Windows Media Player 12は、ミキサー、EQ、その他のオーディオ調整(audio tweaking)デバイスを備えた、物理的なホームステレオまたはシアターシステム(home stereo or theater system)で見られる機能の多くを複製するように設計されています。ハイエンドのステレオ機器(end stereo equipment)に見られる無数のノブやスライダーに(myriad knobs and sliders)相当するソフトウェア(software equivalent)は、Windows Media Player 12の(Windows Media Player 12)再生拡張機能(playback enhancements)と呼ばれ、物理的なものよりもさらに使いやすくなっています。Windows Media Player 12に組み込まれている再生機能拡張機能(playback enhancements)を使用すると、状況に合わせてオーディオとビデオ(audio and video)をその場で調整および最適化できます。スピーカーシステムと好み(speaker system and tastes)。このチュートリアルでは、Windows Media Player 12ですべての(Windows Media Player 12)再生拡張機能(playback enhancements)を使用する方法と、それらがどのように機能するかについて少し説明します。
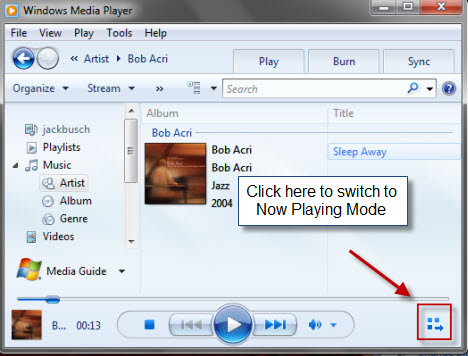
再生拡張機能(playback enhancements)にアクセスするには、 「再生中モード」('Now Playing Mode')になっている必要があります。プレーヤーライブラリ(Player Library)の右下にあるアイコンをクリックして、[再生モード]('Now Playing Mode')に切り替えます。
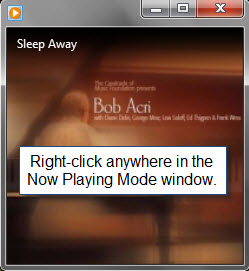
次に、[再生中(Now Playing)]ウィンドウの任意の場所を右クリックし、[拡張機能(Enhancements)]を選択して、使用可能な再生拡張機能のリストを表示します。
右側のドロップダウンメニューのオプションのいずれかをクリックして、[拡張機能(Enhancements)]ウィンドウを開きます。

ボリュームの強化(Volume Enhancements & How)とその使用方法(Them)
Windows Media Player 12には、曲間および曲自体の内部の両方で、大きな音と小さな音の不一致を減らすのに役立つ機能が組み込まれています(つまり、正規化)。これは、非常に静かな曲の後に耳障りな大音量の曲(loud song)が続くという煩わしさを回避するのに役立ちます。これは、さまざまなアルバムから取得され、さまざまなパラメータでエンコードされたトラックで構成されるプレイリストを聴くときによく発生します。たとえば、1972年のニールヤング(Neil Young)のハーヴェストの曲を、(Harvest)クイーンズオブザ(Queens)ストーンエイジ(Stone Age)のソングス(Songs)オブザデフの曲と連続して再生してみてください。(Deaf)2002年から、あなたは私たちが話していることを正確に聞くでしょう。録音がどんどん大きくなっている理由の説明については、NPRのこの記事をチェックしてください:ラウドネスウォー(The Loudness War)。
これらの再生機能の強化により、ハードウェアやその他の要因に応じてマイレージは確実に異なりますが、すべての曲を(比較的)レベルの高い音量で再生するための適切なステップです。これらの機能を含む2つのペインがあります:「クロスフェードと自動音量レベリング」('Crossfading and auto volume leveling')とクワイエットモード(Quiet mode)。以下では、 Windows(Windows Media Player 12) MediaPlayer12のさまざまなボリューム調整の機能強化について説明します。
Crossfading - in the Crossfading and auto volume leveling window, click 'Turn on Crossfading' to have Windows Media Player 12 gradually fade out the song at the end and then have the next song on the playlist gradually fade in. Move the slider to the left to shorten the overlap between songs. Move the slider to the right to lengthen the overlap. (On a personal note: I don't particularly like this feature since it will fade songs out before their natural end, meaning you might miss something. So, if you want to hear the songs as the producers intended, skip this feature.)
自動音量レベリング(Auto volume leveling)- [クロスフェードと自動音量レベリング]('Crossfading and auto volume leveling')ウィンドウで、[自動音量レベリングをオン('Turn on Auto volume leveling')にする]をクリックして、Windows MediaPlayer12で曲間の(Windows Media Player 12)音量レベル(volume level)を自動的に調整してより類似させます。Windows Media Player 12は、再生中に曲を分析し、曲が最後まで再生された後に自動音量(volume level)レベリング情報を追加することでこれを行います(したがって、次に曲を再生するまで効果は聞こえません)。

