
先に進む前に、BIOS設定でハードウェア仮想化が有効になっていることを確認してください。有効になっていない場合、次の手順は機能しません。
これで、VirtualBoxの左側のサイドバーにUbuntuが表示されます。それを選択し、[設定]をクリックします(Settings)。

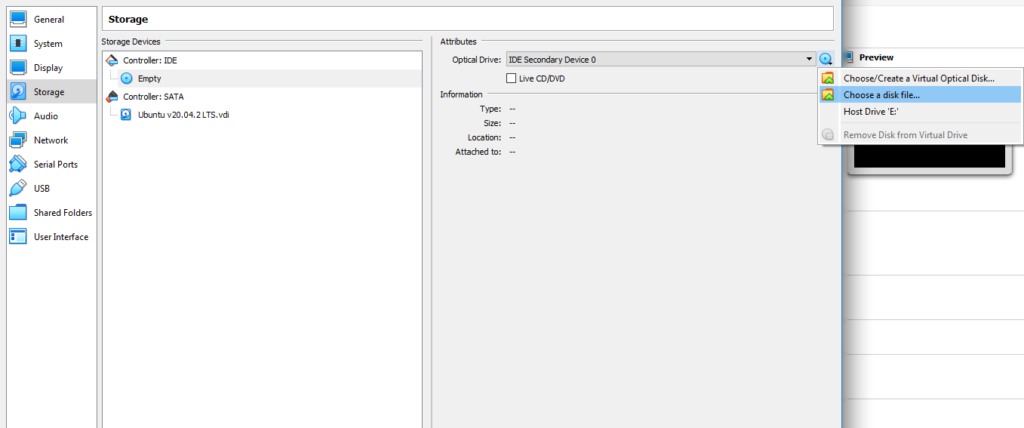
[設定(Settings)]ダイアログボックスの左側のサイドバーで[ストレージ(Storage)]を探します。[(Click)属性(Attributes)]セクションの小さなディスクアイコンをクリックし、 [ディスクファイルの(Choose a disk file)選択]を選択し、ISOに移動して、[ OK ]を選択します。
これで、仮想マシンにUbuntuをインストールする準備が整いました。
4.Ubuntuのインストールを開始します
VirtualBoxのホーム画面で[スタート(Start )]ボタンをクリックして開始します。ポップアップ表示されるダイアログボックスで起動ディスクとしてUbuntuISOを選択し、[開始(Ubuntu ISO)]を(Start)選択します。
マシンがプロセスを開始するのがわかります。これには数分かかる場合があります。

この時点で2つのオプションがあります。インストールを進める前にUbuntuを試す(Try Ubuntu)か、すでに自信がある場合はUbuntuをインストールすることができます。(Install Ubuntu)

