どこを向いても、レジストリ(Registry)に近づかないようにみんなに言っている人がいます。私はある程度これに同意しますが、私たちが行っていることの多くは、私たちがそれを知っているかどうかにかかわらず、レジストリに関係していることに気づきました。(Registry)ある時点でWindowsオペレーティングシステムをカスタマイズしようとしている場合は、レジストリ(Registry)を処理する必要があります。初心者の場合は、Windowsレジストリの基本(Windows Registry Basics)に関するこの投稿を読むことをお勧めします。ただし、この投稿は上級ユーザーを対象としているため、レジストリに触れる前に必ずレジストリをバックアップする必要があります。
Windowsレジストリエディタのヒント(Registry Editor Tips)と機能
あなたがレジストリ(Registry)をいじり回すのが不快なら、私はあなたがそれをいじるべきだとは決して言いません。Windowsオペレーティングシステム(Windows Operating System)をカスタマイズするのが好きなユーザーの場合、真実は、手動で行うか、フリーウェアプログラムを使用してカスタマイズするかにかかわらず、すべてレジストリ(Registry)を処理するため、避けられません。
レジストリ(Registry)を操作するためのこのヒントのリストは、不快感を和らげ、管理を少し簡単にすることを願っています。ただし、確信が持てない場合は、近づかないようにするのが最善であることを忘れないでください。
Windowsレジストリにアクセスするか開く
Windowsレジストリファイルはsystem32 /configフォルダーにありますが、もちろん、次の場所からアクセスできるレジストリ(Registry)を処理するには、 Regeditと呼ばれる組み込みのレジストリ編集ユーティリティを使用する必要があります。(Regedit)
- [Start Button > Run >Regeditと入力してEnterキーを押します。
- Task Manager > File > New Task >を開き、Regeditと入力してEnterキーを押します。
- コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)で「Regedit」と入力し、Enterキーを押します。
ヒント(TIP):Windows 11/10のユーザーは、アドレスバー を使用して、任意のレジストリキーに直接ジャンプしたり、フォントを変更したりできます。
デスクトップショートカットを作成して Windowsレジストリを開きます(Windows Registry)
必要に応じて、次の手順を実行して、デスクトップにショートカットをRegeditに追加できます。
- (Right-click)デスクトップの空白の領域を右クリックし、[新規]を押してから、[(New)ショートカット(Shortcut)]を押します。[場所(Location)]に「Regedit 」と入力し、[次へ]をクリックしてショートカット(Shortcut)の名前を選択し、最後に[完了]をクリックし(Finish)ます。
読む(Read):レジストリエディタでHKLMとHKCUをすばやく切り替える方法
拡張子が.regのファイル
拡張子が.regのファイルをダウンロードしましたが、何ができるかわからない場合は、ファイルを右クリックして[編集(Edit)]または[メモ帳(Notepad)で開く]を選択すると、ファイルが操作する(Open)レジストリ(Registry)キーの場所を確認できます。
たとえば、次の.regファイルをメモ帳(Notepad)で開くと、次のようになり、場所が太字で、値が下に表示されます。
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\InternetExplorer\Main\WindowsSearch]
"Version"="6.1.7600.16385"
"User Favorites Path"="file:///C:\\Users\\Lee\\Favorites\\"
"UpgradeTime"=hex:fe,27,f3,41,02,91,cc,01
"ConfiguredScopes"=dword:00000005
"LastCrawl"=hex:3e,26,a3,a1,cd,90,cc,01
"Cleared"=dword:00000001
"Cleared_TIMESTAMP"=hex:23,9d,94,80,24,48,cc,01
.regファイルの機能がわからない場合は、いつでも場所をコピーしてオンラインで検索できます。
読む(Read):Windowsで別のユーザーのレジストリを編集する方法。
Windowsレジストリ(Windows Registry)にアクセスする前にバックアップする
Regeditで作業している場合、レジストリ(Registry)を台無しにすることを避けるために、簡単にできることがいくつかあります。
- レジストリ(Registry)に変更を加える前に、最初にシステムの復元ポイントをすばやく作成することを常にお勧めします。これにより、変更を行う前の前の状態に戻ることができます。
- レジストリキーのバックアップ(create a backup of a Registry key )を作成するか、他の人と共有するためにキーをエクスポートする場合は、キーを(Export)右クリックし(Right-Click)て[エクスポート](Export)を選択し、名前を選択して、形式として.regを追加します。フリーウェアのRegbackまたはERUNTguiを使用してレジストリ(Registry)をバックアップすることもできます。
読む(Read):絵文字はWindowsレジストリパスで使用されています; 知ってますか!?
