Windows 10では、管理者としてプログラムを実行する方法を知ることが非常に重要です。既定では、 Windows 10の(Windows 10)アプリとゲーム(apps and games)は、システムへの不正な変更を防ぐために、管理者のアクセス許可なしで実行されます。ただし、一部のプログラムでは、正しく機能したり、特定のコマンドを実行したりするために管理者権限が必要な場合があります。Windows 10は、何も無効にすることなく、管理者としてプログラムを実行する機能を提供します。Windows10のデスクトップアプリで「管理者として実行」("Run as administrator")を使用するすべての方法は次のとおりです。
まず(First)最初に:UACと(UAC and Run)管理者として実行について
Windowsの初期のバージョンでは、アプリケーションにはシステム全体の特権があり、これはセキュリティ上のリスク(security risk)でした。Windows10を含む(Windows 10)WindowsVista以降のすべてのMicrosoftのオペレーティングシステムには、UACまたはユーザーアカウント制御(User Account Control)が含まれています。これは、オペレーティングシステム(operating system)への不正な変更を防ぐセキュリティ機能(security feature)です。管理者としてアプリケーションを実行しようとすることは、管理者権限を必要とする変更の1つです。選択したプログラムが起動する前に、UACプロンプトがトリガーされ、許可を求められます。管理者権限のないアカウントからアプリケーションを実行する場合、UACプロンプトでは、(UAC)管理者パスワード(administrator password)の入力を求められます。管理者パスワード(admin password)がないと、プログラムは起動しません。

Windows 10では、デスクトップアプリの場合にのみ、管理者権限でプログラムを実行できます。セキュリティソフトウェア(security software)など、これらのアプリケーションの一部は、管理者権限がないと正しく実行できません。Microsoft Storeからインストールされた(Microsoft Store)Windowsアプリは、 Windows10の管理者権限で実行することはできません。さらに、通常のユーザーアカウント(user account)と同じレベルのアクセス許可を持っているため、システムの詳細設定やWindowsレジストリ(Windows Registry)を変更することはできません。
デスクトップアプリとUWPアプリ(desktop apps and UWP apps)の違いについて詳しく学び、 「 Windowsアプリ(Windows app)とは」を読むことで、「管理者として実行」("Run as administrator")できるアプリを見つけることができます。デスクトップアプリ(desktop app)やプログラムとどう違うのですか?
1.スタートメニュー(Start Menu)のショートカットまたはタイルのコンテキストメニューから管理者としてプログラムを実行します
Windows 10では、スタートメニュー(Start Menu)ショートカットのコンテキストメニューを使用して、管理者権限でプログラムを起動できます。まず、スタートメニュー(Start Menu)を開きます。次に、起動するプログラムのショートカットを[すべてのアプリ(All apps)]リストで見つけ、右クリックまたは長押ししてコンテキストメニューを開きます。[その他]オプションを(More)クリック(Click)、タップ、またはカーソルを合わせてから、[管理者として実行("Run as administrator)]をクリックまたはタップします(")。
![ショートカットのコンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行]を選択します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-XtkK6XVFTmw/YjdUYwbk49I/AAAAAAAAyws/ab8zwZfSsRsabvk2wXQyYPngQ6psXkqFQCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhwXhoxRfnCMzWoHOZ2642jZ_nuj0EzODXF5t1Q7BvL6a7rrN0krzmheUzsmY-MFPIvNElQtdb00p33blXdN7JKeWt40N8Z0Vjt0E5MzyV5q3K7ry34pqpX8okL7_Y21dPg0-ZjOB9BNW7cIeN7NeCNqh7dU4NQvftqlAepEp8qUf80-MONtpq3m9Tz54R59CdV0sSzvnmgh58TofhWiCd-3XY6S45gXs9apEd7wD9e7eQRv-OlfefiD1J7nhsO-VNpIePZXuYt8wH91-7xNeqMUsNvU8riJ4kEeaOdNAmzHs2vMofp2hexnesEIn4hQ49RORjmXR1EllxdTXA-_mnNBIqgBmt5sVi3ma-ytXDvYiGIu86LJm_BC3FpwKW6cZcBvMvhHvy8-0WwbqbpsqXyJZ5YLV2dWHiLbyifFEMd2GK8QlsVqaUZMn4nvXUyhp57e8xJd31k1YO35UcfL9WGPPd7j_bA0i0uYnC7fJa64Ibqw2Ap1gC7pmjiDzLiwvrkOm49a_jHa1qL7wtyHlrwJwnCAg1GXbJE3SP1tqSPSRxAvQRhkBLcZef3d-lfmexy1KCeGwg7Vp2gvonUpPrdxWONogD5_RueQHuhrQ9djY0v663ay1mkH7t7DID1nzRqWKoC8qdPME3pZMOTl3ZEG/s0/Ze80yec_slLXdIET3E-kXDIB_Ls.png)
デスクトップアプリ(desktop app)のタイルを[スタート]メニュー(Start Menu)で使用できる場合は、そのタイルを右クリックまたは長押しして、コンテキストメニューを開きます。[その他(More)]にアクセスし、[管理者として実行("Run as administrator)]をクリックまたはタップします(")。
2.スタートメニュー(Start Menu)のショートカットまたはタイルで「 Ctrl + Shift + Click」を使用して管理者として実行します(Run)
スタートメニュー(Start Menu)を開き、管理者として起動するプログラムのショートカットを見つけます。キーボードのCtrl(Ctrl)キーとShiftキーの両方を押したまま、そのプログラムのショートカットをクリックまたはタップします。

