アップル(Apple)がパーソナルコンピュータの世界でマイクロソフト(Microsoft)の次点者だったのは久しぶりです。それでも、Windowsは最も人気のあるデスクトップオペレーティングシステム(OS)です。あなたが主にWindowsユーザーであるなら、あなたはめったにMacの世界に足を踏み入れる必要がないかもしれない。MacBookを購入する代わりに、 WindowsPC(Windows)の仮想マシンにmacOSをインストールできます。

WindowsでmacOSを実行できますか?(Can I Run macOS on Windows?)
Windowsのパワーユーザーであれば、 Hyper-V内でLinuxまたは他のバージョンのWindowsを実行できることをご存知でしょう。Macのパワーユーザーであれば、 Boot Campを搭載したMac、またはVMWare Fusion、Parallels、VirtualBoxなどの仮想マシンでWindowsを実行(run Windows on a Mac)できることをご存知でしょう。しかし、 Windows(Windows)でmacOSを実行できますか?WindowsのVMWareでmacOSを実行(run macOS on VMWare in Windows)できますが、VirtualBoxの使用は無料です。
次の場合は、 Windowsの(Windows)VirtualBoxにmacOSをインストールできます。
- 法的に入手したmacOSのコピー
- 少なくとも2GBのスペアRAM
- 少なくとも4つの論理CPUを備えた64ビットベースのCPU(CPUs)
- PCでの管理者アクセス
幸いなことに、今日の多くのコンピューターは最小ハードウェア要件を超えています。
macOSのコピーを入手する(Get a Copy of macOS)
Apple App Storeを開き、BigSurのコピーをダウンロードします。これはオペレーティングシステム全体であるため、大量のダウンロードになります。ダウンロードするスペースと時間があることを確認してください。AppStoreからmacOSBigSur(BigSur)をダウンロードするアクセス権がない場合は、セキュリティ上の理由から、インターネット上にある他のバージョンを使用することはお勧めしません。(App Store)
WindowsにVirtualBoxをインストールする(Install VirtualBox on Windows)
このプロセスで動作するように見えるVirtualBoxの最新バージョンは、VirtualBoxv6.1.26(VirtualBox)です。VirtualBox 6.1.26ダウンロード(VirtualBox 6.1.26 download)サイトにアクセスし、VirtualBox-6.1.26-145957-Win.exeを選択します。また、VirtualBox拡張(VirtualBox Extension)パックOracle_VM_VirtualBox_Extension_Pack-6.1.26-145957.vbox-extpackを(Oracle_VM_VirtualBox_Extension_Pack-6.1.26-145957.vbox-extpack)選択します。

- (Install VirtualBox)ダウンロードしたインストーラーを実行してVirtualBoxをインストールします。

- VirtualBoxのインストールが完了したら、VirtualBox拡張(VirtualBox)パックをインストールします。

VirtualBoxで仮想マシンを作成する(Create a Virtual Machine In VirtualBox)
仮想マシンを作成することは、コンピューター内にコンピューターを構築することと考えてください。これにより、macOSにインストールする独自の場所が与えられ、動作するために必要なリソースが割り当てられます。
- [新規(New )]ボタンを選択します。

- [名前](Name)フィールドに仮想マシンの名前を入力します。macOSのように、単純な名前の方が扱いやすいです。[マシンフォルダ](Machine Folder)フィールドで、macOS仮想マシンをインストールする場所を選択します。マルチディスクPCの場合は、100GB以上の空き容量のあるディスクを選択してください。可能であれば、SSDディスクを選択してください。それはパフォーマンスに役立ちます。または、デフォルトのままにします。VirtualBoxは、VMに入力された名前に基づいて、タイプ(Type )をMac OS Xに、バージョン(Version )をMac OS X(64ビット)(Mac OS X (64-bit) )に自動的に設定します。

- 合計メモリの50%を超えないように、 macOSVM(Allocate)にできるだけ多くのメモリを割り当てます。あなたのPCもまだリソースを必要としています。

- [今すぐ仮想ハードディスクを作成する](Create a virtual hard disk now )が選択されていることを確認し、[作成](Create )を選択して続行します。

