Windows 11で管理者として実行(run as administrator)するということは、昇格された特権でアプリケーションを起動することを意味します。オペレーティングシステム(operating system)への不正な変更を防ぐために、Windows 11アプリとゲーム(apps and games)はデフォルトで標準のアクセス許可で起動しますが、セキュリティソフトウェア(security software)など、正しく実行したり特定のタスクを実行したりするために管理者権限を必要とする特定のプログラムがあります。幸いなことに、プロセスは簡単です。必要なのは、管理者の資格情報と手順だけです。このガイドを読んで、Windows11で(Windows 11)管理者(Administrator)として実行する方法を学習してください。
注:(NOTE:)このガイドのほとんどの方法を使用して管理者として実行すると、UACプロンプト(UAC prompt)がトリガーされ、さらに確認を求められます。通常のアカウントを使用してアプリを起動する場合は、管理者パスワード(administrator password)が表示されます。
1.アプリの固定されたスタートメニューショートカットから管理者として実行する方法(Start Menu shortcut)
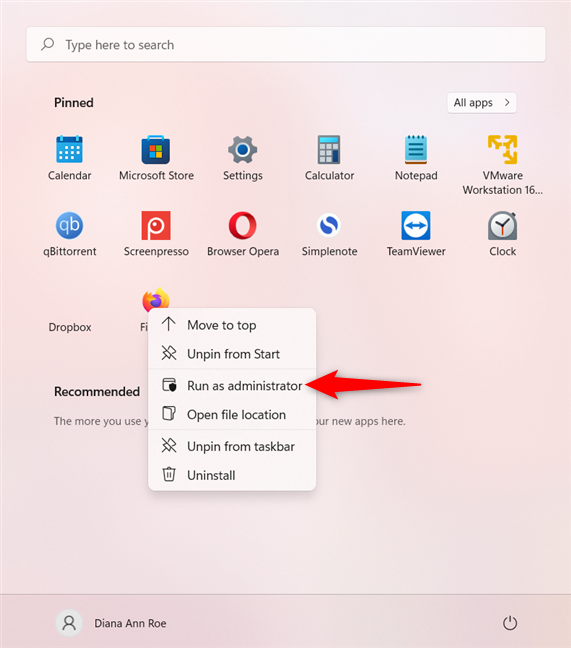
Windows 11では、固定されたアプリのコンテキストメニューを使用して、管理者権限でアプリを実行できます。まず、Windows 11の(Windows 11) スタートメニューを開き、起動するアプリを[(Start Menu)固定(Pinned)]セクションで見つけます。次に、右クリックまたは長押ししてコンテキストメニューを開き、[管理者として実行(“Run as administrator)]をクリックまたはタップします。」
![固定されたアプリのコンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行]を選択します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-UMWtyHFRdp8/YjdXSeGb4wI/AAAAAAAAxNU/MyO1Y2mhqv8-uiE-lqDxV4_Gp9UrSs7NACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCe4d2RBg/s0/TvHwZY9QOgBnsjyhOxB_SLCS1R8.png)
固定されたアプリのコンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行(Run)]を選択します
または、キーボードのCtrlキーとShiftキーを押しながら、 Windows 11で管理者として実行するアプリをkeyboard and click/tapするか、キーボードを使用して強調表示してから、Ctrl + Shift + Enterキーボードショートカットを使用してそれを起動します。
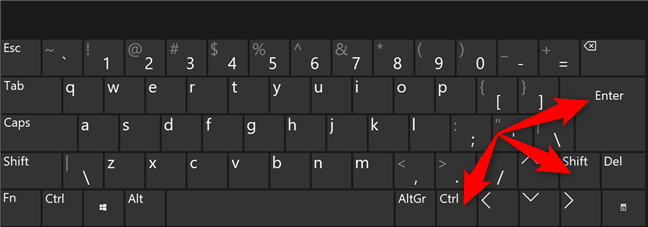
Use Ctrl + Shift + Enter強調表示された固定アプリでCtrl+Shift+Enterを使用します
ヒント:この方法が気に入った場合は、アプリを(TIP:)Windows11の(Windows 11) スタートメニュー(Start Menu)に固定する方法について詳しく知りたいと思うかもしれません。
2. Windows 11(Windows 11)スタートメニューの[(Start Menu)すべての(All)アプリ]リストからショートカットを使用して、管理者としてプログラムを実行します
スタートメニュー(Start Menu)の[すべてのアプリ(All apps)]セクションを使用して、 Windows11の管理者として実行することもできます。まず、 (First)[スタート]メニュー(Start Menu)を開き、 [すべてのアプリ(All apps)]にアクセスします。
![Windows11の[すべてのアプリ]リストにアクセスする](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-OhxihgxPM-k/YjcJaBekAwI/AAAAAAAAm3I/fn_J3avsK_AeT9cjNGZydeYAK-3uDT4bACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCRz9yRBg/s0/6YzJeF9-cQRUvJofDuHje31aTfo.png)
Windows11の[(Windows 11)すべての(All)アプリ]リストにアクセスする
リストからプログラムのショートカットを見つけ、右クリックまたは長押ししてコンテキストメニューを開きます。次に、[その他(More)]オプションをクリック、タップ、またはカーソルを合わせて、[管理者として実行(“Run as administrator.”)]を押します。
![ショートカットのコンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行]を選択します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-uGAHfcFpGD4/Yjc-ZGPY0GI/AAAAAAAAu0U/qoqDQY0_QXU2Ia3eMUs4zYUVU2oM_PAZgCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhxcrfjNL0kpApMdsYcrhR6ibP9yFPgid8tif1XJf590Y_S6I5KKOmSt3l5FGY4xSNyvZdonIyhAy17tqtmX612OyJ04O3L0FlnNcNc0C54eOcYAIPck3FI_krYDif6TAC-yzKxFLqijseiFajZsn5zZb5ikZDEoD98WADPb77Q8xJjOH9YzrQe3CB3fICtjnubLwJfl_5qf96x98EvSIMovAxNksn1luuo0L_dnicCPkBgBf5wN0-gtGg1mLEXM8O7RQ9uZx49lRm7ceAFzzMt_6Cq2w-eXXuubN_kNKoT7juKeFa2-L0zW6YGXdHX_H-uPut3z-kosp-leDwO3y29zBsAOH0aOENAJ-JGeAnRJ7TKv4t2I6l2cfc-lF9kRTKX6aYwsM79CQqNoNt61sae4bD0zEcPXA9px0izvU6TWFBY_0eJV8U_jRs_hFuQGd3mv42XGA9AF9USp0pq4reDvfzEUbUScBDJxV2FH0gc74fjQOnfl4a2FntrUFG4TIrLZdM1piJaWyZ1PgX8v43nHC1Hi9uMmXsWiYFo5NX1MHFRWVJnhLyCAzaIwxq_hg3o27aMIgAeS-fQ5cwlLgvZliezsqr04t33qG12AvR8NX8glkuNvFAGVed6Q_NgxRGKhvGXPVRSd4G8WMJ6g3ZEG/s0/pqgiRB-nnHvCLwEDGdaXbTpvqTY.png)
ショートカットのコンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行(Run)]を選択します
または、キーボードのCtrlキーとShiftキーを押しながら、 (Shift)Windows11で管理者として実行するアプリを(Windows 11)クリック(keyboard and click)またはタップすることもできます。

