AdobePhotoshopはベクター画像エディターではありません。AdobeIllustratorはその仕事をうまく処理します。しかし、 AdobeCreativeCloud(Adobe Creative Cloud)の基本的なメンバーシッププランの1つを利用している場合はどうでしょうか。それとも、Photoshopだけを購読しているだけですか?
Photoshopには、ベクトルの形状とパスを最初から描画できるツールがいくつかあります。複数のパスを選択し、ライブシェイププロパティ(Live Shape Properties)などの機能を使用して外観を変更することもできるようになりました。それでも、 Photoshop(Photoshop)で画像をベクトル化する方法を学ぶには、もう少し手間がかかります。

ラスター画像(Raster Image)をベクター(Vector)画像に変換する方法
ベクター画像(Vector images)は、解像度が変更された場合にピクセル化する写真とは異なり、任意のサイズに拡大縮小できます。それらは、任意の解像度にスケーラブルな数式で描かれた「線」のようなパスで構成されています。

ピクセルベースのラスター画像をベクター画像に変換するには:
- ピクセルを選択します。
- それらをパスに変換します。
- それらに色を付けて、ベクター画像として保存します。
いつものように、Photoshopでさまざまなレイヤーを操作し(layers in Photoshop)て、ラスターイメージからパスを抽出します。これは、最初のラスターポートレートと、ベクトル化された後の最終的な画像を示しています。

スクリーンショットはAdobePhotoshopCC(21.2.0)のものです。ただし、 Photoshop(Photoshop)の最近のバージョンのほとんどで、この簡単なチュートリアルに従うことができるはずです。
1.Photoshopで(Photoshop)ラスター画像(Raster Image)を開きます
(Drag)ラスター画像をPhotoshopに(Photoshop)ドラッグアンドドロップするか、File > Openから開きます。この例のサンプル画像は単純なポートレートです。ベクトル化するオブジェクトの背景がビジーである場合は、最初 にPhotoshopで背景を削除します。
2.画像の周囲を選択します
Photoshopで選択を行うために使用できるさまざまな方法があります。選択する方法は、画像の性質によって異なります。たとえば、画像のエッジがまっすぐな場合は、長方形マーキー(Rectangular Marquee)ツールを選択できます。色で選択したい場合は、マジックワンド(Magic Wand)またはクイック選択(Quick Selection)ツールがオプションです。
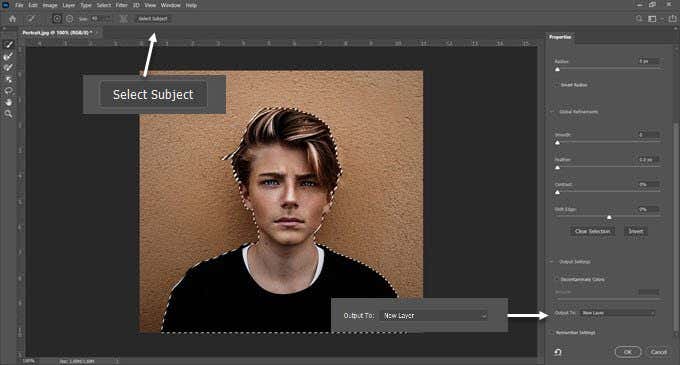
ポートレートの場合、[被写体の選択](Select Subject)コマンドを使用すると、写真の主要な被写体を自動的に選択できます。これは、スマートアルゴリズムを使用して画像内の人物を検出するコンテンツ認識ツールです。選択ツールを選択すると、ツールバーに[件名(Select Subject)の選択]ボタンが表示されます。[選択(Select)]メニューにもあります。