アプリのスタートメニュー(Start Menu)タイルで"Ctrl + Shift + Click/Tap"Windows10の管理者権限でアプリを実行することもできます。
テスト中、この方法は毎回機能するわけではなかったため、その場合は、再試行するか、別の方法で管理者としてアプリを実行することを検討してください。
3.デスクトップショートカットから管理者としてプログラムを実行します(desktop shortcut)
管理者として実行するプログラムのデスクトップショートカット(desktop shortcut)を見つけるか、自分で作成します。次に、右クリックまたは長押ししてコンテキストメニューを開きます。[管理者として実行("Run as administrator")]オプションをクリック(Click)またはタップします。
![コンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行]を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-BQqaV0nVQns/YjczEyYe58I/AAAAAAAAHV8/5iXp75eG9pAuE1wbdvGOJ3B2Y9hlkXDYgCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxqHo63eC-w2z6yviSn9DYRDJuWMKm_sPX6g-BI1OEFwv6L01SgCY8x7NMPafCADWrqG-5bpVDJ9v1dX5VJUMKLtB4dJOAcVJsEhFbbXtL-XEojuNI5AruC6OEcs4cjQnBRmHxiidG_bT2PUln-JyMDeM9aSWLAKSXNGv7-yc7yQmIvhyUYhbDkEh81nfEAWmrpABM29e2_Sw9E50aw52PTBbSFGr-9f2F_zVQ6X8hhfsueD2Q3TAAeasc4-YpuzFdw2-e8Er4zY_PbIim0s6V3-GMF_pNVuXyk43N0cVPAQ4d5EcEKzOSQZl94Dd4hs_80k2TqFQdbSNhpq9D9NQyskK8FU-cfokIaFU0zhsWLLuGZVsuH1NRNGn4YNiKEV3QCAPqc9kzi1dPCRqXGd--4GOATbeSeKcQVgEuAwUTG5knE2W6mc6eg3LAB05feSMp5RK6QTKY72osxAAWsYKriaD-cjcVT3-YNVM5UanAfvczKJd_aCqsMi7kY2O-rOOq_hTYACxmVLcoKulU2T9PDKqZObOmLUWvpw1LFqfbIcIgdTfhTJx2pOU5yBgXu92TP53dU475DxGW5MnLmd0KwZo4qU3vaO3OQOutgpXWW1yHWLDsgvUWG4wybPqFh4idUvTQRR786lrgNYjAwl6DdkQY/s0/NBjGOb1oYoV6mA-7KUKX8vwNgno.png)
4.タスクバー(taskbar shortcut)のショートカットから管理者としてデスクトップアプリを実行します(desktop app)
Windows 10では、タスクバーのショートカット(taskbar shortcut)から管理者権限でデスクトップアプリ(desktop app)を実行することもできます。ショートカットを右クリックまたは長押ししてから、プログラム名をもう一度右クリックまたは長押しします。(right-click or press-and-hold)次に、開いたメニューから[管理者として実行("Run as administrator)]を選択します。

アプリのタスクバーショートカットで(taskbar shortcut)"Ctrl + Shift + Click/Tap"Windows10の管理者権限でアプリを実行することもできます。
5.右クリックメニューから管理者としてプログラムを実行します
見つけるのは簡単ですが、Windows10で管理者としてプログラムを実行する方法はショートカットだけではありません。メインの実行可能ファイルのコンテキストメニューから同じアクションを実行できます。
ファイルエクスプローラーを開き、(Open File Explorer)デスクトップアプリ(desktop app)の実行可能ファイルを見つけます。右クリックまたは長押ししてコンテキストメニューを開き、[管理者として実行]をクリックまたはタップし("Run as administrator)ます(")。
![[管理者として実行]をクリックまたはタップします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-ozqFiz8z0Dw/YjckZQKjw6I/AAAAAAAAphw/BHldylevQqEUcTzM0NX05X121p6u-rsxwCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhx6X5i_8Az7IZXV3nb-PxX1CSUHSFmSc6oq9vMrVLAbkuNkObNOx3wv8obBV9AhzeiTlD78bCwmRvOTWK6NxsO3KVaKRhu0GcC2-gQqplQ4oq48y5ES2OxM57FQOPj7TTSh85yzCb1G0Jvfmg0dRTuWcf1hBXCZJClrDNE2tqRNmjUClvACg8pnm2lMUeUV9sRv-61UT4BFvPub4bkJRzhSZo-lIQf88tdgqR4NXC36JYfvFUVcdYifCuvaIBbuDlAvnDamnMayhUWKLv_r_ZD_R93UUSIupOOtPlKpzEKe_McqWU4WCD0Y7Z8MXIGmAUamlCPkmmPnhPKy8s8rmW4CqRIKN8W29cYUdLYZ9ZXaF9u6ttm7UKPEztnyVUX0dxFBv8wLKPJI3GdgQ_CZCSkMpF3L8H6yXYHlCJjxk5Zv6OwC_viVRMRaodnvZv1masoT0jn1nct-tqNkGPdTVoOY3dJ8jiLz-F5-8FtIxNDMtNqEkD0lXuwR7iAdsGlTn9t2ZXQgB2WWLJS1z1BaE5HUh0k4y7Ih1Nn8Vff5um66JDZaSmxdUNtWVQZBdG8e05deeWdbRTEB01NVcNrlB_JirUo3wudC4080_bI5DDRtDgmwuUp8mbcIDP3XsJznVtAzUJ4DhTILjuGVMJ3Q3JEG/s0/hlOZ8X-Zm1w0NOolpvsbPNEdMyM.png)
6.ファイルエクスプローラー(File Explorer)のリボンから「管理者として実行」を使用します(Run)
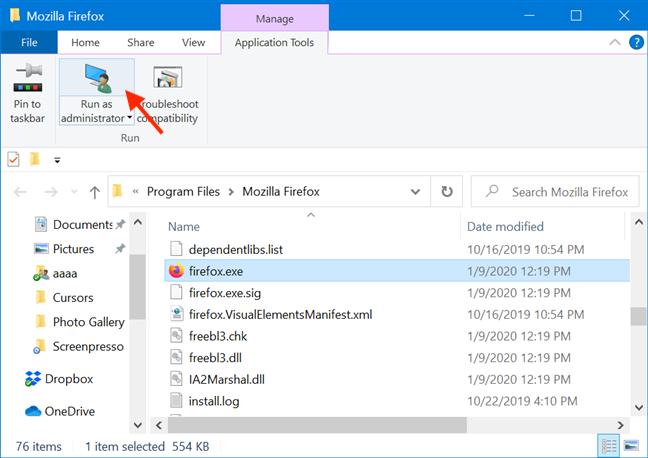
ファイルエクスプローラー(File Explorer)でプログラムのメインの実行可能ファイルを見つけます。それを選択し、リボンから[管理(Manage)]タブをクリックまたはタップします。

