Windows 11をインストールできず、このPCでWindows 11エラーを実行できませんか?PCヘルスチェックアプリケーションの「このPCはWindows11を実行できません」エラーを修正するために、TPM2.0とSecureBootを有効にする方法は次のとおりです。(Unable to install Windows 11 and getting This PC can’t run Windows 11 error? Here’s how to enable TPM 2.0 and SecureBoot, in order to fix the “This PC Can’t Run Windows 11” error in the PC Health Check application.)
世界中で最も使用されているコンピューターオペレーティングシステムであるWindows10の待望のアップデートが、数週間前(2021年6月)に(June 2021)Microsoftによってようやく発表されました。予想どおり、Windows 11には多数の新機能、ネイティブアプリケーションが導入され、一般的なユーザーインターフェイスには、ビジュアルデザインの見直し、ゲームの改善、Androidアプリケーション、ウィジェットなどのサポートが提供されます。(Android)スタート(Start)メニュー、アクションセンターなどの要素、およびMicrosoft Storeも、最新バージョンのWindows用に完全に刷新されました。現在の(Current)Windows10ユーザーはにアップグレードできます (Windows 11)最終バージョンが一般に公開される2021年の終わりに、追加費用なしのWindows11 。

修正このPCはWindows11エラーを実行できません(Fix This PC can’t run Windows 11 Error)
お使いのPCがWindows11(Run Windows 11)エラーを実行できない場合の修正手順
Windows11のシステム要件(System Requirements for Windows 11)
Microsoftは、Windows 11によってもたらされるすべての変更の詳細に加えて、新しいOSを実行するための最小ハードウェア要件も明らかにしました。それらは次のとおりです。
- クロック速度が1ギガヘルツ(Gigahertz)(GHz)以上でコアが2つ以上の最新の64ビットプロセッサ( Windows 11を実行できるIntel、AMD、およびQualcommプロセッサ(Qualcomm processors)の完全なリストは次のとおりです)。
- 少なくとも4ギガバイト(GB)のRAM
- 64 GB以上のストレージデバイス(HDDまたはSSD、どちらも動作します)
- 最小解像度が1280x720で、9インチより大きいディスプレイ(対角線)
- システムファームウェアは、UEFIとセキュアブートをサポートしている必要があります(Secure Boot)
- トラステッドプラットフォームモジュール(Platform Module)(TPM)バージョン2.0
- グラフィックカードは、 (Card)DirectX12以降とWDDM2.0ドライバーと互換性がある必要があります。
作業を簡単にし、ユーザーがワンクリックで現在のシステムがWindows 11と互換性があるかどうかを確認できるようにするために、 (Windows 11)Microsoftは(Microsoft)PCヘルスチェックアプリケーション(PC Health Check application)もリリースしました。ただし、アプリケーションのダウンロードリンクはオンラインではなくなり、ユーザーは代わりにオープンソースのWhyNotWin11ツールをインストールできます。
ヘルスチェック(Health Check)アプリを手に入れることができた多くのユーザーは、チェックの実行時に「このPCはWindows11を実行できません」というポップアップメッセージを受け取ったと報告しています。ポップアップメッセージには、Windows 11をシステムで実行できない理由に関する詳細情報も表示されます。その理由には、プロセッサがサポートされていない、ストレージ容量が64 GB未満である、TPMおよびセキュアブート(Secure Boot)がサポートされていない/無効になっているなどがあります。最初の2つの問題を解決するには、ハードウェアコンポーネントを変更する必要がありますが、TPMとセキュアブート(Secure Boot)の問題は非常に簡単に解決できます。