簡単な補足として、自動ボリュームレベリングは、ボリュームレベリング値を含む(Auto volume leveling)Windows Media Audio(WMA)またはMP3ファイルに対してのみ機能することに注意してください。この値はエンコード中に追加されますが、プレーヤーライブラリ(Player Library)に曲を追加するときに追加することもできます。これを行うには、プレーヤーライブラリに移動し、[(Player Library)ツール(Tools)]をクリックして[オプション(Options)]を選択します。[ライブラリ(Library)]タブで、[メディアライブラリ設定]の('Media Library Settings')下の[新しいファイルのボリュームレベリング情報値の追加]をオンにし、[('Add volume leveling information values for new files')適用(Apply)]をクリックして[ OK ]を選択します。以降のすべてのWMAおよびMP3(WMA and MP3)ライブラリ(Library)に追加されたファイルには、ボリュームレベリング値がまだ追加されていない場合は、自動的に追加されます。

クワイエットモード- (Quiet Mode)「自動音量レベリング」('Auto volume-leveling')と同様の機能はクワイエットモード(Quiet mode)で、独自のウィンドウがあります。クワイエットモード(Quiet mode)は、(2つのトラック間ではなく)トラック内の急激な音量変化を緩和します。これは、The Pixies(Pixies)とNirvanaによって開拓されたラウド/ソフト/ラウドダイナミックにあまり慣れていない場合に便利です(しかし、真剣に、プログラムに参加してください。これは90年代です!)。
クワイエットモード(quiet mode)の機能は非常に簡単です。左上のテキストをクリックしてオンまたはオフにし、下のラジオボタンで「中程度の違い」('medium difference')と「少しの違い」を切り替えることができます。('little difference')かなり(Pretty)自明です。

ただし、注意点が1つあります。クワイエットモード(Quiet mode)を機能させるには、Windows MediaAudio9(Windows Media Audio 9)またはWindowsMediaAudio10Lossless(Windows Media Audio 10) またはProfessionalコーデック(Lossless or Professional codec)を使用して曲をエンコードする必要があります。ロスレスWindowsMediaAudio(Lossless Windows Media Audio)ファイルは、Windowsエクスプローラーで「.WMA」ファイルとして表示されます。
低音ブースト(Bass Boost)、イコライザー(Equalizer)、その他のサウンドシェーピング(Sound Shaping)の強化
Windows Media Player 12には、スタジオでのプロデューサーの(Media Player 12)ノブの回転や、(knob twiddling)ステレオシステム(stereo system)のさまざまなスライダーやエフェクトをシミュレートする一連の機能もあります。これらは、ジャンル、スピーカーサイズ(speaker size)、およびその他の変数に従って再生を最適化するために、再生している曲のダイナミクスを大幅に変更する可能性があります。このセクションでは、これらの各機能について1つずつ説明します。
グラフィックイコライザー(Graphic Equalizer)-今では、グラフィックイコライザー(EQ)の機能についてはよく知っています。Windows Media Player 12のグラフィックイコライザー(graphic equalizer)は期待どおりに機能し、さまざまなサウンド周波数を微調整したり、いくつかのプリセットを選択したりできます。
何をしているのかわからない場合は、聴いている音楽の種類に応じてプリセットを選択するのが最善の策です。右上のテキストの横にある矢印をクリックして(最初はデフォルト(Default)と表示される可能性があります)、プリセットのリストを表示します。これらのプリセットは、ジャンルに応じて周波数を最適化するために最善を尽くします(たとえば、ロック(Rock)は高低をブーストしてボーカル、ドラム、ベース、ギター駆動の音楽に対応し、スピーチ(Speech)は中音域に焦点を合わせて高音域を緩和します終わり、それらのヒスノイズが住んでいるところ)。ご覧のとおり、プリセットを選択すると、スライダーが自動的に所定の位置に移動します。

