Windows 10タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)は、システムリソースの監視に関して多くの機能を提供します。[プロセス(Processes)]タブはこれまで以上に多くの情報を共有し、必要に応じて表示されるデータをカスタマイズできます。次に、 Windows 10で(Windows 10)タスクマネージャーの(Task Manager's) [プロセス(Processes)]タブを微調整し、関連するデータが(data relevant)デフォルト(default view)のビューよりもニーズに合った方法で表示されるようにすることで、より効率的にする方法を示します。
[プロセス]タブ(Processes tab)とは何ですか。また、それにアクセスする方法は何ですか。
[プロセス(Processes)]タブには、任意の時点で実行されているすべてのアプリ、バックグラウンドプロセス、およびWindowsプロセスが一覧表示され、それぞれに関する有用なデータが提供されます。(Windows)タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)のフルバージョンで利用できます。タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)を開くために利用できるオプションはいくつかありますが、最も快適なのはキーボードショートカット(keyboard shortcut) "Ctrl + Shift + Esc」です。Windows8をスキップした場合、およびツールに初めてアクセスする場合は、次のように開きます。コンパクトビューと呼ばれ、Windows10デバイスで現在実行されているすべてのアプリのリストを表示します。タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)のフルバージョンを開くには、をクリックまたはタップします(More details)コンパクトビューの下部に詳細があります。
![[詳細]をクリックして、タスクマネージャーのフルバージョンを開きます](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-m1WtF1kqJhk/YjcxuTQffeI/AAAAAAAAKvg/TChJoq7iQ448y4viHGjkvGO01OdVyDPYQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxqHo63eC-w2z6yviSn9DYRDJuWMKm_sPX6g-BI1OEFwv6L01SgCY8x7NMPafCADWrqG-5bpVDJ9v1dX5VJUMKLtB4dJOAcVJsEhFbbXtL-XEojuNI5AruC6OEcs4cjQnBRmHxiidG_bT2PUln-JyMDeM9aSWLAKSXNGv7-yc7yQmIvhyUYhbDkEh81nfEAWmrpABM29e2_Sw9E50aw52PTBbSFGr-9f2F_zVQ6X8hhfsueD2Q3TAAeasc4-YpuzFdw2-e8Er4zY_PbIim0s6V3-GMF_pNVuXyk43N0cVPAQ4d5EcEKzOSQZl94Dd4hs_80k2TqFQdbSNhpq9D9NQyskK8FU-cfokIaFU0zhsWLLuGZVsuH1NRNGn4YNiKEV3QCAPqc9kzi1dPCRqXGd--4GOATbeSeKcQVgEuAwUTG5knE2W6mc6eg3LAB05feSMp5RK6QTKY72osxAAWsYKriaD-cjcVT3-YNVM5UanAfvczKJd_aCqsMi7kY2O-rOOq_hTYACxmVLcoKulU2T9PDKqZObOmLUWvpw1LFqfbIcIgdTfhTJx2pOU5yBgXu92TP53dU475DxGW5MnLmd0KwZo4qU3vaO3OQOutgpXWW1yHWLDsgvUWG4wybPqFh4idUvTQRR786lrgNYjAwlqDdkQY/s0/MtDu3Lfk-rlI-bsd--9arREBGnk.png)
タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)のフルバージョンが開き、 [プロセス(Processes)]タブがデフォルトのタブになります。
![フルバージョンのタスクマネージャの[プロセス]タブ](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-wlaTiGkiqfw/YjcH28vxX3I/AAAAAAAAm5I/2NtPv8khqWsj61a9VpIY9egJnMpAPGnkQCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCRz9yRBg/s0/6GrQipy4h1nmoEsC7esPtqH37Lo.png)
ヒント:(TIP:)タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)は、任意のタブで開くようにカスタマイズできます。詳細については、「Windows10タスクマネージャーの(Task Manager)default view/tabを設定する方法」を参照してください。
1.タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)の[プロセス]タブ(Processes tab)でデータ列を追加または削除する方法
[プロセス(Processes)]タブでは、コンピューターで現在実行されているすべてのアプリ、バックグラウンドプロセス(background process)、およびWindowsプロセスに関する情報を取得します。(Windows process)このデータは構造化され、列に表示されます。列のヘッダーをクリック(Click)またはタップし、それをドラッグして、希望する順序で列を並べ替えます。列を追加および削除することにより、[プロセス(Processes)]タブに表示される情報を選択できます。既存の列のヘッダーを(header and select)右クリックまたは長押しして、タスクマネージャーの[(Task Manager)プロセス(Processes)]タブに表示される14個のオプションの列のどれを選択します。名前(Name)を覚えておいてくださいcolumnは、非表示にできない唯一の列です。
![[プロセス]タブで使用できるオプションの列は14個あります](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-zi854JoF6m0/Yjc69jPQ3VI/AAAAAAAAr4Q/rjBAKEZVXUoifdt3dUyp64M9Y-czQ_xJwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwCXdzMJo7Wy553Aab3IZfOcw-mLQTdmC4hM2tdUzSWs4kfq4JkoKacm2dcmiXk_lz8R0wls265Moyy3wuNaVsnq-WRgFjO_g6jIIA0z4UcLfbp5OSpexjAMt1MPlFLsqd11iAcc2q3-vnx2pbUltMYmtCvDHn8913LB0YagLYUztW6LL99jHPxoNDfJV-VRQw1VU6BzKNgZigC1RnuEe_Z1OKbhBf5_Os7MrqGIJN8PSviPXrUAxQVJPkJV0J9TYOsa0KL5Y5KDXH5I0JOltaY5xDdlJq0pSEUYuMc34yqT9IZHXVxomR9MPmvM0KXWAOVQMvqqCuV0YaEOlvZakcX5oQ_f7-rpZXL2VMObbH-GM4TiplrfKmfFxHplCqA6PaiKPNwpIKRY6yejrQRKB7wrgbFZz6rLPDaNHbT2uVjnNMrdL5H-gWEn3XTzoL1Qn51kZCcfLC5L1qmSoK0uQK7ZDR3eT3dAaqQHSI0aPeKW3GcnREgQYRdljNChhFutZpWHKZvIzbesmhsvphyR609wQ9kmts6IC_BuC_O7TMsj35HzoCsCP9QlXujZLExO7mrwLuBQjCqqtuxizkyA9_9mgzkeDk8xyBwzVKh8C4GTmKyzd-LbNX_CUazBZpV4bWInTWPlDCFoN2RBg/s0/j1IhUO4xCd3UFWQ4OjEtmE7s5kI.png)
