Windowsの(Windows)システム構成(msconfig.exe)(System Configuration (msconfig.exe) )ツールがどれほど優れているか知っていますか?これは小さくてやや隠されたツールですが、 Windows(Windows)の動作方法についてかなり多くのことを変更できます。特に、システム構成(System Configuration )ツールを使用すると、 Windowsの起動方法の構成、(Windows)起動手順(boot procedure)の変更、起動サービスとプログラムの選択、および一連の便利な管理プログラムの開始を行うことができます。システム構成(System Configuration)で実行できることについて詳しく知りたい場合は、次の記事をお読みください。
注:(NOTE:)この記事では、 Windows 10、Windows 7、およびWindows8.1について説明します。それを読む前に、システム構成(System Configuration)を開始する方法をすでに知っていることを前提としていることを知っておく必要があります。そうでない場合は、最初にこれを読んでください:Windows(すべてのバージョン)でシステム構成を開始する8つの方法。(System Configuration)また、使用しているWindows(Windows)のバージョンがわからない場合は、このチュートリアルが役立ちます。どのバージョンのWindowsをインストールしましたか?
1.Windowsの起動時(Windows startup)にロードするドライバーとサービスを選択します
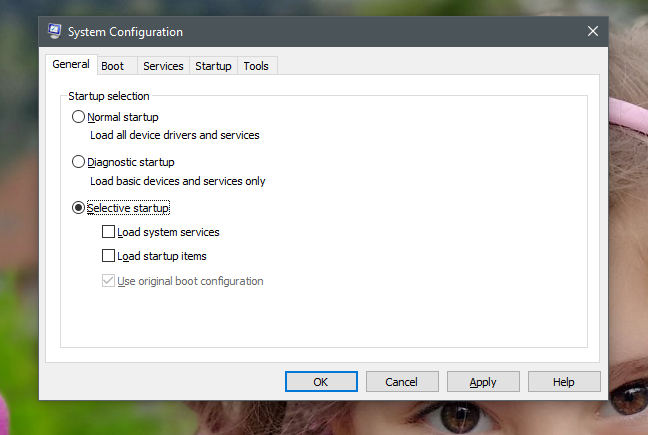
システム構成(System Configuration)ツールは、msconfig.exeとも呼ばれ、設定(msconfig.exe)とショートカットを備えたウィンドウです。それらはすべていくつかのタブに分割されており、各タブからさまざまなものにアクセスできます。[システム構成(System Configuration)]ウィンドウの最初のタブは[全般(General)]と呼ばれ、Windowsの起動方法を構成できる場所です。