方法1:BIOSからTPM2.0を有効にする方法(TPM 2.0)
トラステッドプラットフォームモジュール(Trusted Platform Module)またはTPMは、暗号化キーを安全に保存することにより、ハードウェアベースのセキュリティ関連機能を最新のWindowsコンピューターに提供するセキュリティチップ(暗号化プロセッサ)です。TPMチップには複数の物理的セキュリティメカニズムが含まれているため、ハッカー、悪意のあるアプリケーション、およびウイルスがそれらを変更することは困難です。Microsoftは、 2016年以降に製造されたすべてのシステムにTPM 2.0(TPMチップの最新バージョン。以前のバージョンはTPM 1.2と呼ばれていました)の使用を義務付けました。したがって、コンピュータが古風ではない場合、セキュリティチップはマザーボードに事前にはんだ付けされている可能性がありますが、単に無効になっています。
また、Windows11を実行するためのTPM2.0の要件は、ほとんどのユーザーを驚かせました。以前、Microsoftは最小ハードウェア要件としてTPM 1.2をリストしていましたが、後でTPM2.0に変更しました(TPM 2.0)。
TPMセキュリティテクノロジはBIOSメニューから管理できますが、起動する前に、システムにWindows11互換のTPMが装備されていることを確認しましょう。これをする -
1. [スタート]メニュー(Start menu)ボタンを右クリックし、パワーユーザーメニューから[ファイル名を指定して実行]を選択します。(Run )
![[スタート]メニューボタンを右クリックして、[ファイル名を指定して実行]、[ファイル名を指定して実行]の順に選択します。 修正:このPCはWindows11エラーを実行できません](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-rD5l6ZC12Hs/YZGfsLjz58I/AAAAAAAANKI/yvN4mQz8ewgIh6bhNQupfgreQ5HpomUpwCEwYBhgLKtMDABHVOhysbsXm9iUvKTwZLDdan-9yqjqjEee0tchsgrdNO6LfVDGwSyjuFjQw9AjHSo8z2aLpulv6NSkWDLe0tBOzY8wzzbiJWJ0gg_Gvi3fExsctxqjzfcduPYM9aEU6Lru9642geMu2f0Agt45jM8impxHx9MtIkSEHhpD2fw1ayJVnLufiWbXoLu1LGfkJmeeBdgxL8BvvlVn3llCVjiNlRvnSHJ3SLjThUxg8breERRAOSsit_424xqo7rOhhRrHi11p16deJ6Ig6a_w-d6ul2miH0emmeHSbek2s2cdLVvYc-LmhZPWSj3MQkISYoiSjOaBHOFcBX1_bj8gnzupeskBRyjUG2SJpNnn9hfjEMQpcJygMWTTfQpnyXT6f_0sXq86dAE1KkPp4XlGxNsGJjtXv-s1lqG8izEL4C_SwqfgotANXfgn01Siy1vvbEZ9VQX0dLBwaFca4c-VIkd2DE4ARwFSgALlHKSC6kHnCRiYhbW7r_qQvSCGVtPF0UKE6_kQ7zkLLvFFLEaaKvfi_tqX8ayIdJOpm9jjlXKaBLDlLTmISr3aHm0oBQ5XefBIf4qmcBi7vDBlebtFevxIHP0kfBXc-dx1ZXLkOKnUSIbgwueDGjAY/s0/d4m4eAszpIwYCWugynZ6zbM9JS8.png)
2.テキストフィールドにtpm.mscと入力し、[OK]ボタンをクリックします。
![テキストフィールドにtpm.mscと入力し、[OK]ボタンをクリックします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-5imK6eL8ExQ/YZMnjvtEShI/AAAAAAAAfu0/nub1mvtJGQMcMzzjacg-hOGoJD-hzO-GgCEwYBhgLKtMDABHVOhz0Yv1aeBYkerQCB_m-YeLyTFOl3JarAk7ZvmmbmTWvUt9Yo5rcaOx8EetpKoEL5zdi6suJqUPqAMnxCNuWFELSyYPq9TGqd1jnPKxLLCNEoDi-ct7BqNP-qrbr-_RAl4PoEh475JURNwrog8TvSNIAwgKm8fv1N7Y0r_6nG4wQkDL6C8yGOReu2_Ysux0VBDtLMOjJWsbF9oOg8knIx0aNUu7iH9x6OAe5nc8qRJ9JAfDdFJmfsyBLbmby05oQAwRcYF061FhRQc169j-3E3ddF3CAISoZaxsVDG9lFLs98mBoKFMmsRq6iJFORCnOlZ4IsGocFYnRrZdUe-I4bTCtkcQ9hyQN2aHc_JtkDgLTnMCjw2C-kmdV5lhmq6SURgSQhsiwskhB0jsfLSu6fKpSmvjKtAimgTsvdxHIumJhgyKx-3RFlngT5244xJqqroLbFRwtwF6y_J_UJd60TlpZ9rUuI2n6rMQ6gXfesIgyHREDRQh69fCGUlcpsq2rkfglCulysq_MpkoHq7kYDJJ8xPwL3fJFE5QV81NicQe3qg9AZ13NyW4zD5VEu6yFe7b5GAzmw1OvfPHjCTW3Oj-ksy5LpuID3J49jsi5z10wzfrNjAY/s0/rpthcAPWBw_QM1Nlmp2DMVxCkKA.png)
3. ローカルコンピューター(Local Computer)アプリケーションのTPM管理(TPM Management)が起動するのを辛抱強く待ち、(Wait)ステータス(Status )と仕様のバージョン( Specification version)を確認します。[ステータス(Status)]セクションに[ TPMを使用する準備ができました]と表示され、バージョンが2.0の場合、Windows11ヘルスチェック(Health Check)アプリが問題の原因である可能性があります。Microsoft自身がこの問題に対処し、アプリケーションを削除しました。ヘルスチェック(Health Check)アプリの改良版は後でリリースされます。