または、カスタム設定(custom setting)を使用してスライダーを自分で移動することもできます。スライダーをいじり始めると、プリセットは自動的にカスタムにキックオーバーします。(Custom)
スライダーを動かすには3つの方法があります。
-
スライダーを個別(Move sliders independently)に移動します。クリックして上下にドラッグすると、1つのスライダーのみが移動します。
-
ゆるいグループで一緒に移動し(Move together in a loose group)ます-1つのスライダーを移動すると、両側のスライダーも上下に移動して波形が作成されます。緩いグループ設定は、より弧を描く曲線になります。
-
緊密なグループで一緒に(Move together in a tight group)移動します。1つのスライダーを移動すると、両側のスライダーも上下に移動して、より緩やかな波が作成されます。タイトなグループ設定は、それほど劇的な弧を作成しません。スクリーンショットでは、タイトモードを使用しています。移動中のスライダーの周りに作成された波に注意してください。
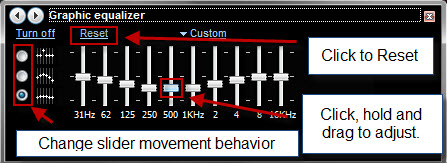
スライダーをリアルタイムで動かして、何が良い音かを判断できます。本当に混乱した場合は、[リセット(Reset)]をクリックしてすべてを通常の状態に戻します。
注:(Note:)EQ設定(EQ setting)(そのほとんどは録音と制作を対象としています)については膨大な量の情報がありますが、特にハードウェアと好みの違いを考慮すると、「最良の」 (hardware and taste)EQ設定(EQ setting)はありません。バンド間の違いを本当に理解したい人は、識別周波数トレーニングテスト(discriminative frequency training test)とこの要約された等化の概要を(overview of equalization)チェックしてください。
SRS Wow Effects-低周波数(低音)とステレオサウンドのパフォーマンス(sound performance)(つまり、左右のチャンネル間のパン)を強化できます。ここでのオプションも非常に簡単です。
TruBassスライダー(TruBass slider)を左に動かすと低周波効果が減少し、(low-frequency effect)右に動かすと低周波音がブーストされます。
WOW Effectスライダー(WOW Effect slider)を左に動かすとステレオサウンドのパフォーマンス(stereo sound performance)が下がり、右に動かすとステレオサウンドのパフォーマンスが上がります。この機能強化により、より多くの「サラウンドサウンド(surround sound)」効果が作成されます。
最後に、左上のテキストの横にある矢印をクリックして、SRSWowをスピーカー(SRS Wow)タイプ(speaker type)に合わせて最適化することができます。ノーマル(Normal)スピーカー、ヘッドホン(Headphones)、ラージスピーカーからお選びいただけます。
SRS WOWエフェクトをオンにすることで、低周波およびステレオサウンドのパフォーマンスを向上させることができます。(sound performance)

SRS WOWエフェクトの唯一の問題は、 DVD再生(DVD playback)に適用できないことです。
ドルビーデジタル設定(Dolby Digital Settings)-これらの設定は、SRSWowエフェクトのスピーカータイプ設定(speaker type setting)に似ています。ただし、これらの設定はドルビーデジタルコンテンツ(Dolby Digital content)にのみ影響します(たとえば、多くのDVD(DVDs)には、スターウォーズ(Star Wars)の前編などのドルビーデジタルサウンド(Dolby Digital sound)が含まれています)。このメニューでは、3つの異なるプリセットから選択できます。
-
通常(Normal)-ドルビーデジタルの全範囲を縮小して、より静かな再生を実現します。
-
夜(Night)-他の音を和らげながら、対話を促進します。ラップトップに適しています。
-
シアター(Theater)-すべてのサウンドのダイナミックレンジを拡大して、ソフトサウンドとラウドサウンドの劇的な違いと、より充実したリスニング体験を実現します。ホームシアターシステムに適しています。

