テクノロジーに精通しているほとんどの人は、SoCまたはシステムオンチップ(System on a Chip)という用語を聞いたことがあると思います。20(thing 20)年前はそれほど重要ではなかったか、少なくとも現在ほど広く使用されていませんでしたが、現在のSystem on a Chipは、電子デバイスをより小さく、より強力に、これまで以上にエネルギー効率(energy efficient)が高くなります。それはすべて素晴らしくて簡単ですが、Socが何であるか知っていますか?SoCまたはシステムオンチップ(System on a Chip)とはどういう意味ですか?スマートフォン、タブレット、ワイヤレスルーター、ウェアラブル、その他のモバイルデバイスにとってなぜこれほど重要なのですか?どのSoC(SoC)についてもっと知りたい場合つまり、それが何をするのか、そしてなぜそれがそんなに大事なのか、この記事を読んでください、そしてあなたはいくつかの答えを見つけるでしょう:
SoC(システムオンチップ)とは何ですか?
SoCは、System onaChipの略語(System on a Chip)です。システムオンチップ(System on a Chip)は、共通の目標を達成するために連携して動作するように設計されたさまざまな電子コンポーネントを含む電子集積回路です。用語の最初の部分であるシステム(System)は、すべてが複雑な電子アセンブリに関するものであり、最後の部分であるチップ(Chip)は、そのシステムのすべてのコンポーネントが単一の集積回路にまとめられていることを示しています。
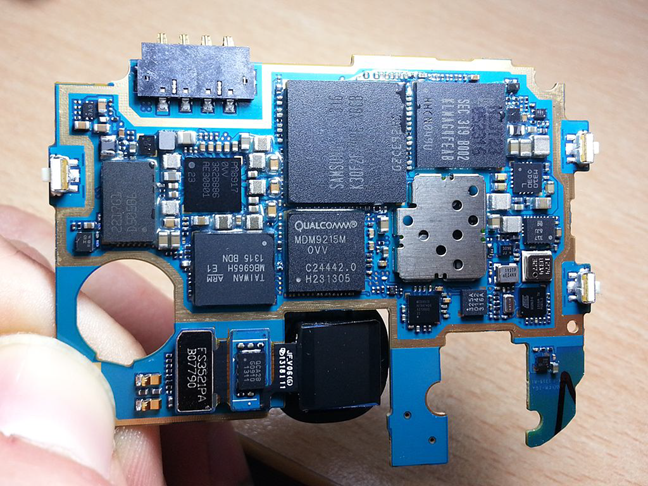
System on a Chipとは何かをよりよく理解するために、単一のチップに収まるように小型化および圧縮された完全なコンピューターとして想像してみてください。たとえば、SoCは、マザーボード、プロセッサ、グラフィックカード、ネットワークカードなどを備えた(network card)ミニチュアシステム(miniature system)と比較できます。より良い画像を取得するには、この段落の下を見てください。SamsungGalaxy S IIIスマートフォン(Samsung Galaxy S III smartphone)の回路基板上で、 (circuit board)Exynos 4 Quad(4412)システムオンチップ(System on a Chip)がどのように見えるかがわかります。

出典:ウィキペディア(Wikipedia)。
SoCの一般的な用途は何ですか?