[全般(General)]タブの[スタートアップの選択("Startup selection")]リストで、Windowsに次のことを実行させることを選択できます。
-
「通常のスタートアップ」: Windowsは、インストールされている("Normal startup": )すべて(ALL )のスタートアップアイテム、ドライバー、およびサービスを使用して、そのまま起動することを意味します。このモードは、起動時(boot time)にロードされるドライバー、サービス、またはアプリにすでにいくつかの変更を加えている場合を除いて、ほとんどのWindowsデバイスでデフォルトで選択されている必要があります。
-
「診断起動」 :このモードは、("Diagnostic startup")セーフモード(Mode)での起動に似ています。セーフモードは、 (Safe Mode)Windowsサービスとドライバーのみを実行します。それらに加えて、診断スタートアップ(Diagnostic startup)は、それらに加えて、ネットワークサービス、またはウイルス対策、ファイアウォール、セキュリティスイート(firewall or security suite)などのサードパーティアプリケーションからの重要なサービスを実行する場合があります。このモードは、システムの不安定性(system instability)の問題の原因としてWindowsファイルとサービスを除外する場合に役立ちます。「診断スタートアップ」を選択し、「("Diagnostic startup" )適用(Apply)」をクリックまたはタップすると、「選択的スタートアップ」("Selective startup")に注意してください。選択されたものとして表示されます。ただし、これはごく普通のことなので、心配する必要はありません。これは、「診断スタートアップ」("Diagnostic startup")が事前定義された設定のセットを持つ「選択的スタートアップ」であるために発生します。("Selective startup" )
-
「選択的スタートアップ」:("Selective startup":)Windowsをその重要なサービスとドライバーだけで起動させます。さらに、[サービス]タブと[スタートアップ](Services and Startup)タブから、実行する他のサービスとスタートアップ項目を選択することもできます。
また、スタートアップモードを切り替え、トラブルシューティングを行ってから、再び「通常のスタートアップ」("Normal startup")の使用に戻ると、すべてのサービスとスタートアップ項目がスタートアップ時に有効になることに注意することも重要です。
一部のアプリ、ドライバー、またはサービスがWindowsで自動的に起動しないようにする場合は、サービスとスタートアップアイテムのリストを確認し、それらを再度編集する必要があります。このガイドの後半で、その方法を確認できます。ただし、今のところ、変更を加えると、「選択的スタートアップ」がアクティブな("Selective startup")スタートアップ選択(startup selection)としてチェックされることに注意してください。
2. PCにインストールされているオペレーティングシステムを確認し、デフォルトのオペレーティングシステムを選択します
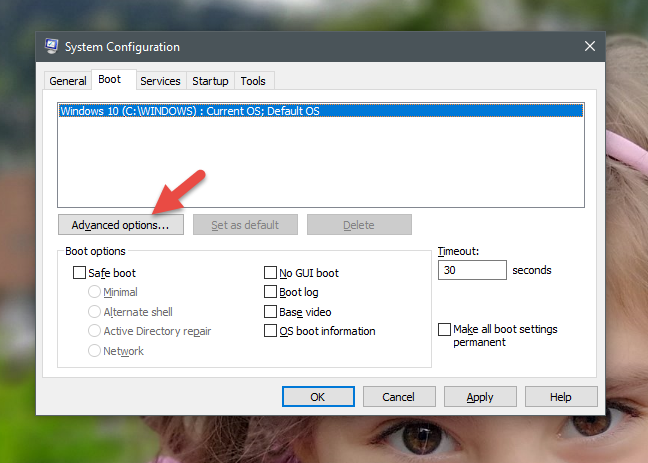
システム構成(System Configuration)ツールは、PCにインストールされているオペレーティングシステムのどれを最初にロードするかをグラフィカルに選択する方法も提供します。[システム構成]ツールで[(System Configuration)ブート(Boot)]タブに切り替えると、コンピューターにインストールされているすべてのオペレーティングシステムを表示し、マルチブートセットアップがある場合はデフォルト(default one)のオペレーティングシステムを選択できます。新しいデフォルトのオペレーティングシステムを選択するには、それを(default operating system)クリックまたはタップ(click or tap)してから、 [デフォルトとして設定]をクリックします。("Set as default.")

3.起動するオペレーティングシステム(operating system)を選択するためにPCが待機する時間を選択します
マルチブート設定の場合、もう1つの重要な設定はタイムアウト(Timeout )設定です。設定した秒数は、起動時に使用可能なオペレーティングシステムの1つを選択するのをPCが待機する時間を表します。設定時間(set time)内に選択がない場合、デフォルトのオペレーティングシステムが起動します。