オプションを選択してアクティブにします。[リセット](Reset)をクリックして、設定を通常に戻します。
オーディオとビデオ(Audio & Video)のその他の再生機能の強化(Playback Enhancements)
さらに、Windows Media Player 12では、オーディオファイルとビデオファイルの(audio and video files)再生速度(playback speed)を変更したり、ビデオの色とズームレベル(zoom level)を微調整したりできます。このセクションでは、これら2つの機能の使用方法を説明します。
再生速度の設定-(Play Speed Settings)再生速度(Play speed)を調整すると、曲やビデオ(song or video)内の特定の部分を見つけたり、ファイルの速度を落としたりして分析を進めたり(analysis or speed)、コミック効果のために速度を上げたりできます(他になぜこれを行うのですか?)。これを行うには、いくつかの異なる方法があります。
曲の早送りが始まるまで[次へ(Next)]ボタンをクリックして押し続けると、ファイルを早送りできます。ボタンを離すと、通常の再生が再開されます。
曲の巻き戻しが始まるまで[前(Previous)へ]ボタンをクリックして押したままにして、ファイルを巻き戻します。離すと通常の再生に戻ります。(注:(Note:)巻き戻しはビデオファイルにのみ適用されます)。
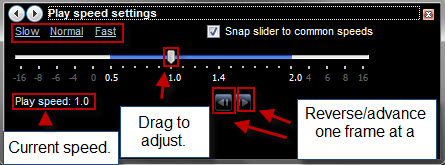
拡張(Enhancements)メニューからも再生速度(Play speed)を変更できます。スライダーは通常の再生である1.0から始まります。スライダーを0.5に動かすと、半分の速度で再生されます。負の数に移動すると、ファイルが逆に再生されます。スライダーを1.0より大きい数値に移動すると、再生が高速化されます。[スライダーを一般的な速度(Snap slider to common speeds)にスナップ]ボタンをオンにして、半速、倍速などの速度をすばやく選択します。左上の[低速]、[通常(Slow, Normal)]、または[高速]をクリックして一般的な速度を選択することもできます。(Fast)
また、下部の矢印をクリックすると、一度に1フレームずつ前進または後退できます。これは、サポートされているビデオファイルにのみ適用されます。
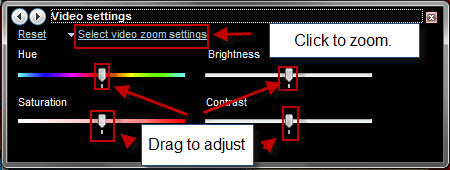
ビデオ設定(Video Settings)-最後に、Windows Media Player 12では、ビデオ再生中に色相、明るさ、(Windows Media Player 12)コントラスト、彩度(contrast and saturation)、ズームの設定を微調整することもできます。スライダーを左右(left and right)にドラッグして設定を調整します。これらの機能については、写真は千の言葉に値するので、Microsoft.comでこれらのビデオ設定の(video settings)Microsoftのデモンストレーションをチェックしてください。
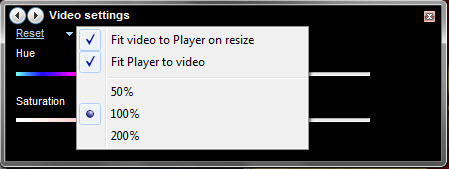
左上のテキストをクリックしてアクセスできる、わかりやすいビデオズーム設定(video zoom settings)もいくつかあります。また、 ALT-1を押すと50%、 (ALT-1)ALT-2を押すと100%、ALT-3を押すと200%にすばやくズームできます。
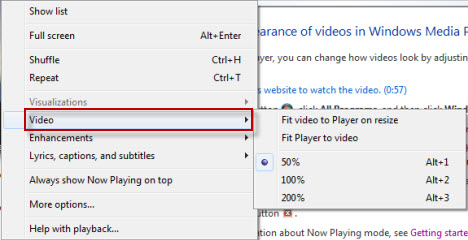
または、再生中に[再生中]ウィンドウを右クリックし、 [ビデオ(Video)]を選択してズーム設定を選択することもできます。(Now Playing)
結論
ご覧のとおり、Windows Media Player 12は、あらゆる種類のオーディオおよびビデオファイルに対応する(audio and video files)多用途のプレーヤー(versatile player)であるだけでなく、フル機能の再生エンハンサー(playback enhancer)でもあります。さまざまな設定をいじって、セットアップで耳に最もよく聞こえるものを見つけることをお勧めします。注意:いつでも[リセット(Reset)]をクリックして通常に戻ることができるため、失うものは何もありません。
How to Use Playback Enhancements in Windows Media Player 12
Windows Media Player 12 is designed to replicatе many of the features you'd see on a physical home stereo оr theater system, complete with a mixer, EQ and other audio tweaking devices. The software equivalent of the myriad knobs and sliders yоu'd see оn high end stereо equipment are called playback enhancements on Windows Media Player 12 and they are even easier to use than their physical counterparts. Using the built-in playback enhancements for Windows Media Player 12, you can adjust and optimize audio and video on the fly to best suit your situation, speaker system and tastes. In this tutorial, we'll cover how to use all of the playback enhancements in Windows Media Player 12 as well as explain a bit about how they work.
To access playback enhancements, you must be in 'Now Playing Mode'. Click the icon in the bottom-right of the Player Library to switch to 'Now Playing Mode'.