必要なオプションは、アプリケーションツールの[(Application Tools)実行(Run)]セクションに表示されます。[管理者として実行("Run as administrator")]ボタンの上半分をクリック(Click)またはタップして、選択したアプリに管理者(app admin)権限を付与します。
![[管理者として実行]ボタンの上半分を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-mJi8SB_gRjc/Yjb8LT3HEsI/AAAAAAAAhY8/v2cWJ5nNLW4isjRkpS2pBAARqGgE5eM2gCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwW0CBk7YkolKRhlb6URWa_IgJhlV6Uh5HTXSA46rtPZTzcTVDH5E3Inr1300PCuFmPfzlhV9-wZ0cgm5eyq7ZHFxRZXVbHy0npWVZFQ1PONMxdTopZNqunXwLBLiLb67ib1SygjFUxfYmkgsM2KWbfxsJ0dJUmw1O8_eCdFnl3uawCEzgsMAIg1Qc5NZzeL_r4wLfEjXahBctYEmz8PuHb0PPtvGp-r6YtKLJySOhlKEvT2KQlPP_m8uuAu4nd9hM73lCbqdlSPO8Zq50PdX0wx8st7wB0bPkCKfKneQLRTuZCoubxrSAYYcR0TPzO_mZA9q14hTQoKUUP0yEF1F69JKIE4VMhscEvH2o_SFK7IDwFOJoGP2ZHxPnq1oEr-THgN0QuqzqlZwBKlRjYLmCuyWmtQEJcFb0y83vg4HNMcHMnH4lEEvT9qrp3Mqtom7UIrB2jajclGsNQdwU2a7PVl9MgQ1x74JGCA2gUeIiNlJDd9HgeDJzjAFR5NnV04Ho1gVSVvXEJNT-wQ-v1MGrgxZvOE1OzaWw9ezHrC91jfyv8d8BV4tQ7x9Ll0_Vn7OfNGviasNi0v1rdTERPCA9bQI_7ffue7P4Pk2Q2IPY6_4g-aCGST5HqVmLuxaNKxzTo79CRHjCziNyRBg/s0/5HhYZ4BHkuvNldqCV5h9PQLE0hA.png)
別の方法として、[管理者として実行("Run as administrator")]ボタンの下半分を押してから、ドロップダウンメニューから[管理者として実行("Run as administrator")]オプションをクリックまたはタップすることもできます。
![ドロップダウンメニューから[管理者として実行]を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-yaYEBHvMcG8/YjdcfLvhkCI/AAAAAAAAQFA/aassN2BUgjwxp7NKdqK3QpSuFWtE4yeHwCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhyU0JW91iiU4HdUNyWpEBsKLTw-6rQ88JJcf3GF8lMk7uR2vURQvSrLKx3HPJ-0bFTSQRDYtFiF0xXMnzMqjkeinj0p4_6R1kO7c7YxY5qQhApZ0W4keaxtQNkUgY3tkRT5-ypFY9VCwWOdWlQjQXqnqqmUhUOHojDHDyRxOdzXgn83uL9cUhyZQAyqoLNXwTuyPI3w7jMVLY_X3G_jMusEXoZHkAYQKZqBgUhPxBxFlPwhH-2DdZDXsVjKZqfavx4quKoI8Dn5vbKBw1fBP2LP-TMONu3R7eOkf34NH9fhPJJ8dtB0a9Nr9Lbun4wsDt2UkPoVWdXK-T5WEyqL8jtJIZzuNmeYS32rgbNJxt2MkVJe0ECNAjwjXY1oCKwCAja-lwWv2MG2WdS5jNcBqq8uNpsf5TXfjQaewupijbNsp_viGHOdMXhU68bv9CYzh3Jg897TZj113lNc9x2yiPm9ZLpb68caNxrHKk6kQvdPMHMRzJzCFsHGdrcsGW8UUQ6Ht3UrJUSKHvNnPH9C-EavJf8LBHVfter4gT7dO0uaIhreDldhomF7fI1DE1HmW7QFlecOcn2MqpmjESsYDZlEqVL_O7bu6l5iDcDGvhsDH0Fhqz9rIOYRCpkWkIV1yugxhdBnKN3LY3H2ntww_uXdkQY/s0/XNwXY3Gy20kKXE_J3jvn2sQc8VA.png)
7.検索ウィンドウ(Search window)から管理者としてデスクトップアプリを実行します(desktop app)
タスクバーの検索フィールド(taskbar search field)に、管理者権限で実行する必要のあるプログラムの名前を入力します。次に、検索(Search)ウィンドウの右側に表示される[管理者として実行]オプションを("Run as administrator")クリックまたはタップ(click or tap)します。

明らかに、管理者としてアプリを実行する許可を求めるUACプロンプトが表示されたら、[(UAC prompt)はい]を(Yes)クリックまたはタップ(click or tap) します。
8.タスクバーの検索結果で「 (taskbar search result)Ctrl + Shift + Enter」を使用して、管理者としてプログラムを実行します
タスクバーの検索フィールド(search field)にプログラムの名前を入力します。複数の結果がある場合は、キーボードの矢印キーを使用して、管理者として実行するプログラムを強調表示します。Ctrl + Shift + Enterキーを同時に押します。

9.[実行]ウィンドウから管理者としてプログラムを実行します(Run window)
[実行]ウィンドウを(Run window and type)開き、管理者として実行するプログラムの実行可能ファイルの名前を入力します。次に、キーボードのCtrlキーとShiftキーを押しながら、[ OK ]をクリック(keyboard and click)またはタップします。

または、プログラムのメイン実行可能ファイルの名前を入力した後、キーボードのCtrl + Shift + Enterキーを同時に押します。

10.タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)から管理者として実行します(Run)
Windows 10で管理者としてプログラムを起動する別の方法は、タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)を使用してプログラムを起動することです。開始するには、タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)を開きます。次に、コンパクトビューで開いた場合は、 [詳細]ボタンを(More details)クリックまたはタップ(click or tap)します。

展開されたタスクマネージャで、 (Task Manager)[ファイル(File)]メニューを開き、 [新しいタスクの実行("Run new task)]をクリックまたはタップします(")。
![[ファイル]メニューから[新しいタスクの実行]にアクセスします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-owHcxTDD8Ps/YjdXqU3VsBI/AAAAAAAAxN8/5Zw4l3lMrMc3aVlYeZQpfjwCMpyPmuA0QCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCe4d2RBg/s0/U0FTfuDPv9BHR4xBnEn9pA5M7wo.png)
これにより、[新しいタスクの作成]("Create new task")ウィンドウが開きます。[開く(Open)]フィールドを使用して、管理者として起動するプログラムへのパスを入力するか、[参照(Browse)]をクリックまたはタップしてそのプログラムに移動できます。次に、 「管理者権限でこのタスクを作成("Create this task with administrative privileges.")する」を必ず確認してください。オプションをクリックするか、[ OK(OK) ]をタップします。
![[OK]をクリックする前に、必ずチェックボックスをオンにしてください](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-vvbh5W7PZkI/YjcFU0DZjUI/AAAAAAAAm4I/vyXFLYM4SkUPQHqzDxxbios60DHKJdZtACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCRz9yRBg/s0/5VrJR5fOsVRGi7DWsrWYc4Ho6o0.png)
ヒント:(TIP:)この方法を使用して管理者としてプログラムを起動する利点は、プロセスのUAC部分をスキップできることです。これは、アプリがタスクマネージャー(Task Manager)のアクセス許可(この場合は管理者アクセス許可)を自動的に継承するためです。上記のように、チェックボックスをオンにしてオプションを有効にするだけです。デバイスに対する標準のユーザー権限しかない場合、このオプションはありません。