Windowsレジストリの(Windows Registry)キー(Rename keys)の変更、追加(Add)、名前の変更
- 設定をレジストリキーに(Registry)変更(change)する場合は、変更する値をダブルクリックして、必要な変更を追加することで簡単に変更できます。
- (Renaming) レジストリキーの(Registry)名前の変更:必要なのは、キーまたは値を右クリックして、名前の変更を選択することだけです。(Right-Click)
- キーを追加(Add)するにはサブキーとして追加するキーを右クリックし、値と同じように[(Right-Click)新しいキー(New Key)]を選択します。
読む(Read):レジストリエディタが開かない、クラッシュする、または動作を停止する。(Registry Editor not opening, crashing or stopped working.)
レジストリキーの所有権を取得する
レジストリ(Registry)キーを操作しようとして、権限がないというエラーが発生した場合は、(error)レジストリキーを右クリックして、[(Registry)権限](Permissions)を選択します。これを行う場合、10回のうち9回は、昇格されたアクセス許可を自分に与える前に、最初にレジストリキーの所有権を取得する必要があります(Registry)。(Ownership)所有権(Ownership)を取得するには、[レジストリ(Registry)キーのプロパティ]ウィンドウで[ Advanced\Owner ]をクリックし、ユーザー名が表示されていない場合は、[その他のユーザー]または[グループ(Groups)]を選択して、テキストボックスにユーザー名を入力します。次に、[名前の確認]をクリックします(Check Names)正しいユーザー名を入力したことを確認してください。[OK](Click OK)をクリックすると、権限を変更できます。レジストリキーの完全な所有権を取得(take full ownership of registry keys)する方法の詳細をご覧ください。
注意すべき点の1つ:所有権とアクセス許可を復元する場合は、最初に元の所有者とアクセス許可に注意してください。以下は、他のユーザーまたはグループで所有者を選択するときに使用するデフォルトの所有者リストです。
- 信頼できるインストーラー:NT SERVICE\TrustedInstallerと入力し、[名前の確認]をクリックして、[OK]をクリックします。
- システム: [システム]と入力し、[(System,)名前の確認(Check Names)]をクリックして、[OK]をクリックします。
- 管理者: 「管理者(Administrators)」と入力し、[名前の確認]をクリックして、[OK]をクリックします。
- ユーザー名:ユーザー(Your Username)名を入力し、[名前の確認]をクリックして、[OK]をクリックします。
- ユーザー: 「ユーザー(Users)」と入力し、「名前の確認」をクリックしてから「OK」をクリックします。
読む(Read): レジストリへの変更はいつ保存されますか?
レジストリキーをお気に入りに追加する
Regeditで気に入っている機能の1つは、お気に入り(Favorites)です。私はレジストリ(Registry)の同じ領域内で多くの作業を行う傾向があるため、お気に入りにキーを追加すると、これらのキーにすばやくアクセスするのに役立ちます。
レジストリ(Registry)キーをお気に入り(Favorites)に追加するには、キーを選択してトップメニューに移動し、[お気に入り]を選択して[お気に入り(Favorites)Favorites\Add追加]を選択します。
完了すると、[お気に入り]の下に、そのレジストリ(Registry)キーに移動するときにクリックするだけでよいエントリが表示されます。
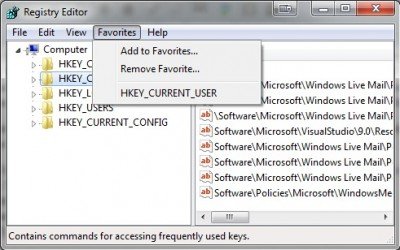
探しているレジストリ(Registry)キーがわかっていて、 Regeditをクリックしたくない場合は、[Edit > Find]を選択 して場所を入力すると、レジストリ(Registry)キーにすばやく移動できます。
読む:(Read:) Windowsでレジストリキーを作成する方法。
コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)を使用してレジストリを操作する
コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)での作業に慣れている場合は、次のコマンドを使用してレジストリを処理できます。
- Reg add:新しいサブキーまたはエントリをレジストリ(Registry)に追加します。
- Reg compare:指定されたレジストリサブキーまたはエントリを比較します。
- Reg copy:サブキーを別のサブキーにコピーします。
- Reg delete :レジストリ(Registry)からサブキーまたはエントリを削除します。
- Reg export:指定されたサブキー、エントリ、および値のコピーをREG(テキスト)形式のファイルに作成します。
- Reg import:エクスポートされたレジストリ(Registry)サブキー、エントリ、および値を含むREGファイルをレジストリ(Registry)にマージします。
- Reg load:保存されたサブキーとエントリをハイブ形式で別のサブキーに書き戻します。
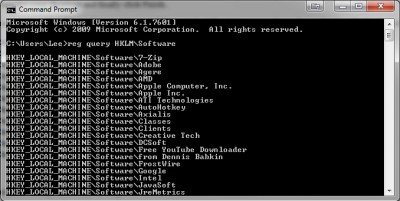
- Reg query:サブキーまたは値のデータを表示します。
- Reg restore:保存されたサブキーとエントリをハイブ形式でレジストリ(Registry)に書き戻します。
- Reg save :レジストリ(Registry)の指定されたサブキー、エントリ、および値のコピーをハイブ(バイナリ)形式で保存します。
- Reg undo(Reg unload) :regloadを使用してロードされたレジストリ(Registry)のセクションを削除します。
Example: Reg query HKLM\Software will list all the subkeys
Reg /?と入力すると、コマンドプロンプトで 使用可能なコマンドが一覧表示されます。
Windowsには、 (Windows)Reginiなどの上級ユーザー向けの組み込みのコマンドライン(Command Line)ツールがいくつかあり ますが、それらは別の投稿に任せて、基本的な使用のために保持します。ちなみに、Windowsレジストリ(Windows Registry)ファイルがディスクのどこにあるのか疑問に思った場合は、ここ(here)にアクセスして調べてください。
読む:(Read:)
- Windowsでレジストリの複数のインスタンスを開く方法
- レジストリファイルを比較またはマージする方法(How to Compare or Merge Registry files)
- レジストリへの変更を監視する方法(How to monitor changes to the Registry)
- Windowsレジストリのキー、値、および設定を検索する方法。