選択した列が関連データを確実に提供するために、以下にそれらが提供するものの概要を示します。
-
タイプ(Type)-プロセスがアプリ、バックグラウンドプロセス、またはWindowsプロセスのいずれであるかを表示します。[タイプ別にグループ("Group by type")化]を選択すると、この列は冗長になります
-
ステータス(Status)-プロセスが一時停止されているかどうかを表示します。何かが一時停止されると、バックグラウンドで実行されますが、CPUサイクルにアクセスできず、メモリをほとんど使用しません。
- パブリッシャー-プロセスのパブリッシャーの名前を表示します。
-
PID-実行中のプロセスごとに一意のプロセス識別子を表示します。これらの番号を使用して、実行中のプロセスをPIDをリストするエラーまたはイベントと照合できます。
-
プロセス名(Process name)-プロセスの実行可能ファイルの名前を表示します。たとえば、7-Zipファイルマネージャの場合は(7-Zip File Manager)7zFM.exeです。
-
コマンドライン(Command line)-各プロセスで実行されるコマンドライン構文を表示します。これにより、特別なコマンドラインパラメーターを使用してアプリまたはプロセスが起動されているかどうかを確認したり、各プロセスの実行可能ファイルの場所を確認したりできます。
-
CPU-各プロセスのプロセッサ使用率を表示します。
-
メモリ-(Memory -)各プロセスのRAM使用量を表示します。
-
ディスク(Disk)-各プロセスのハードディスク使用量を表示します。
-
ネットワーク(Network)-各プロセスのネットワーク使用状況を表示します。
-
GPU-各プロセスのビデオカードの使用状況を表示します。
-
GPUエンジン(GPU engine)-各プロセスで使用されているGPUエンジンを共有します。Microsoftによると、GPUエンジンは、グラフィックカード上のシリコンの独立したユニットを表しており、スケジュールを設定して、別のユニットと並行して動作させることができます。この概念の詳細については、こちら(here)をご覧ください。
-
電力使用量(Power usage)-各プロセスで使用されている電力を表示します。
-
電力使用量の傾向(Power usage trend)-各プロセスの電力使用量の全体的な傾向を示します。
2.タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)の[プロセス]タブ(Processes tab)で実行中のアプリとプロセスを並べ替える方法(apps and processes)
デフォルトでは、タスクマネージャのプロセス(Task Manager's Processes)リストはプロセスタイプ(process type)ごとに論理的にソートされています。これは、すべてのアプリ、バックグラウンドプロセス、およびWindows 10プロセスがグループ化され、名前(Name)と呼ばれるタブのこの最初の列のグループ内で並べ替えられることを意味します。私たちはこのシステムの大ファンですが、代わりにリストをアルファベット順に並べ替えることもできます。すべてのアクティブなアプリとプロセスをアルファベット順のリストで表示する場合は、[表示]を(View)クリック(Click)またはタップし、[タイプ別にグループ化("Group by type")]の選択を解除します。
![[タイプでグループ化]オプションは、アプリとプロセスの並べ替え方法を変更します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-YPYxnedQ0ik/YjdGavNcZsI/AAAAAAAAuwI/Se2Prg-8S481Wh-bLaZ0Pyg4rTew5NU-QCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhxcrfjNL0kpApMdsYcrhR6ibP9yFPgid8tif1XJf590Y_S6I5KKOmSt3l5FGY4xSNyvZdonIyhAy17tqtmX612OyJ04O3L0FlnNcNc0C54eOcYAIPck3FI_krYDif6TAC-yzKxFLqijseiFajZsn5zZb5ikZDEoD98WADPb77Q8xJjOH9YzrQe3CB3fICtjnubLwJfl_5qf96x98EvSIMovAxNksn1luuo0L_dnicCPkBgBf5wN0-gtGg1mLEXM8O7RQ9uZx49lRm7ceAFzzMt_6Cq2w-eXXuubN_kNKoT7juKeFa2-L0zW6YGXdHX_H-uPut3z-kosp-leDwO3y29zBsAOH0aOENAJ-JGeAnRJ7TKv4t2I6l2cfc-lF9kRTKX6aYwsM79CQqNoNt61sae4bD0zEcPXA9px0izvU6TWFBY_0eJV8U_jRs_hFuQGd3mv42XGA9AF9USp0pq4reDvfzEUbUScBDJxV2FH0gc74fjQOnfl4a2FntrUFG4TIrLZdM1piJaWyZ1PgX8v43nHC1Hi9uMmXsWiYFo5NX1MHFRWVJnhLyCAzaIwxq_hg3o27aMIgAeS-fQ5cwlLgvZliezsqr04t33qG12AvR8NX8glkuNvFAGVed6Q_NgxRGKhvGXPVRSd4G8WMKKg3ZEG/s0/rbk3b91O-FsK-Hiy-bufP6n4x4M.png)
列のヘッダーをクリックまたはタップすると、その列に表示されている値に基づいて、実行中のアプリとプロセスを並べ替えることができます。(running apps and processes)たとえば、[メモリ(Memory)]をクリックすると、プロセスが使用しているRAMの量でリストが並べ替えられます。これは、どのプロセスがコンピューター上で最も多くまたは最も少ないリソースを消費するのか疑問に思っている場合に役立ちます。使用している並べ替え方法に関係なく(Regardless)、任意の時点でデフォルトの並べ替えに戻したい場合は、 [表示]メニューの[(View)タイプ別にグループ化("Group by type")]オプションを選択します。
3. [プロセス]タブ(Processes tab)でのデータ値の表示方法を変更する方法
表示する情報をカスタマイズできることに加えて、 [プロセス(Processes)]タブでは、そのデータの一部をどのように表示するかを決定することもできます。[メモリ](Memory)、 [ディスク](Disk)、および[ネットワーク]列では、値(メモリのMB、 (Network)MB/s disk usage and Mbps network usage)を使用してデータを表示するか、使用可能なリソースの合計のパーセンテージとしてデータを表示するかを選択できます。タスクマネージャの[(Task Manager)プロセス(Processes)]タブで任意の列のヘッダーまたはプロセス(header or process)を右クリックまたは長押しして、[リソース値(Resource values)]に移動します。リソースの1つを選択してから、パーセント(Percents)または値のいずれかを選択します(Values)ニーズや好みに応じてデータを表示します。

