Windows 10コンピューターに複数のユーザーアカウントをログインさせると、それらの間のスワッピングが高速になりますが、コンピューターが2つの別々の環境をメモリに維持する必要があるため、リソースを浪費する可能性もあります。このアクションのメリットとコストを比較検討する機会が必要な場合は、タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)がお手伝いします。タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)のどのタブにオンラインユーザーが表示されているか知っていますか?これは[ユーザー(Users)]タブです。ログインしているユーザーアカウントを表示したり、オンラインを維持するためにコンピューターのリソースがどれだけ使用されているかを確認したりできます。タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)の[ユーザー(Users)]タブでは、他のユーザーが開いたアプリを閉じたり、ログアウトしたりすることもできます。さらに面倒なことをせずに、これが何であるかを見てみましょう:
Windowsタスクマネージャ(Windows Task Manager)で[ユーザー]タブを表示する方法
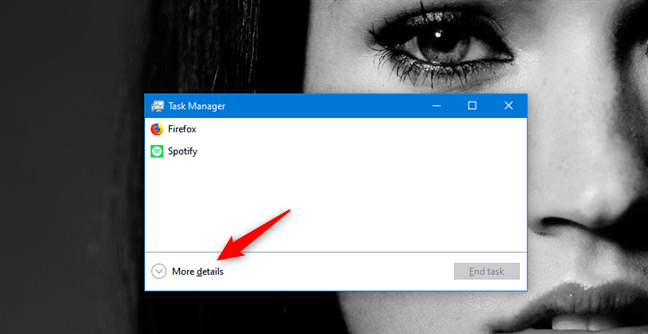
タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)を開きます。これを行う最も速い方法の1つは、キーボードのCtrl + Shift + Escキーを同時に押すことです。開いているアプリのみが一覧表示されるコンパクトなビューで開く場合は、何よりも先に[詳細]を("More details")クリックまたはタップ(click or tap)します。
![タスクマネージャで[詳細]をクリックします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-l_yjiRLF3sw/Yjc-49jPV2I/AAAAAAAAr4A/-LngrW4N0VYEsSfgIv4q3nxbp27oXyrUgCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwCXdzMJo7Wy553Aab3IZfOcw-mLQTdmC4hM2tdUzSWs4kfq4JkoKacm2dcmiXk_lz8R0wls265Moyy3wuNaVsnq-WRgFjO_g6jIIA0z4UcLfbp5OSpexjAMt1MPlFLsqd11iAcc2q3-vnx2pbUltMYmtCvDHn8913LB0YagLYUztW6LL99jHPxoNDfJV-VRQw1VU6BzKNgZigC1RnuEe_Z1OKbhBf5_Os7MrqGIJN8PSviPXrUAxQVJPkJV0J9TYOsa0KL5Y5KDXH5I0JOltaY5xDdlJq0pSEUYuMc34yqT9IZHXVxomR9MPmvM0KXWAOVQMvqqCuV0YaEOlvZakcX5oQ_f7-rpZXL2VMObbH-GM4TiplrfKmfFxHplCqA6PaiKPNwpIKRY6yejrQRKB7wrgbFZz6rLPDaNHbT2uVjnNMrdL5H-gWEn3XTzoL1Qn51kZCcfLC5L1qmSoK0uQK7ZDR3eT3dAaqQHSI0aPeKW3GcnREgQYRdljNChhFutZpWHKZvIzbesmhsvphyR609wQ9kmts6IC_BuC_O7TMsj35HzoCsCP9QlXujZLExO7mrwLuBQjCqqtuxizkyA9_9mgzkeDk8xyBwzVKh8C4GTmKyzd-LbNX_CUazBZpV4bWInTWPlDCGoN2RBg/s0/jpPD-uTT0PfJRICxOwXogVbAD0c.png)
タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)のフルバージョンが表示されたら、[ユーザー(Users)]タブを選択します。
![タスクマネージャーの[ユーザー]タブ](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-VgknYy4nh0o/YjcO9JJ4wrI/AAAAAAAAmzs/fFLmG179RX4ZmDj_OKNAbnpKc5pH7uONQCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCRz9yRBg/s0/7k6CkAAf47wlLOJqClIICKk1_qk.png)
[ユーザー(Users)]タブでは、現在ログインしているユーザーアカウントが最初の列に一覧表示され、その後に、それぞれが使用しているシステムリソースを示すいくつかの列が表示されます。