- ハードディスクのファイルタイプを選択します。デフォルトのVHDが適切です。または、必要なものに基づいて別のものを選択してください。
- VDI(VirtualBoxディスクイメージ) : (VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image))VirtualBoxでのみ機能します。VMをHyper-V(Hyper-V)やVMWareなどの別のVMホストに移行する可能性がある場合は、これを選択しないでください。
- VHD(仮想ハードディスク) :VMを(VHD (Virtual Hard Disk))Hyper-Vに移行するのに適しています。
- VMDK(仮想マシンディスク)(VMDK (Virtual Machine Disk)):VMをVMWareに移行するのに適しています。

- SSDまたはnvMeドライブに macOSを作成している場合は、 [動的に割り当てられ(Dynamically allocated)た]を選択できます。SSDは、パフォーマンスに大きな影響を与えることなくサイズを変更するのに十分な速度です。よくわからない場合は、[固定サイズ](Fixed size)を選択してください。[次へ](Next )を選択して続行します。
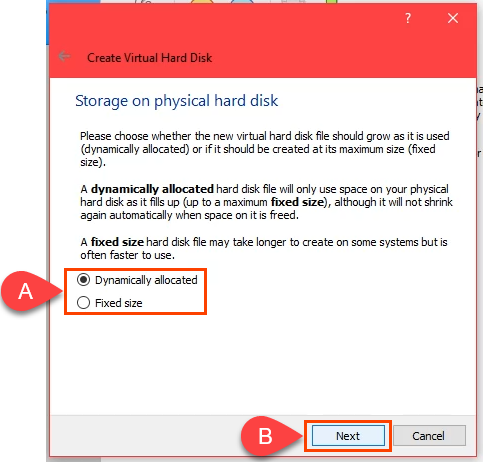
- [ファイルの場所とサイズ(File location and size)]画面で、デフォルトのフォルダーパスのままにします。仮想ハードディスクに最低60GBを割り当てます。複数のプログラムをインストールしたり、macOSをMontereyにアップグレードしたりする場合は、少なくとも100GBを使用してください。[作成](Create )を選択して続行します。

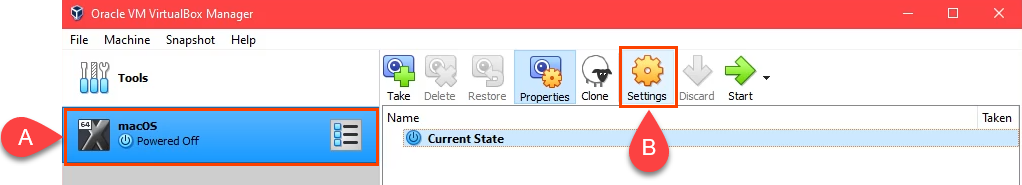
- VMの作成プロセスが終了したら、macOS VMを選択し、[設定](Settings )ボタンを選択します。
- [システム(System )]ページに移動し、 [マザーボード(Motherboard )]タブに移動します。[起動順序(Boot Order)]フィールドで[フロッピー(Floppy)]のチェックを外します。上下の矢印を使用して起動順序を調整し、オプティカル(Optical )が最初で、ハードディスク(Hard Disk )が2番目になるようにします。残りのオプションのデフォルトはそのままにしておくとよいでしょう。

- [プロセッサ(Processor )]タブに移動します。プロセッサ(Processor(s) )を少なくとも2つのCPU(CPUs)に調整します。CPUに4つのコアと8つの論理プロセッサがある場合、VirtualBoxは(VirtualBox)最大8つのCPU(CPUs)を使用していることを示します。半分以上使用しないでください。実行上限(Execution Cap )を100%のままにし、Enable PAE/NXを有効にするもデフォルトで選択されている必要があります。[ OK]を選択して続行します。

- [表示(Display )]ページに移動し、次に[画面(Screen )]タブに移動します。ビデオメモリ(Video Memory )を128MBに最大化します。このタブの他のオプションのデフォルトを選択したままにします。

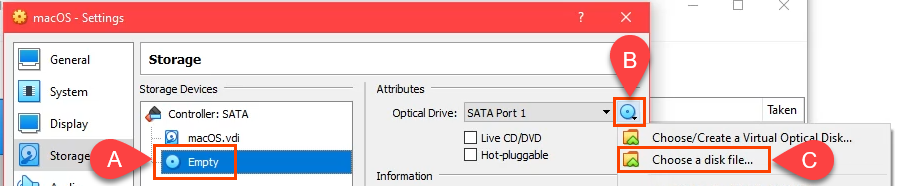
- [ストレージ](Storage )ページに移動します。Controller:SATAを選択し、 Use Host I/O Cache ボックスをチェックします。次に、空(Empty )のストレージデバイスを選択します。

