インターネットを閲覧するとき、 「クッキー」("cookies.")という用語に出くわすことがよくあります。多くのWebサイトは、Cookieの使用について通知し、承認を求めています。Webブラウザーには、Cookieを管理するための多くの設定があり、ブラウザーのアドオンでさえ、あらゆる種類のCookieをブロックすることに言及しています。これらの「クッキー」("cookies")が必ずしも甘いデザートではないことを知っていても、インターネット上でそれらが何であり、その目的が何であるかを正確に知らない場合があります。そのため、この記事では、Cookieとは何か、Cookieの機能と動作、およびインターネットで最も頻繁に使用されるCookieの種類について説明します。始めましょう:
インターネット上のCookieとは何ですか?
クッキーは、あなた、あなたのウェブブラウザ、およびインターネット上でのあなたの行動に関する情報を保持するファイルです。これらは、 PCまたはデバイス(PC or device)に保存されている小さなファイルであり、WebサイトまたはWebアプリで使用してオンラインエクスペリエンスを調整できます。
クッキーは何をしますか?
Cookieは、送信者(通常はWebサイトまたはWebアプリ)と受信者(デバイス)の間で送信されます。Cookieは送信者によって作成および解釈されますが、受信者はCookieを保持し、送信者が要求した場合にのみCookieを送り返します。
Webを閲覧する場合、送信者はWebサイトを実行するサーバーであり、受信者はそのWebサイトにアクセスするユーザーのWebブラウザーです。彼らの目的は、ユーザーを特定し、Webサイトでの過去の活動を確認し、このデータに基づいて適切なコンテンツを提供することです。

ユーザーが初めてWebサイトにアクセスすると、サーバーはそのユーザーのWebブラウザー(web browser)に特定のCookieを保存します。その後Webサイトにアクセスすると、サーバーはCookieを要求し、それを読み取り、その特定のユーザーのWebサイトの特定の構成をロードします。Cookieは、Webサーバーによってすべてのユーザーに適用されるタグのように考えることができます。このタグは、Webサーバーによって読み取られてユーザーを識別します。
この識別は、リアルタイムのユーザーデータが重要なWebサイトで役立ちます。たとえば、オンラインショップ(online shop)を使用する場合、Cookieを使用しないと何も購入できません。Webページをロードするたびに、ショップはあなたを新しいユーザーと見なし、最初から訪問を開始するため、ショップはあなたを識別してショッピングカートを作成することはできません。
クッキーの中身は何ですか?
最新のWebブラウザ(web browser)はすべてCookieをサポートしており、Cookieのサイズは約4KBと小さいです。Cookieの構造を理解しやすくするために、当社のWebサイトであるDigitalCitizenから送信される「cfduid」Cookieを(Digital Citizen)例("cfduid")として使用してみましょう。GoogleChromeを使用して分析しました。
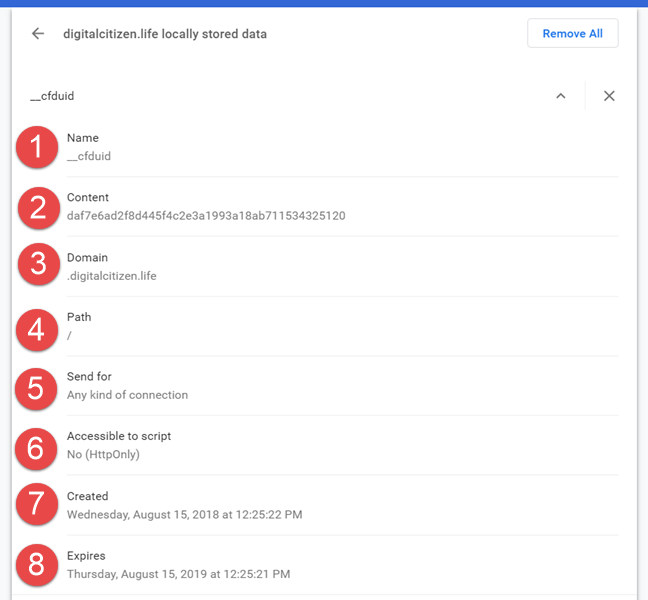
その構造は次のとおりです。
- 名前-Cookie(Name)の名前。
- コンテンツ(Content)-Cookieに含まれる情報。
- ドメイン(Domain)-このCookieを使用するドメイン。
- パス(Path)-Cookieが使用されるドメインのページ。パスが「/」の場合は、CookieがWebサイト全体で使用されていることを意味します。
- 送信(Send for)-接続がCookieを使用するために必要なセキュリティのレベル。
- スクリプトにアクセス可能(Accessible to script)-HTML以外の方法でCookieにアクセスできるかどうかを示します。
- 作成済み(Created)-ユーザーのWebブラウザ(web browser)でCookieが作成された日付。
- 有効期限-Cookie(Expires)の有効期限が切れ、ブラウザがCookieを削除した瞬間。
クッキーの種類はいくつありますか?