デフォルトでは、ユーザー(User)列の近くに6つまたは7つの列が表示されます。彼らです:
-
ステータス(Status)-リストされているアカウントとプロセスのステータスを示します。
-
CPU-各アカウントで使用された合計CPUサイクルのパーセンテージ、および各アカウントで実行されたプロセスを表示します。
-
メモリ(Memory)-選択したアカウント(または選択したプロセス)が使用しているメモリの合計量を示します。
-
ディスク(Disk)-ハードドライブとの間で転送されるデータの量を示します。
-
ネットワーク(Network)-選択したユーザーアカウントまたはプロセスのネットワーク使用状況を表示します。
-
GPU -PC上のすべてのグラフィックチップまたはカードの中で最も高いビデオ使用率を示します。
-
GPUエンジン(GPU engine)-複数のビデオカードがインストールされている場合(専用のビデオカードを搭載したラップトップだけでなく、プロセッサにビデオチップも搭載されている場合など)、GPUエンジン(GPU engine)は専用のグラフィックカードの使用率を示します。
列を追加して詳細情報を表示するには、列ヘッダーを右クリック(または(column header)タップアンドホールド(tap and hold))して、他のエントリを選択します。オプションは次のとおりです。
-
(ID)ID-各アカウントの一意のセッションIDを示します。
-
セッション(Session)-各アカウントのセッションのタイプを表示します。これは、ユーザーがリモートサービスを使用してログインできるサーバーシステムでのみ役立ちます。
-
クライアント名(Client Name)-リモートユーザーがログインしているコンピューターの名前を表示します。

閉じる必要のない列は選択解除できます。これにより、ビューが整理され、ウィンドウが小さくなります。
各ユーザーアカウント(user account)によって開かれたプロセスを管理する方法
管理者権限がある場合は、 [ユーザー]タブで、各(Users)ユーザーアカウント名(user account name)の横にある小さな矢印をクリックまたはタップして、そのアカウントによって開かれたすべてのプロセスのリストを展開できます。または、アカウントを(account and click)右クリックまたは長押しして、[展開]をクリックまたはタップすることもできます。(Expand.)

管理者権限を持たない標準のユーザーアカウントでサインインしている場合は、自分のプロセスのリストのみを展開して表示できます。(If you are signed in with a standard user account that does not have administrative privileges, you can expand and see only your own list of processes. You cannot see the processes run by other users)Windows10PCに接続している他のユーザーによって実行されているプロセスを表示することはできません。
どちらの方法でも、実行する必要のないものがないか、開いているプロセスのリストを確認できます。リソースをかみ砕いて閉じても、アカウント所有者(account holder)の側に過度の問題が発生しないアプリケーションを見つけた場合は、そのアプリケーションを右クリック(または長押し(press and hold))して、 [タスクの終了]を("End Task.")クリックまたはタップします。(click or tap) これでプロセスが終了します。

プロセスを(process and click)選択して、画面の右下隅にある[タスクの終了("End Task")]ボタンをクリックまたはタップすることもできます。

アカウントの処理が完了したら、矢印をもう一度タップするか、アカウントを右クリックまたは長押しして[折りたたみ]を(Collapse)選択(account and select) し、展開されたリスト(list and display)を非表示にして、名前のみをもう一度表示します。

Windowsタスクマネージャー(Windows Task Manager)で開いているユーザーアカウントを管理する方法
複数の口座を開設している場合、それらを管理するために実行できるさまざまなタスクがあります。まず(First)、アカウントを右クリックまたは長押しして、使用可能なオプションを表示します。

コンテキストメニューから[接続(Connect)]を選択して、選択したアカウントに切り替えます。表示されたフィールドにアカウントのパスワード(account password)を入力し、[OK field and click/tapします。(OK.)

選択したアカウント(chosen account)をサインアウトする場合は、「サインオフ」("Sign off")を選択します。開く必要がない場合、これはリソースを解放するための優れた方法です。データが失われる可能性があるため、他のユーザーが未保存の情報を持っていないことを確認するように注意してください。そのアカウントからログアウトすることに確信がある場合は、警告ウィンドウ(warning window)から[ユーザーのサインアウト]を("Sign out user")クリック(Click)またはタップします。

サインアウトまたは別のアカウントに切り替える別の方法は、アカウントを選択し、ウィンドウの右下隅にある適切なボタンをクリックまたはタップすることです。(account and click)

他のアカウントのユーザーにメッセージを送信する場合は、上記のコンテキストメニュー(context menu)から[メッセージの送信("Send message")]を選択します。表示されたスペースにメッセージを入力し、必要に応じてタイトルを入力して、[OK]をクリックまたはタップします。(OK.)

