(Windows 11)新しいWindowsバージョンであるWindows11は、10月にMicrosoftによってWindows10(Windows)ユーザー(October)に(Microsoft)提供さ(Windows 10)れました。古くないPCを使用しているほとんどのユーザーはWindows11を実行できるため、この時点で多くのPCがWindows11を実行しています。(Windows 11)これはかなり安定したオペレーティングシステムですが、すべてのバージョンのWindowsと同様に、1つか2つの問題に直面する可能性があります。
このガイドは、組み込みツールを使用してWindows11の問題を修復するのに役立ちます。Windows 11の問題の原因がすでにわかっている場合は、フープのジャンプをスキップして、最適なソリューションを選択できる可能性があります。ただし、理由がわからない場合でも、このガイドを順番に実行してください。

セーフモードに入ることから始めます
ほとんどの修正では、オペレーティングシステムを起動する必要があります。Windowsを起動できない場合は、セーフモード(Mode)で起動する必要があります。初めての場合は、Windows11をセーフモードで起動(starting Windows 11 in Safe Mode)するためのクイックガイドがあります。理想的には、DISMなどのツールを使用するには、ネットワーキングを使用して(Networking)セーフモード(Mode)で起動する必要があります。
組み込みのWindowsトラブルシューティングを使用する(Use Built-In Windows Troubleshooters)
新しい(Newer)バージョンのWindowsには、さまざまな問題に対する組み込みのトラブルシューティングツールのラインナップが用意されています。以前のバージョンのWindowsで(Windows)コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)を使用する必要があったトラブルシューティングを、ユーザーフレンドリーなGUIで実行できるようになりました。
トラブルシューティングは、原因がわからない場合にWindows11の問題を修正するための優れた方法です。(Windows 11)たとえば、カメラが正しく機能しておらず、その理由がわからない場合は、カメラ(Camera)のトラブルシューティングを使用して、Windowsが問題を自動的に識別して修正できるかどうかを確認できます。
- Win + Iを押して開始し、 [システム(System )] >[トラブルシューティング(Troubleshoot )] >[その他のトラブル(Other troubleshooters)シューティング]に移動します。
- ここにリストされているすべての組み込みのトラブルシューティングが表示されます。問題の横にある[実行(Run)]ボタンを選択して、問題に基づいて関連するトラブルシューティングツールを選択します。

- プロンプトに従い、トラブルシューティング担当者にプロセスを完了させます。

トラブルシューティング担当者が問題を特定すると、問題を自動的に修正しようとします。ただし、問題を特定できない場合、または特定できた問題を修正できない場合は、通知するだけなので、別の修正を試す必要があります。
WindowsUpdateをアンインストールします
Windowsは、コンピューターを安全で最新の状態に保つために、ドライバーを頻繁に更新し、その他のセキュリティ更新プログラムをインストールします。ただし、更新によって問題が発生する場合があります。最近の更新後にWindows(Windows)の不具合が発生した場合は、最近インストールした更新をアンインストールしてみてください。
- Win + Iを押して、[WindowsUpdate] >[更新履歴(Update history)]に移動します(Windows Update )。
- [更新のアンインストール(Uninstall updates )]を選択して、コントロールパネルを起動します。
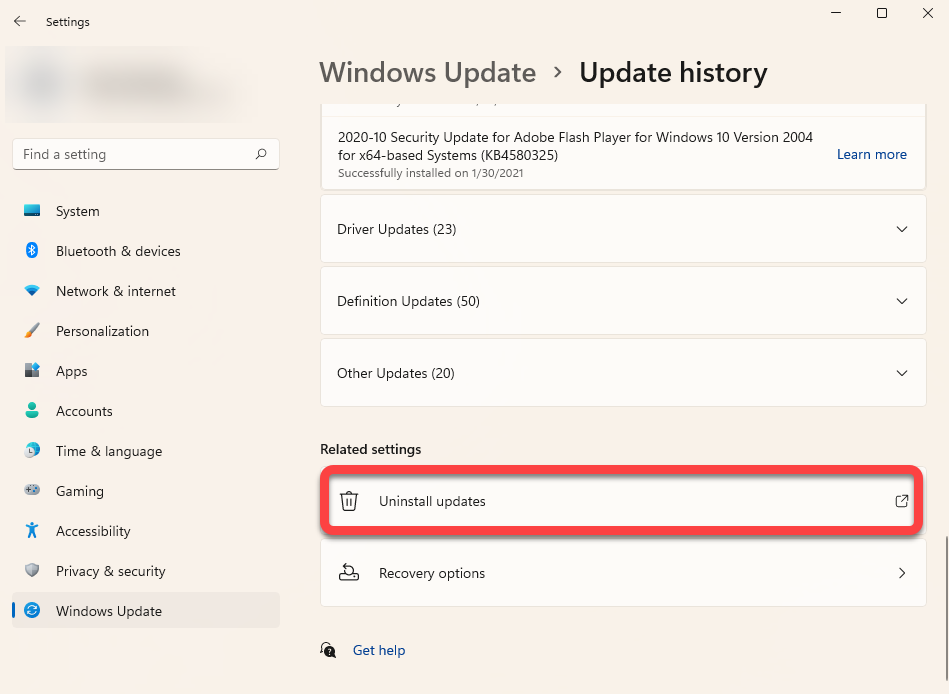
- (Sort)[インストール(Installed On )先]列のラベルをクリックして、更新をインストール日で並べ替えます。最近インストールしたアップデートを選択し、上部から[アンインストール(Uninstall)]ボタンを選択します。または、更新を右クリックして[アンインストール(Uninstall)]を選択することもできます。
特定の更新プログラムの[アンインストール(Uninstall )]オプションが表示されない場合は、Windowsがセキュリティまたは(Windows)Windowsの適切な実行にとって重要であると見なしているためです。