[オプティカルドライブ(Optical Drive )]フィールドの横にあるDVDアイコンを選択します。次に、[ディスクファイルの(Choose a disk file)選択]を選択します。macOS.iso(.iso)ダウンロードを保存した場所に移動して選択します。[ OK]を選択して続行します。
- 次のステップを完了するには、VirtualBoxを終了します。次のステップは、終了しないか、ゾンビプロセスとして実行され続けると機能しません。macOSVMを作成することはできません。VirtualBoxを閉じた後、タスクマネージャー(Task Manager )を開き、プロセスがリストされていないことを確認します。

- GitHubに移動して、VirtualBoxmacOSコード(VirtualBox macOS codes)を取得します。そこからコピーして、メモ帳(Notepad)に貼り付けます。macOS VMの状況に合わせて、コードを編集する必要があります。
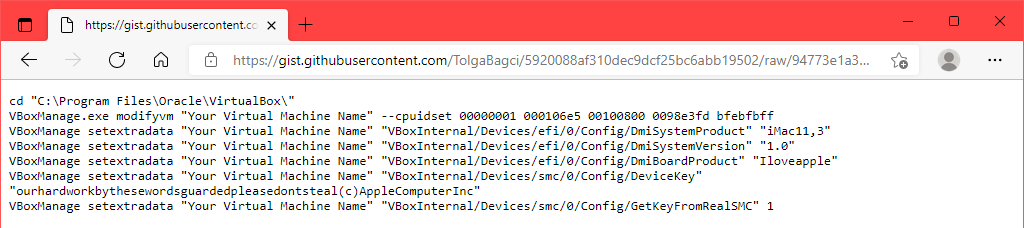
最初の行に表示されている場所とは異なる場所にVirtualBox(VirtualBox)をインストールした場合は、最初の行を編集して一致させます。

残りの行で、仮想マシン名(Your Virtual Machine Name)をこのVMに付けた名前であるmacOSに変更します。
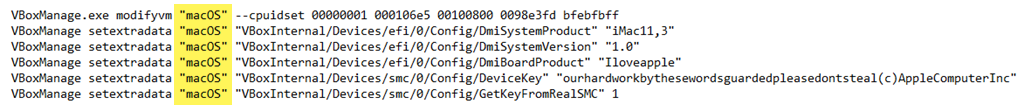
- 管理者(Administrator)としてコマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt )を 開きます。コードの最初の行をコピーして入力します。これにより、コマンド(Command)プロンプトのベースディレクトリがVirtualBoxをインストールした場所に変更されます。次に、コマンド(Command)プロンプト で各行をコピーして貼り付け、単独で実行します。

macOSBigSurをインストールする(Install macOS Big Sur)
- 最後のコマンドが終了したら、コマンドプロンプトを閉じて、 (Command Prompt)VirtualBoxを再度開きます。macOS VMを選択し、[スタート](Start)を選択します。
- 黒の背景に白のテキストがたくさん表示されます。これには数分かかる場合があります。白いテキストと黒い背景の手順が15〜20分以上続く場合は、おそらく機能しません。Appleアイコンとプログレスバーが表示されます。ここまで進んだら、おそらくうまくいくでしょう。

- 次に、言語(Language )画面が表示されます。好みの言語を選択し、次の矢印を選択してmacOSリカバリ(Recovery)画面に移動します。

- ディスクユーティリティ(Disk Utility)を選択します。
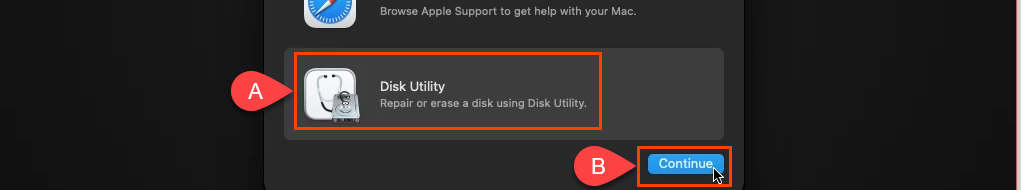
- [ディスクユーティリティ](Disk Utility )画面で、左側の列の[ VBOX HARDDISK MEDIA ]を選択し、[(VBOX HARDDISK MEDIA )消去(Erase)]を選択します。