(Use Ctrl and Shift)管理者として実行するアプリでCtrlキーとShiftキーを使用します
3.アプリのショートカットから管理者として実行する方法
デスクトップまたはその他の場所で管理者として実行するアプリのショートカットがある場合は、その右クリックメニューを開くことができます。次に、「管理者として実行」を(“Run as administrator)クリックまたはタップ(click or tap)します。」
![コンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行]を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-0ot8QVQ-AKc/YjciTaSa0NI/AAAAAAAAEW8/yNqleYAbPRc-8vWX_OLc2Plo-CbGW-FVwCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxeSqmKu1BtuATYSULyy9OK0vUZJMh4EEreX9rzJid57_Lr5itgoyxzXecCdHil_kcjllNp636SB8ECcTxmI--8us7mIs7_4fcnjy5EcSKFLsehZVlA79dQvMROYqrbbfCkZz25BePPjbkt5vMp0a-Ffrw5A99b5RlKddBRMXeM9g_FOe-xFzRbvRW7TYY6HykLA9PekQsEvOV8jpg0SHFKFaAgGIgHmS8N7Z4b0t8oAyxaq09z-wMB1q859mpaUbsnf4wcrBa-aLiovkCSe0-odM-A-9luIU_P030lCRFTGU9BY0zVaY2-1KUD4qSF0CxrUZ63BI5AN1rY-GLaYkrr6q6sLymszIx_5ReHwutHRLMCol2Y3bqo8_EmWqm1xKORC4FaaCfGnEFVJB_wg7045IZzS73d4lf5GevtJPILvrX6AAn4MdBndWPI54Il_GyriQm-PvgqlWRU8VIZSbskQDSr606f1DhUT0lFbEm55jRTZO5fxh4ah9Me-2zfxCotjHRzCLkIkXarR56jt-M2SgQLbI-FEfyKwUTPXJ4v_RR4iPWc90tJKVi01D3pbDGX5WGBgfwItEcVTJrbT3YKakmk0mweSX3-I0kynawDx1NIRHydgBsBNyU99ZZWyYdyYcFCu2SsV1d5Oa8w39XckQY/s0/d-Tn6tcwZJVR5PxirYKdIEeec4A.png)
コンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行(Run)]を押します
4.タスクバーのショートカットから管理者としてアプリを実行します(taskbar shortcut)
Windows 11では、管理者権限でアプリを実行する別の方法は、タスクバーのショートカット(taskbar shortcut)を使用することです。まず(First)、ショートカットを右クリックまたは長押しします。次に、プログラム名を右クリックするか、もう一度押し続けます。最後に、このメニューから「管理者として実行」を(“Run as administrator”)クリックまたはタップ(click or tap)します。

タスクバーのショートカット(taskbar shortcut)を使用して、 Windows11で管理者として実行します
Ctrl + Shiftキーを押しながら、アプリのタスクバーショートカットをクリック/タップして、Windows11の管理者権限でアプリを実行することもできます。