プロンプトが表示されたら、アンインストールを確認します。最近インストールしたすべての更新プログラムをアンインストールしたら、Windowsを再起動して、すべてが正常に機能するかどうかを確認します。
システムファイルチェッカー(SFC)スキャン
システムファイルチェッカー(System File Checker)(SFC)は、破損したシステムファイルを見つけて復元するのに役立つWindowsユーティリティです。(Windows)システムファイルは、Windowsが正しく動作するために必要なコアファイルです。
Windowsオペレーティングシステムで予期しないエラーが発生し、それを引き起こした可能性のある特定の理由を考えることができない場合は、ファイルの欠落または破損が問題である可能性があります。
- Win + Rを押し、cmdと入力し、 Ctrl + Shift + Enterを押して、管理者権限でコマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)を起動します。

- 次のコマンドを実行します。
sfc /scannow
- スキャンを完了させます。
スキャンが完了すると、コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)ウィンドウに、スキャンでファイルの整合性違反が見つかったかどうかを示すメッセージが表示されます。SFCは、関連するファイルを自動的に復元することにより、これらの違反も修正します。
チェックディスク(CHKDSK)スキャン
Chkdskは、ファイルシステムのメタデータをスキャンすることでファイルシステムのエラーをチェックして修正(checks and fixes file system errors)する組み込みのユーティリティです。ハードドライブ上の論理的問題と物理的問題の両方を探し、それらを自動的に修正しようとします。
- (Start)昇格したコマンドプロンプトを(Command Prompt)起動することから始めます。タスクバーから[スタート(Start)]メニューを開き、cmdと入力して、右側のウィンドウから[管理者として実行(Run as administrator)]を選択します。
- コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)に次のコマンドを入力し、 Enterキー(Enter)を押します。
chkdsk e: /f /r /x
- Would you like to force a dismount on the volume> (Y/N)という質問が表示されたら、Yと入力してEnterキー(Enter)を押します。
スキャンを終了します。完了したら、PCを再起動して、すべてが正常に戻っているかどうかを確認します。
展開イメージのサービス(Deployment Image Servicing)と管理(Management)(DISM)スキャン(Scan)
DISMは、Windows 11の修復に役立つもう1つの組み込みコマンドラインユーティリティです。SFCやCHKDSKよりも強力であり、SFCまたはCHKDSKツール(SFC)を使用(CHKDSK)して問題を修正できなかった場合、またはできなかった場合にのみ使用してください。SFCを実行します。
DISMは、 (DISM)Windowsを最初 からインストールしなくても、インターネットからWindowsイメージをダウンロードしてPCに展開することにより、破損したシステムコンポーネントを修正するのに役立ちます。
セーフモードで(Safe Mode)DISMを使用する場合は、ネットワークが有効になっているセーフモード(Safe Mode)で起動し、インターネット接続が機能していることを確認してください。DISMは、エラーを修正するためにWindows Updateからファイルをプルするため、インターネットアクセスが必要です。
- Ctrl + Rを押し、cmdと入力し、 Ctrl + Shift + Enterを押して、昇格したコマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)を起動します。
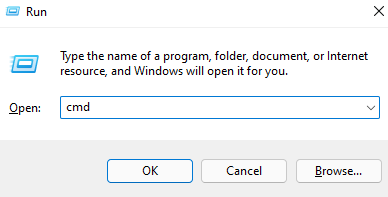
- 次のコマンドを実行して、何も変更せずにコンポーネントストアの状態をスキャンします。
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth
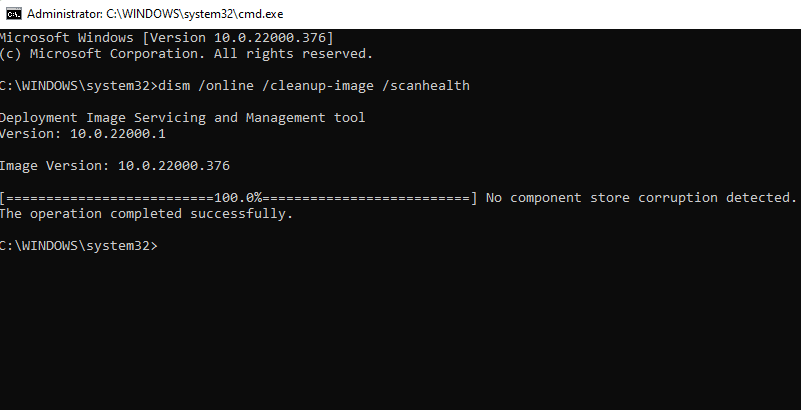
- DISMがシステムイメージに問題を見つけた場合は、次のコマンドを実行して問題を修復します。
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth

このプロセスには時間がかかる場合があります。プロセスを完了させてから、PCを再起動して、すべてが正常に機能するかどうかを確認します。
システムの復元を使用する
システムの復元は、 (System Restore)Windows用(Windows)のタイムトラベルマシンです。システムの復元(System Restore)を使用して、PCを以前の動作状態(復元ポイントを作成した時点)に戻すことができます。
ただし、 Windows(Windows)はデフォルトで復元ポイントを作成しないため、最初にPCに復元ポイントがあるかどうかを確認する必要があります。復元ポイントを手動で作成するか、Windowsで時々自動的に復元ポイントを作成する(create a restore point manually)場合は、システムの復元を有効にする(enable System Restore)必要があります。
- タスクバーから[スタート(Start)]メニューを開き、リカバリ(recovery)を検索します。結果から[リカバリ](Recovery)を選択します。

- [システムの復元を開く](Open System Restore)を選択します。

- システムの復元(System Restore)ウィンドウがポップアップするはずです。推奨される復元ポイントが表示されている場合は、PCに復元ポイントがあり、PCを以前の動作状態に復元できることを意味します。
別の復元ポイントを選択する場合は、[推奨される復元ポイント]を選択する(Choose a different restore point )か、(Recommended restore)別の復元ポイントを選択して、[次へ](Next)を選択します。復元ポイントの作成日以降にインストールしたアプリはすべて削除されることに注意してください。

- [完了](Finish )を選択して、復元プロセスを開始します。
この時点でWindowsが再起動し、PCの復元を開始します。プロセスが完了したら、すべてが正常に機能するかどうかを確認します。
Windows11スタートアップ修復
以前の方法でWindows11を修復できなかった場合は、 Windows11の起動修復を使用してみてください。スタートアップ(Startup)修復は特にスタートアップの問題のみを検索するため、問題がスタートアップに関連していない場合は、この方法をスキップしてください。
- タスクバーから[スタート(Start)]メニューを開き、電源ボタンを選択します。Shiftキーを押したまま、[再起動]オプションを選択します(Restart)。コンピューターが再起動し、Windows回復環境(Windows Recovery Environment)(RE)に入ります。
- [トラブルシューティング](Troubleshoot) >[詳細オプション](Advanced options) >[スタートアップ修復](Startup Repair)に移動します。