リモートユーザーが選択したアカウントをアクティブに使用している場合、そのユーザーはすぐにメッセージを受け取ります。他のアカウントのユーザーがコンピューターを使用していない場合は、次にアカウントのロックを解除したときにメッセージが表示されます。

最後に、右クリックメニューで、[ユーザーアカウントの管理("Manage user accounts")]を選択して、古いコントロールパネルから(Control Panel)[ユーザーアカウント](User Accounts)セクションを開くことができます。
![コントロールパネルの[ユーザーアカウント]セクション](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-LJFhoywNCWM/YjdXLknhYTI/AAAAAAAAxNs/n_P0KySeZzoe3579xP2le2wY5yh0ugICwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCe4d2RBg/s0/TsQSfrDmFrZ4_i-gio_cQOQCwnQ.png)
そこから、アカウントの設定を変更できます。
サインインしたユーザーを管理するためにタスクマネージャー(Task Manager)を使用していますか?
タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)の[ユーザー(Users)]タブには多くの機能はありませんが、実用的な目的を果たします。少しの努力で、開いているすべてのアカウント、システムのパフォーマンスへの影響を表示し、リソースを回復するためにそれらを管理できます。別のアカウントに切り替えてプログラムを閉じて元に戻すよりもはるかに高速です。Windowsでの(Windows)タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)の利用の詳細については、以下の推奨記事をお読みください。
How to manage signed-in user accounts with the Task Manager in Windows 10
Having multiple user accounts logged in on your Windows 10 computer can make swapping between them faster, but it can also waste resources as your computer is forced to maintain two separate environments in memory. If you want the chance to weigh the benefits of this action against the costs, the Task Manager can help. Do you know which tab of the Task Manager shows you the online users? It's the Users tab: it lets you view which user accounts are logged in and also see how much of the computer's resources are being used to keep them online. The Users tab from Task Manager also lets you close the apps opened by other users or even log them out. Without further ado, let's see what this is all about:
How to view the Users tab in the Windows Task Manager
Open the Task Manager. One of the fastest ways to do it is to simultaneously press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys on your keyboard. If it opens in its compact view, which only lists your open apps, click or tap on "More details" before anything else.
Once you see the full version of the Task Manager, select the Users tab.

On the Users tab, the user accounts currently logged in are listed in the first column, followed by some columns depicting system resources being used by each.

By default, you see six or seven columns displayed near the User column. They are:
-
Status - shows the status of the accounts and processes listed.
-
CPU - displays the percentage of total CPU cycles used by each account, and the processes run by each account.
-
Memory - shows the total amount of memory the selected account (or the chosen process) is utilizing.
-
Disk - indicates the amount of data being transferred to/from your hard drive.
-
Network - displays the network usage of the selected user account or process.
-
GPU - shows the highest video utilization across all the graphics chips or cards on your PC.
-
GPU engine - if you have more than one video card installed (like on a laptop with a dedicated video card but also a video chip found on the processor), GPU engine shows the utilization of the dedicated graphics card.
To add additional columns and display more information, right-click (or tap and hold) a column header and select other entries. Your options are:
-
ID - shows the unique session ID for each account.
-
Session - displays the type of session for each account. This is only useful for a server system where users may log in using remote services.
-
Client Name - displays the name of the computer a remote user is logging in from.

You can deselect any column you do not need to close it. This helps declutter the view and keep the window smaller.
How to manage the processes opened by each user account
If you have administrative rights, from the Users tab, you can click or tap the small arrow next to each user account name to expand a list of all processes opened by that account. Alternatively, you can right-click or long-press an account and click or tap Expand.

If you are signed in with a standard user account that does not have administrative privileges, you can expand and see only your own list of processes. You cannot see the processes run by other users that are connected to your Windows 10 PC.
Either way, you can check the list of open processes for anything that does not need to be running. If you find an application that is chewing up resources and closing it would not cause any undue hardship on the part of the account holder, you can right-click on it (or press and hold) and click or tap "End Task." This closes the process.