Next, right-click anywhere in the Now Playing window and choose Enhancements to see the list of available playback enhancements.

Open the Enhancements window by clicking any of the options on the drop-down menu to the right.

Volume Enhancements & How to Use Them
Windows Media Player 12 has built-in features that help reduce the disparities between loud and soft sounds both between songs and within songs themselves (i.e. normalization). This helps circumvent the annoyance of having a very quiet song followed by a jarringly loud song which is a common occurrence when listening to playlists composed of tracks pulled from various albums and encoded with different parameters. For example, try playing a song off of Neil Young's Harvest from 1972 back-to-back with any song off of Queens of the Stone Age's Songs of the Deaf from 2002 and you'll hear exactly what we're talking about. For an explanation of why recordings are getting louder and louder, check out this article from NPR: The Loudness War.
Your mileage will definitely vary with these playback enhancements depending on your hardware and other factors, but it's a decent step towards getting all of your tunes on a (relatively) level playing field, volume-wise. There are two panes that contain these features: 'Crossfading and auto volume leveling' and Quiet mode. Below, we'll go over all the different volume tweaking enhancements for Windows Media Player 12.
Crossfading - in the Crossfading and auto volume leveling window, click 'Turn on Crossfading' to have Windows Media Player 12 gradually fade out the song at the end and then have the next song on the playlist gradually fade in. Move the slider to the left to shorten the overlap between songs. Move the slider to the right to lengthen the overlap. (On a personal note: I don't particularly like this feature since it will fade songs out before their natural end, meaning you might miss something. So, if you want to hear the songs as the producers intended, skip this feature.)
Auto volume leveling - in the 'Crossfading and auto volume leveling' window, click 'Turn on Auto volume leveling' to have Windows Media Player 12 automatically adjust the volume level between songs to make them more similar. Windows Media Player 12 does so by analyzing the song during playback and then adding the auto volume leveling information after the song has played all the way through (so you won't hear the effects until the next time you play the song).

As a quick sidebar, note that Auto volume leveling only works for Windows Media Audio (WMA) or MP3 files that contain a volume-leveling value. This value is added during encoding, but you can also add it while adding songs to your Player Library. To do so, navigate to the Player Library and click Tools and choose Options. From the Library tab, check 'Add volume leveling information values for new files' under 'Media Library Settings' and click Apply and choose OK. All subsequent WMA and MP3 files added to your Library will now automatically have a volume leveling value added to them, if they don't already have one.

Quiet Mode - a similar feature to 'Auto volume-leveling' is Quiet mode, which has its own window. Quiet mode mellows out the sharp volume changes within a track (rather than between two tracks). This might be handy if you're not quite accustomed to the loud/soft/loud dynamic pioneered by The Pixies and Nirvana (But seriously, man, get with the program. This is the 90s!).
The functionality of quiet mode is pretty straightforward. You can turn it on or turn it off by clicking the text in the upper-left and change between 'medium difference' and 'little difference' with the radio buttons below. Pretty self-explanatory.

There is one caveat, however: your songs must be encoded using the Windows Media Audio 9 or Windows Media Audio 10 Lossless or Professional codec in order for Quiet mode to work. Lossless Windows Media Audio files will appear as '.WMA' files in Windows Explorer.
Bass Boost, Equalizer and Other Sound Shaping Enhancements
Windows Media Player 12 also has a fleet of features that simulate the knob twiddling of a producer in a studio or the various sliders and effects on a stereo system. These can drastically change the dynamics of the songs you are playing in order to optimize the playback according to genre, speaker size and other variables. In this section, we'll cover each of these features one-by-bone.
Graphic Equalizer - by now, we're all familiar with what a graphic equalizer (EQ) does. Windows Media Player 12's graphic equalizer works as you'd expect, allowing you to tweak various sound frequencies as well as choose some presets.
If you don't know what you're doing, your best bet is to choose a preset according to the type of music you're listening to. Click the text in the top-right with the arrow next to it (will likely read Default at first) to see your list of presets. These presets will do their best to optimize the frequencies according to the genre (for example, Rock boosts the highs and lows to accommodate the vocal, drum, bass and guitar-driven music while Speech focuses on the mid-range while easing off the high end, where those hissy s-sounds live). As you'll see, the sliders automatically shift into place when you choose a preset.