4.タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)で実行中のプロセスを展開および折りたたむ方法
一部のプロセスは他のプロセスよりも複雑で、メインプロセス以上のものが含まれます。タスクマネージャの(Task Manager's) [プロセス(Processes)]タブでは、一覧表示されたプロセスを展開し、その下で実行されているサブプロセスの詳細を取得できます。サブプロセスの数は、各プロセスに続く括弧内の数字で示されます。単一のプロセスを展開するには、そのプロセスを右クリックまたは長押しして、[展開]をクリック(Expand)またはタップ(click or tap) します。これを行う簡単な方法は、プロセスの左側にある矢印をクリックまたはタップすることです。
![サブプロセスの詳細については、左側の矢印を使用するか、[展開]をクリックまたはタップしてください](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-So9wuMnuhgg/YjctbafvKbI/AAAAAAAAsCw/CJ8On6-AkcEaOmR71OdWfN0XLN1AhbNIwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwCXdzMJo7Wy553Aab3IZfOcw-mLQTdmC4hM2tdUzSWs4kfq4JkoKacm2dcmiXk_lz8R0wls265Moyy3wuNaVsnq-WRgFjO_g6jIIA0z4UcLfbp5OSpexjAMt1MPlFLsqd11iAcc2q3-vnx2pbUltMYmtCvDHn8913LB0YagLYUztW6LL99jHPxoNDfJV-VRQw1VU6BzKNgZigC1RnuEe_Z1OKbhBf5_Os7MrqGIJN8PSviPXrUAxQVJPkJV0J9TYOsa0KL5Y5KDXH5I0JOltaY5xDdlJq0pSEUYuMc34yqT9IZHXVxomR9MPmvM0KXWAOVQMvqqCuV0YaEOlvZakcX5oQ_f7-rpZXL2VMObbH-GM4TiplrfKmfFxHplCqA6PaiKPNwpIKRY6yejrQRKB7wrgbFZz6rLPDaNHbT2uVjnNMrdL5H-gWEn3XTzoL1Qn51kZCcfLC5L1qmSoK0uQK7ZDR3eT3dAaqQHSI0aPeKW3GcnREgQYRdljNChhFutZpWHKZvIzbesmhsvphyR609wQ9kmts6IC_BuC_O7TMsj35HzoCsCP9QlXujZLExO7mrwLuBQjCqqtuxizkyA9_9mgzkeDk8xyBwzVKh8C4GTmKyzd-LbNX_CUazBZpV4bWInTWPlDCFoN2RBg/s0/J21oHlprEXBU7plWDmkYMPXVW5I.png)
矢印をもう一度クリックするか、そのプロセスを右クリックまたは長押しして、サブプロセスを再度非表示にする場合は[折りたたみ]に移動します。(Collapse)
![左側の矢印を使用するか、[折りたたみ]をクリックまたはタップして詳細を非表示にします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-E7upTPJfsyw/YjdR1vKmWgI/AAAAAAAAxSg/cWoVaG1MTOEvim1TgrCCQeNLahiTKo-tgCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCd4d2RBg/s0/SV9KENhtr2Gs-iAM2Y0At34mLFI.png)
[表示](View)をクリックまたはタップしてから[すべて展開]をクリックして、折りたたまれたエントリを展開することもできます(Expand all)。
![[すべて展開]をクリックまたはタップして、すべてのプロセスを展開します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Ejwl7nBsTpw/YjcX0OLX-EI/AAAAAAAAC_Q/QFvknDpIlVwTf2AFbDX1vG72KeNfteZJQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxeSqmKu1BtuATYSULyy9OK0vUZJMh4EEreX9rzJid57_Lr5itgoyxzXecCdHil_kcjllNp636SB8ECcTxmI--8us7mIs7_4fcnjy5EcSKFLsehZVlA79dQvMROYqrbbfCkZz25BePPjbkt5vMp0a-Ffrw5A99b5RlKddBRMXeM9g_FOe-xFzRbvRW7TYY6HykLA9PekQsEvOV8jpg0SHFKFaAgGIgHmS8N7Z4b0t8oAyxaq09z-wMB1q859mpaUbsnf4wcrBa-aLiovkCSe0-odM-A-9luIU_P030lCRFTGU9BY0zVaY2-1KUD4qSF0CxrUZ63BI5AN1rY-GLaYkrr6q6sLymszIx_5ReHwutHRLMCol2Y3bqo8_EmWqm1xKORC4FaaCfGnEFVJB_wg7045IZzS73d4lf5GevtJPILvrX6AAn4MdBndWPI54Il_GyriQm-PvgqlWRU8VIZSbskQDSr606f1DhUT0lFbEm55jRTZO5fxh4ah9Me-2zfxCotjHRzCLkIkXarR56jt-M2SgQLbI-FEfyKwUTPXJ4v_RR4iPWc90tJKVi01D3pbDGX5WGBgfwItEcVTJrbT3YKakmk0mweSX3-I0kynawDx1NIRHydgBsBNyU99ZZWyYdyYcFCu2SsV1d5Oa8w3dXckQY/s0/bBrDTsmvprcHSCdPrUbknkuMqmg.png)
展開されたすべてのエントリをすぐに折りたたむには、 [表示(View)]メニューから[すべて折りたたむ]を(Collapse all)クリックまたはタップ(click or tap) します。
![[すべて折りたたむ]をクリックまたはタップして、すべてのプロセスを折りたたむ](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-AZpqJ9tIsb0/YjdRrRmfGzI/AAAAAAAAxQs/eBK-P6WxrMQjFhuhbCrh9BF5wKuc5OdAwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCd4d2RBg/s0/SU-iCulYdcyWlnogwq9Pb9xJ96Q.png)
ヒント:(TIP:)マルチプロセスアプリケーションの場合、メイン(親)プロセスを右クリックまたは長押しすると、コンテキストメニューに灰色のオプションが表示されます。(right-clicking or pressing-and-holding)各サブプロセスを右クリックまたは長押しして、サブプロセスを操作します。