Select > Select & Mask > Select Subjectの選択]に移動すると、写真で最も目立つ被写体がスマートに選択されます。
必要に応じて、[グローバルリファインメント](Global Refinements)スライダーを使用して選択範囲のエッジを微調整してから、選択範囲を新しいレイヤーに出力します。
写真内のより複雑なオブジェクトの場合、オブジェクト選択ツール(Object Selection tool)はPhotoshopの強力な機能です。[件名(Select Subject)の選択]と同じように機能しますが、より多くのコントロールを使用して選択を微調整するのに役立ちます。写真にオブジェクト(または人物)のグループがある場合にこれを使用します。
3.しきい値効果を作成します
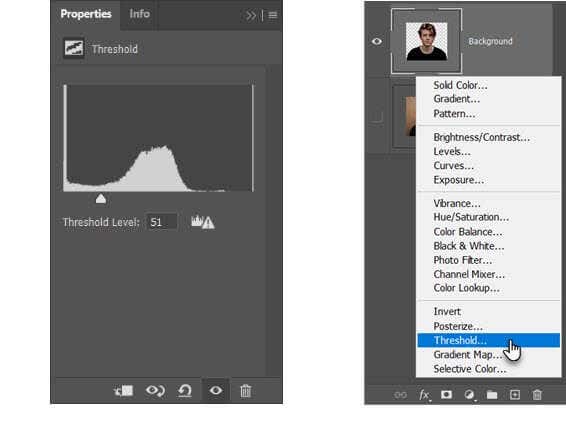
しきい値調整(Threshold Adjustment)レイヤーは、現在のレイヤーを白黒画像に変換し、プロセスの後半でカラー画像にきれいな単色の外観を与えることができます。
[レイヤー]パネルで、 [新しい塗りつぶしまたは調整レイヤー(Create new fill or adjustment layer)の作成]アイコンを選択して、新しいしきい値(Threshold)レイヤーを追加します。希望の外観になるまでスライダーを調整します。例の画像では、51の値を使用しています。
4. [色の範囲]コマンドを使用して、(Color Range Command)色調領域(Select Tonal Areas)を選択します
[選択(Select)]メニューの[色の範囲]コマンドは、魔法の(Color Range command)杖の選択(Magic Wand)に似ています。ただし、画像のその領域でスポイトツールと同じまたは類似の色を共有するピクセルを選択できるため、より優れています。画像のさまざまな領域でツールを繰り返し使用することにより、さまざまな色を選択できます。
このPhotoshopチュートリアルでは、 [色の範囲](Color Range)コマンドを使用して、すべての白と黒の色調領域を選択します。
Select > Color Rangeに移動します。
スポイトツール(Eyedropper tools)を使用して、画像内のさまざまな色調領域をすべて選択します。ドロップダウンでグレースケール(Grayscale)プレビューを 選択すると、選択した領域がわかります。
[ OK ]をクリックしてダイアログを閉じ、ポートレートを選択した状態でしきい値レイヤーに戻ります。

5.選択内容(Selection Into)をパスに変換します
Photoshopのパスは、両端にアンカーポイントがある線に他なりません。つまり、ベクトル線画です。パスは直線でも曲線でもかまいません。すべてのベクトルと同様に、詳細を失うことなく、それらを伸ばして形作ることができます。Photoshopは、選択範囲をパスに変換したり、その逆を行ったりすることができます。
マーキー(Marquee)ツールまたは任意の選択ツールを選択します。画像を右クリックし、コンテキストメニューから[作業パスの作成]を選択します。(Make Work Path)

また、表示される小さなボックスに 許容値を設定します。(Tolerance Value)
6.パスの(Path)許容値(Tolerance Value)を設定します
パスをスムーズにするには、ポップアップするダイアログボックスで許容値を設定します。(Tolerance)ポートレートの周りの不規則なパスには、「1.0」の値が理想的です。

Tolerance値は、パスが画像の輪郭にどれだけ「くっつく」かを決定します。値が小さいほど、選択はパスに厳密に従います。値を大きくすると、アンカーポイントの数が減り、パスがスムーズになります。親指のルールは次のとおりです—オブジェクトが単純であるほど、許容範囲は高くなります。
ただし、画像の複雑さに応じて、この値を試してください。
7.新しい単色レイヤーを作成します
どこもクリックせずに、[レイヤー(Layers)]パネルに移動し、[新しい塗りつぶしの(new fill or adjustment Layer)作成(Create) ]または[レイヤーの調整]を選択します。
次に、メニューから[単色]を選択し(Solid Color)ます。あなたはどんな色でも選ぶことができます。