クッキーという用語(term cookie)はかなり一般的ですが、クッキーを使用する方法はたくさんあります。これが、インターネット上にさまざまな種類のCookieがある理由です。最も一般的なタイプは次のとおりです。
- セッションCookie-(Session cookies)最も一般的なものの1つ。これらは、 Webブラウザ(web browser)が閉じられるまで一時メモリに存在します。ブラウジングセッション(browsing session)が終了するとすべての情報が削除されるため、これらは有害ではありません。
- 永続的なCookie-(Persistent cookies)トラッキングCookieとも呼ばれます。それらは、削除されるか、有効期限(expiry date)に達するまで、ユーザーのデバイス上に残ります。これらは、ユーザーに関する情報を収集し、特定のWebサイトで一定期間にわたってユーザーの行動を記録するために使用されます。
- 安全なCookie-安全な(Secure cookies)HTTPS接続(HTTPS connection)を使用している場合にのみ機能する暗号化されたCookie 。これらのCookieは、ユーザーと同じネットワークに接続している潜在的なハッカーによって情報が盗まれないようにするために使用されます。これらはユーザーに関する重要な情報を保持し、主にユーザーが金融取引を行うWebサイトで使用されます。それらは暗号化されているため、他の種類のCookieよりもはるかに安全です。
- HttpOnlyCookie - (HttpOnly cookies)HTTP以外のプロトコルでは使用できません。このようなCookieは、Cookieを作成したWebサイトのみがCookieを使用できるようにします。HttpOnlyにできるのはセッションCookieのみであり、通常、ユーザーのプライバシーやセキュリティのリスク(privacy or security risks)を意味するものではありません。
- サードパーティ(Third-party cookies)のCookie-これらのCookieは、送信したドメイン以外の別のドメインに属しています。これらは通常、広告によって送信され、同じ広告ネットワーク(advertising network)を使用する複数のWebサイトにわたるユーザーの閲覧履歴を保存できます。これらのCookieは、ターゲットを絞った広告を表示するために、Cookieを使用してユーザーに関する大量のデータを追跡するため、プライバシーを損なう可能性があります。
- ゾンビクッキー(Zombie cookie)-削除された後に自分自身を再作成するクッキー。これらは通常、Web分析サービスによって使用され、同じコンピューターにインストールされているブラウザー間で使用できるため、ブラウザーの外部に保存されます。それらが自分で再作成する理由は、ユーザーがCookieを削除した後にデータが断片化されるのを防ぐためです。また、 Webブラウザ(web browser)ではその存在を制御できないため、悪意のある目的で使用される可能性があります。セキュリティ製品のみがゾンビCookieを識別して削除できます。
クッキーはいつ発明されましたか(簡潔な歴史(concise history))?