5.タスクマネージャーを使用して実行中のプロセスを終了する方法(Task Manager)
タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)の主な用途は、応答しなくなった実行中のプロセスを閉じることです。任意のプロセスを右クリックまたは長押しすると、コンテキストメニューが開きます。[タスクの終了]を(End task)クリック(Click)またはタップして、プロセスを閉じます。
アプリを(app and click)選択し、 [プロセス(Processes)]タブの右下隅にある[タスク(End task)の終了]ボタンをクリックまたはタップして、プロセスを閉じることもできます。
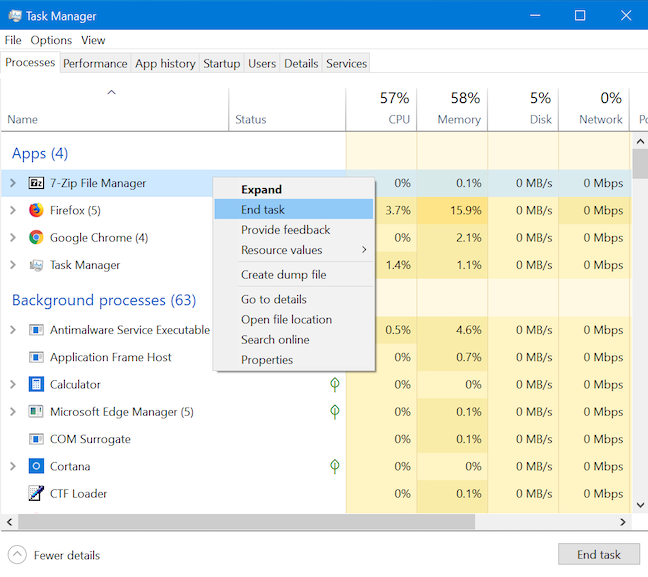
6.実行中のプロセスに関するフィードバックをMicrosoftに提供する方法(Microsoft)
フィードバックハブ(Feedback Hub)にはタスクマネージャー(Task Manager)から簡単にアクセスできるため、実行中のプロセスに関するフィードバックを提供できます。任意のプロセスを右クリックまたは長押しして、フィードバックの提供(Provide feedback)を選択します。