- 消去するかどうかの確認を求められます。ボリュームにも新しい名前を付ける必要があります。どんな名前でもかまいません。[消去](Erase )を選択して続行します。

- ボリュームが消去されて名前が変更されたら、[完了](Done )を選択して続行します。

- ディスクユーティリティ(Disk Utility )ウィンドウを閉じます。

- [リカバリ](Recovery )画面で、[ macOS Big Surのインストール]を選択して、[(Install macOS Big Sur )続行(Continue)]を選択します。

- もう一度続行(Continue )するように求められます。次に、ソフトウェア使用許諾契約(SLA)に2回同意するように求められます。続行する場合は同意します。
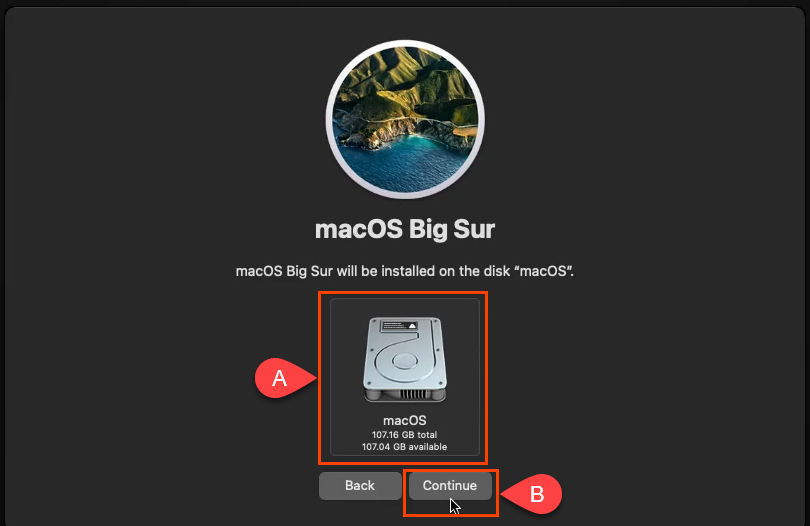
- macOSBigSur(Big Sur)をインストールするディスクを選択します。macOSディスクのみが表示されるはずなので、それをクリックします。次に、[続行](Continue)を選択します。
- インストールを開始します。画面には、残り約12〜18分と表示される場合があります。この部分には1時間かかることがあるため、正しくありません。

- 白いテキストの黒い画面に移動し、次に「残り1分未満…」というAppleロゴの付いた灰色の画面に移動します。残り時間は1分をはるかに超えています。(Apple)

- 最終的に、[国または地域の選択](Select Your Country or Region )画面が表示されます。これで、新しくインストールしたmacOSのセットアップが完了しました。セットアップを実行します。

- セットアップが完了したら、新しくインストールした状態のスナップショットを撮ります。これにより、将来macOS VMで問題が発生した場合に、簡単に元に戻すことができます。

macOS仮想マシンの解像度を変更する(Change the Resolution of the macOS Virtual Machine)
VirtualBoxのデフォルトよりも高い解像度が必要な場合は、それも可能です。
- macOS仮想マシンをシャットダウンし、 (Shut)VirtualBoxを完全に終了します。
- 管理者(Administrator)としてコマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)を開きます。
- VirtualBoxがインストールされている場所に移動します。
- 次のコマンドを入力します。
VBoxManage setextradata“ macOS ” VBoxInternal2/EfiGraphicsResolution 1920×1080
コマンドの最後の部分である1920×1080が解像度です。1280×720、1920×1080、2560×1440、2048×1080、3840×2160、5120×2880、または7680×4320でサポートされている解像度のいずれかに変更できます。ただし、うまくいかないものもあります。コマンドが完了したら、VirtualBoxとmacOS VMを再起動して、変更が機能することを確認します。
VirtualBoxでmacOSを使用するためのヒント(Tips on Using macOS in VirtualBox)
インストール中に、駐車禁止標識のような丸スラッシュが表示された場合、インストールは機能しません。待つ意味がないので、マシンをシャットダウンします。