(Use Ctrl and Shift)管理者として実行するアプリでCtrlキーとShiftキーを使用します
ヒント:アプリをタスクバーに固定するには、 (TIP:)Windows11でタスクバーにショートカットを追加する方法に関するガイドをお読みください。
5.実行可能ファイルのコンテキストメニューから管理者として実行する方法
ショートカットは簡単に見つけることができますが、メインの実行可能ファイルのコンテキストメニューからWindows11の管理者としてプログラムを実行することもできます。(Windows 11)ファイルエクスプローラー(File Explorer)で、アプリの実行可能ファイルに移動します。右クリックまたは長押ししてコンテキストメニューを開き、[管理者として実行(“Run as administrator)]をクリックまたはタップします。」
![[管理者として実行]をクリックまたはタップします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-iQKzY-jsG4Q/YjctUNZQD8I/AAAAAAAAKzA/DmhkgTKY424C4PFS2wpMHCSqX8AMJHoMACEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxqHo63eC-w2z6yviSn9DYRDJuWMKm_sPX6g-BI1OEFwv6L01SgCY8x7NMPafCADWrqG-5bpVDJ9v1dX5VJUMKLtB4dJOAcVJsEhFbbXtL-XEojuNI5AruC6OEcs4cjQnBRmHxiidG_bT2PUln-JyMDeM9aSWLAKSXNGv7-yc7yQmIvhyUYhbDkEh81nfEAWmrpABM29e2_Sw9E50aw52PTBbSFGr-9f2F_zVQ6X8hhfsueD2Q3TAAeasc4-YpuzFdw2-e8Er4zY_PbIim0s6V3-GMF_pNVuXyk43N0cVPAQ4d5EcEKzOSQZl94Dd4hs_80k2TqFQdbSNhpq9D9NQyskK8FU-cfokIaFU0zhsWLLuGZVsuH1NRNGn4YNiKEV3QCAPqc9kzi1dPCRqXGd--4GOATbeSeKcQVgEuAwUTG5knE2W6mc6eg3LAB05feSMp5RK6QTKY72osxAAWsYKriaD-cjcVT3-YNVM5UanAfvczKJd_aCqsMi7kY2O-rOOq_hTYACxmVLcoKulU2T9PDKqZObOmLUWvpw1LFqfbIcIgdTfhTJx2pOU5yBgXu92TP53dU475DxGW5MnLmd0KwZo4qU3vaO3OQOutgpXWW1yHWLDsgvUWG4wybPqFh4idUvTQRR786lrgNYjAwlaDdkQY/s0/LpzjSGR4-KmSlkDpvVNg7TJzGNU.png)
(Click)[管理者として実行]を(Run)クリックまたはタップします
6. Windows 11 Searchを使用して、管理者としてプログラムを実行します(Search)
まず、Windows 11 Searchを使用して、管理者として実行するプログラムを見つけます。右側のペインで、 [管理者として実行]を(“Run as administrator)クリックまたはタップ(click or tap)します。」
![CMDの場合、[管理者として実行]オプションがすぐに利用可能になります](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Q6zyJWWhE-8/Yjb7eELFU-I/AAAAAAAAhaM/J0ncV8H4VJsyv0c5QSdk2jqTt2TTzrFTwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwW0CBk7YkolKRhlb6URWa_IgJhlV6Uh5HTXSA46rtPZTzcTVDH5E3Inr1300PCuFmPfzlhV9-wZ0cgm5eyq7ZHFxRZXVbHy0npWVZFQ1PONMxdTopZNqunXwLBLiLb67ib1SygjFUxfYmkgsM2KWbfxsJ0dJUmw1O8_eCdFnl3uawCEzgsMAIg1Qc5NZzeL_r4wLfEjXahBctYEmz8PuHb0PPtvGp-r6YtKLJySOhlKEvT2KQlPP_m8uuAu4nd9hM73lCbqdlSPO8Zq50PdX0wx8st7wB0bPkCKfKneQLRTuZCoubxrSAYYcR0TPzO_mZA9q14hTQoKUUP0yEF1F69JKIE4VMhscEvH2o_SFK7IDwFOJoGP2ZHxPnq1oEr-THgN0QuqzqlZwBKlRjYLmCuyWmtQEJcFb0y83vg4HNMcHMnH4lEEvT9qrp3Mqtom7UIrB2jajclGsNQdwU2a7PVl9MgQ1x74JGCA2gUeIiNlJDd9HgeDJzjAFR5NnV04Ho1gVSVvXEJNT-wQ-v1MGrgxZvOE1OzaWw9ezHrC91jfyv8d8BV4tQ7x9Ll0_Vn7OfNGviasNi0v1rdTERPCA9bQI_7ffue7P4Pk2Q2IPY6_4g-aCGST5HqVmLuxaNKxzTo79CRHjCyiNyRBg/s0/5Ae3u5Hv_rQYrdH3OkgAaFwyoS8.png)
CMDの場合、 [管理者として実行(Run)]オプション(administrator option)がすぐに利用可能になります
右側のペインにオプションが表示されない場合は、下矢印を使用してオプションのリストを展開します。
![下矢印を使用して、[管理者として実行]オプションを表示します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-9Aeqo2TM8Hc/Yjbvc2CNR3I/AAAAAAAAhkg/gj8y7ngiKnQRTtsm2BYlvMfUfVUZp4-PACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwW0CBk7YkolKRhlb6URWa_IgJhlV6Uh5HTXSA46rtPZTzcTVDH5E3Inr1300PCuFmPfzlhV9-wZ0cgm5eyq7ZHFxRZXVbHy0npWVZFQ1PONMxdTopZNqunXwLBLiLb67ib1SygjFUxfYmkgsM2KWbfxsJ0dJUmw1O8_eCdFnl3uawCEzgsMAIg1Qc5NZzeL_r4wLfEjXahBctYEmz8PuHb0PPtvGp-r6YtKLJySOhlKEvT2KQlPP_m8uuAu4nd9hM73lCbqdlSPO8Zq50PdX0wx8st7wB0bPkCKfKneQLRTuZCoubxrSAYYcR0TPzO_mZA9q14hTQoKUUP0yEF1F69JKIE4VMhscEvH2o_SFK7IDwFOJoGP2ZHxPnq1oEr-THgN0QuqzqlZwBKlRjYLmCuyWmtQEJcFb0y83vg4HNMcHMnH4lEEvT9qrp3Mqtom7UIrB2jajclGsNQdwU2a7PVl9MgQ1x74JGCA2gUeIiNlJDd9HgeDJzjAFR5NnV04Ho1gVSVvXEJNT-wQ-v1MGrgxZvOE1OzaWw9ezHrC91jfyv8d8BV4tQ7x9Ll0_Vn7OfNGviasNi0v1rdTERPCA9bQI_7ffue7P4Pk2Q2IPY6_4g-aCGST5HqVmLuxaNKxzTo79CRHjCxiNyRBg/s0/2DWhVYNYrSTKBWr0RYQ-__J-iLA.png)
下矢印を使用して、[管理者(administrator option)として実行]オプションを表示します(Run)
または、正しい検索結果を(search result and click)右クリックまたは長押しして、コンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行(“Run as administrator”)]をクリックまたはタップします。
![コンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行]を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-EauHEUDH438/Yjc2JaN3Y2I/AAAAAAAAu5s/ChfbHEiTLtgUzDxKZ9rtuaZC37jcG0IPQCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhxcrfjNL0kpApMdsYcrhR6ibP9yFPgid8tif1XJf590Y_S6I5KKOmSt3l5FGY4xSNyvZdonIyhAy17tqtmX612OyJ04O3L0FlnNcNc0C54eOcYAIPck3FI_krYDif6TAC-yzKxFLqijseiFajZsn5zZb5ikZDEoD98WADPb77Q8xJjOH9YzrQe3CB3fICtjnubLwJfl_5qf96x98EvSIMovAxNksn1luuo0L_dnicCPkBgBf5wN0-gtGg1mLEXM8O7RQ9uZx49lRm7ceAFzzMt_6Cq2w-eXXuubN_kNKoT7juKeFa2-L0zW6YGXdHX_H-uPut3z-kosp-leDwO3y29zBsAOH0aOENAJ-JGeAnRJ7TKv4t2I6l2cfc-lF9kRTKX6aYwsM79CQqNoNt61sae4bD0zEcPXA9px0izvU6TWFBY_0eJV8U_jRs_hFuQGd3mv42XGA9AF9USp0pq4reDvfzEUbUScBDJxV2FH0gc74fjQOnfl4a2FntrUFG4TIrLZdM1piJaWyZ1PgX8v43nHC1Hi9uMmXsWiYFo5NX1MHFRWVJnhLyCAzaIwxq_hg3o27aMIgAeS-fQ5cwlLgvZliezsqr04t33qG12AvR8NX8glkuNvFAGVed6Q_NgxRGKhvGXPVRSd4G8WMKKg3ZEG/s0/RIvIgu3qIQDHftR4Q1svGV4xTZI.png)
コンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行(Run)]を押します
矢印キーを使用して、左側のペインで適切な検索結果を強調表示することもできます。(search result)次に、Ctrl + Shift + Enter キーボードショートカット(keyboard shortcut)を使用して、そのプログラムを管理者として実行します。
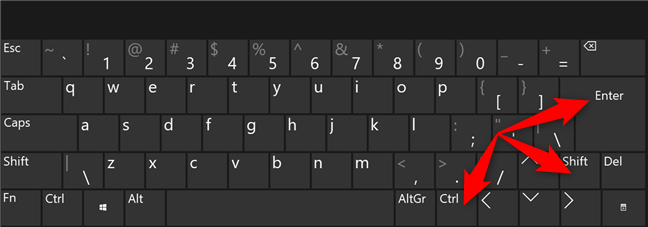
Use Ctrl + Shift + Enter強調表示された検索結果で(search result)Ctrl+Shift+Enterを使用します
7.実行ウィンドウからWindows11で管理者として実行する方法(Run window)
まず、[実行]ウィンドウ(Run window)を開き、管理者として実行するプログラムの実行可能ファイルの名前を挿入します。
![[実行]ウィンドウに実行可能ファイルの名前を入力します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-CMvMnTv9Ybg/YjdH6PVRS3I/AAAAAAAAKiA/eE77DcsgK8gvvpY-nY_P0U_q2eRwM5EZgCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxqHo63eC-w2z6yviSn9DYRDJuWMKm_sPX6g-BI1OEFwv6L01SgCY8x7NMPafCADWrqG-5bpVDJ9v1dX5VJUMKLtB4dJOAcVJsEhFbbXtL-XEojuNI5AruC6OEcs4cjQnBRmHxiidG_bT2PUln-JyMDeM9aSWLAKSXNGv7-yc7yQmIvhyUYhbDkEh81nfEAWmrpABM29e2_Sw9E50aw52PTBbSFGr-9f2F_zVQ6X8hhfsueD2Q3TAAeasc4-YpuzFdw2-e8Er4zY_PbIim0s6V3-GMF_pNVuXyk43N0cVPAQ4d5EcEKzOSQZl94Dd4hs_80k2TqFQdbSNhpq9D9NQyskK8FU-cfokIaFU0zhsWLLuGZVsuH1NRNGn4YNiKEV3QCAPqc9kzi1dPCRqXGd--4GOATbeSeKcQVgEuAwUTG5knE2W6mc6eg3LAB05feSMp5RK6QTKY72osxAAWsYKriaD-cjcVT3-YNVM5UanAfvczKJd_aCqsMi7kY2O-rOOq_hTYACxmVLcoKulU2T9PDKqZObOmLUWvpw1LFqfbIcIgdTfhTJx2pOU5yBgXu92TP53dU475DxGW5MnLmd0KwZo4qU3vaO3OQOutgpXWW1yHWLDsgvUWG4wybPqFh4idUvTQRR786lrgNYjAwmKDdkQY/s0/o9rxUtpfyNmYhodCLW4XKDBi6Y4.png)
[実行]ウィンドウ(Run window)に実行可能ファイルの名前を入力します
次に、キーボードのCtrlキーとShiftキーを押しながら、[ (Shift)OK ]またはEnterキーをクリック/タップします。