システムオンチップ(Systems on Chips)は、スマートフォン、タブレット、ウェアラブル、デジタルカメラ、ワイヤレスルーターなど、さまざまな目的で多くの業界で広く使用されています。ただし、おそらく今日の最も一般的な用途はスマートフォンへの電力供給です。理由がわからない場合は、スマートフォンとタブレットの両方が動作するために多くの処理能力を必要とする小さなデバイスであり、それらはすべて、ますます要求が厳しくなるユーザーの要件を満たす必要があることに注意してください。
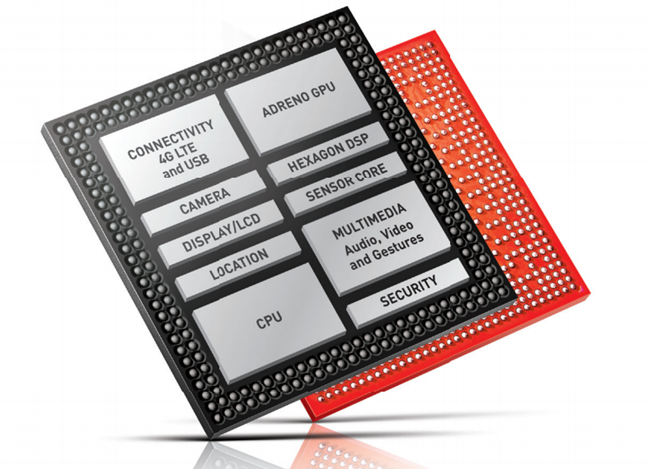
QualcommのSnapdragon600 システムオンチップ(System on a Chip )がいかに複雑であるかを次に示します。これは、古いSamsungGalaxyS4スマートフォンで使用されていた(Samsung Galaxy S4 smartphone)SoCです。新しい電話はさらに複雑で、さらに小型化されたSoCを備えています。(SoCs)
出典:(Source:) ウィキペディア(Wikipedia)
たとえば、人々はスマートフォンを使用してインターネットを閲覧したり、音楽を聴いたり、ビデオを視聴したり、 (watch videos)GPSナビゲーション(GPS navigation)を使用したり、写真や映画のビデオを撮影したり、ゲームをプレイしたり、常にソーシャルネットワークに接続したりできるようにしたいと考えています。これらはすべて、優れたプロセッサだけでなく、優れたグラフィックチップ、高速ワイヤレスおよびBluetoothチップ(wireless and Bluetooth chip)、4Gネットワークへの接続のサポート、GPSチップ(GPS chip)、およびリストを続けることができるものを必要とするものです。そして、それはすべて最小の電力消費(power consumption)で起こらなければなりません可能。結局のところ、ほんの数時間の使用後にデバイスがシャットダウンすることを誰も望んでいません。答えは、小型化できるすべてのものを小型化し、より小さな表面にできるだけ多くのコンポーネントを詰め込むことです。その結果、処理能力が高くなり、(processing power)消費電力(power consumption)が低くなります。それはまさにシステムオンチップ(System on a Chip)が提供するものです。
SoCの通常のコンポーネントはどれですか?
システムオンチップ(System on a Chip)は、その目的に応じて、さまざまな要素を持つことができます。ただし、圧倒的多数のSoC(SoCs)がスマートフォンで使用されているため、このようなデバイスの最も一般的なコンポーネントのリストを次に示します。
- CPU-中央処理装置(Central Processing Unit)またはプロセッサは、SoC内のすべてのものの中核です。これは、ほとんどの計算と決定を行う責任があるSoCの一部です。他のハードウェアコンポーネントおよびソフトウェア(software and delivers)から入力を受け取り、適切な出力応答を提供します。CPUがなければ、SoCはありません。今日のほとんどのCPUは、並列処理を実行できるように、内部に2つ、4つ、または8つのコアを備えています。
- GPU - Graphical Processing Unitの略で、ビデオチップ(video chip)とも呼ばれます。GPUは、スマートフォンでプレイできる3Dゲームと、SoCを使用するデバイスのユーザーインターフェイスに表示されるすっきりとした視覚的な遷移を担当します。
- RAMメモリ(Memory)-すべてのコンピューティングデバイスが機能するにはメモリが必要です。アプリとソフトウェアを実行できるようにするには、データを使用する必要があります。そのためには、システムオンチップ(System on a Chip)にRAMメモリが必要です。
- ROMメモリ(ROM memory)-デバイスがアプリやその他のソフトウェアを実行できるようにするためにRAMメモリ(RAM memory)が必要なのと同様に、デバイスが実行するファームウェアやオペレーティングシステムなどのソフトウェアを保存できるようにするためにも(operating system)ROMメモリ(ROM memory)が必要です。
- モデム(Modem)-無線ネットワークに接続できなければ、スマートフォンは電話にはなりません。そしてそれによって、私たちはワイヤレスネットワークと3Gまたは4Gモバイルネットワークの両方を指します。モデムは、ネットワークまたはセルラー接続を処理します。
QualcommのSnapdragon410と呼ばれるSystemonaChipに含まれるコンポーネントの図を次に示します。
プロセッサとメモリ(processor and memory)に加えて、ワイヤレスルーターや他の同様のネットワークデバイスに見られるような他のSoC(SoCs)には、無線トランシーバーを接続するように設計されたPCIeインターフェイス、ストレージデバイスに接続するためのSATAおよび/またはUSBインターフェイスも含まれる場合があります。(USB)次の図では、Broadcomの(Broadcom)BCM5862XSoC内にあるものを確認できます。また、ルーターのシステムオンチップ(Systems on Chips)について詳しく知りたい場合は、ルーターSoC101(Router SoC 101)を参照してください。

出典:(Source:) トムスハードウェア(Tom's Hardware)
上記の段落にリストしたコンポーネントのリストは、システムオンチップ(System on a Chip)のいくつかのコアで必須の要素のみを示しています。ただし、SystemsonChipに(Systems on Chips)は他の部分も含まれる場合があります。たとえば、多くのコンポーネントには、位置情報サービス、センサー、セキュリティ、またはより優れたカメラや大画面で動作するインターフェイスと連携するように設計されたコンポーネントがあります。リストは続きます。
モバイルSoC(SoCs)の最大のメーカーはどれですか?また、今日(SoC today)最高のSoCはどれですか?