フィードバックHub(Feedback Hub)が開いたら、 Microsoftアカウント(Microsoft account)でサインインし、それを使用して問題、批判、または提案をMicrosoftに送信できます。

7.タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)を使用して実行中のプロセスのダンプファイルを作成する方法(dump file)
ダンプファイルは、 (dump file)DMP形式(DMP format)を使用する大きなファイルであり、ダンプファイル(dump file)が作成された正確な時点で特定のプロセスまたはアプリケーション(process or application)が実行していることの詳細を提供します。これは通常、そのプロセスのバグや問題を解決しようとするソフトウェア開発者にとって便利です。ダンプファイル(dump file)を作成するには、任意のプロセスを(process and click)右クリックまたは長押しして、[ダンプファイルの作成]をクリックまたはタップします。("Create dump file.")

8.タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)で実行中のプロセスの詳細を表示する方法
タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)の[詳細(Details)]タブには、当然のことながら、実行中のプロセスに関する正確な詳細が表示されます。ただし、このタブの並べ替えオプションは制限されているため、特定のプロセスについて詳しく知ることは、特にコンピューターで多数のプロセスを実行している場合は、ちょっとした宝探し(treasure hunt)に変わる可能性があります。幸いなことに、[プロセス]タブは、[(Processes)詳細(Details)]タブで対応するプロセスを強調表示するオプションを提供することでそれを補います。任意のプロセスを右クリックまたは長押ししてから、[詳細に移動("Go to details)]をクリックまたはタップします(")。

フォーカスが[詳細(Details)]タブに移動し、対応する実行可能ファイルが強調表示されます。
![[詳細]タブが開き、対応する実行可能ファイルが強調表示されます](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-3NAvUkzAw9g/YjdkUAu67zI/AAAAAAAAP3Y/lJEBrYqx3lo4h8rQbc36OwmFLHlWNMaawCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhyU0JW91iiU4HdUNyWpEBsKLTw-6rQ88JJcf3GF8lMk7uR2vURQvSrLKx3HPJ-0bFTSQRDYtFiF0xXMnzMqjkeinj0p4_6R1kO7c7YxY5qQhApZ0W4keaxtQNkUgY3tkRT5-ypFY9VCwWOdWlQjQXqnqqmUhUOHojDHDyRxOdzXgn83uL9cUhyZQAyqoLNXwTuyPI3w7jMVLY_X3G_jMusEXoZHkAYQKZqBgUhPxBxFlPwhH-2DdZDXsVjKZqfavx4quKoI8Dn5vbKBw1fBP2LP-TMONu3R7eOkf34NH9fhPJJ8dtB0a9Nr9Lbun4wsDt2UkPoVWdXK-T5WEyqL8jtJIZzuNmeYS32rgbNJxt2MkVJe0ECNAjwjXY1oCKwCAja-lwWv2MG2WdS5jNcBqq8uNpsf5TXfjQaewupijbNsp_viGHOdMXhU68bv9CYzh3Jg897TZj113lNc9x2yiPm9ZLpb68caNxrHKk6kQvdPMHMRzJzCFsHGdrcsGW8UUQ6Ht3UrJUSKHvNnPH9C-EavJf8LBHVfter4gT7dO0uaIhreDldhomF7fI1DE1HmW7QFlecOcn2MqpmjESsYDZlEqVL_O7bu6l5iDcDGvhsDH0Fhqz9rIOYRCpkWkIV1yugxhdBnKN3LY3H2ntww_OXdkQY/s0/vooj14PM6EQAkqAB4jlXrWwe6uk.png)
9.タスクマネージャーで実行中のプロセスの場所を見つける方法(Task Manager)
アプリまたはプロセスに対応する実行可能ファイルのハードドライブ上の正確な場所を見つけることも、タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)を使用して簡単になります。[プロセス(Processes)]タブでプロセスを右クリックまたは長押しし、[(Right-click or press-and-hold)ファイルの場所を開く("Open file location.")]をクリックまたはタップします。

ファイルエクスプローラー(File Explorer)は、アプリケーションの実行可能ファイルが保存されているフォルダーで開きます。フォルダを開くと、対応するファイルが選択されます。

10.タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)を使用して未知のプロセスまたはアプリを調査する方法(process or app)
タスクマネージャーの[プロセス(Task Manager's Processes) ]タブ(tab show)には、現在開いているアプリが表示されるだけでなく、バックグラウンドプロセスも表示されます。これらのプロセスは、主に上級ユーザーが関心を持っています。不明なアプリまたはプロセスを調査するには、 (app or process)[プロセス(Processes)]タブで右クリックまたは長押ししてから、 [オンラインで検索(Search online)]をクリックまたはタップします。
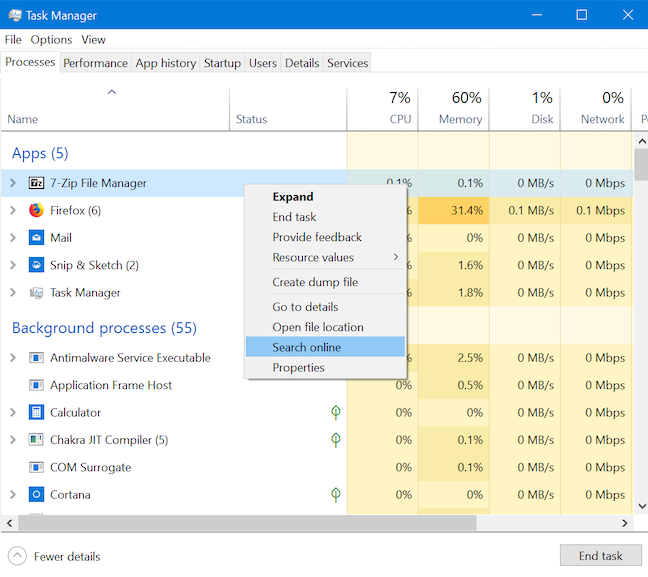
新しいタブでは、デフォルトのWebブラウザーがBing(Bing)上のプロセスまたはアプリの実行可能ファイルの名前でWeb検索を実行し(デフォルトの検索エンジン(default search engine)に関係なく)、より多くの情報を取得するのに役立ちます。