デフォルトでは、タイムアウト(Timeout)は30秒に設定されています。マルチブート設定をしている場合は、それをより小さな値に設定することをお勧めします。たとえば、タイムアウト(Timeout)を10秒に設定することをお勧めします。このように、別のオペレーティングシステムを選択しない場合、デフォルトの(default one)オペレーティングシステム(operating system)の合計起動タイミング(boot timing)はそれほど影響を受けません。
4.プロセッサコアの数や使用できるRAMの量など、Windowsの起動方法に関するいくつかの詳細設定を変更します(Windows)
コンピューターにインストールされているWindowsオペレーティングシステムの場合、システム構成(Windows operating)ツール(System Configuration)を使用すると、起動方法に関する複雑な詳細を構成することもできます。
既存のオペレーティングシステムごとに、[詳細オプション]ボタンをクリックまたはタップすると、起動時に("Advanced options")オペレーティングシステム(operating system)に割り当てられるプロセッサ(コア)の数や、使用可能なRAMの最大量などを設定できます。それ。
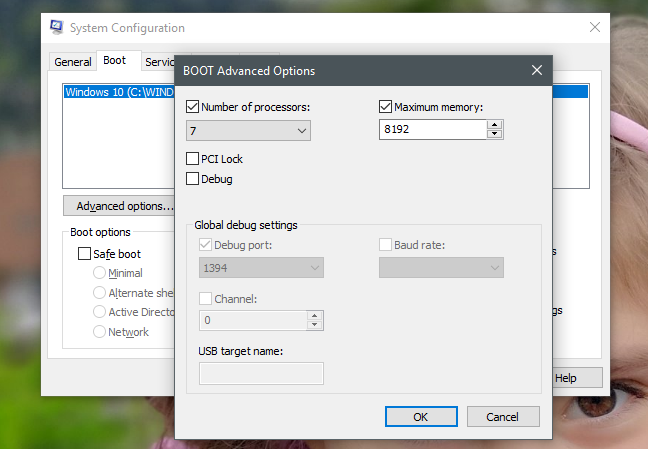
プロセッサコアとRAMの最大数を設定すると、Windowsは、プロセッサが持つ実際のコア数と物理(Windows)RAMの量を正しく識別し続けます。ただし、使用できるプロセッサコアの数は限られており、設定した最大メモリしか使用できません。
5.Windowsをセーフモードで起動します
PCにインストールされているWindows オペレーティングシステム(operating system)ごとに、システム構成ツールを使用して、(System Configuration)セーフモード(Safe Mode)で起動するかどうかを選択することもできます。これを行うには、 [ブート(Boot)]タブで、[セーフブート("Safe boot")]というオプションをオンにして、使用可能なオプションの1つを選択する必要があります。
-
最小限-(Minimal - )ユーザーインターフェイスがあり、ネットワークサービスが有効になっていない、通常のセーフブート。
-
代替シェル-(Alternate shell)セーフモードで(Safe Mode)コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)を開きます。ネットワークサービスとグラフィカルユーザーインターフェイス(user interface)が無効になっています。
-
ActiveDirectoryの修復-ActiveDirectory(Active Directory repair)の(Active Directory)サービスと機能に加えて、実行される通常のセーフブート。
-
ネットワーク(Network)-ネットワークサービスが有効になっている通常のセーフブート。