また読む:(Also Read:) Windows10でセキュアログインを有効または無効にする(Enable or Disable Secure Login in Windows 10)
ただし、ステータスが(Status)TPMがオフであるか見つからないことを示している場合は、次の手順に従って有効にします。
1.前述のように、TPMは(TPM)BIOS/UEFIメニューからのみ有効にできるため、アクティブなすべてのアプリケーションウィンドウを閉じることから始め、デスクトップが表示されたらAlt + F4 選択メニューから[シャットダウン]を選択し、[OK]をクリックします。(Shut Down )
![選択メニューから[シャットダウン]を選択し、[OK]をクリックします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-JzxJf-XXxEw/YZENG3A3IeI/AAAAAAAAG2U/8ceGwPJbyLcn0v7-iYpbIwDwGjIUoiW2gCEwYBhgLKtMDABHVOhyxHaX9fPu7MRJnePcU5CX5XFFJjmDP8ssqBuNrH196SSHVPc45k3-6bS4UNNLx78XUASKnsal9GTYWhXV0Y14dJ7gLDX48Xp7xh6XmJofxoHxt-NieaZ96hhxOVG7akaEPUGCG06SiDLfR3OOHKDr9HV47dddUg52s7cK0MT8b4_5uQj7mWgYpjFnDNNdS5bbLqj1dVnAtWC9pwXNrhR20rdyAat93b1c8_EU9cQ2Lcc1qIqKXtNDjX94lpgYvw3qq3qbnU1A7vIBKqmkznt2nr3q8YfRvZwDhZ5t6LAaX3sNwrA2jgeJPyHhNBF2TlTCn2Bql7_F8xvjwjziWgaH149pLuEAYA8VX97P5B3b8UFSusV5s3g9oQRXh0TEL9oMnbEJULOibaLhMmr9yqskMcNBdQkKNfR0IP9dy4Eo5KQcJBAL9B2zMebvOX3Rlrf4Cb7PMNechMrLQh4edqJfJgZ0qWZpWmIkl90PhKJKlfn5siWc6SgbLHUjpVmMPFxSnZoTC9SjeuMXu8iYH86JTFFtFnTzeavw8bhXIAVvjrKbWQe8SMZBYOX3X3MZi_wS55nKXLSxickiVBl_FMDEqYjTp2-I_QhmPraDuXFMw39bFjAY/s0/9-C24sKOue8897xjAzRqavdtwnM.png)
2.次に、コンピュータを再起動し、BIOSキーを押してメニューに入ります。BIOSキー( BIOS key)はメーカーごとに固有であり、Googleですばやく検索するか、ユーザーマニュアルを読むことで見つけることができます。最も一般的なBIOSキーは、F1、F2、F10、F11、またはDelです。
3. BIOS(BIOS)メニューに入ったら、[セキュリティ(Security )]タブ/ページを見つけ、キーボードの矢印キーを使用してそれに切り替えます。一部のユーザーの場合、[セキュリティ(Security)]オプションは[詳細設定](Advanced Settings)の下にあります。
4.次に、TPM設定(TPM settings)を見つけます。正確なラベルは異なる場合があります。たとえば、一部のIntel搭載システムでは、「PTT 」、「Intel Trusted Platform Technology」、または(PTT)AMDマシンでは単に「TPMSecurity」と「fTPM」の場合があります。
5. TPMデバイス( TPM Device)のステータスを使用可能(Available )に設定し、TPMの状態(TPM State)を有効(Enabled)に設定します。(他のTPM関連の設定を台無しにしないでください。)(Make)