11.タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)から実行中のアプリのプロパティを表示する方法
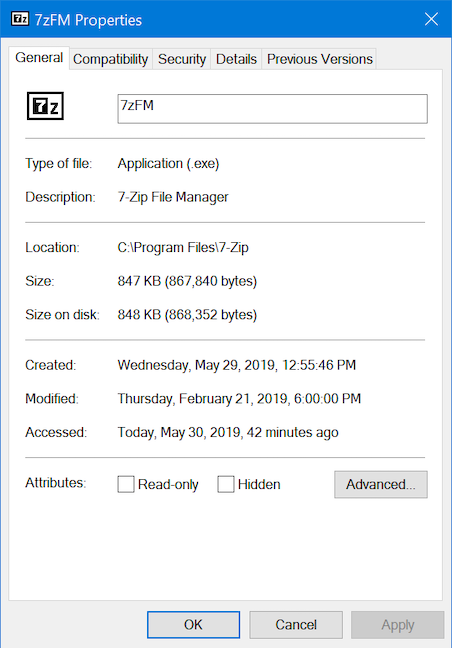
プロセスまたはアプリケーションのプロパティは、それを実行する実行可能ファイルに関する多くの情報を提供します。ファイルのサイズ、場所、アクセス日、セキュリティ設定が表示され、互換性の問題のトラブルシューティングが可能になります。タスクマネージャの(Task Manager)[プロセス(Processes)]リストからアプリまたはプロセス(app or process)を右クリックまたは長押しして、[プロパティ(Properties)]を選択します。
![[プロパティ]を押すと、アプリまたはプロセスに関する詳細情報が表示されます](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-nUbE8sXk23A/YjdSQDKNv8I/AAAAAAAAxQc/Q7Rh-95fk6wXoUuoDEQ_rvf1n7nwtmOfwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCd4d2RBg/s0/SZbfu781jOeBVIldgnQ6iSNOwfQ.png)
[プロパティ](Properties)ウィンドウが開き、アプリに関する有用な情報にアクセスできます。
タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)の[プロセス]タブ(Processes tab)はどのくらい混雑していますか?
このタブをカスタマイズするさまざまな方法を検討したので、タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)に何を表示するかをお知らせください。大多数のユーザーのように基本的なものにしますか、それともより詳細なビューを好みますか?以下にコメント(Comment)して、話し合いましょう。
11 ways to manage running processes with the Task Manager in Windows 10
The Windows 10 Task Manager gives you a lot of power when it comes to monitoring system resources. The Processes tab shares more information than ever before, allowing you to customize the data it shows according to your needs. Here is how to tweak the Task Manager's Processes tab in Windows 10 and become more efficient, by ensuring the data relevant to you is displayed in a way that suits your needs better than the default view:
What is the Processes tab and how to access it?
The Processes tab lists all the apps, background processes, and Windows processes running at any given time, providing useful data about each of them. It is available in the full version of the Task Manager. There are several options available to open the Task Manager, but we think the most comfortable is the keyboard shortcut "Ctrl + Shift + Esc." If you skipped Windows 8, and if this is your first time accessing the tool, it opens in what we call the compact view, showing you a list of all the apps currently running on your Windows 10 device. To open the full version of the Task Manager, click or tap More details at the bottom of the compact view.

The full version of the Task Manager opens, and the Processes tab is the default tab.

TIP: The Task Manager can be customized to open in any tab you want. To find out more, read How to set the default view/tab for the Windows 10 Task Manager.
1. How to add or remove data columns in Task Manager's Processes tab
In the Processes tab, you get information on every app, background process, and Windows process currently running on your computer. This data is structured and displayed in columns. Click or tap on a column's header, and drag it to reorder the columns in the order you prefer. You can pick and choose the information shown in the Processes tab by adding and removing columns. Right-click or press-and-hold on an existing column's header and select which of the fourteen optional columns are displayed in the Processes tab of the Task Manager. Keep in mind that the Name column is the only column that you cannot hide.

To ensure that the columns you select provide you with relevant data, here is a run-down of what they have to offer:
-
Type - Displays whether the process is an app, a background process, or a Windows process. If "Group by type" is selected, this column becomes redundant
-
Status - Displays whether or not a process is suspended. When something is suspended, it is running in the background, but it has no access to CPU cycles and uses little memory.
- Publisher - Displays the name of the process's publisher.
-
PID - Displays a unique Process Identifier for each running process. These numbers can be used to match a running process with an error or event that lists the PID.
-
Process name - Displays the name of the process's executable. E.g., 7zFM.exe for 7-Zip File Manager.
-
Command line - Displays the command-line syntax run for each process. This lets you see if any apps or processes have been launched with special command-line parameters and also gives you the location of each process's executable file.
-
CPU - Shows each process's processor usage.
-
Memory - Shows each process's RAM usage.
-
Disk - Shows each process's hard disk usage.
-
Network - Shows each process's network usage.
-
GPU - Shows each process's usage of the video card.
-
GPU engine - Shares which GPU engine is utilized by each process. According to Microsoft: a GPU engine represents an independent unit of silicon on the graphics card, that can be scheduled and can operate in parallel with another. You can find our more about this concept, here.
-
Power usage - Displays the power used by each process.
-
Power usage trend - Shows the overall trend in power usage for each process.
2. How to sort running apps and processes in Task Manager's Processes tab
By default, the Task Manager's Processes list is sorted logically by process type. This means that all apps, background processes, and Windows 10 processes are grouped together and sorted within their group in this first column of the tab, called Name. While we are big fans of this system, you may wish to sort the list alphabetically instead. Click or tap View and deselect "Group by type" if you want all the active apps and processes to be displayed in an alphabetical list.