Windowsの(Windows)セーフモード(Safe Mode )について詳しく知りたい場合は、次のガイドに興味があるかもしれません。
- Windows10で(Windows 10)セーフモード(Mode)で起動する7つの方法
- Windows10でネットワーク(Networking)を使用してセーフモード(Mode)で起動する6つの方法
- Windows7で(Windows 7)セーフモード(Mode)で起動する3つの方法
- Windows8.1で(Windows 8.1)セーフモードで起動(Boot Into Safe Mode)する5つの方法(Ways)
6. Windowsの起動(Windows boot)読み込み画面を無効にし、起動プロセス(startup process)をログに記録し、標準のビデオドライバーなどを使用します
また、 [ブート(Boot)]タブの[システム構成]ツールには、標準と(System Configuration)セーフモード(Safe Mode )の両方のブート手順に適用できる一連の高度なオプションがあります。
-
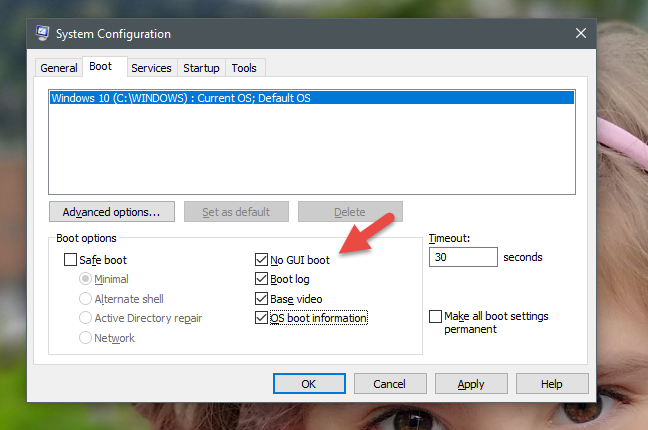
「GUIブートなし」("No GUI boot") -ブート中、通常のロード画面(loading screen)は表示されず、情報のない黒い画面のみが表示されます。
-
「起動ログ」("Boot log") -起動中に、 Windowsは(Windows)起動プロセス(startup process)に関する情報を含む完全なログを書き込みます。通常、次の場所にあります:「C:WindowsNtbtlog.txt」。
-
「ベースビデオ」("Base video") -このオプションは、お粗末なビデオドライバをインストールしたばかりの場合に便利です。これにより、標準のWindowsが起動しますが、(Windows startup)ビデオカード(video card)に固有のドライバではなく、Windowsに付属している標準のビデオドライバのみが読み込まれるという違いがあります。
-
「OSブート情報」 -このオプションは("OS boot information")「GUIブートなし」("No GUI Boot.")と一緒に使用する必要があります。通常のWindowsのロード画面は黒い画面に置き換えられ、起動プロセス(startup process)中にロードされたドライバーに関する完全な情報が表示されます。起動中にWindows(Windows)がクラッシュした場合、この視覚化モード(visualization mode)は、クラッシュの原因となったドライバーを特定するのに役立ちます。
7.Windowsで開始するサービスを選択します
[システム構成(System Configuration)]ツールの[サービス]タブには、Windowsの起動時に開始されるすべてのサービスのリストが表示さ(Services)れます(Windows)。サービスごとに、名前、製造元、現在のステータス、および無効にされた場合は無効にされた日付が表示されます。
起動時に実行するサービスをチェックし、実行しないサービスのチェックを外すことができます。アプリケーションによってインストールされたサードパーティのサービスのみを表示する場合は、[すべてのMicrosoftサービスを非表示にする]チェックボックスをオンにします。("Hide all Microsoft services.")

このタブで行った選択は、[全般(General)]タブからの現在のスタートアップの選択(startup selection)にのみ適用されます。「通常のスタートアップ」("Normal startup,")を使用していて、一部のサービスを無効にした場合、スタートアップの選択(startup selection)は自動的に「選択的スタートアップ」に変更されます。("Selective startup.")
起動時に実行を停止するサービスを決定する際にヘルプが必要な場合は、このガイドをお読みください:どのWindowsサービスをいつ無効にしても安全ですか?
8.スタートアッププログラムを管理します(Windows 7のみ)
Windows10またはWindows8.1を使用している場合、 [スタートアップ]タブには、 (Startup)[タスクマネージャー("Open Task Manager.")を開く]へのリンクが表示されます。これは、コンピューターのスタートアップアプリの管理が(startup apps)タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)を使用して行われるためです。

ただし、 Windows 7(Windows 7)を使用している場合は、 [スタートアップ]タブに、 (Startup)Windowsの起動時に起動するすべてのプログラムとファイルのリストが表示されます。各アイテムについて、名前、製造元、起動に使用されたコマンド(通常、プログラムへのパスと使用されている場合は追加のパラメーター)、およびアイテムが保存されているレジストリの起動場所(registry startup location)と無効にされた日付が表示されます。無効になりました。