繰り返しになりますが、 VirtualBox(VirtualBox)コードが正しく適用されていることを確認してください。VirtualBoxを完全に閉じて、必要に応じて再適用します。
それでも問題が解決しない場合は、VM設定を変更してRAMまたはCPU(CPUs)の使用量を減らします。PCがより高い設定に追いつかない場合があります。
インストールが完了したら、ホストPCで他に何もしていない限り、VM設定を変更して、より多くのRAMまたはCPUを使用してパフォーマンスを向上させることができます。(CPUs)
新しいmacOS仮想マシンをお楽しみください!
How to Install macOS Big Sur in VirtualBox on Windows
It’s been a lоng time since Apple was a distant rυnner-up to Miсrosoft in the personal computer world. Stіll, Windows is the most popular desktop operаting system (OS). If you’re primarily a Windows user, уou may need to dip your toes in the Mac world infrequently. Inѕtead of buying a MacBook, You could install macOS in a virtual machine on your Windows PC.

Can I Run macOS on Windows?
If you’re a Windows power user, you know you can run Linux or other versions of Windows within Hyper-V. If you’re a Mac power user, you know you can run Windows on a Mac with Boot Camp, or a virtual machine like VMWare Fusion, Parallels, or VirtualBox. But, can you run a macOS on Windows? You could run macOS on VMWare in Windows, but using VirtualBox is free.
You can install macOS in VirtualBox on Windows if you have:
- A legally obtained copy of a macOS
- At least 2 GB of spare RAM
- A 64-bit based CPU with at least 4 logical CPUs
- Administrator access on the PC
Fortunately, many computers today exceed the minimum hardware requirements.
Get a Copy of macOS
Open the Apple App Store and download a copy of BigSur. It’s an entire operating system, so it’s a large download. Make sure you’ve got the space and time to download it. If you don’t have access to download macOS BigSur from the App Store, we don’t recommend using other versions found on the internet, for security reasons.
Install VirtualBox on Windows
The newest version of VirtualBox that this process appears to work with is VirtualBox v6.1.26. Go to the VirtualBox 6.1.26 download site and select VirtualBox-6.1.26-145957-Win.exe. Also select the VirtualBox Extension pack Oracle_VM_VirtualBox_Extension_Pack-6.1.26-145957.vbox-extpack.

- Install VirtualBox by running the downloaded installer.

- When the VirtualBox installation is complete, Install the VirtualBox extension pack.

Create a Virtual Machine In VirtualBox
Think of creating a virtual machine as building a computer inside your computer. This gives macOS its own place to install to and allocates the resources it needs to work.
- Select the New button.

- Enter a name for the virtual machine in the Name field. A simple name is easier to work with, like macOS. Select where the macOS virtual machine will be installed in the Machine Folder field. For a multi-disk PC, pick a disk with at least 100GB of free space. If possible, pick an SSD disk. That will help performance. Or leave it as the default. VirtualBox will automatically set the Type to Mac OS X and Version to Mac OS X (64-bit) based on the name entered for the VM.

- Allocate as much memory as possible for the macOS VM without exceeding 50% of total memory. Your PC still needs resources too.

- Ensure that Create a virtual hard disk now is selected and select Create to continue.

- Choose a hard disk file type. The default VHD is good. Or choose another one based on what you need.
- VDI (VirtualBox Disk Image): Only works in VirtualBox. If you might migrate the VM to another VM host like Hyper-V or VMWare, don’t choose this one.
- VHD (Virtual Hard Disk): Good for migrating the VM to Hyper-V.
- VMDK (Virtual Machine Disk): Good for migrating the VM to VMWare.

- If you’re creating the macOS on an SSD or nvMe drive, you can select Dynamically allocated. SSDs are fast enough to resize without affecting performance much. If you’re not certain, choose Fixed size. Select Next to continue.

- On the File location and size screen, leave the default folder path. Allocate a minimum of 60 GB for the virtual hard disk. If you plan on installing several programs or upgrading the macOS to Monterey, use at least 100 GB. Select Create to continue.

- When the VM creation process ends, select the macOS VM and select the Settings button.

- Go to the System page then the Motherboard tab.In the Boot Order field uncheck Floppy. Use the up and down arrows to adjust the boot order so Optical is first, and Hard Disk is second. The defaults for the remaining options are good to leave as is.