6.新しいTPM設定を保存し、コンピューターを再起動します。(Save )Windows 11チェックを再度実行して、修正できるかどうかを確認します。このPCはWindows11エラーを実行できません。
方法2:セキュアブートを有効にする(Method 2: Enable Secure Boot)
セキュアブート(Secure Boot)は、その名前が示すように、信頼できるソフトウェアとオペレーティングシステムのみを起動できるセキュリティ機能です。従来のBIOS(traditional BIOS)またはレガシーブートはチェックを実行せずにブートローダーをロードしますが、最新のUEFIブートテクノロジーは公式のMicrosoft証明書を保存し、ロードする前にすべてをクロスチェックします。これにより、マルウェアがブートプロセスに干渉するのを防ぎ、一般的なセキュリティを向上させます。(セキュアブートは、特定のLinuxディストリビュー(Linux)ションおよびその他の互換性のないソフトウェアをブートするときに問題を引き起こすことが知られています。)
コンピューターがセキュアブート(Secure Boot)テクノロジをサポートしているかどうかを確認するには、[ファイル名を指定して実行]ボックスにmsinfo32(Run Command)と(msinfo32)入力し(Windowsロゴキー+ R)、Enterキーを押します。
![[コマンドの実行]ボックスにmsinfo32と入力します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-51WJE0Hx1mM/YZFyxIf6cpI/AAAAAAAAKDo/Tfks1HRQU9wS24fuwcTzFyL_GqrrMdvwwCEwYBhgLKtMDABHVOhysbsXm9iUvKTwZLDdan-9yqjqjEee0tchsgrdNO6LfVDGwSyjuFjQw9AjHSo8z2aLpulv6NSkWDLe0tBOzY8wzzbiJWJ0gg_Gvi3fExsctxqjzfcduPYM9aEU6Lru9642geMu2f0Agt45jM8impxHx9MtIkSEHhpD2fw1ayJVnLufiWbXoLu1LGfkJmeeBdgxL8BvvlVn3llCVjiNlRvnSHJ3SLjThUxg8breERRAOSsit_424xqo7rOhhRrHi11p16deJ6Ig6a_w-d6ul2miH0emmeHSbek2s2cdLVvYc-LmhZPWSj3MQkISYoiSjOaBHOFcBX1_bj8gnzupeskBRyjUG2SJpNnn9hfjEMQpcJygMWTTfQpnyXT6f_0sXq86dAE1KkPp4XlGxNsGJjtXv-s1lqG8izEL4C_SwqfgotANXfgn01Siy1vvbEZ9VQX0dLBwaFca4c-VIkd2DE4ARwFSgALlHKSC6kHnCRiYhbW7r_qQvSCGVtPF0UKE6_kQ7zkLLvFFLEaaKvfi_tqX8ayIdJOpm9jjlXKaBLDlLTmISr3aHm0oBQ5XefBIf4qmcBi7vDBlebtFevxIHP0kfBXc-dx1ZXLkOKnUSIbgwuODGjAY/s0/Ag-nXWub_P0AtM8UqanNkLlfS-I.png)
SecureBootStateラベルを確認してください。
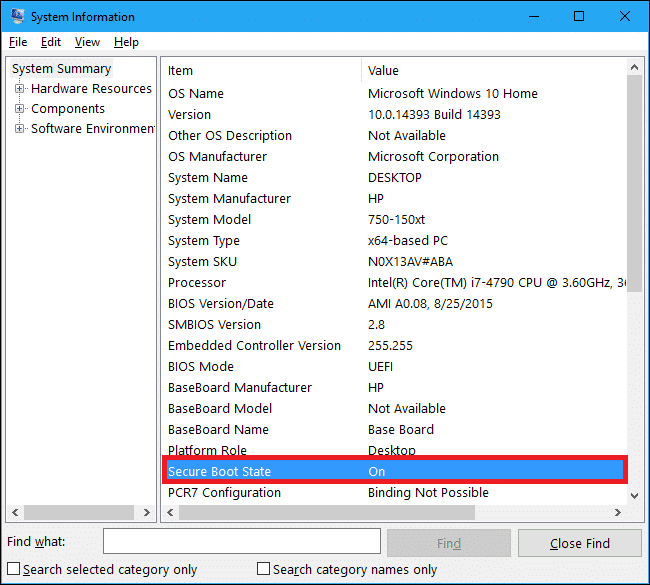
「サポートされていません」と表示されている場合、 Windows 11(Windows 11)をインストールすることはできません(トリックなしで)。一方、「オフ」と表示されている場合は、以下の手順に従ってください。
1. TPMと同様に、セキュアブートは(Secure Boot)BIOS/UEFIメニュー内から有効にできます。前の方法のステップ1と2に従って(Follow)、BIOSメニューに入ります(enter the BIOS menu)。
2. [ブート(Boot )]タブに切り替え、矢印キーを使用してセキュアブートを有効にします。(enable Secure Boot )
一部の場合、セキュアブート(Secure Boot)を有効にするオプションは、[詳細(Advanced)設定]メニューまたは[セキュリティ(Security)]メニューにあります。セキュアブート(Secure Boot)を有効にすると、確認を求めるメッセージが表示されます。[同意する]または[はい]を選択して続行します。(Choose Accept)