レジストリ(registry location)の場所について覚えておくべきことの1つは、 HKLMで始まるものが表示された場合、スタートアップ項目が「グローバル」であることを意味します。これは、アクティブなオペレーティングシステム(operating system)で定義されたすべてのユーザーアカウント(user account)に適用されます。1つのユーザーアカウント(user account)からそれらを無効にすると、すべてのユーザーアカウント(user account)でそれらが無効になります。
HKCUで始まる場所は、現在のユーザーアカウント(user account)でのみアクティブなスタートアップアイテム用です。他のユーザーアカウント(user account)では起動しない可能性があります。また、完全に起動しないようにする場合は、ユーザーアカウント(user account)ごとに個別に無効にする必要があります。
[サービス(Services)]タブと同様に、行った選択は、[全般(General)]タブからの現在のスタートアップの選択(startup selection)に適用されます。
9.管理プログラムとパネルを起動します
システム構成の[(System Configuration)ツール(Tools)]タブとその機能について知っている人はほとんどいません。それをクリックすると、システム情報(System Information)、レジストリエディタ(Registry Editor)、イベントビューア(Event Viewer)、パフォーマンスモニタなどの(Performance Monitor)Windows管理ツールのリストが表示されます。
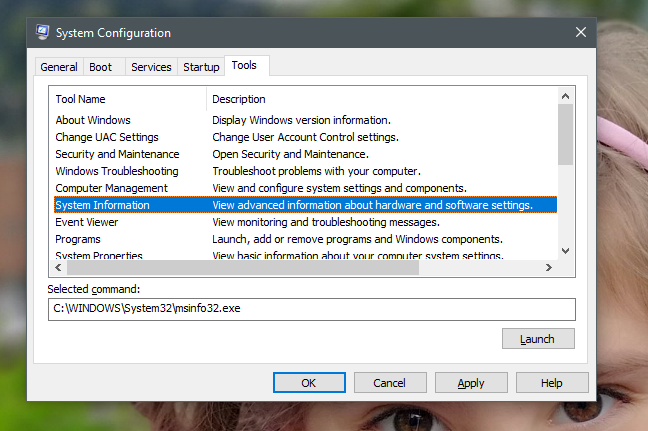
ツールごとに、システム構成(System Configuration)にその名前と説明(name and description)が表示されます。クリックまたはタップすると、[選択されたコマンド(Selected command)]フィールドに起動に使用されたコマンドが表示されます。使用可能なツールのいずれかを実行するには、必要なツールを選択し、[起動(Launch)]をクリックまたはタップします。

ご覧のとおり、 [システム構成]の[(System Configuration)ツール(Tools)]タブには、システムの安定性やパフォーマンスの問題(system stability or performance problems)のトラブルシューティング中に一般的に使用される管理ツールが一覧表示されているので便利です。
システム構成(System Configuration)で行った変更を保存します
必要な変更をすべて行ったら、[適用](Apply)または[ OK ]を押すことを忘れないでください。変更が適用されます。また、ツールを初めて使用する場合は、ツールを閉じるときに、新しい設定を有効にするためにPCを再起動する必要があることが通知される場合があります。
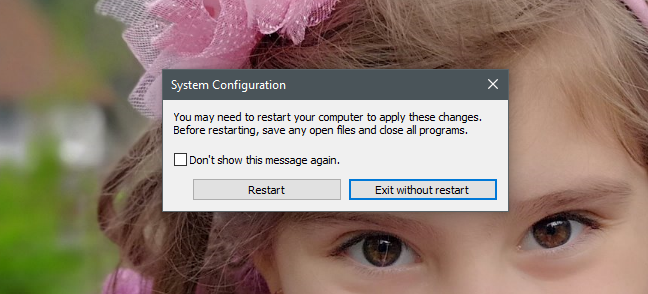
このメッセージを再度表示したくない場合は、[このメッセージを再度表示しない]チェックボックスをオンにして、希望する("Don't show this message again")再起動オプション(restart option)を選択してください。
(Are)システム構成ツール(System Configuration tool)を使用して、Windowsの動作方法を変更していますか?
ご覧のとおり、システム構成(msconfig.exe)ユーティリティは、 (System Configuration (msconfig.exe) )Windowsの起動方法と動作方法を変更したい人に役立つ機能を提供する、用途の広いツールです。これは、Windowsコンピューターの(Windows computer)起動プロセスを管理するだけでなく、(startup process)安定性とパフォーマンスの問題(stability and performance problems)をトラブルシューティングするための優れたツールになる可能性があります。Windowsの構成に使用していますか?何か問題がありましたか?以下のコメントセクションで議論しましょう。(Let)
9 things you can do with System Configuration, in Windows
Do yоu know how exсеllent thе System Configuration (msconfig.exe) tool from Windows is? Although it is a small and somewhat hidden tool, it allows you to change quite a few things about the way Windows works. Among other things, the System Configuration tool lets you configure how Windows starts, change the boot procedure, select startup services, and programs, and also start a series of useful administrative programs. If you want to know more about the things you can do with System Configuration, read this article:
NOTE: This article covers Windows 10, Windows 7 and Windows 8.1. Before reading it, you should know that we assume you already know how to start System Configuration. If you do not, read this first: 8 ways to start System Configuration in Windows (all versions). Also, if you do not know the version of Windows that you are using, this tutorial should help: What version of Windows do I have installed?
1. Choose what drivers and services are loaded at Windows startup
The System Configuration tool, also known as msconfig.exe, is a window with settings and shortcuts. They are all split into several tabs, and each tab gives you access to different things. The first tab in the System Configuration window is called General, and it is the place where you can configure how Windows starts.