- Move to the Processor tab. Adjust Processor(s) to at least 2 CPUs. If your CPU has 4 cores and 8 logical processors, VirtualBox will show that you have up to 8 CPUs to use. Don’t use more than half. Leave Execution Cap at 100% and Enable PAE/NX should be selected by default as well. Select OK to continue.

- Go to the Display page, then the Screen tab. Max out Video Memory to 128MB. Leave the defaults for the other options on this tab selected.

- Go to the Storage page. Select Controller: SATA and then check the Use Host I/O Cache box. Then select the Empty storage device.

Select the DVD icon next to the Optical Drive field. Then select Choose a disk file. Navigate to where you stored the macOS .iso download and select it. Select OK to continue.

- To complete the next step, exit VirtualBox. The next step won’t work if you don’t exit it or it keeps running as a zombie process. You will not be able to create the macOS VM. After closing VirtualBox, open Task Manager and ensure the process is not listed.

- Go to GitHub and get the VirtualBox macOS codes. Copy them from there and paste them into Notepad. The codes will need to be edited to match your macOS VM situation.

If you installed VirtualBox to a location different from what’s shown in the first line, edit the first line to match.

In the remaining lines, change Your Virtual Machine Name to macOS, the name you gave this VM.

- Open the Command Prompt as Administrator. Copy the first line of code and enter it. This will change the base directory in the Command prompt to where you installed VirtualBox. Then copy, paste, and run each line by itself in the Command prompt.

Install macOS Big Sur
- When the last command finishes, close the Command Prompt and open VirtualBox again. Choose your macOS VM and select Start.

- You’ll see a lot of white text on a black background. This can take a few minutes. If the white text and black background step continues for more than 15-20 minutes, it’s probably not going to work. You’ll see the Apple icon and a progress bar. If you get this far, it’s probably going to work.

- Next you’ll see the Language screen. Choose the language you prefer and select the next arrow to go to the macOS Recovery screen.

- Select Disk Utility.

- On the Disk Utility screen, select the VBOX HARDDISK MEDIA in the left column and select Erase.

- It will ask you to confirm that you want to erase it. You need to give the volume a new name, too. Any name will do. Select Erase to continue.

- Once the volume is erased and renamed, select Done to continue.

- Close the Disk Utility window.

- On the Recovery screen, select Install macOS Big Sur and then Continue.

- It asks you to Continue again. Then it will ask you to agree to the software license agreement (SLA) twice. Agree if you want to continue.
- Select the disk to install macOS Big Sur on. Only your macOS disk should be showing so click on that. Then select Continue.

- It starts installing. The screen might say that there’s about 12 to 18 minutes remaining. It’s not correct as this part can take an hour.

- It will go to a black screen with white text, then to a gray screen with the Apple logo that says, “Less than a minute remaining…” There is a lot more than a minute remaining.

- Eventually, you’ll see the Select Your Country or Region screen. You’re now in the setup of your freshly installed macOS. Go through the set up.

- Once you’ve completed the setup, take a snapshot of the freshly installed state. This allows you to revert back to it easily should something go wrong with the macOS VM in the future.

Change the Resolution of the macOS Virtual Machine
If you prefer greater resolution than the VirtualBox default, you can do that too.
- Shut down the macOS virtual machine and completely exit VirtualBox.
- Open the Command Prompt as Administrator.
- Navigate to where VirtualBox is installed.
- Enter the following command:
VBoxManage setextradata “macOS” VBoxInternal2/EfiGraphicsResolution 1920×1080
The last part of the command, 1920×1080 is the resolution. It can be changed to any of 1280×720, 1920×1080, 2560×1440, 2048×1080, 3840×2160, 5120×2880, or 7680×4320 supported resolutions. Some may not work for you though. After the command completes, restart VirtualBox and your macOS VM to make sure the change works.
Tips on Using macOS in VirtualBox
During the install, if you see a circle-slash like a no parking sign, the installation isn’t going to work. Shut the machine down as there’s no sense waiting.

Again, check to ensure that you applied the VirtualBox codes correctly. Completely close VirtualBox and reapply them if needed.
If that doesn’t work, change the VM settings to use less RAM or CPUs. Sometimes the PC can’t keep up with a higher setting.
Once the install is complete, you can change the VM settings to use more RAM or CPUs to increase the performance, as long as you’re not doing anything else on the host PC.
Enjoy your new macOS virtual machine!





































