新しいデジタル一眼レフカメラ(DSLR camera)、アクションカメラ(action camera)、または新しいスマートフォンをお持ちですか?メモリーカード(memory card)を入れますか?あなたは正しい(Are)メモリーカード(memory card)を選ぶ方法を考えていますか?その前に、さまざまな種類のメモリカード(memory card)があり、特定のデバイスに適しているかを理解する必要があります。この記事を読んで、現在使用されている最も一般的なメモリカード、その名前の意味、(memory card)スピードクラス(Speed Class)の評価などを確認してください。
メモリーカードとは?
メモリーカードは、情報を保存するために設計された小さな電子機器です。(Memory cards are small electronic devices designed to store information.)通常、USBメモリ(USB memory)スティックやソリッドステートドライブと同じように、フラッシュメモリを使用します。メモリカードは、デジタルカメラ、スマートフォン、タブレット、メディアプレーヤー、ラップトップ、モバイルコンソール、監視カメラ、さらには一部のデスクトップコンピューターでも使用されます。フラッシュメモリを使用しているため、メモリカード(memory card)を抜いても情報が失われることはありません。また、ファイルをコピー、移動、削除したり、(you can copy, move, and delete files, as well as)いつでもメモリカードをフォーマットしたりできることを意味します。
USBフラッシュ(USB flash)ドライブとは異なり、メモリカードの場合、 USBポート(USB port)を使用して他のデバイスに接続することはありません。代わりに、メモリカードは、スロット(slots)と呼ばれる特別なハードウェアインターフェイスを介して直接接続し、それらをサポートするデバイスで利用できます。

メモリーカードの種類はいくつありますか?
数十年前、多くのハードウェアメーカーによって作成された、さまざまな種類のメモリカードが利用可能でした。(memory card)多くの企業が独自のメモリーカード(memory card)標準を設定しようとしましたが、競争に勝つことができたのはほんのわずかです。現在、ほとんどのメモリカードは、(memory card)セキュアデジタル(Secure Digital)とコンパクトフラッシュ(CompactFlash)の2つの主要なファミリのいずれかの一部です。それらのそれぞれが提供するものを見てみましょう:

SDカードの種類は何ですか?
(Secure Digital)SDの頭字語でよく知られているSecureDigitalには、さまざまな形やサイズのさまざまな種類のSDカードが含まれています。
- SD(セキュアデジタル)(SD (Secure Digital)) -最大2 GBのストレージ容量を持つ古いタイプのメモリカード(memory card)で、デフォルトでFAT16でフォーマットされています。SDカードの物理サイズは32×24×2.1mmです。このサイズは、 SDHC(SDHC)、SDXC、SDUCなどの他のすべての新しいバージョンのSDカードの標準になっています。現在(Nowadays)、多くの人がSDという用語を使用して、新しいSDHC、SDXC、またはSDUCメモリ(SDUC memory)カードを指しています。
- microSDはSDカードの小型化バージョンで、標準サイズは15×11×1mmです。microSDも古いタイプのメモリカード(memory card)で、最大ストレージ容量(storage capacity)は2GBです。それらの物理的なサイズは、microSDHC、microSDXC、およびmicroSDUCカードの新しいバージョン用に維持されました。また、技術的には正しくありませんが、人々はこれらのカードをmicroSDカードと呼んでいます。
- miniSDカードは通常のSDカードよりも小さいですが、microSDカードよりも大きいです:21.5×20×1.4mm。SD/microSDカードと同じストレージ容量範囲(storage capacity range)になります。
- SDHC(Secure Digital High Capacity)カードは、サイズ、サイズ、速度の点でSDと同じですが、2GBから32GBの範囲のストレージ容量があります。(storage capacity)また、SDHCカードはデフォルトでFAT32でフォーマットされています。
- microSDHCは、 (microSDHC)SDHCの小型化バージョンです。マイクロSDHCカードには、最大32GBのデータを保存することもできます。
- miniSDHCカードの本体サイズ(body size)はminiSDカードと同じですが、仕様はSDHCと同じで、最大32GBのストレージサイズがあります。(storage size)
- SDXC(Secure Digital Extended Capacity)は、SDHCの改良版です。SDと同じ物理的側面を維持しながら、SDXCカードは最大2 TBのファイルを保持でき、より高速なデータ転送速度も提供します。SDXCカードは、デフォルトでexFATファイルシステム(exFAT file system)を使用してフォーマットされます。
- microSDXCカードの物理サイズはmicroSDおよびmicroSDHCカードと(microSD and microSDHC cards)同じですが、より高速で、理論的には最大2TBのストレージ容量があります。(storage capacity)
- SDUC(Secure Digital Ultra Capacity)カードは、 (SDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity))SD/SDHC/SDXCカードと同じ物理ビルドを保持しますが、最大ストレージ容量(storage capacity)ははるかに大きく、理論上の最大容量は128TBです。デフォルトでは、SDUCカードはexFATを使用してフォーマットされています。
- microSDUCは、 (microSDUC)SDUCの小型化バージョンです。それらはmicroSD/microSDHC / microSDXCカードと同じサイズですが、通常のSDUCカードの速度とストレージスペースのすべての利点があります。(speed and storage space)
このすべてのデータを理解しやすくするために、以下の比較をご覧ください。
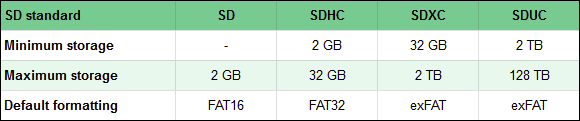
リストからお気づきかもしれませんが、miniSDXCまたはminiSDUCカード(miniSDXC or miniSDUC cards)については触れませんでした。これは、このサイズのフォーマット(size format)が廃止され、そのようなメモリカードが市場に出回っていないためです。