Use Ctrl + Shift + Enterして、管理者としてアプリを起動します
8.タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)から管理者として実行します(Run)
タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)を使用して、Windows11で管理者としてプログラムを起動することもできます。まず(First)、タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)を起動し、コンパクトビューで開いたら、 [詳細]を(More details)クリックまたはタップ(click or tap)します。
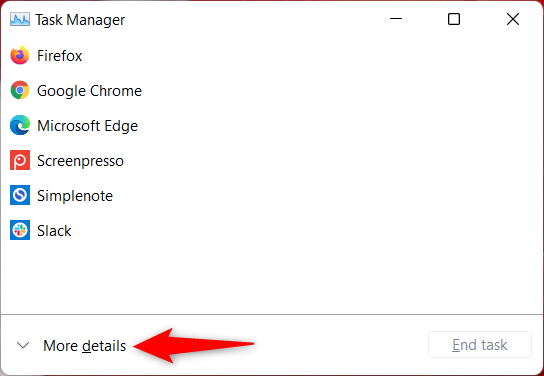
クリックまたはタップして詳細をご覧ください
左上隅から[ファイル(File)]メニューを開き、 [新しいタスクの実行(“Run new task)]をクリック(corner and click)またはタップします。」
![[ファイル]メニューから[新しいタスクの実行]にアクセスします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-94Z2LanyTqI/YjcfNtF1ihI/AAAAAAAAmoY/zTbZ6j3U0xoQY8IS_Us_1GwKVZbuTiwpACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCTz9yRBg/s0/aJlunhEfE57XewS004C0x2Zj9Sk.png)
(Access Run)[ファイル]メニュー(File menu)から[新しいタスクの実行]にアクセスします
[新しいタスク(“Create new task”)の作成]ウィンドウで、[開く(Open)]フィールドを使用して、管理者として起動するプログラムへのパスを入力するか、 [参照]を(Browse)クリックまたはタップ(click or tap)して移動します。「管理者権限でこのタスクを作成する」(“Create this task with administrative privileges”)オプションを必ずチェックしてから、 「 OK 」をクリックまたはタップしてください。
![プログラムへのパスを入力し、チェックボックスをオンにして、[OK]をクリックします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-OB7m_UtMW-8/Yjdgmxph1zI/AAAAAAAAxGA/-NGgMcB7_jUmlsspOzhw3SUCXnbI1gSFQCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCe4d2RBg/s0/tG0QJv4ujIsONByUHlXvaZwCGvg.png)
プログラムへのパスを入力(Enter)し、チェックボックスをオンにして、[OK]をクリックします
ヒント:(TIP:)管理者としてプログラムを起動するこの方法を使用すると、アプリがタスクマネージャー(Task Manager)のアクセス許可(この場合は管理者アクセス許可)を自動的に継承するため、プロセスのUAC部分をスキップできます。デバイスに対する標準のユーザー権限しかない場合は、チェックボックスがありません。
9. Windowsターミナル(Windows Terminal)、PowerShell、またはCMDを使用して、 (CMD)Windows11で管理者として実行します
コマンドライン環境が好きな場合は、Windowsターミナル(Windows Terminal)、PowerShell、またはコマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)にアクセスして、管理者としてプログラムを実行します。Windowsターミナル(Windows Terminal)、CMD、またはPowerShellウィンドウ(PowerShell window)で次のコマンドを入力します。
runas / user: " your_computer_name\administrator_name " " C:\path\program.exe "
your_computer_nameをコンピューターの名前に、administrator_nameをシステムの(your_computer_name)管理(administrator_name)者権限を持つユーザーアカウント(user account)の名前に、C:\path\program.exeを管理者として実行するアプリへの完全なパスに置き換えます。コマンドを正しく入力すると、管理者のパスワードを入力するように求められます。次に、キーボードのEnterキー(Enter)をもう一度押します。

Windowsターミナル(Windows Terminal)から管理者としてプログラムを実行する
ヒント:(TIP:)この方法はより複雑ですが、プロセスのUAC部分をスキップすることができます。
10.常に管理者権限でプログラムを実行します
常に管理者権限で実行するようにプログラムを設定するには、まず、そのメインの実行可能ファイルを見つけます。右クリックまたは長押しして、[プロパティ(Properties)]をクリックまたはタップします。
![右クリックして[プロパティ]にアクセスします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-S8tfqGHr4Es/YjbrvkqLBdI/AAAAAAAAhmc/50lFszDApOMXNr4ROsOZ90BD02sl4p6iQCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwW0CBk7YkolKRhlb6URWa_IgJhlV6Uh5HTXSA46rtPZTzcTVDH5E3Inr1300PCuFmPfzlhV9-wZ0cgm5eyq7ZHFxRZXVbHy0npWVZFQ1PONMxdTopZNqunXwLBLiLb67ib1SygjFUxfYmkgsM2KWbfxsJ0dJUmw1O8_eCdFnl3uawCEzgsMAIg1Qc5NZzeL_r4wLfEjXahBctYEmz8PuHb0PPtvGp-r6YtKLJySOhlKEvT2KQlPP_m8uuAu4nd9hM73lCbqdlSPO8Zq50PdX0wx8st7wB0bPkCKfKneQLRTuZCoubxrSAYYcR0TPzO_mZA9q14hTQoKUUP0yEF1F69JKIE4VMhscEvH2o_SFK7IDwFOJoGP2ZHxPnq1oEr-THgN0QuqzqlZwBKlRjYLmCuyWmtQEJcFb0y83vg4HNMcHMnH4lEEvT9qrp3Mqtom7UIrB2jajclGsNQdwU2a7PVl9MgQ1x74JGCA2gUeIiNlJDd9HgeDJzjAFR5NnV04Ho1gVSVvXEJNT-wQ-v1MGrgxZvOE1OzaWw9ezHrC91jfyv8d8BV4tQ7x9Ll0_Vn7OfNGviasNi0v1rdTERPCA9bQI_7ffue7P4Pk2Q2IPY6_4g-aCGST5HqVmLuxaNKxzTo79CRHjCxiNyRBg/s0/1I8Sn3p5fD4yh7wXg8qjoUKXXvw.png)
右クリックして[プロパティ]にアクセスします
[互換性(Compatibility)]タブで、 [このプログラムを管理者として実行(“Run this program as an administrator”)する]の横のチェックボックスをオンにして、[適用(Apply)]または[ OK ]をクリックまたはタップします。
![管理者として実行するオプションを有効にして、[OK]を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Wv6WiVqPaZA/YjdSv8x4w-I/AAAAAAAAxQE/7NM3PasOyrMIY4rRMtq1Wl2tD45ZAkmDACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCd4d2RBg/s0/SeAime1BMdoanAmzSUguJD4ol-8.png)
管理者として実行するオプションを有効にして、[ OK]を押します(admin and press OK)
この設定が適用され、今後、プログラムは常に管理者権限で実行されます。
ヒント:(TIP: )プログラムのショートカットのプロパティ(Properties)を編集しても、同じ結果を得ることができます。
11. Windowsタスクスケジューラ(Windows Task Scheduler)を使用して、管理者権限でプログラムを実行します
タスクスケジューラ(Task Scheduler)を使用すると、 UAC(ユーザーアカウント制御)( UAC (User Account Control))プロンプトなしで管理者としてプログラムを実行できます。このステップバイステップガイドから、Windowsタスクスケジューラを使用して(Windows Task Scheduler)UACプロンプトなしでアプリを実行する方法を学ぶことができるため、プロセスは単純です。