注:(Note:)セキュアブート(Secure Boot)オプションがグレー表示されている場合は、ブートモードが(Boot Mode)レガシー(Legacy)ではなくUEFIに設定されていることを確認してください。
3.変更を保存(Save )して終了します。「このPCはWindows11を実行できません」というエラーメッセージは表示されなくなります。
おすすめされた:(Recommended:)
Microsoftは、 (Microsoft)Windows 11を実行するために、TPM2.0とセキュアブート(Secure Boot)の要件でセキュリティを正当に倍増しています。とにかく、現在のコンピューターが(Anyway)Windows 11の最小システム要件を満たしていない場合でも心配はいりません。これは、OSの最終ビルドがリリースされたら、非互換性の問題の回避策が確実に理解されるためです。これらの回避策は、他のいくつかのWindows 11(Windows 11)ガイドとともに、利用可能な場合はいつでも説明しますので、ご安心ください。
Fix This PC can't run Windows 11 Error
Unable to install Windows 11 and getting This PC can’t run Windows 11 error? Here’s how to enable TPM 2.0 and SecureBoot, in order to fix the “This PC Can’t Run Windows 11” error in the PC Health Check application.
The long-awaited update to Windows 10, the most used computer operating system across the world, was finally announced by Microsoft a couple of weeks ago (June 2021). As expected, Windows 11 will introduce a host of new features, the native applications, and the general user interface will receive a visual design overhaul, gaming improvements, support for Android applications, widgets, etc. Elements such as the Start menu, action center, and the Microsoft Store have also been completely revamped for the latest version of Windows. Current Windows 10 users will be allowed to upgrade to Windows 11 without any additional cost at the end of 2021, when the final version is made available to the public.

Fix This PC can’t run Windows 11 Error
Steps to Fix if Your PC Can’t Run Windows 11 error
System Requirements for Windows 11
Along with detailing all the changes that Windows 11 will bring forth, Microsoft also revealed the minimum hardware requirements to run the new OS. They are as follows:
- A modern 64-bit processor with a clock speed of 1 Gigahertz (GHz) or higher and 2 or more cores (Here is a complete list of Intel, AMD, and Qualcomm processors that will be able to run Windows 11.)
- At least 4 gigabytes (GB) of RAM
- 64 GB or larger storage device (HDD or SSD, either of them will work)
- A display with a minimum resolution of 1280 x 720 and larger than 9-inch (diagonally)
- The system firmware must support UEFI and Secure Boot
- Trusted Platform Module (TPM) version 2.0
- Graphics Card should be compatible with DirectX 12 or later with WDDM 2.0 driver.
To make things easier and allow users to check whether their current systems are compatible with Windows 11 by the press of a single click, Microsoft also released the PC Health Check application. However, the download link for the application is no longer online, and users can instead install the open-source WhyNotWin11 tool.
Many users who were able to get their hands on the Health Check app have reported receiving a “This PC can’t run Windows 11” pop-up message upon running the check. The pop-up message also provides more information on why Windows 11 can’t be run on a system, and the reasons include – processor is not supported, storage space is lesser than 64GB, TPM and Secure Boot are not supported/disabled. While resolving the first two issues will require changing hardware components, the TPM and Secure Boot issues can be resolved quite easily.