- アカウントを選択してパスワードを入力するように求められる場合があります。それらを入力(Enter)すると、Windowsがプロセスを開始します。
Windowsが問題を検出すると、問題を自動的に修正しようとします。ただし、Windowsが問題を識別しない場合、またはWindowsが識別した問題を修正できない場合は、「スタートアップ修復はPCを修復できませんでし(Startup Repair couldn’t repair your PC)た」というメッセージが表示されます。その場合は、別の方法を試す必要があります。
Bootrecでブートローダーを修正
Windowsを起動できないことが問題である場合は、 Bootrecユーティリティを使用できます。Bootrecは(Bootrec)、マスターブートレコード(fixes the master boot record)とブート構成データ(BCD)を修正する修復ツールです。
- スタート(Start)メニューを開き、電源ボタンを選択します。Shiftキーを押したまま、[再起動]を選択します(Restart)。再起動すると、WindowsREに入ります(Windows RE)。
セーフモード(Safe Mode)でも起動できない場合は、PCの電源がオンになっているときにPCの電源ボタンを押したままにして、ハードリブートします。これを2回実行すると、3回目は自動的にWindowsREに入ります(Windows RE)。
- [トラブルシューティング](Troubleshoot ) >[詳細オプション](Advanced options ) >[コマンドプロンプト](Command Prompt)に移動します。

- (Run)次の各コマンドを1つずつ実行します(つまり、コマンドを入力し、 Enterキー(Enter)を押して、繰り返します)。
- bootrec /fixmbr
- bootrec /fixboot
- bcdedit /export c:\bcdbackup
- attrib c:\boot\bcd -h -r -s
- ren c:\boot\bcd bcd.old
- bootrec /rebuildbcd
この時点で、 [インストールをブートリストに追加しますか?(Add installation to boot list?) ]という質問が表示されます。Yと入力し、 Enterキー(Enter)を(Y)押します。また、 bootrec / fixbootコマンドの後にAccessdenied(Access is denied)エラーが発生した場合は、次のコマンドを実行してから、bootrec/fixbootを再度実行してください。
bootsect /nt60 sys
完了したら、コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)を終了し、PCを再起動します。
Windows11をリセットする
リセット後にすべてのプログラムをPCに再インストールする必要があるため、前の方法を試した後でのみPCをリセットしてください。ただし、個人ファイルを保存するオプションがあります。他の修正が機能しなかった場合、またはWindows 11を新品同様にしたい場合は、リセットを検討する必要があります。
- 開いているすべてのウィンドウを終了し、Win + Iシステム(System )] >[回復(Recovery)]に移動します。

- [ PCのリセット(Reset PC)]ボタンを選択します。

- 個人データやファイルをそのまま保持する場合は、[ファイルを保持する(Keep my files)]オプションを選択します。または、ハードディスク上のすべてを消去する場合は、 [すべて削除](Remove everything)を選択します。どちらのオプションでも、インストールされているすべてのアプリと設定が失われるため、リセット後にそれらを再インストールする必要があることに注意してください。

プロンプトに従い、リセットプロセスを完了させます。ほとんどの場合、Windows 11をリセットすると、ソフトウェア関連の問題がすべて修正されます。そうでない場合は、ハードウェアの問題である可能性があり、技術者の支援が必要になる場合があります。
Windows11を再インストールします
Windows 11をクリーンインストールすると、ハードウェアの問題でない限り、直面しているほとんどすべての問題に対処できます。ただし、インストールされているすべてのプログラムが失われます。セットアップでフォーマットが必要な場合は、Windowsをインストールしているドライブに保存されているファイルも失われます。
リセットとは異なり、クリーンインストールでは、起動可能なUSBまたはWindows(Windows)メディア作成ツールを使用する必要があります。Windows(ISOファイルとして)またはメディア作成ツール(download Windows (as an ISO file) or the media creation tool)(EXEファイルとして)をダウンロードして、起動可能なUSBドライブを作成できます(create a bootable USB drive)。起動可能なUSBを作成したら、Windows11の新しいコピーを(install the new copy of Windows 11)PCにインストールします。
修正されたWindows11の問題
上記の方法で、Windows11オペレーティングシステムに固有のハードウェア以外の問題のほとんどを解決できるはずです。ただし、問題のトラブルシューティングと修正を自分で行うことにあまり興奮していない場合は、Windows11を修復するための無料のサードパーティツールを試してみてください。(free third-party tools)
How to Repair Windows 11 to Fix Problems
Windows 11, the new Windows versiоn, was made available bу Microsoft to Windows 10 users back in October. Most users with PCs that aren’t ancient can run Windows 11, ѕo many PCs run Windows 11 at this pоint. It’s a fairly stable operating system, but like with all vеrsions of Windows, you might faсe an ocсasional problеm or two.
This guide will help you repair Windows 11 problems using built-in tools. If you already know what caused your Windows 11 problem, you might be able to skip jumping through hoops and choose the best solution. However, even if you’re not sure about the reason, just step through this guide in order.