SDメモリー(SD memory)カードの速度と、カード速度クラスとはどういう意味(class mean)ですか?
SDカード(SD card)の速度を参照する場合、 SDカードに表示される評価と分類は、順次読み取りおよび/または書き込み速度を示します。SDカード(SD card)のアドバタイズされた速度を見るときに考慮すべき主な要因は、そのバスの速度です。たとえば、一部のSDカードでは、 (SD card)UHSやUHS-II(UHS or UHS-II)などのメーカーが印刷したものが表示される場合があります。

この情報は、通常の状態でSDカード(SD card)がどのくらいの速さで評価されているかを理解するのに役立ちます。現在SDカード(SD card)で一般的に使用されているバスは次のとおりです。
- デフォルトの(Default) バス速度(bus speed)とは、この定格の(または定格がまったくない) SDカードが最大12.5 (SD card)MB/sでデータを読み書きできることを意味します。
- 高速(HS)は、デフォルトの2倍の速度( (High Speed (HS))SDカード(SD card)でのデータの読み取りと書き込みの両方で25 MB/s )を提供します。
- UHS-I(超高速I) SDカードは、データが双方向で転送される場合は50 (UHS-I (Ultra High Speed I))MB/s(全二重)、データが片道のみで転送される場合は最大104 MB/s s(半二重)の読み取り/書き込み速度に達することができます。-二重、読み取りまたは書き込み)。
- UHS-II(Ultra High-Speed II)は、全二重で最大156 (UHS-II (Ultra High-Speed II))MB/s、半二重で312 MB/sの読み取り/書き込み速度を向上させます。
- UHS-III(Ultra High Speed III)はさらに高くなり、全二重モードで312 MB/s、半二重モードで624 MB/sに達します。
UHSバスは、SDHC 、(SDHC) SDXC 、(SDXC) SDUCカード(SDUC)、およびそれらのマイクロバリアントでのみ検出されます。UHSバスは、第1世代のSDカードではサポートされていません。