この手順では、しきい値(Threshold)レイヤーの上にベクトルシェイプレイヤーを作成します。

この単色の塗りつぶしレイヤーは、任意の色にカスタマイズできます。次のステップでは、このレイヤーをSVGイメージとしてエクスポートします。
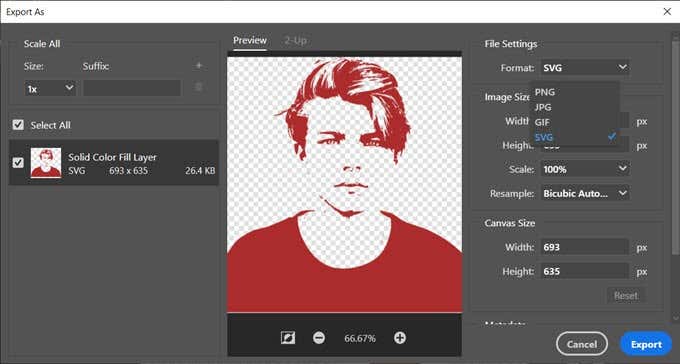
8.ベクター画像(Vector Image)をSVGファイルとして保存します
レイヤーを右クリックして、[名前を付けてエクスポート(Export As)]を選択します。File > Export Asからベクター画像を保存することもできます。

[名前を付けてエクスポート]ダイアログで、 (Export As)[ファイル設定](File Settings)から[SVG]を選択し、[エクスポート(Export)]をクリックします。
これで、 AdobeIllustrator(Adobe Illustrator)またはその他のベクター画像エディター でベクターファイルを開くことができます。
または、 Photoshop(Photoshop)からIllustratorにベクターパスをエクスポートすることもできます。[File > Export > Paths to Illustratorクリックします。これにより、単色塗りつぶしパス(Solid Color Fill Path)がインストールされている場合はIllustratorに エクスポートされます。
Photoshopで画像をベクトル化する方法は他(Are More Ways)にもあります
この特定の方法は、カラー写真から単調なベクトル画像を取得する簡単な方法です。Photoshop(image modification in Photoshop)の他の画像変更のテンプレートとして使用できます。次に、紙または別の媒体で任意のサイズに拡大または縮小します。
Photoshopで画像をベクトル化する方法は他にもあります。フォローするものは、ベース写真と希望する結果によって異なります。
How to Vectorize an Image in Photoshop
Adobe Photoѕhop is not a vеctor image editor. Adobe Illustrator аbly handles that job. But what if you are on one of the baѕіc Adobe Creativе Сloud membership plans? Or you just have a subscription to Photoshop alone?
Photoshop has a few tools that allow you to draw vector shapes and paths from scratch. You can now even select multiple paths and change the appearance with features like Live Shape Properties. Still, learning to vectorize an image in Photoshop takes a bit more effort.

How to Convert a Raster Image to a Vector Image
Vector images can be scaled to any size unlike a photo that will pixelate if there’s a change in resolution. They are made of paths which are like “lines” drawn with mathematical equations that are scalable to any resolution.

To convert a pixel-based raster image to a vector image:
- Select the pixels.
- Convert them to paths.
- Colorize them and save as a vector image.
As always, you will be working with different layers in Photoshop to extract the paths from a raster image. Here’s a glimpse of the initial raster portrait and the final image after it has been vectorized.