Start by Entering Safe Mode
Most fixes require you to boot into your operating system. If you can’t boot into Windows, you’ll need to boot into Safe Mode. If it’s your first time, we have a quick guide on starting Windows 11 in Safe Mode. Ideally, you should boot into Safe Mode with Networking to use tools like DISM.
Use Built-In Windows Troubleshooters
Newer versions of Windows come armed with a line-up of built-in troubleshooters for various problems. Troubleshooting that would have required using the Command Prompt in earlier versions of Windows can now be done with a user-friendly GUI.
Troubleshooters are a great way to fix Windows 11 problems when you don’t know the cause. For instance, if your camera isn’t functioning correctly and you don’t know why, you can use the Camera troubleshooter to see if Windows can automatically identify and fix the problem.
- Start by pressing Win + I and navigate to System > Troubleshoot > Other troubleshooters.
- You’ll see all built-in troubleshooters listed here. Select a relevant troubleshooter based on your problem by selecting the Run button next to it.

- Follow the prompts and let the troubleshooter complete the process.

If the troubleshooter identifies the issue, it will try to fix the problem automatically. However, if it can’t identify the problem or is unable to fix a problem that it was able to identify, it will simply notify you, and you’ll need to try a different fix.
Uninstall Windows Update
Windows frequently updates drivers and installs other security updates to keep your computer safe and up-to-date. However, updates can sometimes cause problems. If your Windows started glitching after a recent update, you can try uninstalling recently installed updates.
- Press Win + I and navigate to Windows Update > Update history.
- Select Uninstall updates to launch the Control Panel.

- Sort the updates by install date by clicking on the Installed On column label. Select the recently installed updates and select the Uninstall button from the top. Alternatively, you can right-click on an update and select Uninstall.
If you don’t see the Uninstall option for a certain update, it’s because Windows deems it important for security or running Windows properly.

When prompted, confirm the uninstallation. Once you’ve uninstalled all recently installed updates, try to reboot Windows and see if everything works as it should.
System File Checker (SFC) Scan
System File Checker (SFC) is a Windows utility that helps find and restore corrupted system files. System files are core files that Windows requires for operating correctly.
If you’re experiencing unexpected errors with your Windows operating system, and can’t think of any particular reason that could have caused it, a missing or corrupted file could be the problem.
- Press Win + R, type cmd, and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to launch the Command Prompt with administrative privileges.

- Execute the following command:
sfc /scannow
- Let the scan complete.
Once the scan completes, you’ll see a message in the Command Prompt window that will tell you if the scan found any file integrity violations. SFC will also fix those violations by restoring the relevant files automatically.
Check Disk (CHKDSK) Scan
Chkdsk is a built-in utility that checks and fixes file system errors by scanning the file system metadata. It looks for both logical and physical problems on your hard drive and tries to fix them automatically.
- Start by launching an elevated Command Prompt. Open the Start menu from the taskbar, type cmd, and select Run as administrator from the right pane.

- Type the following command into the Command Prompt and press Enter:
chkdsk e: /f /r /x
- When asked the question Would you like to force a dismount on the volume> (Y/N), type Y and press Enter.
Let the scan finish. Once done, restart your PC to check if everything is back to normal.
Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) Scan
DISM is another built-in command-line utility that can help you repair Windows 11. It’s more powerful than the SFC and CHKDSK, and should be used only if you couldn’t fix your problem using the SFC or CHKDSK tools, or couldn’t run SFC at all.
DISM helps you fix corrupted system components by downloading a Windows image from the internet and deploying it on your PC, without having to install Windows from scratch.
If you use DISM in Safe Mode, make sure you’ve booted into Safe Mode with networking enabled and have a working internet connection. DISM needs internet access because it will pull files from Windows Update to fix errors.
- Press Ctrl + R, type cmd, and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to launch an elevated Command Prompt.