SDカード(SD card)の読み取り速度と書き込み速度を決定する際の2番目の重要な要素は、そのクラスの評価(Class rating)です。この評価は、転送されたメガバイト/秒で測定された、メモリカード(memory card)の最小持続速度を示します。SDクラスの評価(Class rating)は、次の3つのカテゴリに分類されます。
- 速度クラス(Speed Class)はSDHCメモリ(SDHC memory)カードに使用され、2、4、6、8、または10に等しくなります。各数値はMB/sで表される最低速度を示します。たとえば、速度クラス(Speed Class)2は、メモリカード(memory card)の最小持続速度が2 MB/sであることを意味します。クラス(A Class 10) 10SDカード(SD card)の最低速度はMB/sなどです。
- UHS Speed Classは、 UHSバス(UHS bus)を使用するSDHCおよびSDXCメモリーカード(SDHC and SDXC memory cards)に使用される速度定格(speed rating)です。UHS速度クラス(UHS Speed Classes)は、1または3の2つの値のいずれかになります。UHSクラス1のメモリ(UHS Class 1)カードは、最小速度が10 (memory card)MB/sに等しいことを意味し、UHSクラス3(UHS Class 3)カードの最小速度は30 MB/sです。
- ビデオスピードクラス(Video Speed Class)、または略してVクラス(V Class)は、ビデオ録画デバイスで動作するように設計されたメモリカードの評価として使用されます。この評価により、カードがビデオの録画に必要な最低速度をサポートできることが保証されます。5つのVクラス(V Class)があります:V6、V10、V30、V60、およびV90。V(V tell)の後に続く数字は、カードの最低持続速度を示しています。たとえば、V10は、カードの転送速度(transfer speed)が最悪のシナリオで少なくとも10 MB/sV60は最低速度60 MB/sで動作します。
速度の違いを要約するには、以下の表を見てください。
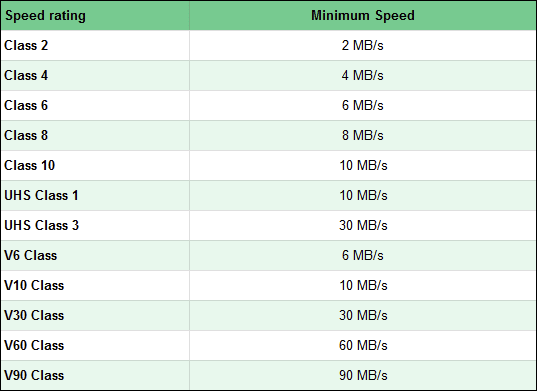
SDカードの最も一般的な使用例の1つは、ビデオ録画用のストレージスペースを提供することです。(storage space)ビデオカメラ(video camera)、アクションカム(action cam)、さらにはスマートフォンのいずれを使用する場合でも、録画用に十分なスペースのあるメモリカード(memory card)を購入するだけでは不十分です。また、メモリカード(memory card)の速度をよく調べて、好みの解像度でビデオ録画を処理できることを確認する必要があります。以下の表をお読みください。さまざまなタイプのビデオ録画シナリオでカードに必要な速度クラスを確認できます。(Speed)

コンパクトフラッシュとは何ですか? (Flash)CFメモリー(CF memory)カードを使用しているのは誰ですか?
(CompactFlash)頭字語CFで多くの人に知られているコンパクトフラッシュは、主にプロ仕様およびハイエンドのデジタル写真およびビデオカメラで使用される(photo and video cameras)メモリカード(memory card)形式です。キヤノンとニコン(Canon and Nikon)は、電子機器にコンパクトフラッシュ(CompactFlash)を使用することを選択した企業の1つです。
以前は、CFカードは、他のタイプのメモリカードよりも大きなストレージ容量と高速なデータ転送速度の両方を提供していました。そのため、コンパクトフラッシュカードは写真やビデオの専門家(photo and video professionals)に好まれました。また、物理的なサイズが大きいため、CFカードの方が好きな人もいました。これにより、CFカードは扱いやすく、紛失しにくくなりました。
コンパクトフラッシュ(CompactFlash)カードは、より大きなストレージ容量(storage capacity)と高速性により、市場で堅調に推移しており、現在でも使用され、利用可能です。CFカードには次の2種類があります。
- CompactFlash Iカードのストレージ容量は、最大128 PB(現在、現実の世界(world right)で利用可能な最大容量は512 GB)で、標準の物理サイズは43×36×3.3mmです。
- コンパクトフラッシュII(CompactFlash II)カードの仕様はタイプIと同じですが、43×36×5mmと厚くなっています。