Clicking or tapping on a column's header allows you to sort the running apps and processes based on the values displayed in that column. E.g., clicking on Memory sorts the list by how much RAM the processes are using. This can come in handy if you are wondering what processes consume the most or the least resources on your computer. Regardless of the sorting method you are using, select the "Group by type" option in the View menu if you wish to return to the default sorting at any point.
3. How to change the way data values are displayed in the Processes tab
On top of allowing you to customize which information is shown, the Processes tab also lets you decide how some of that data is displayed. For the Memory, Disk and Network columns you can choose whether to display the data using values - MB of memory, MB/s disk usage and Mbps network usage - or as a percentage of the total available resource. Right-click or press-and-hold on any column's header or process in the Processes tab of theTask Manager, and go to Resource values. Choose one of the resources and then select either Percents or Values to have the data displayed according to your needs and preferences.

4. How to expand and collapse running processes in the Task Manager
Some processes are more complex than others, involving more than just the main process. The Task Manager's Processes tab allows you to expand listed processes and get more details about the subprocesses running under them. The number of subprocesses is indicated by a number in brackets following each process. To expand a single process, right-click or press-and-hold on it, and click or tap Expand. An easier way to do this is by clicking or tapping the arrow to the left of the process.

You can click the arrow again, or you can right-click or press-and-hold on that process, and go to Collapse if you want to hide the subprocesses again.
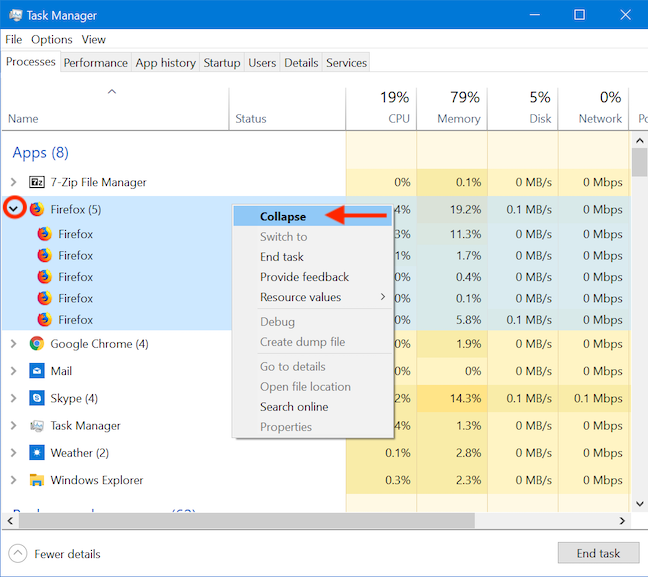
You can also expand any collapsed entries by clicking or tapping View and then Expand all.

To instantly collapse all expanded entries, click or tap Collapse all from the View menu.
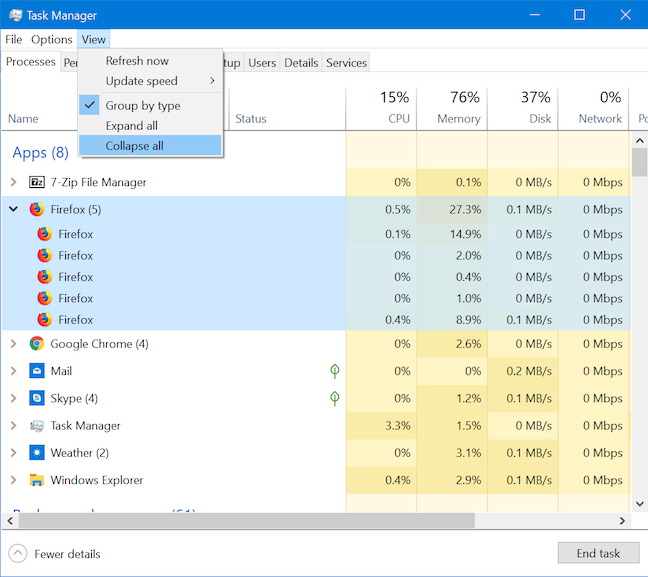
TIP: For multi-process applications, the contextual menu displays greyed out options when right-clicking or pressing-and-holding the main (parent) process. Right-click or press-and-hold on each subprocess to interact with it.

5. How to end running processes using the Task Manager
The primary use of the Task Manager is to close running processes that are no longer responding. Right-click or press-and-hold on any process and a contextual menu opens. Click or tap End task to close the process.
You can also select the app and click or tap the End task button on the bottom-right corner of the Processes tab to close the process.

6. How to provide feedback on a running process to Microsoft
The Feedback Hub is easily accessible from the Task Manager, allowing you to offer feedback on a running process. Right-click or press-and-hold on any process, and then choose to Provide feedback.

When the Feedback Hub opens, you can sign in with your Microsoft account and use it to send your issue, criticism, or suggestion to Microsoft.

7. How to create a dump file for a running process using the Task Manager
A dump file is a large file that uses the DMP format and provides details on what a particular process or application is doing at the exact time the dump file is created. This usually comes in handy to software developers trying to solve a bug or a problem with that process. To create a dump file, right-click or press-and-hold on any process and click or tap "Create dump file."