- Execute the following command to scan your component store’s health without changing anything:
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealth

- If DISM finds issues with the system image, run the following command to repair them:
Dism /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth

The process can take a while. Let the process complete and then restart your PC to see if everything works as it should.
Use System Restore
System Restore is a time travel machine for Windows. You can use System Restore to bring your PC back into a previous working state—a point in time when you created the restore point.
However, you’ll first need to check if you have any restore points on your PC because Windows doesn’t create them by default. You’ll either need to create a restore point manually or enable System Restore if you want Windows to create one automatically every once in a while.
- Open the Start menu from your taskbar and search for recovery. Select Recovery from the results.

- Select Open System Restore.

- A System Restore window should pop up. If you see a recommended restore point, it means your PC does have a restore point, and you’ll be able to restore your PC to its previous working condition.
Select the Recommended restore point or Choose a different restore point if you’d like to select a different restore point, and select Next. Note that any apps you installed after the date of creation of the restore point will be removed.

- Select Finish to start the restore process.
Windows will restart at this point and begin restoring your PC. Once the process is complete, check if everything works fine.
Windows 11 Startup Repair
If you couldn’t repair Windows 11 with the previous methods, try using Windows 11 startup repair. Startup repair specifically looks for startup problems only, so skip this method if your problem isn’t related to startup.
- Open the Start menu from the taskbar and select the power button. Press-hold the Shift key and select the Restart option. The computer will restart and enter Windows Recovery Environment (RE).
- Navigate to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Repair.

- You might be asked to select an account and enter the password. Enter them and Windows should start the process.
If Windows finds a problem, it will try to fix the problem automatically. However, if Windows doesn’t identify a problem, or can’t fix a problem it has identified, you’ll see a message that reads Startup Repair couldn’t repair your PC. In that case, you’ll need to try a different method.
Fix Boot Loader with Bootrec
If your problem is that you cannot boot into Windows, you can use the Bootrec utility. Bootrec is a repair tool that fixes the master boot record and boot configuration data (BCD).
- Open the Start menu and select the power button. Press-hold the Shift key and select Restart. Upon reboot, you’ll enter the Windows RE.
If you can’t boot into Safe Mode either, hold-press the power button on your PC while the PC is on for a hard reboot. Do this twice, and the third time, you’ll automatically enter the Windows RE.
- Navigate to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Command Prompt.

- Run each of the following commands one-by-one (i.e., type a command, press Enter, and repeat):
- bootrec /fixmbr
- bootrec /fixboot
- bcdedit /export c:\bcdbackup
- attrib c:\boot\bcd -h -r -s
- ren c:\boot\bcd bcd.old
- bootrec /rebuildbcd
At this point, you’ll see a question that asks Add installation to boot list? Type Y and press Enter. Also, if you get an Access is denied error after the bootrec /fixboot command, execute this command and then execute bootrec /fixboot again:
bootsect /nt60 sys
Once done, exit the Command Prompt and restart your PC.
Reset Windows 11
Reset your PC only after you’ve tried the previous methods because you’ll need to reinstall all programs on your PC after the reset. You will have the option to preserve personal files, though. If none of the other fixes worked or if you want your Windows 11 good as new, you should consider a reset.
- Exit all open windows, press Win + I, and navigate to System > Recovery.

- Select the Reset PC button.

- Select the Keep my files option if you’d like to keep any personal data or files intact. Alternatively, choose Remove everything if you want to erase everything on your hard disk. Note that with both options, you’ll lose all installed apps and settings, so you’ll need to reinstall them after the reset.

Follow the prompts and let the reset process complete. In most cases, resetting Windows 11 should fix all your software-related problems. If it doesn’t, it’s likely a hardware problem that might require a technician’s help.
Reinstall Windows 11
A clean install of Windows 11 will take care of pretty much any problem you’re facing unless it’s a hardware issue. However, you’ll lose all installed programs. You’ll also lose your files stored on the drive on which you’re installing Windows, if the setup requires you to format it.
Unlike resetting, a clean install requires you to use a bootable USB or the Windows media creation tool. You can download Windows (as an ISO file) or the media creation tool (as an EXE file) and create a bootable USB drive. Once you’ve created a bootable USB, install the new copy of Windows 11 on your PC.
Windows 11 Problems Fixed
You should be able to resolve most non-hardware issues specific to your Windows 11 operating system with the methods discussed above. However, if you’re not too excited about the idea of troubleshooting and fixing problems yourself, you should try free third-party tools for repairing Windows 11.


