多くの知識がなくても、ユーザーがレジストリキーを簡単に処理できるようにするツール:(Tools to make handling Registry keys easy, for users, without a lot of knowledge:)
RegOwnit
SetACL
Registrar Registry Manager
ヒント(TIP): regedit.exeを使用せずにWindowsレジストリ(Windows Registry)を編集する方法を確認してください。代わりに、Windows11/10でReg.exeを使用してください。
Registry Editor: Use, Edit, Open, Modify, Save, Backup, Import, Export
Everywhere you turn you find ѕomeone telling еveryone to stay clear of the Registry. While I agree with this to an extent, I have comе to realize that a lot of whаt we do involves the Registry whether wе know it or not. If you’re looking to customize your Windows Operating System at some point, yоu аre going to have to deal with the Registry. If you are a novice, you may want to read this poѕt on Windows Registry Basics – but do remember that this post is meant for advanced users, and one must always back up the Registry before touching it.
Windows Registry Editor Tips & Features

If you are uncomfortable messing around the Registry, then I would never say that you should mess with it. If your a user who loves to customize your Windows Operating System then the truth is, whether you do it manually or use some freeware program to customize with – it all deals with the Registry and is unavoidable.
This list of tips to work with the Registry, I hope, will ease your discomfort some and make it a little bit easier to manage. But remember, if you are unsure, its best to stay away from it.
Access or open the Windows Registry
The Windows Registry files are located in the system32/config folder, but you, of course, need to use the built-in registry editing utility called Regedit to handle Registry which you can access by the following locations:
- Hit the Start Button > Run > type Regedit and hit enter.
- Open the Task Manager > File > New Task > type Regedit and hit enter.
- In a Command Prompt type Regedit and hit enter.
TIP: Users of Windows 11/10 can use the Address Bar to jump directly to any registry key or change the Font.
Create a desktop shortcut to open Windows Registry
If you prefer you can add a shortcut to the desktop to Regedit by doing the following:
- Right-click a blank area on the desktop, press New and then press Shortcut. For Location, type Regedit click next and choose a name for your Shortcut and finally click Finish.
Read: How to switch between HKLM and HKCU quickly in Registry Editor
Files with .reg extension
Downloaded a file with the extension .reg but you are unsure of what it may do? Right-click the file and select Edit or Open in Notepad and you will be able to see the location of the Registry key it will manipulate.
For example, the following .reg file when opened in Notepad will look like the following with the location in bold and values underneath.
[HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\InternetExplorer\Main\WindowsSearch]
"Version"="6.1.7600.16385"
"User Favorites Path"="file:///C:\\Users\\Lee\\Favorites\\"
"UpgradeTime"=hex:fe,27,f3,41,02,91,cc,01
"ConfiguredScopes"=dword:00000005
"LastCrawl"=hex:3e,26,a3,a1,cd,90,cc,01
"Cleared"=dword:00000001
"Cleared_TIMESTAMP"=hex:23,9d,94,80,24,48,cc,01
If you are unsure of what the .reg file is going to do, you can always copy the location and search online for it.