Method 1: How to Enable TPM 2.0 from BIOS
A Trusted Platform Module or TPM is a security chip (cryptoprocessor) that provides hardware-based, security-related functions to modern Windows computers by securely storing encryption keys. TPM chips include multiple physical security mechanisms making it difficult for hackers, malicious applications, and viruses to alter them. Microsoft mandated the use of TPM 2.0 (the latest version of TPM chips. The previous one was called TPM 1.2) for all systems manufactured post-2016. So if your computer isn’t archaic, it is likely that the security chip is pre-soldered onto your motherboard but is simply disabled.
Also, the requirement of a TPM 2.0 in order to run Windows 11 caught most users by surprise. Earlier, Microsoft had listed TPM 1.2 as the minimum hardware requirement but later changed it to TPM 2.0.
The TPM security technology can be managed from the BIOS menu but before booting into it, let’s ensure your system is equipped with a Windows 11 compatible TPM. To do this –
1. Right-click on the Start menu button and select Run from the power user menu.

2. Type tpm.msc in the text field and click on the OK button.

3. Wait patiently for the TPM Management on Local Computer application to launch, check Status and the Specification version. If the Status section reflects ‘The TPM is ready for use’ and the version is 2.0, the Windows 11 Health Check app might be the one at fault here. Microsoft themselves have addressed this issue and have taken down the application. An improved version of the Health Check app will be released later.

Also Read: Enable or Disable Secure Login in Windows 10
However, if the Status indicates that the TPM is off or cannot be found, follow the below steps to enable it:
1. As mentioned earlier, TPM can only be enabled from the BIOS/UEFI menu, so start by closing down all the active application windows and press Alt + F4 once you are on the desktop. Choose Shut Down from the selection menu and click on OK.
2. Now, restart your computer and press the BIOS key to enter the menu. The BIOS key is unique for each manufacturer and can be found by performing a quick Google search or by reading the user manual. The most common BIOS keys are F1, F2, F10, F11, or Del.
3. Once you have entered the BIOS menu, find the Security tab/page and switch to it using the keyboard arrow keys. For some users, the Security option will be found under Advanced Settings.
4. Next, locate the TPM settings. The exact label may vary; for example, on some Intel-equipped systems, it might be “PTT,” “Intel Trusted Platform Technology,” or simply “TPM Security” and “fTPM” on AMD machines.
5. Set the TPM Device status to Available and TPM State to Enabled. (Make sure you do not mess with any other TPM-related setting.)

6. Save the new TPM settings and reboot your computer. Run the Windows 11 check again to confirm if you’re able to fix This PC can’t run Windows 11 error.
Method 2: Enable Secure Boot
Secure Boot, as the name suggests, is a security feature that only allows trusted software and operating systems to boot. The traditional BIOS or the legacy boot would load the bootloader without performing any checks, while the modern UEFI boot technology stores official Microsoft certificates and cross-checks everything before loading. This prevents malware from messing with the boot process and, thus, results in improved general security. (Secure boot is known to cause issues when booting certain Linux distributions and other incompatible software.)
To check whether your computer supports the Secure Boot technology, type msinfo32 in the Run Command box (Windows logo key + R) and hit enter.

Check the Secure Boot State label.

If it reads ‘Unsupported,’ you won’t be able to install Windows 11 (without any trickery); on the other hand, if it reads ‘Off,’ follow the below steps.
1. Similar to TPM, Secure Boot can be enabled from within the BIOS/UEFI menu. Follow steps 1 and 2 of the previous method to enter the BIOS menu.
2. Switch to the Boot tab and enable Secure Boot using the arrow keys.
For some, the option to enable Secure Boot will be found inside the Advanced or Security menu. Once you enable Secure Boot, a message requesting confirmation will appear. Choose Accept or Yes to continue.