11.コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)(CMD)またはPowerShellの(PowerShell)RunAsコマンド(RunAs command)を使用して、管理者としてデスクトップアプリを実行します(desktop app)
コマンドライン(command line)がコンピューターに必要な処理を実行するように要求するお気に入りの方法である場合は、コマンドプロンプトまたはPowerShellにアクセス(access Command Prompt or PowerShell)して、管理者としてプログラムを実行することもできます。CMDまたはPowerShellウィンドウ(CMD or PowerShell window)で次のコマンドを入力し、ニーズに合わせて調整します。
runas / user: " your_computer_name\"(administrator_name") " C:\path\program.exe "
your_computer_nameをコンピューターの名前に、administrator_name(your_computer_name)をシステムの管理者であるユーザーアカウントの名前に、C (administrator_name):(user account) pathprogram.exeC:\path\program.exe管理者として実行するプログラムへの完全なパスに置き換えます。
下の画像に示すように、コマンドを正しく入力すると、管理者のパスワードも入力するように求められます。次に、キーボードのEnterキー(Enter)をもう一度押します。

ヒント:(TIP:)この方法を使用して管理者としてプログラムを起動するには、プロセスのUAC部分をスキップします。
12.常に管理者権限でプログラムを実行します
定期的にアクセスするデスクトップアプリ(desktop apps)で上記の方法を常に使用する必要がないように、プログラムを常に管理者権限で実行するように設定できます。
まず、ファイルエクスプローラー(File Explorer)を開き、実行するプログラムのメインの実行可能ファイルを見つけます。右クリックまたは長押し(Right-click or press)して、コンテキストメニューを開きます。次に、 [プロパティ]をクリックまたはタップ(click or tap)します(Properties)。

[プロパティ(Properties)]ウィンドウで、 [互換性(Compatibility)]タブに移動します。ウィンドウの下部にある[このプログラムを管理者として実行する]オプションの横にあるチェックボックスをオンにして、[("Run this program as an administrator")適用(Apply)]または[ OK ]をクリックまたはタップします。

この設定が適用され、今後、プログラムは常に管理者権限で実行されます。オプションを無効にする場合は、同じ手順に従います。プログラムのショートカットのプロパティ(Properties)を編集して、メインの実行可能ファイルが改ざんされないようにすることもできます。開始するには、プログラムのショートカットを右クリックまたは長押ししてコンテキストメニューにアクセスし、[プロパティ]をクリックまたはタップ(click or tap)します(Properties)。