タスクスケジューラ(Task Scheduler)は、管理者としてプログラムを実行できます
管理者として実行(Run)する方法はどちらが好きですか?
Windows11で実際に昇格された特権を必要とするプログラムはほとんどありません。ただし、管理者権限でアプリを実行する必要があるまれなケースでは、上記の11の方法で十分です。このガイドを閉じる前に、使用する予定の方法をお知らせください。あなた(Did)はすでにそれらのいくつかを使用しましたか?コメントで教えてください。
How to Run as administrator in Windows 11: 11 ways -
To run as administrator in Windows 11 means launching an application with elevated privileges. To prevent unauthorized changes to the operating system, Windows 11 apps and games start, by default, with standard permissions, but there are certain programs, like security software, that require admin rights to run correctly or perform specific tasks. Luckily, the process is easy: all you need are administrator credentials and our instructions. Read this guide to learn how to run as Administrator in Windows 11:
NOTE: Using most of the methods in this guide to run as administrator triggers a UAC prompt asking for further confirmation and, if you’re launching an app using a regular account, an administrator password.
1. How to Run as administrator from an app’s pinned Start Menu shortcut
In Windows 11, you can use the contextual menu of any pinned app to run it with administrative permissions. To begin, open the Windows 11 Start Menu and find the app you want to launch in the Pinned section. Next, right-click or press and hold on it to open its contextual menu, and then click or tap on “Run as administrator.”
Choose Run as administrator from a pinned app's contextual menu
Alternatively, you can also hold down the Ctrl and Shift keys on your keyboard and click/tap on the app you want to run as administrator in Windows 11, or use your keyboard to highlight it and then the Ctrl + Shift + Enter keyboard shortcut to launch it.

Use Ctrl + Shift + Enter on the highlighted pinned app
TIP: If you like this method, you may be interested in learning more about pinning apps to the Windows 11 Start Menu.
2. Run a program as admin using its shortcut from the All apps list of the Windows 11 Start Menu
The All apps section of the Start Menu can also be used to run as administrator in Windows 11. First, open the Start Menu and access All apps.

Access the All apps list in Windows 11
Find the program's shortcut in the list, and right-click or press-and-hold on it to open a contextual menu. Next, click, tap, or hover over the More option, and then press on “Run as administrator.”

Choose Run as administrator from the shortcut's contextual menu
Alternatively, you can hold down Ctrl and Shift on your keyboard and click or tap on the app you want to run as administrator in Windows 11.

Use Ctrl and Shift on the app you want to run as administrator
3. How to Run as administrator from an app’s shortcut
If you have a shortcut for the app you want to run as admin on your desktop or anywhere else, you can open its right-click menu. Then, click or tap on the “Run as administrator.”

Press Run as administrator from the contextual menu
4. Run an app as administrator from its taskbar shortcut
In Windows 11, another way to run an app with administrator permissions is from its taskbar shortcut. First, right-click or press-and-hold on the shortcut. Next, right-click or press-and-hold again on the program’s name. Finally, click or tap on “Run as administrator” from this menu.

Use a taskbar shortcut to run as administrator in Windows 11
You can also hold down Ctrl + Shift and click/tap on an app’s taskbar shortcut to run it with administrator permissions in Windows 11.

Use Ctrl and Shift on the app you want to run as administrator
TIP: To pin an app to the taskbar, read our guide about adding shortcuts to the taskbar in Windows 11.
5. How to run as administrator from an executable’s contextual menu
While shortcuts are easy to find, you can also run a program as administrator in Windows 11 from the main executable file's contextual menu. In File Explorer, navigate to the app’s executable file. Right-click or press-and-hold on it to open the contextual menu, and then click or tap on “Run as administrator.”

Click or tap on Run as administrator
6. Run a program as admin using the Windows 11 Search
First, use the Windows 11 Search to find the program you want to run as admin. On the right pane, click or tap on “Run as administrator.”

For CMD, the Run as administrator option is immediately available
If you don’t see the option in the right pane, use the down arrow to expand the list of options.
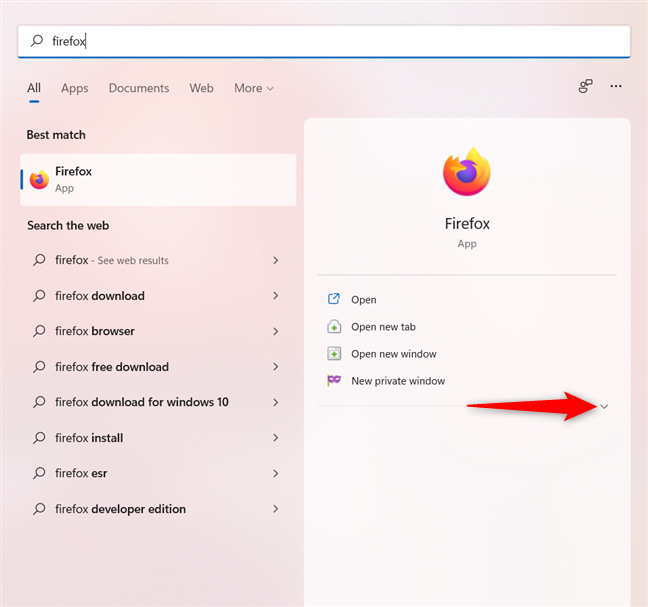
Use the arrow down to reveal the Run as administrator option
Alternatively, right-click or press-and-hold on the correct search result and click or tap on “Run as administrator” from the contextual menu.

Press Run as administrator from the contextual menu
You can also use the arrow keys to highlight the appropriate search result in the left pane. Then, use the Ctrl + Shift + Enter keyboard shortcut to run that program as administrator.

Use Ctrl + Shift + Enter on the highlighted search result
7. How to run as administrator on Windows 11 from the Run window
First, open the Run window and insert the name of the executable for the program you want to run as admin.

Type the name of the executable in the Run window
Then, hold down Ctrl and Shift on your keyboard and click/tap OK or the Enter key.