In the "Startup selection" list from the General tab, you can choose to make Windows do a:
-
"Normal startup": meaning that Windows starts as is, with ALL the installed startup items, drivers, and services. This mode should be selected by default on most Windows devices, except when you have already made some changes to what drivers, services or apps are loaded at boot time.
-
"Diagnostic startup": this mode is similar to booting into Safe Mode. Safe Mode runs only Windows services and drivers. Besides them, the Diagnostic startup might also run, on top of them, networking services or important services from third-party applications such as your antivirus, firewall or security suite. This mode is useful if you want to rule out Windows files and services as being the source of system instability problems. Note that if you select the "Diagnostic startup" and then click or tap Apply, the "Selective startup" is the one shown as selected. However, there is nothing to worry about, as this is quite normal. It happens because the "Diagnostic startup" is a "Selective startup" with a predefined set of settings.
-
"Selective startup": makes Windows start only with its essential services and drivers. Furthermore, it also allows you to select other services and startup items that you want to run, from the Services and Startup tabs.

It is also important to note that if you switch between startup modes, do some troubleshooting and then go back to using the "Normal startup" again, all the services and startup items are going to be enabled at startup.
If what you want is to stop some apps, drivers or services from starting automatically with Windows, you need to go through the list of services and startup items and edit them again. You can see how to do that, later in this guide. For now though, note that once you make changes, the "Selective startup" is going to be checked as the active startup selection.
2. See what operating systems are installed on your PC and choose which one is the default
The System Configuration tool also offers a graphical way of choosing which of the operating systems installed on your PC loads first. In the System Configuration tool, switch to the Boot tab, and you can view all the operating systems installed on your computer and select the default one if you have a multi-boot setup. To select a new default operating system, click or tap on it and then on "Set as default."

3. Choose how long the PC waits for you to select the operating system to be booted
If you have a multi-boot setup, another important setting is the Timeout setting. The number of seconds you set represents how long your PC waits for you to select one of the available operating systems when booting. If no choice is made during the set time, the default operating system starts.

By default, the Timeout is set to 30 seconds. If you have a multi-boot setup, you might want to set it to a smaller value. We, for instance, prefer to set the Timeout to only 10 seconds. This way, if we do not select another operating system, the total boot timing of the default one is not affected that much.
4. Change some advanced settings about how Windows boots, like how many processor cores or how much RAM it can use
For the Windows operating system installed on your computer, the System Configuration tool also lets you configure complicated details about the way it boots.

For each of the existing operating systems, if you click or tap on the "Advanced options" button, you can set things such as the number of processors (cores) allocated to the operating system at boot, or the maximum amount of RAM available to it.

If you set a maximum number of processor cores and RAM, Windows continues to correctly identify the real number of cores that the processor has and the amount of physical RAM. However, it can only use the limited number of processor cores and the maximum memory that you have set.
5. Make Windows boot into Safe Mode
For each Windows operating system installed on your PC, the System Configuration tool also lets you select if you want to make it boot into Safe Mode. To do that, in the Boot tab, you must check the option called "Safe boot" and select one of its available options:
-
Minimal - the normal safe boot, with a user interface and no networking services enabled.
-
Alternate shell - opens the Command Prompt in Safe Mode. The networking services and the graphical user interface are disabled.
-
Active Directory repair - a normal safe boot which runs, additionally, the Active Directory services and features.
-
Network - the normal safe boot with networking services enabled.