次に、ショートカットの[プロパティ(Properties)]ウィンドウで、[ショートカット(Shortcut)]タブを選択します。[詳細(Advanced)]ボタンをクリックまたはタップして、[詳細プロパティ(Advanced Properties)]を開きます。
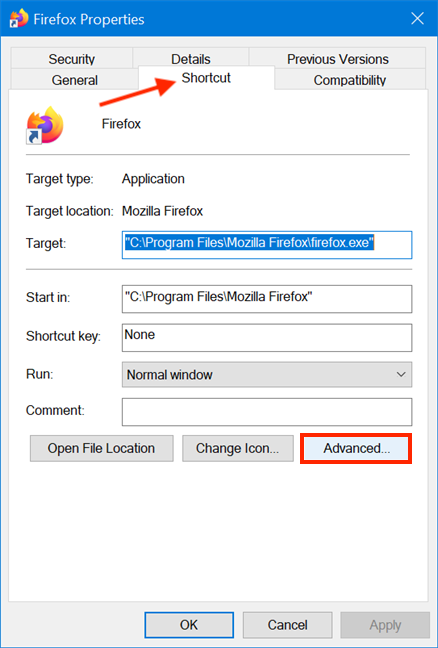
[詳細プロパティ]ウィンドウで、[(Advanced Properties)管理者として実行("Run as administrator")]の横のチェックボックスをオンにして、[ OK ]をクリックまたはタップします。
![チェックボックスをオンにして、[OK]を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-D3Ydty0tJC8/Yjc0ZGrI6pI/AAAAAAAAu4k/THjGaTIEgDkw0sCSdc-118LyoM6YzuL8wCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhxcrfjNL0kpApMdsYcrhR6ibP9yFPgid8tif1XJf590Y_S6I5KKOmSt3l5FGY4xSNyvZdonIyhAy17tqtmX612OyJ04O3L0FlnNcNc0C54eOcYAIPck3FI_krYDif6TAC-yzKxFLqijseiFajZsn5zZb5ikZDEoD98WADPb77Q8xJjOH9YzrQe3CB3fICtjnubLwJfl_5qf96x98EvSIMovAxNksn1luuo0L_dnicCPkBgBf5wN0-gtGg1mLEXM8O7RQ9uZx49lRm7ceAFzzMt_6Cq2w-eXXuubN_kNKoT7juKeFa2-L0zW6YGXdHX_H-uPut3z-kosp-leDwO3y29zBsAOH0aOENAJ-JGeAnRJ7TKv4t2I6l2cfc-lF9kRTKX6aYwsM79CQqNoNt61sae4bD0zEcPXA9px0izvU6TWFBY_0eJV8U_jRs_hFuQGd3mv42XGA9AF9USp0pq4reDvfzEUbUScBDJxV2FH0gc74fjQOnfl4a2FntrUFG4TIrLZdM1piJaWyZ1PgX8v43nHC1Hi9uMmXsWiYFo5NX1MHFRWVJnhLyCAzaIwxq_hg3o27aMIgAeS-fQ5cwlLgvZliezsqr04t33qG12AvR8NX8glkuNvFAGVed6Q_NgxRGKhvGXPVRSd4G8WMKGg3ZEG/s0/QvYvlvqL2mOSZeITMvX61dmmftU.png)
最後に、 [プロパティ]ウィンドウに戻ります。ここで、[ (Properties)OK ]または[適用(Apply)]をクリックまたはタップする必要があります。これで完了です。
![[OK]または[適用]を押して変更を保存します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-cVRk0GdyutU/YjdPLS3zYiI/AAAAAAAAy10/sTaSpkejr48QC77ibJJqQFyE5mgqv9VVgCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhwXhoxRfnCMzWoHOZ2642jZ_nuj0EzODXF5t1Q7BvL6a7rrN0krzmheUzsmY-MFPIvNElQtdb00p33blXdN7JKeWt40N8Z0Vjt0E5MzyV5q3K7ry34pqpX8okL7_Y21dPg0-ZjOB9BNW7cIeN7NeCNqh7dU4NQvftqlAepEp8qUf80-MONtpq3m9Tz54R59CdV0sSzvnmgh58TofhWiCd-3XY6S45gXs9apEd7wD9e7eQRv-OlfefiD1J7nhsO-VNpIePZXuYt8wH91-7xNeqMUsNvU8riJ4kEeaOdNAmzHs2vMofp2hexnesEIn4hQ49RORjmXR1EllxdTXA-_mnNBIqgBmt5sVi3ma-ytXDvYiGIu86LJm_BC3FpwKW6cZcBvMvhHvy8-0WwbqbpsqXyJZ5YLV2dWHiLbyifFEMd2GK8QlsVqaUZMn4nvXUyhp57e8xJd31k1YO35UcfL9WGPPd7j_bA0i0uYnC7fJa64Ibqw2Ap1gC7pmjiDzLiwvrkOm49a_jHa1qL7wtyHlrwJwnCAg1GXbJE3SP1tqSPSRxAvQRhkBLcZef3d-lfmexy1KCeGwg7Vp2gvonUpPrdxWONogD5_RueQHuhrQ9djY0v663ay1mkH7t7DID1nzRqWKoC8qdPME3pZMOPl3ZEG/s0/Y9CImTSGDcItlJ7K3RbcgVrR7z4.png)
設定が適用され、同じショートカットを使用してプログラムを開く限り、プログラムは管理者権限で動作します。このセクションの方法を使用すると、アプリを起動しようとするとすぐにUACからプロンプトが表示されます。(UAC)
13.管理者権限を持ち、UACプロンプトなしでプログラムを実行します(UAC prompt)
タスクスケジューラ(Task Scheduler)を使用すると、 UAC(ユーザーアカウント制御)(UAC (User Account Control))によって毎回プロンプトが表示されることなく、管理者としてプログラムを実行できます。これは単純であり、 UAC(UAC)を無効にする必要がないため、 Windows10のセキュリティが損なわれます。詳細なステップバイステップガイド(step guide)をまとめました。Windowsタスクスケジューラ(Windows Task Scheduler)を使用して、UACプロンプトと管理者権限なしでアプリを実行します。
どの方法を使用する予定ですか?
Windows 10では、古いバージョンのWindowsよりも、管理者権限で実行する必要のあるアプリが少なくなっています。ただし、いくつかの正当なプログラムは依然として昇格された特権を必要とします。覚えておくべき主なことは、管理者アカウント(administrator account)でログインしている場合でも、アプリを標準ユーザーとして定期的に実行しているということです。つまり、管理者権限が必要なプログラムを実行する必要がある場合は、上記のいずれかの方法を使用して、UACプロンプトで承認することができます。示されている方法のどれ(Which)を使用する予定ですか?あなた(Did)はすでにそれらのいくつかを使用しましたか?コメントで教えてください。
13 ways to use "Run as administrator" in Windows 10 -
In Windows 10, knowing how to run programs as adminіstrator is νеry important. By default, apps and games in Windows 10 run without administrator permissions, to prevent unauthоrized chаnges to your system. However, there are times when some programs require administrator permiѕsions to work propеrly or to run specific commands. Windows 10 offers you the ability to run programs as admin without having to disable anything. Here are all the methods to use "Run as administrator" on any desktop app in Windows 10:
First things first: About UAC and Run as administrator
In early versions of Windows, applications had system-wide privileges, which was a security risk. All of Microsoft's operating systems from Windows Vista onward, including Windows 10, include UAC or User Account Control, a security feature that prevents unauthorized changes to the operating system. Trying to run an application as administrator is one of the changes that require administrative privileges. Before the selected program is launched, a UAC prompt is triggered, asking for permission. If you run the application from an account without administrator permissions, the UAC prompt asks you to enter an administrator password. Without the admin password, the program does not launch.

In Windows 10, you can only run a program with administrator permissions if it is a desktop app. Some of these applications, like security software, cannot run correctly without having administrative permissions. Windows apps that are installed from the Microsoft Store cannot be run with administrative privileges in Windows 10. Furthermore, they have the same level of permissions as a normal user account, so they are not allowed to make changes to advanced system settings or the Windows Registry.
You can learn more about the difference between desktop apps and UWP apps and figure out which ones you can "Run as administrator" by reading What is a Windows app? How is it different from a desktop app or a program?.
1. Run a program as admin from the contextual menu of its Start Menu shortcut or tile
In Windows 10, you can launch a program with administrative permissions by using the contextual menu of its Start Menu shortcut. First, open the Start Menu. Then, find the shortcut of the program you want to launch in the All apps list, and right-click or press-and-hold on it to open a contextual menu. Click, tap, or hover over the More option, and then click or tap on "Run as administrator."

If you have a tile for your desktop app available in the Start Menu, right-click or press-and-hold on it to open a contextual menu. Access More and then click or tap on "Run as administrator."
2. Run as administrator using "Ctrl + Shift + Click" on its Start Menu shortcut or tile
Open the Start Menu and locate the shortcut of the program you want to launch as administrator. Hold down both the Ctrl and the Shift keys on your keyboard and then click or tap on that program's shortcut.

You can also use the "Ctrl + Shift + Click/Tap" shortcut on an app's Start Menu tile to run it with administrator permissions in Windows 10.
During our tests, this method did not work every time, so if that is the case for you, either try again or consider running the app as administrator another way.
3. Run a program as administrator from its desktop shortcut
Find the desktop shortcut for the program you want to run as admin or create one yourself. Then, right-click or press-and-hold on it to open a contextual menu. Click or tap on the "Run as administrator" option.