「 Ubuntuを試す(Try Ubuntu)」を選択すると、すぐにUbuntuの使用を開始できます。または、 Ubuntuのインストールを(Install Ubuntu)選択することもできます。
Ubuntuをインストールする前に、他のオペレーティングシステムと同じように使用できますが、仮想マシンにデータを保存することはできないことを忘れないでください。すべての再起動は、前のセッションからのデータが保持されていない、新たなスタートです。
インストールオプションを使用して先に進むことを選択した場合は、[ Ubuntu(Install Ubuntu)のインストール]を選択してインストールを開始します。
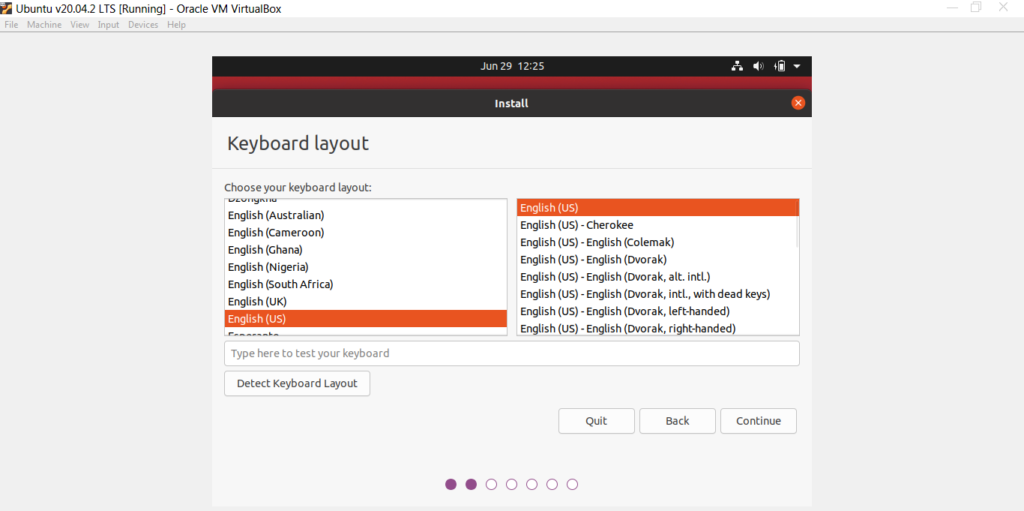
- お好みのキーボードレイアウト(Keyboard layout)を選択してください。
- インストールウィザードのプロンプトに従い続けます。ディスクを消去してUbuntuをインストールする(Erase disk and install Ubuntu)かどうかを尋ねられる場合があります。これは正常です。 [今すぐインストール]を(Install Now )選択して先に進んでください。

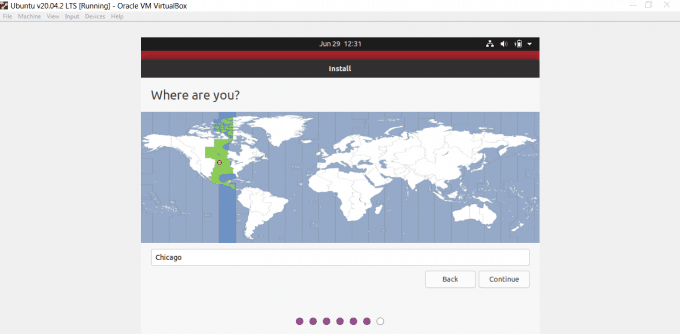
- 次に、地域を選択するように求められます。地域を選択し、[続行](Continue)を選択します。
- 次に、名前、コンピューターの名前、ユーザー名、パスワードなどの詳細を入力するように求められます。
- インストールウィザードは、詳細を収集した後、それ自体でインストールプロセスを続行します。これには数分かかる場合があります。
インストールが完了すると、仮想マシンは自動的に再起動します。仮想マシンを再度実行すると、Ubuntuで起動するはずです。

UbuntuをプライマリOS(Primary OS)として使用する準備はできましたか?
この無料のオープンソースOSに夢中になり、システムに個別にインストールしたくなるかもしれません。UbuntuをプライマリOSとしてインストールするか、Windowsでデュアルブートすることが(dual-boot it with Windows)できます。
How to Install Linux on Windows With VirtualBox
You hear your frіends talk about Linux all thе timе, or maybe you’re just wondering which OS is better for you, Windows or Linux. You’re tempted to try it, but you’re not entirely sure if you’ll like Linux. Is there a way you could just try it out first? Fortunately, there is.
You can use VirtualBox to install a Linux-based OS within Windows 10. While you could dual-boot a Linux OS alongside Windows, VirtualBox offers a much cleaner slate if you choose to abandon the Linux OS after a few days.

How to Install Linux on Windows Using VirtualBox
You can install any Linux OS using this method, but we’ll use Ubuntu for this tutorial since it’s the most popular.
1. Download the ISO for Ubuntu
Start by downloading the ISO for Ubuntu. Don’t worry about not having a spare blank disk or flash drive lying around. Since you’re installing Ubuntu with VirtualBox, all you need is the ISO.
It’s ideal to use the LTS (long-term support) version. The current LTS version is Ubuntu 20.04.2 LTS.