Note: If the Secure Boot option is greyed out, ensure the Boot Mode is set to UEFI and not Legacy.
3. Save the modification and exit. You should no longer receive the “This PC can’t run Windows 11” error message.
Recommended:
Microsoft is rightfully doubling down on security with the requirement of TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot in order to run Windows 11. Anyway, fret not if your current computer does not meet the minimum system requirements for Windows 11, as workarounds to incompatibility issues are sure to be figured out once the final build for the OS is released. You can rest assured that we will be covering those workarounds whenever they are available, along with several other Windows 11 guides.


![[スタート]メニューボタンを右クリックして、[ファイル名を指定して実行]、[ファイル名を指定して実行]の順に選択します。 修正:このPCはWindows11エラーを実行できません](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-rD5l6ZC12Hs/YZGfsLjz58I/AAAAAAAANKI/yvN4mQz8ewgIh6bhNQupfgreQ5HpomUpwCEwYBhgLKtMDABHVOhysbsXm9iUvKTwZLDdan-9yqjqjEee0tchsgrdNO6LfVDGwSyjuFjQw9AjHSo8z2aLpulv6NSkWDLe0tBOzY8wzzbiJWJ0gg_Gvi3fExsctxqjzfcduPYM9aEU6Lru9642geMu2f0Agt45jM8impxHx9MtIkSEHhpD2fw1ayJVnLufiWbXoLu1LGfkJmeeBdgxL8BvvlVn3llCVjiNlRvnSHJ3SLjThUxg8breERRAOSsit_424xqo7rOhhRrHi11p16deJ6Ig6a_w-d6ul2miH0emmeHSbek2s2cdLVvYc-LmhZPWSj3MQkISYoiSjOaBHOFcBX1_bj8gnzupeskBRyjUG2SJpNnn9hfjEMQpcJygMWTTfQpnyXT6f_0sXq86dAE1KkPp4XlGxNsGJjtXv-s1lqG8izEL4C_SwqfgotANXfgn01Siy1vvbEZ9VQX0dLBwaFca4c-VIkd2DE4ARwFSgALlHKSC6kHnCRiYhbW7r_qQvSCGVtPF0UKE6_kQ7zkLLvFFLEaaKvfi_tqX8ayIdJOpm9jjlXKaBLDlLTmISr3aHm0oBQ5XefBIf4qmcBi7vDBlebtFevxIHP0kfBXc-dx1ZXLkOKnUSIbgwueDGjAY/s0/d4m4eAszpIwYCWugynZ6zbM9JS8.png)
![テキストフィールドにtpm.mscと入力し、[OK]ボタンをクリックします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-5imK6eL8ExQ/YZMnjvtEShI/AAAAAAAAfu0/nub1mvtJGQMcMzzjacg-hOGoJD-hzO-GgCEwYBhgLKtMDABHVOhz0Yv1aeBYkerQCB_m-YeLyTFOl3JarAk7ZvmmbmTWvUt9Yo5rcaOx8EetpKoEL5zdi6suJqUPqAMnxCNuWFELSyYPq9TGqd1jnPKxLLCNEoDi-ct7BqNP-qrbr-_RAl4PoEh475JURNwrog8TvSNIAwgKm8fv1N7Y0r_6nG4wQkDL6C8yGOReu2_Ysux0VBDtLMOjJWsbF9oOg8knIx0aNUu7iH9x6OAe5nc8qRJ9JAfDdFJmfsyBLbmby05oQAwRcYF061FhRQc169j-3E3ddF3CAISoZaxsVDG9lFLs98mBoKFMmsRq6iJFORCnOlZ4IsGocFYnRrZdUe-I4bTCtkcQ9hyQN2aHc_JtkDgLTnMCjw2C-kmdV5lhmq6SURgSQhsiwskhB0jsfLSu6fKpSmvjKtAimgTsvdxHIumJhgyKx-3RFlngT5244xJqqroLbFRwtwF6y_J_UJd60TlpZ9rUuI2n6rMQ6gXfesIgyHREDRQh69fCGUlcpsq2rkfglCulysq_MpkoHq7kYDJJ8xPwL3fJFE5QV81NicQe3qg9AZ13NyW4zD5VEu6yFe7b5GAzmw1OvfPHjCTW3Oj-ksy5LpuID3J49jsi5z10wzfrNjAY/s0/rpthcAPWBw_QM1Nlmp2DMVxCkKA.png)