1994年7月、 (July 1994)NetscapeCommunicationsの従業員はeコマースアプリケーションを開発する必要がありました。彼は、サーバーに過負荷をかけることなく、すべてのユーザーのショッピングカート(shopping cart)を維持する簡単な方法を見つける必要があったため、この情報をすべてのユーザーのWebブラウザーに保存するのが最善の方法であると判断しました。(web browser)クッキーはすでにIT業界(IT industry)のさまざまな分野で使用されていたため、Webブラウジングにも使用できると彼は判断しました。
Cookieを使用およびサポートする最初のブラウザは、1994年10月の(October 1994)MosaicNetscapeでした。1年後、InternetExplorer2もCookieをサポートしました。それ以来、すべてのWebブラウザがCookieのサポートを提供してきました。それらが作成された理由は肯定的なものですが、Cookieは現在、あらゆる種類の目的で使用されており、その一部は倫理的または合法ではありません。
すべてのWebサイトにCookieに関するメッセージが表示されるのはなぜですか?
ヨーロッパ(Europe)に住んでいる場合、またはヨーロッパ(Europe)のIPアドレス(IP address)を使用してWebを閲覧している場合は、アクセスする多くのWebサイトでのCookieの使用に関するプロンプトが表示されます。これらのプロンプトは、欧州連合(European union)を形成するすべての国、および欧州ユーザーがいるすべてのWebサイトとオンラインサービス(website and online services)に適用される一般データ保護規則(GDPR)法のために表示されます。(General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR))
これらのプロンプトの目的は、すべてのヨーロッパのユーザーにCookie、Cookieの使用方法、およびその理由を通知し、明示的な同意を求めることです。これらのプロンプトを読み、問題のない使用のみを許可することをお勧めします。
WebサイトによってWebブラウザに保存されているCookieを表示および管理する方法
Webブラウザがデバイスに保存するCookieを表示および管理する方法を知りたい場合は、すべての主要なWebブラウザを網羅したガイドがあります。どうぞ:
- Google Chromeに保存されているCookieを表示(および削除)する2つの方法
- MozillaFirefoxに保存されているCookieを表示および削除する方法
- MicrosoftEdgeに保存されているCookieを表示および削除する方法
- Operaに保存されているCookieを表示および削除する2つの方法
- Chrome、Firefox、Edge、Opera、InternetExplorer(Opera and Internet Explorer)でサードパーティのCookieを無効にする
結論
Cookieは、すべてのユーザーに最も有用なコンテンツを提供することでWebサイトをより強力にすることができるため、インターネットで広く使用されています。場合によっては、Cookieを使用しないとWebサイトが機能しないことがあります。また、Webサイトがユーザーとアクセスしているページについて学習できるようにします。ただし、他のテクノロジーと同様に、非倫理的な目的にも使用できます。そのため、Cookieがどのように機能し、どのように使用されるかを知ることは、Webを閲覧するデジタル市民にとって有用なスキルです。クッキーについて質問がある場合は、下にコメントを残すことを躊躇しないでください。
Simple questions: What are cookies and what do they do?
When browsing thе intеrnet, you often encounter the term "cookies." Many websites inform you about using cookies, and ask for your approval. Web browsers have many settings for managing cookies and even browser add-ons mention blocking cookies of all kinds. Even though you know that these "cookies" are not exactly a sweet dessert, you may not know precisely what they are and what their purpose is on the internet. This is why, in this article, we explain what cookies are, what they do and how they work, and what kind of cookies are most frequently used on the internet. Let's get started:
What are cookies on the internet?
Cookies are files that hold information about you, your web browser and your behavior on the internet. They are tiny files stored on your PC or device, which can be used by websites or web apps to tailor your online experience.
What do cookies do?
Cookies are sent between a sender (usually a website or a web app) and a receiver (your device). A cookie is created and interpreted by the sender, while the receiver only holds it and sends it back if the sender asks for it.
When browsing the web, the sender is the server on which a website runs, and the receiver is the web browser of the user who visits that website. Their purpose is to identify the user, check for his or her past activity on the website and provide appropriate content based on this data.

The first time a user visits a website, the server stores a particular cookie in the web browser of that user. On subsequent visits to the website, the server asks for its cookie, reads it and loads a particular configuration of the website for that specific user. You can think of cookies like a tag applied by web servers to every user, which is read by web servers to identify users.
This identification is beneficial on websites where real-time user data is critical. For example, when using an online shop, you cannot buy anything without the help of cookies. Shops would not be able to identify you and build your shopping cart without them because each time you load a web page, the shop would see you as a new user and start your visit from scratch.