You can also select the process and click or tap the "End Task" button on the lower-right corner of the screen.

Once you have gone through the account's processes, you can tap the arrow once again or right-click or long-press the account and select Collapse to hide the expanded list and display only the name once again.

How to manage open user accounts in the Windows Task Manager
If you have multiple open accounts, there are various tasks you can perform to manage them. First, right-click or press-and-hold the account to view the options available.

Select Connect from the contextual menu to switch to the selected account. Enter the account password in the provided field and click/tap on OK.

Select "Sign off" if you want to sign out the chosen account. If you do not need it open, this is an excellent way to free up resources. Be careful to ensure that the other user does not have any unsaved information as this could result in data loss. Click or tap "Sign out user" from the warning window if you are confident that you want to log out that account.

Another way to sign out of or switch to another account is to select the account and click or tap the appropriate button on the lower-right corner of the window.

Select "Send message" from the context menu described above if you want to send a message to the user of the other account. Type your message in the space provided, enter a title if you wish and then click or tap OK.

If a remote user is actively using the selected account, he or she gets your message immediately. If the user of the other account is not on the computer, he or she will get the message the next time he or she unlocks the account.

Finally, in the right-click menu, you can select "Manage user accounts" to open the User Accounts section from the old Control Panel.

From there, you can change the account's settings.
Do you use the Task Manager to manage signed in users?
The Users tab in the Task Manager does not have a ton of features, but it serves a practical purpose. With a little effort, you can view all open accounts, their impact on your system's performance and manage them to regain resources. It is much faster than swapping over to another account to close a program and switching back. For more information about utilizing the Task Manager in Windows, do not hesitate to read the articles recommended below.
![タスクマネージャで[詳細]をクリックします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-l_yjiRLF3sw/Yjc-49jPV2I/AAAAAAAAr4A/-LngrW4N0VYEsSfgIv4q3nxbp27oXyrUgCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwCXdzMJo7Wy553Aab3IZfOcw-mLQTdmC4hM2tdUzSWs4kfq4JkoKacm2dcmiXk_lz8R0wls265Moyy3wuNaVsnq-WRgFjO_g6jIIA0z4UcLfbp5OSpexjAMt1MPlFLsqd11iAcc2q3-vnx2pbUltMYmtCvDHn8913LB0YagLYUztW6LL99jHPxoNDfJV-VRQw1VU6BzKNgZigC1RnuEe_Z1OKbhBf5_Os7MrqGIJN8PSviPXrUAxQVJPkJV0J9TYOsa0KL5Y5KDXH5I0JOltaY5xDdlJq0pSEUYuMc34yqT9IZHXVxomR9MPmvM0KXWAOVQMvqqCuV0YaEOlvZakcX5oQ_f7-rpZXL2VMObbH-GM4TiplrfKmfFxHplCqA6PaiKPNwpIKRY6yejrQRKB7wrgbFZz6rLPDaNHbT2uVjnNMrdL5H-gWEn3XTzoL1Qn51kZCcfLC5L1qmSoK0uQK7ZDR3eT3dAaqQHSI0aPeKW3GcnREgQYRdljNChhFutZpWHKZvIzbesmhsvphyR609wQ9kmts6IC_BuC_O7TMsj35HzoCsCP9QlXujZLExO7mrwLuBQjCqqtuxizkyA9_9mgzkeDk8xyBwzVKh8C4GTmKyzd-LbNX_CUazBZpV4bWInTWPlDCGoN2RBg/s0/jpPD-uTT0PfJRICxOwXogVbAD0c.png)
![タスクマネージャーの[ユーザー]タブ](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-VgknYy4nh0o/YjcO9JJ4wrI/AAAAAAAAmzs/fFLmG179RX4ZmDj_OKNAbnpKc5pH7uONQCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCRz9yRBg/s0/7k6CkAAf47wlLOJqClIICKk1_qk.png)












![コントロールパネルの[ユーザーアカウント]セクション](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-LJFhoywNCWM/YjdXLknhYTI/AAAAAAAAxNs/n_P0KySeZzoe3579xP2le2wY5yh0ugICwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCe4d2RBg/s0/TsQSfrDmFrZ4_i-gio_cQOQCwnQ.png)