4. Run a desktop app as administrator from its taskbar shortcut
In Windows 10, you can also run a desktop app with administrator permissions from its taskbar shortcut. Right-click or press-and-hold on the shortcut, and then right-click or press-and-hold again on the program's name. Then, from the menu that opens, choose "Run as administrator."

You can also use the "Ctrl + Shift + Click/Tap" shortcut on an app's taskbar shortcut to run it with administrator permissions in Windows 10.
5. Run a program as administrator from its right-click menu
Although easier to find, shortcuts are not the only way to run a program as administrator in Windows 10. You can perform the same action from the main executable file's contextual menu.
Open File Explorer and find the desktop app's executable. Right-click or press-and-hold on it to open the contextual menu, and then click or tap on "Run as administrator."

6. Use "Run as administrator" from File Explorer's ribbon
Find the program's main executable in File Explorer. Select it, and then click or tap on the Manage tab from the ribbon.

The option you need is displayed in the Run section of Application Tools. Click or tap on the upper half of the "Run as administrator" button to give the selected app admin permissions.
As an alternative, you can also press the lower half of the "Run as administrator" button and then click or tap on the "Run as administrator" option from the drop-down menu.

7. Run a desktop app as admin from the Search window
In the taskbar search field, type in the name of the program that needs to run with administrator permissions. Then, click or tap on the "Run as administrator" option displayed on the right side of the Search window.

Obviously, when you see the UAC prompt asking for permission to run the app as admin, click or tap Yes.
8. Run a program as administrator using "Ctrl + Shift + Enter" on its taskbar search result
Type the name of the program in your taskbar's search field. If there are multiple results, use the arrow keys on your keyboard to highlight the program you want to run as administrator. Then, simultaneously press the Ctrl + Shift + Enter keys on your keyboard.

9. Run a program as administrator from the Run window
Open the Run window and type in the name of the executable for the program you want to run as administrator. Then hold down the Ctrl and Shift keys on your keyboard and click or tap on OK.

Alternatively, after typing in the name of the program's main executable, press the Ctrl + Shift + Enter keys on your keyboard at the same time.

10. Run as admin from the Task Manager
Another way to launch a program as administrator in Windows 10 is to start it using the Task Manager. To begin, open the Task Manager. Then, if it opens up in its compact view, click or tap on the More details button.

In the expanded Task Manager, open the File menu and click or tap on "Run new task."

This opens the "Create new task" window. You can use its Open field to enter the path to the program you want to launch as administrator, or you can click or tap on Browse to navigate to it. Then, make sure to check the "Create this task with administrative privileges." option and click or tap on OK.

TIP: An advantage of using this method to launch programs as administrator is that you skip the UAC part of the process. That is because the app automatically inherits the permissions of the Task Manager - in our case, administrator permissions - so all you have to do is check the box to enable the option, as seen above. The option is missing if you only have standard user permissions on the device.

11. Run a desktop app as admin using the RunAs command in Command Prompt (CMD) or PowerShell
If the command line is your favorite way of asking your computer to do what you want, you can also access Command Prompt or PowerShell to run a program as administrator. Enter the following command in the CMD or PowerShell window, adjusting it to fit your needs:
runas /user:"your_computer_name\administrator_name" "C:\path\program.exe"
Replace your_computer_name with your computer's name, administrator_name with the name of a user account that is an administrator on your system, and C:\path\program.exe with the complete path to the program that you want to run as administrator.
As seen in the image below, if you enter the command correctly, you are also asked to enter the administrator's password. Then, press Enter on your keyboard once again.

TIP: Using this method to launch programs as administrators, you skip the UAC part of the process.
12. Always run a program with administrator permissions
To avoid constantly having to use the methods illustrated above on desktop apps accessed on a regular basis, you can set a program to always run with administrator permissions.
First, open File Explorer and find the main executable of the program you want to run. Right-click or press and hold on it to open the contextual menu. Then, click or tap on Properties.

In the Properties window, go to the Compatibility tab. At the bottom of the window, check the box next to the "Run this program as an administrator" option, and then click or tap on Apply or OK.

This setting is applied, and, from now on, the program always runs with administrator permissions. Follow the same steps if you want to disable the option. You can also edit the Properties of a program's shortcut to avoid tampering with its main executable. To begin, right-click or press-and-hold on a program's shortcut to access its contextual menu, and click or tap on Properties.

Then, in the shortcut's Properties window, select the Shortcut tab. Click or tap on the Advanced button to open Advanced Properties.

In the Advanced Properties window, check the box next to "Run as administrator" and then click or tap OK.

Finally, you are returned to the Properties window, where you have to click or tap on OK or Apply, and you are done.

The settings are applied, and your program works with administrative permissions as long as you open it using the same shortcut. When you use the methods in this section, the UAC prompts you as soon as you try to launch the app.
13. Run a program with administrator permissions and without a UAC prompt
Using the Task Scheduler, you can run a program as administrator without being prompted by the UAC (User Account Control) every time. It is simple, and you don't have to disable UAC, thus compromising Windows 10's security. We put together a detailed step by step guide to help you: Use the Windows Task Scheduler to run apps without UAC prompts and admin rights.
Which method(s) do you plan to use?
In Windows 10, there are fewer apps that need to run with administrator permissions than in older versions of Windows. However, a few legitimate programs still require elevated privileges. The main thing to remember is that even if you are logged in with an administrator account, you regularly run apps as a standard user. This means that if you need to run a program that requires administrator permissions, you can just use one of the methods described above and then approve it in the UAC prompt. Which of the method(s) illustrated do you plan to use? Did you already use some of them? Let us know in a comment.

![ショートカットのコンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行]を選択します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-XtkK6XVFTmw/YjdUYwbk49I/AAAAAAAAyws/ab8zwZfSsRsabvk2wXQyYPngQ6psXkqFQCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhwXhoxRfnCMzWoHOZ2642jZ_nuj0EzODXF5t1Q7BvL6a7rrN0krzmheUzsmY-MFPIvNElQtdb00p33blXdN7JKeWt40N8Z0Vjt0E5MzyV5q3K7ry34pqpX8okL7_Y21dPg0-ZjOB9BNW7cIeN7NeCNqh7dU4NQvftqlAepEp8qUf80-MONtpq3m9Tz54R59CdV0sSzvnmgh58TofhWiCd-3XY6S45gXs9apEd7wD9e7eQRv-OlfefiD1J7nhsO-VNpIePZXuYt8wH91-7xNeqMUsNvU8riJ4kEeaOdNAmzHs2vMofp2hexnesEIn4hQ49RORjmXR1EllxdTXA-_mnNBIqgBmt5sVi3ma-ytXDvYiGIu86LJm_BC3FpwKW6cZcBvMvhHvy8-0WwbqbpsqXyJZ5YLV2dWHiLbyifFEMd2GK8QlsVqaUZMn4nvXUyhp57e8xJd31k1YO35UcfL9WGPPd7j_bA0i0uYnC7fJa64Ibqw2Ap1gC7pmjiDzLiwvrkOm49a_jHa1qL7wtyHlrwJwnCAg1GXbJE3SP1tqSPSRxAvQRhkBLcZef3d-lfmexy1KCeGwg7Vp2gvonUpPrdxWONogD5_RueQHuhrQ9djY0v663ay1mkH7t7DID1nzRqWKoC8qdPME3pZMOTl3ZEG/s0/Ze80yec_slLXdIET3E-kXDIB_Ls.png)