Read: How to edit Registry for another User in Windows.
Backup before touching the Windows Registry
If you are working in Regedit, there are a number of things you can do easily, to avoid messing up with the Registry.
- Before making changes to the Registry, it is always recommended to quickly create a System Restore Point first, as this will enable you to return to the previous state before you did changes.
- If you would like to create a backup of a Registry key or Export the key for sharing with someone else, Right-Click the key and select Export, choose a name and add .reg as the format. You can also back up the Registry using freeware Regback or ERUNTgui.
Read: Emojis are being used in the Windows Registry path; Did you know!?
Change, Add, Rename keys in Windows Registry
- If you want to change settings to a Registry key, you can do so easily by Double-Clicking the value you wish to change and add the changes you wish.
- Renaming Registry keys: You need only Right-Click the key or value and select rename.
- To Add a key Right-Click the key you wish to add as a subkey and select New Key, the same with values.
Read: Registry Editor not opening, crashing or stopped working.
Take ownership of Registry keys
If you find yourself trying to manipulate a Registry key and get an error that you do not have permission to do, Right-Click the Registry key and select Permissions. 9 out of 10 times when you do this you will need to Take Ownership of the Registry key first before giving yourself elevated permissions. To Take Ownership, while you are in the Registry key properties window, click Advanced\Owner and if your username is not listed select Other Users or Groups and enter your username in the text box. Next click Check Names to make sure you have entered the correct username. Click OK and then you can change permissions. Learn more about how to take full ownership of registry keys.
One thing to note: If you plan on restoring ownership and permissions, take note first of the original owner and permissions. The following is the default owners list to use when selecting an owner in Other Users or Groups:
- Trusted Installer: Type in NT SERVICE\TrustedInstaller, click Check Names then click OK.
- System: Type in System, click Check Names and then click OK.
- Administrators: Type in Administrators, click Check Names then click OK.
- Your Username: Tye in Your Username, click Check Names then click OK.
- Users: Type in Users, click Check Names then click OK.
Read: When do changes to the Registry get saved?
Add Registry keys to Favorites
One feature I like with Regedit is Favorites. As I tend to work a lot within the same areas in the Registry, adding the keys to Favorites helps to get to these keys quickly.
To add a Registry key to Favorites, simply select a key to go to the top menu and select Favorites\Add to Favorites.
Once done you will see an entry under Favorites that you need only click when you wish to go to that Registry key.

If you know the Registry key you are looking for and do not wish to click through Regedit, select Edit > Find and type the location to quickly navigate to the Registry key.
Read: How to create a Registry Key in Windows.
Using Command Prompt to manipulate the Registry
If you are more comfortable working in a Command Prompt, the following commands can be used to handle the Registry:
- Reg add : Adds a new subkey or entry to the Registry.
- Reg compare : Compares specified registry subkeys or entries.
- Reg copy : Copies a subkey to another subkey.
- Reg delete : Deletes a subkey or entries from the Registry.
- Reg export : Creates a copy of specified subkeys, entries, and values into a file in REG (text) format.
- Reg import : Merges a REG file containing exported Registry subkeys, entries, and values into the Registry.
- Reg load : Writes saved subkeys and entries in hive format back to a different subkey.
- Reg query : Displays the data in a subkey or a value.
- Reg restore : Writes saved subkeys and entries in hive format back to the Registry.
- Reg save : Saves a copy of specified subkeys, entries, and values of the Registry in hive (binary) format.
- Reg unload : Removes a section of the Registry that was loaded using reg load.
Example: Reg query HKLM\Software will list all the subkeys
In a Command Prompt if you type in Reg /? It will list the available commands.

There are several other built-in Command Line tools in Windows for more advanced users as well such as Regini, but I’ll leave those to another post and keep this for basic use. By the way, if you have wondered where the Windows Registry files are located on the disk, go here to find out!
Read:
- How to open multiple instances of the Registry in Windows
- How to Compare or Merge Registry files
- How to monitor changes to the Registry
- How to search Windows Registry Keys, Values and Settings.
Tools to make handling Registry keys easy, for users, without a lot of knowledge:
RegOwnit
SetACL
Registrar Registry Manager
TIP: See how you can edit Windows Registry without using regedit.exe – but instead by using Reg.exe in Windows 11/10