今日の最大のSoCメーカーは、 (SoC)Qualcomm、Samsung、MediaTek、Huawei、NVIDIA、およびBroadcomです。Qualcomm、NVIDIA、およびMediaTekは、主にモバイルSoC(SoCs)を製造し、製造するデバイスでそれらを使用する他のハードウェア企業に販売しています。Broadcomは主にルーターやネットワークデバイスで使用されるSoCを製造しており、 (SoCs)SamsungとHuaweiは(Huawei)SoC(SoCs)を製造しているだけでなく、世界最大のスマートフォン企業の2つでもあります。
どちらが最高のシステムオンチップ(System on a Chip)であるかを言うことは不可能です。業界は急速に成長し、進化しているため、どれが最適なSoCであるかを比較して決定できるようになるまでに、新しいSoCが将来のデバイスに電力を供給するための道を進んでいる可能性があります。
ただし、最適なSoCは、最高のプロセッサや最速のワイヤレス転送を備えたSoCではない可能性があることに注意し(the best )てください( for you)。System on a Chipは、次のスマートフォンやデバイスを(smartphone or device work)適切に機能させ、必要なすべての基本機能を提供し、必要なすべての「周辺機器」(4G LTEサポート(LTE support)、802.11ac標準をサポートするWiFi )を含めることができるシステムです。、USB接続(USB connectivity)など)。
これは、スマートフォンメーカーが各スマートフォンに適したシステムオンチップ(System on a Chip)を選択する方法を示す興味深いビデオです。
SoCの長所と短所は何ですか?
あなたはまだ疑問に思うかもしれません:なぜ誰かがシステムオンチップ(System on a Chip)を設計、製造、販売したいと思うのでしょうか?それにはかなりの理由があります:
- SoCは通常小型(tiny )であり、電子デバイス内に多くのスペースを必要としないため、たとえばスマートフォン、タブレット、ウェアラブルなどの小型デバイスに最適なソリューションになります。そして、これらの3つの例だけで、世界を数千億ドルで満たすのに十分です。
- 手のひらに収まるだけの大きさのデバイスを設計する必要がある場合は、統合(integration )が必要です。つまり、プロセッサ、グラフィックチップ、モデム、およびその他の多くのコンポーネントを同じ平方インチ(square inch)に配置できます。
- SoCは小型であり、1つのチップに多くの異なる部品を統合しているため、製造業者は重要な物理部品の配線や長い回路の作成に時間、お金、リソース(money and resources)を費やす必要がなく、製造コストが低くなります。コスト(lower manufacturing costs)。
- システムオンチップ(Systems on a Chip)は、デスクトップPCやラップトップなどの専用の個別のコンポーネントを備えたシステムよりもはるかに電力効率が高くなります。(power efficient)SoCはバッテリーで長時間動作する可能性があるため、あらゆるモバイルデバイスに適しています。
一方、Systems on Chipsには、まったく適応できないという大きな欠点があります。その性質上、SoC(SoCs)は非常に緊密に統合されており、非常に小さいため、適応できません。つまり、アップグレードできません。System on a Chipは通常、生まれたときと同じように死にます。その寿命の間、何も変わりません。また、 SoC(SoC)内で何かが壊れた場合、その部分だけを修復または変更することはできず、SoC全体を交換する必要がある理由でもあります。
Systems on Chipsがエレクトロニクスの未来であることに同意しますか?