Use Ctrl + Shift + Enter to launch the app as administrator
8. Run as admin from the Task Manager
You can also launch a program as administrator in Windows 11 by using the Task Manager. First, start the Task Manager and, if it opens up in its compact view, click or tap on More details.

Click or tap on More details
Open the File menu from the upper-left corner and click or tap on “Run new task.”

Access Run new task from the File menu
In the “Create new task” window, use the Open field to enter the path to the program you want to launch as administrator, or click or tap on Browse to navigate to it. Make sure to check the “Create this task with administrative privileges” option, and then click or tap on OK.
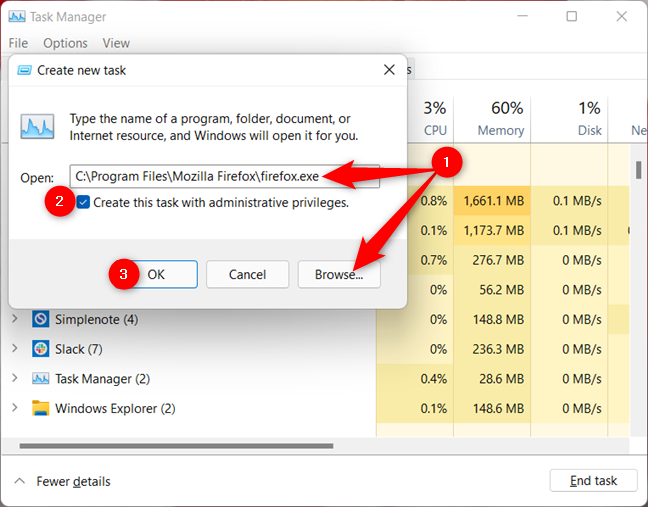
Enter the path to the program, check the box, and hit OK
TIP: Using this method of launching programs as administrator lets you skip the UAC part of the process because the app automatically inherits the permissions of the Task Manager - in our case, administrator permissions. If you only have standard user permissions on the device, the checkbox is missing.
9. Use Windows Terminal, PowerShell, or CMD to run as administrator in Windows 11
If you like command-line environments, access Windows Terminal, PowerShell, or Command Prompt to run a program as administrator. Enter the following command in the Windows Terminal, CMD, or PowerShell window:
runas /user:"your_computer_name\administrator_name" "C:\path\program.exe"
Replace your_computer_name with your computer's name, administrator_name with the name of a user account with administrator permissions on your system, and C:\path\program.exe with the complete path to the app you want to run as administrator. If you enter the command correctly, you are prompted to enter the administrator's password. Then, press Enter on your keyboard once again.

Run a program as administrator from Windows Terminal
TIP: This method is more complicated, but you get to skip the UAC part of the process.
10. Always run a program with administrator permissions
To set a program to always run with administrative permissions, first, locate its main executable file. Right-click or press-and-hold on it, and then click or tap Properties.

Right-click and access Properties
In the Compatibility tab, check the box next to “Run this program as an administrator” and click or tap on Apply or OK.
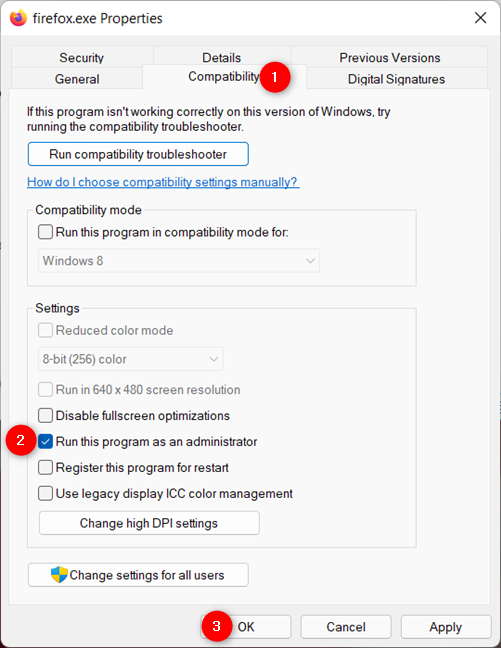
Enable the option to run as admin and press OK
This setting is applied, and, from now on, the program always runs with administrator permissions.
TIP: You can also get the same result by editing the Properties of a program's shortcut.
11. Use the Windows Task Scheduler to run a program with administrative permissions
You can use the Task Scheduler to run a program as administrator without the UAC (User Account Control) prompt. The process is simple, as you can learn from this step-by-step guide on using the Windows Task Scheduler to run apps without UAC prompts.

Task Scheduler can run a program as administrator
Which way to Run as administrator do you prefer?
Very few programs actually require elevated privileges in Windows 11. However, the eleven methods above should be more than enough for those rare cases when you do need to run an app with administrative permissions. Before you close this guide, let us know which method(s) you plan to use. Did you already use some of them? Let us know in a comment.
![固定されたアプリのコンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行]を選択します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-UMWtyHFRdp8/YjdXSeGb4wI/AAAAAAAAxNU/MyO1Y2mhqv8-uiE-lqDxV4_Gp9UrSs7NACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCe4d2RBg/s0/TvHwZY9QOgBnsjyhOxB_SLCS1R8.png)

![Windows11の[すべてのアプリ]リストにアクセスする](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-OhxihgxPM-k/YjcJaBekAwI/AAAAAAAAm3I/fn_J3avsK_AeT9cjNGZydeYAK-3uDT4bACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCRz9yRBg/s0/6YzJeF9-cQRUvJofDuHje31aTfo.png)
![ショートカットのコンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行]を選択します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-uGAHfcFpGD4/Yjc-ZGPY0GI/AAAAAAAAu0U/qoqDQY0_QXU2Ia3eMUs4zYUVU2oM_PAZgCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhxcrfjNL0kpApMdsYcrhR6ibP9yFPgid8tif1XJf590Y_S6I5KKOmSt3l5FGY4xSNyvZdonIyhAy17tqtmX612OyJ04O3L0FlnNcNc0C54eOcYAIPck3FI_krYDif6TAC-yzKxFLqijseiFajZsn5zZb5ikZDEoD98WADPb77Q8xJjOH9YzrQe3CB3fICtjnubLwJfl_5qf96x98EvSIMovAxNksn1luuo0L_dnicCPkBgBf5wN0-gtGg1mLEXM8O7RQ9uZx49lRm7ceAFzzMt_6Cq2w-eXXuubN_kNKoT7juKeFa2-L0zW6YGXdHX_H-uPut3z-kosp-leDwO3y29zBsAOH0aOENAJ-JGeAnRJ7TKv4t2I6l2cfc-lF9kRTKX6aYwsM79CQqNoNt61sae4bD0zEcPXA9px0izvU6TWFBY_0eJV8U_jRs_hFuQGd3mv42XGA9AF9USp0pq4reDvfzEUbUScBDJxV2FH0gc74fjQOnfl4a2FntrUFG4TIrLZdM1piJaWyZ1PgX8v43nHC1Hi9uMmXsWiYFo5NX1MHFRWVJnhLyCAzaIwxq_hg3o27aMIgAeS-fQ5cwlLgvZliezsqr04t33qG12AvR8NX8glkuNvFAGVed6Q_NgxRGKhvGXPVRSd4G8WMJ6g3ZEG/s0/pqgiRB-nnHvCLwEDGdaXbTpvqTY.png)

![コンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行]を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-0ot8QVQ-AKc/YjciTaSa0NI/AAAAAAAAEW8/yNqleYAbPRc-8vWX_OLc2Plo-CbGW-FVwCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxeSqmKu1BtuATYSULyy9OK0vUZJMh4EEreX9rzJid57_Lr5itgoyxzXecCdHil_kcjllNp636SB8ECcTxmI--8us7mIs7_4fcnjy5EcSKFLsehZVlA79dQvMROYqrbbfCkZz25BePPjbkt5vMp0a-Ffrw5A99b5RlKddBRMXeM9g_FOe-xFzRbvRW7TYY6HykLA9PekQsEvOV8jpg0SHFKFaAgGIgHmS8N7Z4b0t8oAyxaq09z-wMB1q859mpaUbsnf4wcrBa-aLiovkCSe0-odM-A-9luIU_P030lCRFTGU9BY0zVaY2-1KUD4qSF0CxrUZ63BI5AN1rY-GLaYkrr6q6sLymszIx_5ReHwutHRLMCol2Y3bqo8_EmWqm1xKORC4FaaCfGnEFVJB_wg7045IZzS73d4lf5GevtJPILvrX6AAn4MdBndWPI54Il_GyriQm-PvgqlWRU8VIZSbskQDSr606f1DhUT0lFbEm55jRTZO5fxh4ah9Me-2zfxCotjHRzCLkIkXarR56jt-M2SgQLbI-FEfyKwUTPXJ4v_RR4iPWc90tJKVi01D3pbDGX5WGBgfwItEcVTJrbT3YKakmk0mweSX3-I0kynawDx1NIRHydgBsBNyU99ZZWyYdyYcFCu2SsV1d5Oa8w39XckQY/s0/d-Tn6tcwZJVR5PxirYKdIEeec4A.png)


![[管理者として実行]をクリックまたはタップします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-iQKzY-jsG4Q/YjctUNZQD8I/AAAAAAAAKzA/DmhkgTKY424C4PFS2wpMHCSqX8AMJHoMACEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxqHo63eC-w2z6yviSn9DYRDJuWMKm_sPX6g-BI1OEFwv6L01SgCY8x7NMPafCADWrqG-5bpVDJ9v1dX5VJUMKLtB4dJOAcVJsEhFbbXtL-XEojuNI5AruC6OEcs4cjQnBRmHxiidG_bT2PUln-JyMDeM9aSWLAKSXNGv7-yc7yQmIvhyUYhbDkEh81nfEAWmrpABM29e2_Sw9E50aw52PTBbSFGr-9f2F_zVQ6X8hhfsueD2Q3TAAeasc4-YpuzFdw2-e8Er4zY_PbIim0s6V3-GMF_pNVuXyk43N0cVPAQ4d5EcEKzOSQZl94Dd4hs_80k2TqFQdbSNhpq9D9NQyskK8FU-cfokIaFU0zhsWLLuGZVsuH1NRNGn4YNiKEV3QCAPqc9kzi1dPCRqXGd--4GOATbeSeKcQVgEuAwUTG5knE2W6mc6eg3LAB05feSMp5RK6QTKY72osxAAWsYKriaD-cjcVT3-YNVM5UanAfvczKJd_aCqsMi7kY2O-rOOq_hTYACxmVLcoKulU2T9PDKqZObOmLUWvpw1LFqfbIcIgdTfhTJx2pOU5yBgXu92TP53dU475DxGW5MnLmd0KwZo4qU3vaO3OQOutgpXWW1yHWLDsgvUWG4wybPqFh4idUvTQRR786lrgNYjAwlaDdkQY/s0/LpzjSGR4-KmSlkDpvVNg7TJzGNU.png)
![CMDの場合、[管理者として実行]オプションがすぐに利用可能になります](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Q6zyJWWhE-8/Yjb7eELFU-I/AAAAAAAAhaM/J0ncV8H4VJsyv0c5QSdk2jqTt2TTzrFTwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwW0CBk7YkolKRhlb6URWa_IgJhlV6Uh5HTXSA46rtPZTzcTVDH5E3Inr1300PCuFmPfzlhV9-wZ0cgm5eyq7ZHFxRZXVbHy0npWVZFQ1PONMxdTopZNqunXwLBLiLb67ib1SygjFUxfYmkgsM2KWbfxsJ0dJUmw1O8_eCdFnl3uawCEzgsMAIg1Qc5NZzeL_r4wLfEjXahBctYEmz8PuHb0PPtvGp-r6YtKLJySOhlKEvT2KQlPP_m8uuAu4nd9hM73lCbqdlSPO8Zq50PdX0wx8st7wB0bPkCKfKneQLRTuZCoubxrSAYYcR0TPzO_mZA9q14hTQoKUUP0yEF1F69JKIE4VMhscEvH2o_SFK7IDwFOJoGP2ZHxPnq1oEr-THgN0QuqzqlZwBKlRjYLmCuyWmtQEJcFb0y83vg4HNMcHMnH4lEEvT9qrp3Mqtom7UIrB2jajclGsNQdwU2a7PVl9MgQ1x74JGCA2gUeIiNlJDd9HgeDJzjAFR5NnV04Ho1gVSVvXEJNT-wQ-v1MGrgxZvOE1OzaWw9ezHrC91jfyv8d8BV4tQ7x9Ll0_Vn7OfNGviasNi0v1rdTERPCA9bQI_7ffue7P4Pk2Q2IPY6_4g-aCGST5HqVmLuxaNKxzTo79CRHjCyiNyRBg/s0/5Ae3u5Hv_rQYrdH3OkgAaFwyoS8.png)
![下矢印を使用して、[管理者として実行]オプションを表示します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-9Aeqo2TM8Hc/Yjbvc2CNR3I/AAAAAAAAhkg/gj8y7ngiKnQRTtsm2BYlvMfUfVUZp4-PACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwW0CBk7YkolKRhlb6URWa_IgJhlV6Uh5HTXSA46rtPZTzcTVDH5E3Inr1300PCuFmPfzlhV9-wZ0cgm5eyq7ZHFxRZXVbHy0npWVZFQ1PONMxdTopZNqunXwLBLiLb67ib1SygjFUxfYmkgsM2KWbfxsJ0dJUmw1O8_eCdFnl3uawCEzgsMAIg1Qc5NZzeL_r4wLfEjXahBctYEmz8PuHb0PPtvGp-r6YtKLJySOhlKEvT2KQlPP_m8uuAu4nd9hM73lCbqdlSPO8Zq50PdX0wx8st7wB0bPkCKfKneQLRTuZCoubxrSAYYcR0TPzO_mZA9q14hTQoKUUP0yEF1F69JKIE4VMhscEvH2o_SFK7IDwFOJoGP2ZHxPnq1oEr-THgN0QuqzqlZwBKlRjYLmCuyWmtQEJcFb0y83vg4HNMcHMnH4lEEvT9qrp3Mqtom7UIrB2jajclGsNQdwU2a7PVl9MgQ1x74JGCA2gUeIiNlJDd9HgeDJzjAFR5NnV04Ho1gVSVvXEJNT-wQ-v1MGrgxZvOE1OzaWw9ezHrC91jfyv8d8BV4tQ7x9Ll0_Vn7OfNGviasNi0v1rdTERPCA9bQI_7ffue7P4Pk2Q2IPY6_4g-aCGST5HqVmLuxaNKxzTo79CRHjCxiNyRBg/s0/2DWhVYNYrSTKBWr0RYQ-__J-iLA.png)
![コンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行]を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-EauHEUDH438/Yjc2JaN3Y2I/AAAAAAAAu5s/ChfbHEiTLtgUzDxKZ9rtuaZC37jcG0IPQCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhxcrfjNL0kpApMdsYcrhR6ibP9yFPgid8tif1XJf590Y_S6I5KKOmSt3l5FGY4xSNyvZdonIyhAy17tqtmX612OyJ04O3L0FlnNcNc0C54eOcYAIPck3FI_krYDif6TAC-yzKxFLqijseiFajZsn5zZb5ikZDEoD98WADPb77Q8xJjOH9YzrQe3CB3fICtjnubLwJfl_5qf96x98EvSIMovAxNksn1luuo0L_dnicCPkBgBf5wN0-gtGg1mLEXM8O7RQ9uZx49lRm7ceAFzzMt_6Cq2w-eXXuubN_kNKoT7juKeFa2-L0zW6YGXdHX_H-uPut3z-kosp-leDwO3y29zBsAOH0aOENAJ-JGeAnRJ7TKv4t2I6l2cfc-lF9kRTKX6aYwsM79CQqNoNt61sae4bD0zEcPXA9px0izvU6TWFBY_0eJV8U_jRs_hFuQGd3mv42XGA9AF9USp0pq4reDvfzEUbUScBDJxV2FH0gc74fjQOnfl4a2FntrUFG4TIrLZdM1piJaWyZ1PgX8v43nHC1Hi9uMmXsWiYFo5NX1MHFRWVJnhLyCAzaIwxq_hg3o27aMIgAeS-fQ5cwlLgvZliezsqr04t33qG12AvR8NX8glkuNvFAGVed6Q_NgxRGKhvGXPVRSd4G8WMKKg3ZEG/s0/RIvIgu3qIQDHftR4Q1svGV4xTZI.png)