If you want to read more about the Safe Mode in Windows, these guides might interest you:
6. Disable the Windows boot loading screen, log the startup process, use standard video drivers and others
Also in its Boot tab, the System Configuration tool gives you a set of advanced options which can be applied to both standard and Safe Mode boot procedures:

-
"No GUI boot" - during boot, you are not shown the usual loading screen, only a black screen with no information.
-
"Boot log" - during boot Windows writes a complete log with information about the startup process. Usually, it can be found at this location: "C:WindowsNtbtlog.txt."
-
"Base video" - this option is handy if you just installed lousy video drivers. It makes a standard Windows startup, with the difference that it loads only the standard video drivers that come with Windows, instead of the ones specific to your video card.
-
"OS boot information" - this option should be used together with "No GUI Boot." The usual Windows loading screen will get replaced with a black screen, displaying complete information about the drivers that are loaded during the startup process. If your Windows crashes during boot, this visualization mode can be useful to identify the driver that causes the crash.
7. Select what services are started with Windows
The Services tab from the System Configuration tool shows a list of all the services that start when Windows starts. For each service, you see its name, the manufacturer, the current status and the date when it was disabled if it was disabled.
You can check the services you want to run at startup and uncheck the ones you do not. If you desire to see only third-party services, installed by your applications, check the box that says "Hide all Microsoft services."

The selections you make in this tab are applied only to your current startup selection, from the General tab. If you were using a "Normal startup," and then you disabled some services, the startup selection gets changed automatically to "Selective startup."
If you need help in deciding which services to stop from running at startup, read this guide: Which Windows services are safe to disable and when?.
8. Manage the startup programs (only in Windows 7)
If you are using Windows 10 or Windows 8.1, the Startup tab gives you just a link to "Open Task Manager." This is because the management of your computer's startup apps is done using the Task Manager.

However, if you are using Windows 7, the Startup tab shows a list of all the programs and files that start when Windows starts. For each item, you see its name, the manufacturer, the command used to start it, which is usually the path towards the program and additional parameters if used, and the registry startup location where it is stored and the date when it was disabled if it was disabled.

One thing to remember about the registry location is that, if you see one starting with HKLM, it means that the startup item is "global" - applied to all user accounts defined on the active operating system. Disabling them from one user account means that they get disabled for all user accounts.
The locations starting with HKCU are for startup items active only for the current user account. They might not be starting up for other user accounts. Also, they need to be disabled individually, for each user account, if you want to prevent them from starting altogether.
Just like the Services tab, the selections you make are applied to your current startup selection, from the General tab.
9. Launch administrative programs and panels
Few people know about the Tools tab in System Configuration and what it does. If you click on it, you get a list of Windows administrative tools such as System Information, the Registry Editor, Event Viewer, Performance Monitor and so on.

For each tool, System Configuration shows its name and description. If you click or tap on it, you can see the command used to start it, in the Selected command field. To run any of the available tools, select the one you want and click or tap Launch.

As you can see, the Tools tab from System Configuration is handy as it lists administrative tools generally used during troubleshooting system stability or performance problems.
Save the changes you have made in System Configuration
After you are done making all the changes you wanted, do not forget to press Apply or OK, so that they are applied. Also, if you are using the tool for the first time, when you close it, you might be informed that you need to restart your PC for the new settings to take effect.

If you do not want to see this message again, check the box that says "Don't show this message again" and choose the restart option you prefer.
Are you using the System Configuration tool to change the way Windows works?
As you can see, the System Configuration (msconfig.exe) utility is a versatile tool that offers useful features for people who want to change the way Windows starts and works. It can be an excellent tool for managing the startup process of your Windows computer but also for troubleshooting stability and performance problems. Are you using it to configure Windows? Have you had any issues with it? Let's discuss in the comments section below.