電子機器、特にコンピューティングデバイスへの従来のアプローチは、別々の独立した部品で実行されるシステムを作成することでした。そのような例は、例えばコンピュータやラップトップです。しかし、私たちの周りのすべてのものが恒久的に小型化されているということは、彼らがますます小型で、より優れた、より電力効率の高い(power efficient) SystemsonChipに(Systems on Chips)依存していることを意味します。スマートフォン、タブレット、ウェアラブル、さらにはIoT(モノのインターネット(Internet))デバイスでさえ、SystemsonChipsを証明してい(Things)ます(Systems on Chips)すべての電子機器の将来の重要な部分です。しかし、それは彼らが世界を引き継ぐことを意味するのでしょうか?それらが非常に小さくなり、ナノロボットが一般的なものになるとしたらどうでしょうか?皆様からのご意見をお待ちしておりますので、お気軽に下記コメント欄にご意見をお寄せください。
Simple questions: What is a SoC (System on a Chip)?
We bet that mоst people whо hаve a good knowledge of technolоgy have hеard the term SoC or System on a Chip. It wasn't much of a thing 20 years ago, or at least it was not something as widely used as it is today, but in the present day, the System on a Chip represents an approach to making electronic devices smaller, more powerful and more energy efficient than ever before. That's all nice and easy but do you know what a Soc is? What does SoC or System on a Chip mean? Why is it such an important thing for smartphones, tablets, wireless routers, wearables and other mobile devices? If you want to learn more about what SoC means, what it does, and why it's such a big deal, read this article, and you'll find some answers:
What is a SoC (System on a Chip)?
SoC is the short term for System on a Chip. A System on a Chip is an electronic integrated circuit that contains various electronic components designed to work together to achieve a common goal. The first part of the term - System - says that it's all about a complex electronic assembly, while the last part - Chip - tells you that all the components of that system are squeezed together on a single integrated circuit.
To get a better idea of what a System on a Chip is, imagine it as a full computer that's miniaturized and compressed to fit on a single chip. For instance, a SoC could be compared to a miniature system that has a motherboard, a processor, a graphics card, a network card and so on. To get a better picture, look below this paragraph, and you'll see what an Exynos 4 Quad (4412) System on a Chip looks like, on a circuit board from a Samsung Galaxy S III smartphone.

Source: Wikipedia.
What are the common uses of SoCs?
Systems on Chips are widely used in many industries for all kinds of purposes such as for smartphones, tablets, wearables, digital cameras, wireless routers and so on. However, probably their most common uses today are for powering smartphones. If you're wondering why, keep in mind that both smartphones and tablets are small devices that need a lot of processing power to work and they all need to meet users' requirements, which are increasingly more demanding.
Here's just how complex the Qualcomm's Snapdragon 600 System on a Chip is - a SoC that was used in the old Samsung Galaxy S4 smartphone. Newer phones are even more complicated and have SoCs that are even more miniaturized.

Source: Wikipedia
For instance, people want to be able to use their smartphones to browse the internet, listen to music, watch videos, use GPS navigation, shoot photos and film videos, play games, be always connected to social networks, and so on. All these are things that need not only a good processor, but also a good graphic chip, a fast wireless and Bluetooth chip, support for connecting to 4G networks, a GPS chip and the list can go on. And all that must happen with the least power consumption possible. After all, nobody wants their devices to shut down after very few hours of use. The answer is to miniaturize everything that can be miniaturized and squeeze as many components as possible on a smaller surface. The consequence is a higher processing power and a lower power consumption. That is exactly what a System on a Chip offers.
Which are the usual components of a SoC?
A System on a Chip can have a variety of elements, depending on its purpose. However, as the overwhelming majority of SoCs are used on smartphones, here's a list of the most common components of such devices:
- CPU - the Central Processing Unit or the processor is the core of all things inside a SoC. It's the part of the SoC that's responsible for making most calculations and decisions. It receives input from other hardware components and software and delivers appropriate output responses. Without a CPU, there would be no SoC. Most CPUs today have two, four or eight cores inside, to be able to do parallel processing.
- GPU - is short for Graphical Processing Unit and it's also known as the video chip. The GPU is responsible for those 3D games you can play on your smartphone and also for the neat visual transitions that you see in the user interface of any device using a SoC.