![[実行]ウィンドウに実行可能ファイルの名前を入力します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-CMvMnTv9Ybg/YjdH6PVRS3I/AAAAAAAAKiA/eE77DcsgK8gvvpY-nY_P0U_q2eRwM5EZgCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxqHo63eC-w2z6yviSn9DYRDJuWMKm_sPX6g-BI1OEFwv6L01SgCY8x7NMPafCADWrqG-5bpVDJ9v1dX5VJUMKLtB4dJOAcVJsEhFbbXtL-XEojuNI5AruC6OEcs4cjQnBRmHxiidG_bT2PUln-JyMDeM9aSWLAKSXNGv7-yc7yQmIvhyUYhbDkEh81nfEAWmrpABM29e2_Sw9E50aw52PTBbSFGr-9f2F_zVQ6X8hhfsueD2Q3TAAeasc4-YpuzFdw2-e8Er4zY_PbIim0s6V3-GMF_pNVuXyk43N0cVPAQ4d5EcEKzOSQZl94Dd4hs_80k2TqFQdbSNhpq9D9NQyskK8FU-cfokIaFU0zhsWLLuGZVsuH1NRNGn4YNiKEV3QCAPqc9kzi1dPCRqXGd--4GOATbeSeKcQVgEuAwUTG5knE2W6mc6eg3LAB05feSMp5RK6QTKY72osxAAWsYKriaD-cjcVT3-YNVM5UanAfvczKJd_aCqsMi7kY2O-rOOq_hTYACxmVLcoKulU2T9PDKqZObOmLUWvpw1LFqfbIcIgdTfhTJx2pOU5yBgXu92TP53dU475DxGW5MnLmd0KwZo4qU3vaO3OQOutgpXWW1yHWLDsgvUWG4wybPqFh4idUvTQRR786lrgNYjAwmKDdkQY/s0/o9rxUtpfyNmYhodCLW4XKDBi6Y4.png)


![[ファイル]メニューから[新しいタスクの実行]にアクセスします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-94Z2LanyTqI/YjcfNtF1ihI/AAAAAAAAmoY/zTbZ6j3U0xoQY8IS_Us_1GwKVZbuTiwpACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCTz9yRBg/s0/aJlunhEfE57XewS004C0x2Zj9Sk.png)
![プログラムへのパスを入力し、チェックボックスをオンにして、[OK]をクリックします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-OB7m_UtMW-8/Yjdgmxph1zI/AAAAAAAAxGA/-NGgMcB7_jUmlsspOzhw3SUCXnbI1gSFQCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCe4d2RBg/s0/tG0QJv4ujIsONByUHlXvaZwCGvg.png)

![右クリックして[プロパティ]にアクセスします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-S8tfqGHr4Es/YjbrvkqLBdI/AAAAAAAAhmc/50lFszDApOMXNr4ROsOZ90BD02sl4p6iQCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwW0CBk7YkolKRhlb6URWa_IgJhlV6Uh5HTXSA46rtPZTzcTVDH5E3Inr1300PCuFmPfzlhV9-wZ0cgm5eyq7ZHFxRZXVbHy0npWVZFQ1PONMxdTopZNqunXwLBLiLb67ib1SygjFUxfYmkgsM2KWbfxsJ0dJUmw1O8_eCdFnl3uawCEzgsMAIg1Qc5NZzeL_r4wLfEjXahBctYEmz8PuHb0PPtvGp-r6YtKLJySOhlKEvT2KQlPP_m8uuAu4nd9hM73lCbqdlSPO8Zq50PdX0wx8st7wB0bPkCKfKneQLRTuZCoubxrSAYYcR0TPzO_mZA9q14hTQoKUUP0yEF1F69JKIE4VMhscEvH2o_SFK7IDwFOJoGP2ZHxPnq1oEr-THgN0QuqzqlZwBKlRjYLmCuyWmtQEJcFb0y83vg4HNMcHMnH4lEEvT9qrp3Mqtom7UIrB2jajclGsNQdwU2a7PVl9MgQ1x74JGCA2gUeIiNlJDd9HgeDJzjAFR5NnV04Ho1gVSVvXEJNT-wQ-v1MGrgxZvOE1OzaWw9ezHrC91jfyv8d8BV4tQ7x9Ll0_Vn7OfNGviasNi0v1rdTERPCA9bQI_7ffue7P4Pk2Q2IPY6_4g-aCGST5HqVmLuxaNKxzTo79CRHjCxiNyRBg/s0/1I8Sn3p5fD4yh7wXg8qjoUKXXvw.png)
![管理者として実行するオプションを有効にして、[OK]を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Wv6WiVqPaZA/YjdSv8x4w-I/AAAAAAAAxQE/7NM3PasOyrMIY4rRMtq1Wl2tD45ZAkmDACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCd4d2RBg/s0/SeAime1BMdoanAmzSUguJD4ol-8.png)