![コンテキストメニューから[管理者として実行]を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-BQqaV0nVQns/YjczEyYe58I/AAAAAAAAHV8/5iXp75eG9pAuE1wbdvGOJ3B2Y9hlkXDYgCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxqHo63eC-w2z6yviSn9DYRDJuWMKm_sPX6g-BI1OEFwv6L01SgCY8x7NMPafCADWrqG-5bpVDJ9v1dX5VJUMKLtB4dJOAcVJsEhFbbXtL-XEojuNI5AruC6OEcs4cjQnBRmHxiidG_bT2PUln-JyMDeM9aSWLAKSXNGv7-yc7yQmIvhyUYhbDkEh81nfEAWmrpABM29e2_Sw9E50aw52PTBbSFGr-9f2F_zVQ6X8hhfsueD2Q3TAAeasc4-YpuzFdw2-e8Er4zY_PbIim0s6V3-GMF_pNVuXyk43N0cVPAQ4d5EcEKzOSQZl94Dd4hs_80k2TqFQdbSNhpq9D9NQyskK8FU-cfokIaFU0zhsWLLuGZVsuH1NRNGn4YNiKEV3QCAPqc9kzi1dPCRqXGd--4GOATbeSeKcQVgEuAwUTG5knE2W6mc6eg3LAB05feSMp5RK6QTKY72osxAAWsYKriaD-cjcVT3-YNVM5UanAfvczKJd_aCqsMi7kY2O-rOOq_hTYACxmVLcoKulU2T9PDKqZObOmLUWvpw1LFqfbIcIgdTfhTJx2pOU5yBgXu92TP53dU475DxGW5MnLmd0KwZo4qU3vaO3OQOutgpXWW1yHWLDsgvUWG4wybPqFh4idUvTQRR786lrgNYjAwl6DdkQY/s0/NBjGOb1oYoV6mA-7KUKX8vwNgno.png)

![[管理者として実行]をクリックまたはタップします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-ozqFiz8z0Dw/YjckZQKjw6I/AAAAAAAAphw/BHldylevQqEUcTzM0NX05X121p6u-rsxwCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhx6X5i_8Az7IZXV3nb-PxX1CSUHSFmSc6oq9vMrVLAbkuNkObNOx3wv8obBV9AhzeiTlD78bCwmRvOTWK6NxsO3KVaKRhu0GcC2-gQqplQ4oq48y5ES2OxM57FQOPj7TTSh85yzCb1G0Jvfmg0dRTuWcf1hBXCZJClrDNE2tqRNmjUClvACg8pnm2lMUeUV9sRv-61UT4BFvPub4bkJRzhSZo-lIQf88tdgqR4NXC36JYfvFUVcdYifCuvaIBbuDlAvnDamnMayhUWKLv_r_ZD_R93UUSIupOOtPlKpzEKe_McqWU4WCD0Y7Z8MXIGmAUamlCPkmmPnhPKy8s8rmW4CqRIKN8W29cYUdLYZ9ZXaF9u6ttm7UKPEztnyVUX0dxFBv8wLKPJI3GdgQ_CZCSkMpF3L8H6yXYHlCJjxk5Zv6OwC_viVRMRaodnvZv1masoT0jn1nct-tqNkGPdTVoOY3dJ8jiLz-F5-8FtIxNDMtNqEkD0lXuwR7iAdsGlTn9t2ZXQgB2WWLJS1z1BaE5HUh0k4y7Ih1Nn8Vff5um66JDZaSmxdUNtWVQZBdG8e05deeWdbRTEB01NVcNrlB_JirUo3wudC4080_bI5DDRtDgmwuUp8mbcIDP3XsJznVtAzUJ4DhTILjuGVMJ3Q3JEG/s0/hlOZ8X-Zm1w0NOolpvsbPNEdMyM.png)