![選択メニューから[シャットダウン]を選択し、[OK]をクリックします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-JzxJf-XXxEw/YZENG3A3IeI/AAAAAAAAG2U/8ceGwPJbyLcn0v7-iYpbIwDwGjIUoiW2gCEwYBhgLKtMDABHVOhyxHaX9fPu7MRJnePcU5CX5XFFJjmDP8ssqBuNrH196SSHVPc45k3-6bS4UNNLx78XUASKnsal9GTYWhXV0Y14dJ7gLDX48Xp7xh6XmJofxoHxt-NieaZ96hhxOVG7akaEPUGCG06SiDLfR3OOHKDr9HV47dddUg52s7cK0MT8b4_5uQj7mWgYpjFnDNNdS5bbLqj1dVnAtWC9pwXNrhR20rdyAat93b1c8_EU9cQ2Lcc1qIqKXtNDjX94lpgYvw3qq3qbnU1A7vIBKqmkznt2nr3q8YfRvZwDhZ5t6LAaX3sNwrA2jgeJPyHhNBF2TlTCn2Bql7_F8xvjwjziWgaH149pLuEAYA8VX97P5B3b8UFSusV5s3g9oQRXh0TEL9oMnbEJULOibaLhMmr9yqskMcNBdQkKNfR0IP9dy4Eo5KQcJBAL9B2zMebvOX3Rlrf4Cb7PMNechMrLQh4edqJfJgZ0qWZpWmIkl90PhKJKlfn5siWc6SgbLHUjpVmMPFxSnZoTC9SjeuMXu8iYH86JTFFtFnTzeavw8bhXIAVvjrKbWQe8SMZBYOX3X3MZi_wS55nKXLSxickiVBl_FMDEqYjTp2-I_QhmPraDuXFMw39bFjAY/s0/9-C24sKOue8897xjAzRqavdtwnM.png)

![[コマンドの実行]ボックスにmsinfo32と入力します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-51WJE0Hx1mM/YZFyxIf6cpI/AAAAAAAAKDo/Tfks1HRQU9wS24fuwcTzFyL_GqrrMdvwwCEwYBhgLKtMDABHVOhysbsXm9iUvKTwZLDdan-9yqjqjEee0tchsgrdNO6LfVDGwSyjuFjQw9AjHSo8z2aLpulv6NSkWDLe0tBOzY8wzzbiJWJ0gg_Gvi3fExsctxqjzfcduPYM9aEU6Lru9642geMu2f0Agt45jM8impxHx9MtIkSEHhpD2fw1ayJVnLufiWbXoLu1LGfkJmeeBdgxL8BvvlVn3llCVjiNlRvnSHJ3SLjThUxg8breERRAOSsit_424xqo7rOhhRrHi11p16deJ6Ig6a_w-d6ul2miH0emmeHSbek2s2cdLVvYc-LmhZPWSj3MQkISYoiSjOaBHOFcBX1_bj8gnzupeskBRyjUG2SJpNnn9hfjEMQpcJygMWTTfQpnyXT6f_0sXq86dAE1KkPp4XlGxNsGJjtXv-s1lqG8izEL4C_SwqfgotANXfgn01Siy1vvbEZ9VQX0dLBwaFca4c-VIkd2DE4ARwFSgALlHKSC6kHnCRiYhbW7r_qQvSCGVtPF0UKE6_kQ7zkLLvFFLEaaKvfi_tqX8ayIdJOpm9jjlXKaBLDlLTmISr3aHm0oBQ5XefBIf4qmcBi7vDBlebtFevxIHP0kfBXc-dx1ZXLkOKnUSIbgwuODGjAY/s0/Ag-nXWub_P0AtM8UqanNkLlfS-I.png)