Alternately, you can use the custom setting and move the sliders yourself. The preset will automatically kick over to Custom once you start fiddling with the sliders.
There are three ways to move the slider:
-
Move sliders independently - only one slider will move when you click and drag it up or down.
-
Move together in a loose group - moving one slider will cause the sliders on either side to also move up or down to create a wave shape. The loose group setting makes a more arcing curve.
-
Move together in a tight group - moving one slider will cause the sliders on either side to also move up or down to create a more gradual wave. The tight group setting creates a less dramatic arc. In the screenshot, we're using tight mode. Notice the wave created around the slider being moved.

You can move the sliders around in real time to figure out what sounds good. If you've really made a mess of things, click Reset to put everything back to normal.
Note: though there is a voluminous amount of reading out there about EQ settings (most of which is geared towards recording and production), there is no 'best' EQ setting, especially when you factor in differences in hardware and taste. For those who really want to understand the difference between the bands, check out the discriminative frequency training test and this condensed overview of equalization.
SRS Wow Effects - they allow you to enhance the low-frequency (bass) and stereo sound performance (i.e. panning between left and right channels). The options here are pretty straightforward as well.
Move the TruBass slider to the left to reduce the low-frequency effect and move it to the right to boost the low-frequency sounds.
Move the WOW Effect slider to the left to decrease the stereo sound performance and move it to the right to increase it. This enhancement creates more of a "surround sound" effect.
Lastly, you can have SRS Wow optimize for your speaker type by clicking the text in the top-left with the arrow next to it. Choose from Normal speakers, Headphones or Large speakers.
You can enhance low-frequency and stereo sound performance by turning on SRS WOW effects.

The only issue with SRS WOW effects is that they cannot be applied to DVD playback.
Dolby Digital Settings - these settings are similar to the speaker type setting in the SRS Wow effects. However, these settings only affect Dolby Digital content (for example, many DVDs have Dolby Digital sound, such as the Star Wars prequels). In this menu, you can choose from three different presets:
-
Normal - reduces entire range of Dolby Digital for quieter playback.
-
Night - boosts dialogue while toning down other sounds. Good for laptops.
-
Theater - increases dynamic range of all sounds for more dramatic differences between soft and loud sounds and a fuller listening experience. Good for home theater systems.

Choose your option to activate it. Click Reset to return the settings to normal.
Other Playback Enhancements for Audio & Video
Additionally, Windows Media Player 12 lets you change the playback speed of audio and video files as well as tweak the colors and zoom level of videos. In this section, we'll show you how to use these two features.
Play Speed Settings - adjusting the Play speed lets you find a certain part within a song or video or simply slow down a file for greater analysis or speed it up for comic effect (why else would you do this?). There are a few different ways to do this.
You can fast-forward a file by clicking and holding the Next button until the song begins fast-forwarding. Release the button resume normal playback.
Rewind a file by clicking and holding the Previous button until the song begins rewinding. Release to resume normal playback. (Note: Rewinding only applies to video files).

You can change the Play speed from the Enhancements menu as well. The slider begins at 1.0, which is normal playback. Moving the slider to 0.5 plays at half speed. Moving to a negative number plays the file in reverse. Moving the slider to a number greater than 1.0 speeds up playback. Check the Snap slider to common speeds button to quickly select such speeds as half speed, double speed, etc. You can also choose common speeds by clicking Slow, Normal or Fast in the top-left.
Also, you can advance or reverse one frame at a time by clicking the arrows at the bottom. This only applies to supported video files.

Video Settings - lastly, Windows Media Player 12 also allows you to tweak the hue, brightness, contrast and saturation and zoom settings during video playback. Drag the sliders to the left and right to adjust the settings. For these features, a picture is worth a thousand words - so check out Microsoft's demonstration of these video settings over at Microsoft.com.

There are also some self-explanatory video zoom settings which can be accessed by clicking the text in the upper-left. You can also quickly zoom to 50% by pressing ALT-1, 100% by pressing ALT-2 and 200% by pressing ALT-3.

Alternately, you can right-click the Now Playing window during playback and select Video to choose the zoom settings.

Conclusion
As you can see, Windows Media Player 12 is not only a versatile player for all types of audio and video files, it is also a full featured playback enhancer. We encourage you to fiddle around with the various settings and discover what sounds best to your ear with your setup. Remember: You can always click Reset to return to normal, so there's nothing to lose.