CompactFlashは、 (CompactFlash)PCI Express 3.0を使用し、 (PCI Express 3.0)NVMeをサポートしているため、非常に高速なメモリカードの一種であるCFexpressに取って代わられました。残念ながら、CFexpressカードは、物理サイズが異なり(38.5×29.8×3.8 mm)、新しいテクノロジーを使用しているため、CFスロットとの下位互換性がありません。
メモリーカードについて他に質問はありますか?
この記事がお役に立てば幸いです。また、さまざまな種類のメモリーカードについて理解を深めていただければ幸いです。クローズする前に、メモリーカードについて他にご不明な点がありましたらお知らせください。ガイドに追加するものはありますか?以下のコメントセクションを使用してお知らせください。
What are the different types of memory cards? What do their specs mean?
Do you have a new DЅLR camera, an action camera, or maуbe a new smartphone? Do you want to add a mеmory card to it? Are you wоndering how tо choose the right memory cаrd? Bеfore you do that, you need to understand what are the different typeѕ of memory cards oυt there, and which fits your specific device. Read this article to see the most common memory cards used right now, what their nameѕ mean, what Speed Class ratings are, and more:
What is a memory card?
Memory cards are small electronic devices designed to store information. They typically use flash memory, just like USB memory sticks or solid-state drives. Memory cards are used inside digital cameras, smartphones, tablets, media players, laptops, mobile consoles, surveillance cameras, and even in some desktop computers. Because they use flash memory, the information saved on a memory card is not lost when you unplug it. It also means that you can copy, move, and delete files, as well as format memory cards whenever you want.
Unlike USB flash drives, for memory cards, you don't use a USB port to plug them into other devices. Instead, memory cards directly connect via special hardware interfaces, called slots, available on the devices that support them.

How many different types of memory cards are there?
Decades ago, there were many different types of memory cards available, created by many hardware manufacturers. Although many companies tried to set their own memory card standards, only a few have managed to win the competition. Today, most memory cards are part of one of the two main families: Secure Digital and CompactFlash. Let's see what each of them has to offer:

What are the different types of SD cards?
Secure Digital, better known by its SD acronym, includes many different types of SD cards, with different shapes and sizes:
- SD (Secure Digital) - an old type of memory card that has storage capacities up to 2 GB, formatted by default in FAT16. SD cards have a physical size of 32 × 24 × 2.1 mm. This size has become the norm for all the other, newer versions of SD cards, such as SDHC, SDXC, or SDUC. Nowadays, many people are using the term SD to refer to the newer SDHC, SDXC, or SDUC memory cards too.
- microSD are miniaturized versions of SD cards, which have a standard size of 15 × 11 × 1 mm. microSD is also an old type of memory card, with a maximum storage capacity of 2 GB. Their physical size was kept for the newer versions of microSDHC, microSDXC, and microSDUC cards. Also, people refer to these cards as microSD cards, although that is not technically correct.
- miniSD cards are smaller than regular SD cards but larger than microSD cards: 21.5 × 20 × 1.4 mm. Otherwise, they have the same storage capacity range as SD/microSD cards.
- SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity) cards are identical to SD in terms of size, dimensions, and speed, but have a range of storage capacity between 2 GB and 32 GB. Also, SDHC cards are formatted by default in FAT32.
- microSDHC is the miniaturized version of SDHC. microSDHC cards can also store up to 32 GB of data on them.
- miniSDHC cards have the same body size as miniSD cards, but the same specs as SDHC, with a storage size of up to 32 GB.
- SDXC (Secure Digital Extended Capacity) is an improved version of SDHC. While keeping the same physical aspects as SD, SDXC cards can hold up to 2 TB of files, and also provide faster data transfer speeds. SDXC cards are formatted, by default, using the exFAT file system.
- microSDXC cards have the same physical size as microSD and microSDHC cards, but they're faster, and their storage capacity can theoretically go up to 2 TB.
- SDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity) cards retain the same physical build of SD/SDHC/SDXC cards, but their maximum storage capacity is much greater, with a theoretical maximum of 128 TB. By default, SDUC cards come formatted using exFAT.
- microSDUC is the miniaturized version of SDUC. They have the same size as microSD/microSDHC/microSDXC cards, but all the benefits in speed and storage space of regular SDUC cards.
To help you make sense of all this data, take a look at the comparison below:

As you might have noticed from the list, we did not mention miniSDXC or miniSDUC cards. That's because this size format has been abandoned, and there are no such memory cards available on the market.

How fast are SD memory cards, and what does card speed class mean?
When referring to the speed of SD cards, the ratings and classifications you see on them refer to the sequential read and/or write speeds. The main factor to take into consideration when you're looking at the advertised speeds of an SD card is how fast its bus is. For example, on some SD cards, you might see things such as UHS or UHS-II printed by their manufacturers.