- RAM Memory - all computing devices need memory to work. For being able to run apps and software data must be used, and to be able to do that, a System on a Chip must have RAM memory.
- ROM memory - just as a device needs RAM memory to be able to run apps and other software, it must also have ROM memory to be able to store software like the firmware or the operating system that it runs.
- Modem - no smartphone would be a phone if it weren't able to connect to radio networks. And by that, we refer to both wireless networks and to 3G or 4G mobile networks. Modems take care of network or cellular connectivity.
Here's an illustration of what components the System on a Chip called Snapdragon 410 from Qualcomm includes:

Besides a processor and memory, other SoCs, like the ones found on wireless routers and other similar networking devices, might also include PCIe interfaces designed to connect the radio transceivers, SATA and/or USB interfaces to connect to storage devices. In the illustration below you can see what's found inside a BCM5862X SoC from Broadcom. And if you're curious to know more about routers Systems on Chips, here's some further reading on the subject: Router SoC 101.

Source: Tom's Hardware
The list of components that we've listed in the paragraphs above shows only a few core, must-have, elements of a System on a Chip. However, Systems on Chips can have other parts as well. For instance, many have components designed to work with location services, sensors, security, or interfaces capable of working with better cameras or larger screens. The list goes on.
Which are the largest manufacturers of mobile SoCs and which is the best SoC today?
The largest SoC manufacturers today are Qualcomm, Samsung, MediaTek, Huawei, NVIDIA, and Broadcom. Qualcomm, NVIDIA, and MediaTek manufacture and sell mostly mobile SoCs to other hardware companies which use them in the devices they produce. Broadcom makes SoCs that are mainly used in routers and networking devices, and Samsung and Huawei not only make SoCs but they are also two of the largest smartphones companies in the world.
To say which is the best System on a Chip is impossible. The industry is growing and evolving so rapidly that, by the time you could compare and decide on which is the best SoC, a new one would probably be on its way to power future devices.
However, keep in mind that the best SoC for you might not be the one with the best processor or the fastest wireless transfers. The System on a Chip for you is the one that can make your next smartphone or device work well, offer all the basics you need, and include all the "peripherals" you want (4G LTE support, WiFi with support for the 802.11ac standard, USB connectivity, etc.).
Here's an interesting video that shows you how smartphone manufacturers choose the right System on a Chip for each of their smartphones:
What are the advantages and disadvantages of a SoC?
You might wonder still: why would somebody want to design, manufacture and sell a System on a Chip? There are quite a few reasons for that:
- A SoC is usually tiny and doesn't take a lot of space inside an electronic device, which makes it a perfect solution for small devices like smartphones, tablets, or wearables, for instance. And these three examples only, are enough to fill the world with hundreds of billions of dollars.
- When you have to design a device that's large enough to fit in your palm at best, integration is a thing you want. That means that you can put a processor, a graphic chip, a modem and many other components in the same square inch.
- Because a SoC is small and because it integrates many different parts on a single chip, it means that its manufacturer doesn't have to spend time, money and resources on wiring significant physical parts and creating long circuits, which in its turn means lower manufacturing costs.
- Systems on a Chip are a lot more power efficient than a system with dedicated, separate components like a desktop PC or a laptop for instance. A SoC can run on batteries for longer times, which makes it a right choice for any mobile device.
On the other hand, Systems on Chips have the big disadvantage of not being adaptable at all. By their nature, SoCs are so tightly integrated and so small that they cannot adapt or, in other words, they cannot be upgraded. A System on a Chip will usually die the same as it was born: nothing changes during its lifetime. And that's also a reason for why if something breaks inside a SoC, you cannot repair or change only that part - you have to replace the whole SoC.
Do you agree that Systems on Chips are the future of electronics?
Traditional approaches to electronics and especially computing devices were about creating systems that run on separate, independent parts. Such examples are computers and laptops for instance. However, the permanent miniaturization of all things around us means that they are relying increasingly more on smaller, better, more power efficient Systems on Chips. Smartphones, tablets, wearables, hell even the IoT (Internet of Things) devices prove that Systems on Chips are an important part of the future of all electronics. But does that mean that they will be taking over the world? What if they will become so small that they will make nanorobots a common thing? We want to hear from you, so don't hesitate to share your opinions in the comments below.