2. Download VirtualBox
You’ll need to download and install VirtualBox on your PC. You can download the Windows package, but there are packages available for Linux and macOS as well. Note that the installation process may vary slightly among them.

Run the installation and follow the prompts. Once installed, check if the Ubuntu ISO has finished downloading. If it has, you can move forward and configure VirtualBox for Ubuntu.
3. Configure VirtualBox for Ubuntu
You’ll see the following welcome screen when you launch VirtualBox. Click on New to begin the configuration process.

A dialog box should pop up. Next, follow these steps:
- Give your Virtual Machine a Name, for instance, Ubuntu v20.04.2 LTS.
- Click on the drop-down menu besides Type and select Linux.
- Choose the Version as Ubuntu (64 bit) or Ubuntu (32 bit).

- Allocate Memory size to your virtual machine. Ideally, you should choose to allocate about a fourth of your PC’s RAM. For instance, if you have 16GB total RAM, allocate 4GB to the virtual machine.
- Select the Next button.
You’ll also need to allocate a portion of your hard disk to the virtual machine. This portion will only be accessible to your virtual operating system, i.e., Ubuntu in this case. You have two options to choose from; you could either use Dynamically allocated storage which grows as you keep using the storage, or allocate a Fixed-size storage limit that offers faster performance.
- On the next screen, you’ll need to create a new hard disk for your virtual machine. Choose the Create a virtual hard disk now option and click Create.
- Next, you’ll need to choose the type of file you’d like to use for the virtual hard disk. Choose VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image) and select Next.
- Choose Dynamically allocated and select Next.
- You’ll see the default VDI storage location and size on the next screen, leave them as they are, and select Create.

This completes the first part of the configuration process. Our virtual machine has been set up, so let’s now move forward and add the Ubuntu ISO to the virtual machine. If you already have an Ubuntu CD/DVD, you could insert that into the drive and use it in the virtual machine too.
Before moving forward, ensure that you have hardware virtualization enabled in your bios settings. If it’s not enabled, the next steps will not work.
You’ll now see Ubuntu listed on VirtualBox’s left sidebar. Select it and click on Settings.

Look for Storage on the left sidebar of the Settings dialog box. Click on the tiny disc icon in the Attributes section, select Choose a disk file, navigate to the ISO, and select OK.

You’re now ready to install Ubuntu on your virtual machine.
4. Begin Ubuntu Installation
Start by clicking the Start button on the VirtualBox home screen. Select the Ubuntu ISO as the start-up disk in the dialog box that pops up and select Start.
You’ll see the machine initiate the process. This may take a few minutes.

You have two options at this point. You could either Try Ubuntu before you move forward with the installation or Install Ubuntu if you feel confident already.

If you choose Try Ubuntu, you can start using Ubuntu right away. Alternatively, you could choose to Install Ubuntu.
Before installing Ubuntu, remember that you can use it like any other operating system, but you can’t store any data on a virtual machine. Every reboot is a fresh start with no data preserved from the previous session.
If you’ve chosen to move forward with the install option, select Install Ubuntu to initiate installation.
- Choose your preferred Keyboard layout.

- Keep following the installation wizard’s prompts. You may be asked if you want to Erase disk and install Ubuntu. This is normal, just select Install Now and move forward.

- Next, you’ll be asked to choose your region. Select your region and select Continue.

- You’ll then be asked to input your details such as your name, computer’s name, username, and password.
- The installation wizard will continue the installation process by itself after collecting the details. This could take a few minutes.
When the installation completes, your virtual machine will automatically reboot. Run the virtual machine again, and it should boot into Ubuntu.

Ready to Use Ubuntu as a Primary OS?
You might just end up falling in love with this free, open-source OS enough to want to install it separately on your system. You can either install Ubuntu as your primary OS or dual-boot it with Windows.