![[管理者として実行]ボタンの上半分を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-mJi8SB_gRjc/Yjb8LT3HEsI/AAAAAAAAhY8/v2cWJ5nNLW4isjRkpS2pBAARqGgE5eM2gCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwW0CBk7YkolKRhlb6URWa_IgJhlV6Uh5HTXSA46rtPZTzcTVDH5E3Inr1300PCuFmPfzlhV9-wZ0cgm5eyq7ZHFxRZXVbHy0npWVZFQ1PONMxdTopZNqunXwLBLiLb67ib1SygjFUxfYmkgsM2KWbfxsJ0dJUmw1O8_eCdFnl3uawCEzgsMAIg1Qc5NZzeL_r4wLfEjXahBctYEmz8PuHb0PPtvGp-r6YtKLJySOhlKEvT2KQlPP_m8uuAu4nd9hM73lCbqdlSPO8Zq50PdX0wx8st7wB0bPkCKfKneQLRTuZCoubxrSAYYcR0TPzO_mZA9q14hTQoKUUP0yEF1F69JKIE4VMhscEvH2o_SFK7IDwFOJoGP2ZHxPnq1oEr-THgN0QuqzqlZwBKlRjYLmCuyWmtQEJcFb0y83vg4HNMcHMnH4lEEvT9qrp3Mqtom7UIrB2jajclGsNQdwU2a7PVl9MgQ1x74JGCA2gUeIiNlJDd9HgeDJzjAFR5NnV04Ho1gVSVvXEJNT-wQ-v1MGrgxZvOE1OzaWw9ezHrC91jfyv8d8BV4tQ7x9Ll0_Vn7OfNGviasNi0v1rdTERPCA9bQI_7ffue7P4Pk2Q2IPY6_4g-aCGST5HqVmLuxaNKxzTo79CRHjCziNyRBg/s0/5HhYZ4BHkuvNldqCV5h9PQLE0hA.png)
![ドロップダウンメニューから[管理者として実行]を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-yaYEBHvMcG8/YjdcfLvhkCI/AAAAAAAAQFA/aassN2BUgjwxp7NKdqK3QpSuFWtE4yeHwCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhyU0JW91iiU4HdUNyWpEBsKLTw-6rQ88JJcf3GF8lMk7uR2vURQvSrLKx3HPJ-0bFTSQRDYtFiF0xXMnzMqjkeinj0p4_6R1kO7c7YxY5qQhApZ0W4keaxtQNkUgY3tkRT5-ypFY9VCwWOdWlQjQXqnqqmUhUOHojDHDyRxOdzXgn83uL9cUhyZQAyqoLNXwTuyPI3w7jMVLY_X3G_jMusEXoZHkAYQKZqBgUhPxBxFlPwhH-2DdZDXsVjKZqfavx4quKoI8Dn5vbKBw1fBP2LP-TMONu3R7eOkf34NH9fhPJJ8dtB0a9Nr9Lbun4wsDt2UkPoVWdXK-T5WEyqL8jtJIZzuNmeYS32rgbNJxt2MkVJe0ECNAjwjXY1oCKwCAja-lwWv2MG2WdS5jNcBqq8uNpsf5TXfjQaewupijbNsp_viGHOdMXhU68bv9CYzh3Jg897TZj113lNc9x2yiPm9ZLpb68caNxrHKk6kQvdPMHMRzJzCFsHGdrcsGW8UUQ6Ht3UrJUSKHvNnPH9C-EavJf8LBHVfter4gT7dO0uaIhreDldhomF7fI1DE1HmW7QFlecOcn2MqpmjESsYDZlEqVL_O7bu6l5iDcDGvhsDH0Fhqz9rIOYRCpkWkIV1yugxhdBnKN3LY3H2ntww_uXdkQY/s0/XNwXY3Gy20kKXE_J3jvn2sQc8VA.png)





![[ファイル]メニューから[新しいタスクの実行]にアクセスします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-owHcxTDD8Ps/YjdXqU3VsBI/AAAAAAAAxN8/5Zw4l3lMrMc3aVlYeZQpfjwCMpyPmuA0QCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCe4d2RBg/s0/U0FTfuDPv9BHR4xBnEn9pA5M7wo.png)
![[OK]をクリックする前に、必ずチェックボックスをオンにしてください](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-vvbh5W7PZkI/YjcFU0DZjUI/AAAAAAAAm4I/vyXFLYM4SkUPQHqzDxxbios60DHKJdZtACEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCRz9yRBg/s0/5VrJR5fOsVRGi7DWsrWYc4Ho6o0.png)






![チェックボックスをオンにして、[OK]を押します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-D3Ydty0tJC8/Yjc0ZGrI6pI/AAAAAAAAu4k/THjGaTIEgDkw0sCSdc-118LyoM6YzuL8wCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhxcrfjNL0kpApMdsYcrhR6ibP9yFPgid8tif1XJf590Y_S6I5KKOmSt3l5FGY4xSNyvZdonIyhAy17tqtmX612OyJ04O3L0FlnNcNc0C54eOcYAIPck3FI_krYDif6TAC-yzKxFLqijseiFajZsn5zZb5ikZDEoD98WADPb77Q8xJjOH9YzrQe3CB3fICtjnubLwJfl_5qf96x98EvSIMovAxNksn1luuo0L_dnicCPkBgBf5wN0-gtGg1mLEXM8O7RQ9uZx49lRm7ceAFzzMt_6Cq2w-eXXuubN_kNKoT7juKeFa2-L0zW6YGXdHX_H-uPut3z-kosp-leDwO3y29zBsAOH0aOENAJ-JGeAnRJ7TKv4t2I6l2cfc-lF9kRTKX6aYwsM79CQqNoNt61sae4bD0zEcPXA9px0izvU6TWFBY_0eJV8U_jRs_hFuQGd3mv42XGA9AF9USp0pq4reDvfzEUbUScBDJxV2FH0gc74fjQOnfl4a2FntrUFG4TIrLZdM1piJaWyZ1PgX8v43nHC1Hi9uMmXsWiYFo5NX1MHFRWVJnhLyCAzaIwxq_hg3o27aMIgAeS-fQ5cwlLgvZliezsqr04t33qG12AvR8NX8glkuNvFAGVed6Q_NgxRGKhvGXPVRSd4G8WMKGg3ZEG/s0/QvYvlvqL2mOSZeITMvX61dmmftU.png)
![[OK]または[適用]を押して変更を保存します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-cVRk0GdyutU/YjdPLS3zYiI/AAAAAAAAy10/sTaSpkejr48QC77ibJJqQFyE5mgqv9VVgCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhwXhoxRfnCMzWoHOZ2642jZ_nuj0EzODXF5t1Q7BvL6a7rrN0krzmheUzsmY-MFPIvNElQtdb00p33blXdN7JKeWt40N8Z0Vjt0E5MzyV5q3K7ry34pqpX8okL7_Y21dPg0-ZjOB9BNW7cIeN7NeCNqh7dU4NQvftqlAepEp8qUf80-MONtpq3m9Tz54R59CdV0sSzvnmgh58TofhWiCd-3XY6S45gXs9apEd7wD9e7eQRv-OlfefiD1J7nhsO-VNpIePZXuYt8wH91-7xNeqMUsNvU8riJ4kEeaOdNAmzHs2vMofp2hexnesEIn4hQ49RORjmXR1EllxdTXA-_mnNBIqgBmt5sVi3ma-ytXDvYiGIu86LJm_BC3FpwKW6cZcBvMvhHvy8-0WwbqbpsqXyJZ5YLV2dWHiLbyifFEMd2GK8QlsVqaUZMn4nvXUyhp57e8xJd31k1YO35UcfL9WGPPd7j_bA0i0uYnC7fJa64Ibqw2Ap1gC7pmjiDzLiwvrkOm49a_jHa1qL7wtyHlrwJwnCAg1GXbJE3SP1tqSPSRxAvQRhkBLcZef3d-lfmexy1KCeGwg7Vp2gvonUpPrdxWONogD5_RueQHuhrQ9djY0v663ay1mkH7t7DID1nzRqWKoC8qdPME3pZMOPl3ZEG/s0/Y9CImTSGDcItlJ7K3RbcgVrR7z4.png)