This information can help you understand how fast an SD card is rated to be, under normal conditions. The commonly used buses on SD cards nowadays are:
- Default bus speed means that the SD card with this rating (or no rating at all) can read and write data at up to 12.5 MB/s.
- High Speed (HS) offers double the default speed - 25 MB/s for both reading and writing data on the SD card.
- UHS-I (Ultra High Speed I) SD cards can reach a read/write speed of 50 MB/s (full-duplex) when data is transferred both ways and up to 104 MB/s when data is transferred one way only (half-duplex, read or write).
- UHS-II (Ultra High-Speed II) increases the read/write speeds up to 156 MB/s in full-duplex and 312 MB/s in half-duplex.
- UHS-III (Ultra High Speed III) goes even higher, reaching 312 MB/s in full-duplex mode and 624 MB/s in half-duplex mode.
The UHS buses are only found on SDHC, SDXC, SDUC cards, and their micro variants. UHS buses are not supported by first generation SD cards.

The second important factor in determining the read and write speeds of an SD card is its Class rating. This rating tells us the minimum sustained speed of a memory card, measured in transferred megabytes per second. SD Class ratings are divided into three different categories:
- Speed Class is used for SDHC memory cards and can be equal to 2, 4, 6, 8, or 10. Each number tells you the minimum speed expressed in MB/s. For example, a Speed Class of 2 means that the memory card has a minimum sustained speed of 2 MB/s. A Class 10 SD card has a minimum speed of 10 MB/s, and so on.
- UHS Speed Class is a speed rating used for SDHC and SDXC memory cards that use a UHS bus. The UHS Speed Classes can have one of two values: 1 or 3. A memory card with UHS Class 1 means its minimum speed is equal to 10 MB/s, while a UHS Class 3 card has a minimum speed of 30 MB/s.
- Video Speed Class, or V Class in short, is used as a rating for memory cards designed to work with video recording devices. This rating assures you that a card can support the minimum speeds needed for recording video. There are five V Classes: V6, V10, V30, V60, and V90. The numbers that come after V tell you the minimum sustained speed of the card. For example, V10 means that the card has a transfer speed of at least 10 MB/s in the worst scenario, V60 works at a minimum speed of 60 MB/s, and so on.
To summarize the speed differences, take a look at the table below:

One of the most common use cases for SD cards is for providing storage space for video recordings. Whether you use a video camera, an action cam, or even a smartphone, it is not enough to just buy a memory card with a lot of space for your recordings. You should also take a good look at how fast that memory card is, to make sure that it can handle video recording in the resolution you prefer. Read the table below, where you can see what Speed Classes your card should have for different types of video recording scenarios:

What is Compact Flash and who's using CF memory cards?
CompactFlash, known by many under its acronym CF, is a memory card format that's mainly used in professional and high-end digital photo and video cameras. Canon and Nikon are among the companies that choose to use CompactFlash on their electronic devices.
In the past, CF cards used to offer both larger storage capacities and faster data transfer speeds than other types of memory cards did. That's why CompactFlash cards were preferred by photo and video professionals. Some also liked CF cards more because of their bigger physical size, which made them easier to handle and harder to lose.
Because of their larger storage capacity, as well as their fast speeds, CompactFlash cards have held well on the market and are still used and available today. There are two types of CF cards:
- CompactFlash I cards have storage capacities that can go up to 128 PB (maximum available in the real world right now is 512 GB) and a standard physical size of 43 × 36 × 3.3 mm.
- CompactFlash II cards have the same specs as Type I but are thicker: 43 × 36 × 5 mm.

CompactFlash has been superseded by CFexpress, a type of memory cards that can be incredibly fast, as they're using PCI Express 3.0 and support NVMe. Unfortunately, CFexpress cards are not backward compatible with CF slots, as they have both different physical sizes (38.5 × 29.8 × 3.8 mm) and use newer technologies.
Do you have any other questions about memory cards?
We hope that this article has been helpful and that you now have a better grasp of the different types of memory cards. Before closing, tell us if you have any other questions about memory cards. Do you have anything to add to our guide? Use the comments section below to let us know.