What is inside of a cookie?
Every modern web browser supports cookies, and they have a small size, of roughly 4 KB. To help you understand the structure of a cookie, let's use as an example the "cfduid" cookie sent by our website - Digital Citizen. We analyzed it using Google Chrome.

Here is its structure:
- Name - the name of the cookie.
- Content - the information the cookie contains.
- Domain - the domain using this cookie.
- Path - the page of the domain where the cookie is used. If the path is "/" it means that the cookie is used across the whole website.
- Send for - the level of security the connection needs to have to use the cookie.
- Accessible to script - it shows whether or not the cookie can be accessed through other ways than HTML.
- Created - the date the cookie was created on the user's web browser.
- Expires - the moment when the cookie expires and the browser deletes it.
How many types of cookies are there?
Even though the term cookie is rather general, there are many ways a cookie can be used. This is why there are different types of cookies on the internet. The most common types are the following:
- Session cookies - one of the most common. They exist in temporary memory until the web browser is closed. They are not harmful because all their information is deleted when your browsing session is over.
- Persistent cookies - also called tracking cookies. They last on the user's device until they are deleted or reach their expiry date. They are used to gather information about the user, recording his or her behavior on a specific website over a period of time.
- Secure cookies - an encrypted cookie that works only when using a secure HTTPS connection. These cookies are used to ensure that their information cannot be stolen by potential hackers connected to the same network as the user. They keep essential information about the user and are used mostly on websites where users perform financial transactions. Because they are encrypted, they are a lot more secure than other types of cookies.
- HttpOnly cookies - they cannot be used by any protocol other than HTTP. Such cookies ensure that only the website that created them can use them. Only session cookies can be HttpOnly, and they generally do not imply any privacy or security risks for users.
- Third-party cookies - these cookies belong to a different domain, other than the one that sent them. They are usually sent by ads and can store the browsing history of a user across multiple websites that use the same advertising network. These cookies may hurt your privacy because some ad networks use them to track way too much data about you, to display targeted ads.
- Zombie cookie - cookies that recreate themselves after they are deleted. They are generally used by web analytics services and stored outside of the browser because they are available across browsers installed on the same computer. The reason they recreate themselves is to prevent data from becoming fragmented after the user deletes the cookies. They can also be used for malicious purposes because the web browser cannot control their existence. Only security products can identify zombie cookies and remove them.
When were cookies invented (a concise history)?
In July 1994, an employee at Netscape Communications had to develop an e-commerce application. He had to find an easy way to keep the shopping cart for every user, without overloading the server, so he decided that the best way to do this was to store this information in the web browser of every user. Because cookies were already used in different fields of the IT industry, he decided they could also be used for web browsing.
The first browser to use and support cookies was Mosaic Netscape, in October 1994. One year later, Internet Explorer 2 also supported cookies. Since then, all web browsers have offered support for cookies. Even though the reason why they were created is a positive one, cookies are now used for all kinds of purposes, some of which are not ethical or legal.
Why am I seeing messages about cookies on every website?
If you live in Europe, or you are browsing the web using a European IP address, you see prompts about the use of cookies on many websites that you visit. These prompts are shown because of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) legislation that is applied in all the countries that form the European union, and to all the website and online services that have European users.

The purpose of these prompts is to inform all European users about cookies, how they are used and why, and ask for their explicit consent. We recommend that you read these prompts and permit only the uses that you are OK with.
How to see and manage the cookies stored in your web browser by websites
If you want to know how to see and manage the cookies your web browser stores on your device, we have guides that cover all the major web browsers. Here they are:
Conclusion
Cookies are widely used on the internet because they allow websites to be more powerful by providing the most useful content to every user. In some cases, websites cannot function without using cookies. They also allow websites to learn about their users and the pages they are visiting. However, just like any other technology, they can also be used for unethical purposes. That is why knowing how cookies work and how they are used is a useful skill for any digital citizen browsing the web. If you have any questions about cookies, do not hesitate to leave a comment below.