The screenshots are from Adobe Photoshop CC (21.2.0). But you should be able to follow this simple tutorial with most of the recent versions of Photoshop.
1. Open the Raster Image in Photoshop
Drag and drop the raster image into Photoshop or open it from File > Open. The sample image in this example is a simple portrait. If the object you want to vectorize has a busy background, then remove the background in Photoshop first.
2. Make a Selection Around the Image
There are different methods you can use to make a selection in Photoshop. The method you choose will depend on the nature of the image. For instance, if the image has straight edges, you can select the Rectangular Marquee tool. If you want to choose by color, then Magic Wand or the Quick Selection tool is an option.
For portraits, the Select Subject command can select the main subject in a photo automatically. It’s a content-aware tool that uses smart algorithms to detect people in images. The Select Subject button is displayed on the toolbar when you pick a selection tool. You can also find it under the Select menu.

Go to Select > Select & Mask > Select Subject and it will smartly select the most prominent subject in a photograph.
Use the Global Refinements sliders to fine-tune the selection edges if necessary, and then output the selection to a new layer.

For more complex objects in your photo, the Object Selection tool is a powerful feature in Photoshop. It works just like the Select Subject but helps you fine-tune the selection with more controls. Use this if you have a group of objects (or people) in your photo.
3. Create a Threshold Effect
The Threshold Adjustment layer transforms the current layer into a black and white image, and you can give a color image a neat one-color look later in the process.
In the Layers panel, add a new Threshold layer by selecting the Create new fill or adjustment layer icon. Adjust the slider till you get your desired look. In the example image, we have used a value of 51.

4. Use the Color Range Command to Select Tonal Areas
The Color Range command under the Select menu is like the Magic Wand selection. But it’s also better as it can select pixels that share the same or similar color with the eyedropper tool on that area of the image. You can pick up a range of colors by using the tool repeatedly on different areas of an image.
In this Photoshop tutorial, we want to use the Color Range command to select all the white and black tonal areas.
Go to Select > Color Range.
Use the Eyedropper tools to select all the different tonal areas in the image. Choosing the Grayscale preview in the dropdown will give you an idea of the areas selected.
Click OK to close the dialog and come back to the threshold layer with the portrait selected.

5. Convert Your Selection Into a Path
A path in Photoshop is nothing but a line with anchor points at its two ends. In other words, they are vector line drawings. Paths can be straight or curved. Like all vectors, you can stretch and shape them without losing detail. Photoshop can convert selections into paths and vice-versa.
Select the Marquee tool or any selection tool. Right-click on the image, and choose Make Work Path from the context menu.

Also, set a Tolerance Value in the little box that’s displayed.
6. Set a Tolerance Value for the Path
To make the path smoother, set a Tolerance value in the dialog box that pops up. A value of “1.0” should be ideal for the irregular paths around a portrait.

The Tolerance value determines how closely the path should “stick” to the contours of the image. The lower the value, the more closely the selection follows your path. Higher values will decrease the number of anchor points and make the path smoother. The thumb rule is — the simpler the object, the higher the tolerance.
But experiment with this value according to the complexity of your image.
7. Create a New Solid Color Layer
Without clicking anywhere, go to the Layers panel and select Create new fill or adjustment Layer.
Then, choose Solid Color from the menu. You can pick any color.

This step creates the vector shape layer on top of the Threshold layer.

This solid color fill layer can be customized to any color of your choice. In the next step, export this layer as a SVG image.
8. Save the Vector Image as an SVG File
Right click on the layer and choose Export As. You can also save the vector image from File > Export As.

In the Export As dialog, choose SVG from File Settings and click on Export.

You can now open the vector file in Adobe Illustrator or any other vector image editor.
Alternatively, you can export vector paths from Photoshop into Illustrator too. Click File > Export > Paths to Illustrator. This exports the Solid Color Fill Path to Illustrator if you have it installed.
There Are More Ways to Vectorize an Image in Photoshop
This specific method is a simple way to get a monotone vector image from a color photo. You can use it as a template for any other image modification in Photoshop. Then scale it up or down to any size on paper or another medium.
There are other ways to vectorize an image in Photoshop. The one you follow will depend on the base photo and the results you want.