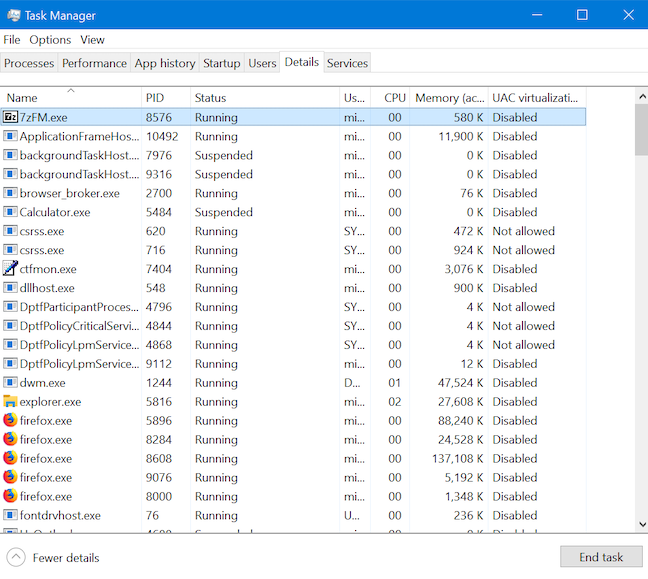
8. How to see details for a running process in the Task Manager
The Details tab of the Task Manager unsurprisingly provides precise details about running processes. However, this tab's sorting options are limited, so finding more about a certain process can turn into a bit of a treasure hunt, especially if you have many processes running on your computer. Luckily, the Processes tab makes up for that by providing an option to highlight the corresponding process in the Details tab. Right-click or press-and-hold on any process, and then click or tap "Go to details."

The focus moves to the Details tab, where the corresponding executable file is highlighted.
9. How to find the location of a running process in the Task Manager
Finding the exact location on your hard drive of the executable file corresponding to an app or a process is also made easier with the Task Manager. Right-click or press-and-hold on the process in the Processes tab and click or tap on "Open file location."

The File Explorer opens at the folder where your application's executable file is stored. The corresponding file is selected when the folder opens.

10. How to research an unknown process or app using the Task Manager
Not only does the Task Manager's Processes tab show apps that are currently open, but it also displays background processes, which are mostly of interest to more advanced users. To research an unknown app or process, right-click or press-and-hold on it in the Processes tab, and then click or tap Search online.

In a new tab, your default web browser runs a web search with the name of the process's or app's executable file on Bing (regardless of your default search engine), helping you get more information.

11. How to view the properties of a running app from the Task Manager
The properties of a process or an application offer a lot of information about the executable that runs it. They show the file's size, location, access dates, and security settings, and let you troubleshoot compatibility issues. Right-click or press-and-hold on an app or process from the Processes list of the Task Manager and choose Properties.
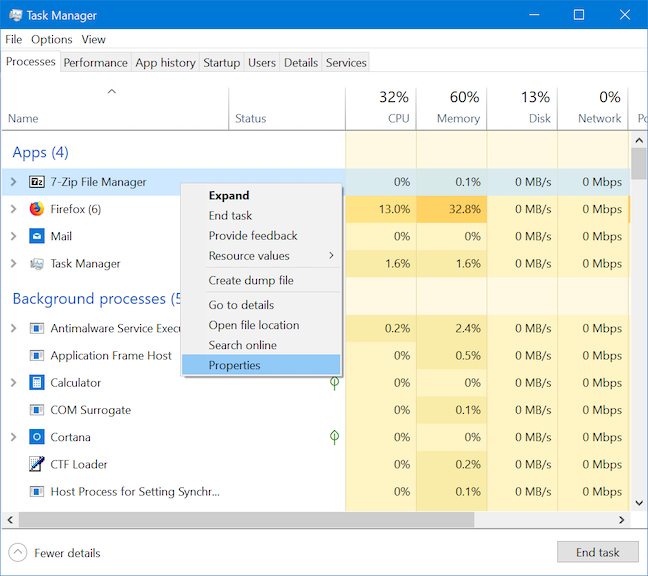
The Properties window opens, providing you access to useful information about the app.

How crowded is your Task Manager's Processes tab?
Since we went over the different ways you can customize this tab, let us know what you choose to see in your Task Manager. Do you keep it basic like the majority of users or prefer a more detailed view? Comment below and let's discuss.
![[詳細]をクリックして、タスクマネージャーのフルバージョンを開きます](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-m1WtF1kqJhk/YjcxuTQffeI/AAAAAAAAKvg/TChJoq7iQ448y4viHGjkvGO01OdVyDPYQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxqHo63eC-w2z6yviSn9DYRDJuWMKm_sPX6g-BI1OEFwv6L01SgCY8x7NMPafCADWrqG-5bpVDJ9v1dX5VJUMKLtB4dJOAcVJsEhFbbXtL-XEojuNI5AruC6OEcs4cjQnBRmHxiidG_bT2PUln-JyMDeM9aSWLAKSXNGv7-yc7yQmIvhyUYhbDkEh81nfEAWmrpABM29e2_Sw9E50aw52PTBbSFGr-9f2F_zVQ6X8hhfsueD2Q3TAAeasc4-YpuzFdw2-e8Er4zY_PbIim0s6V3-GMF_pNVuXyk43N0cVPAQ4d5EcEKzOSQZl94Dd4hs_80k2TqFQdbSNhpq9D9NQyskK8FU-cfokIaFU0zhsWLLuGZVsuH1NRNGn4YNiKEV3QCAPqc9kzi1dPCRqXGd--4GOATbeSeKcQVgEuAwUTG5knE2W6mc6eg3LAB05feSMp5RK6QTKY72osxAAWsYKriaD-cjcVT3-YNVM5UanAfvczKJd_aCqsMi7kY2O-rOOq_hTYACxmVLcoKulU2T9PDKqZObOmLUWvpw1LFqfbIcIgdTfhTJx2pOU5yBgXu92TP53dU475DxGW5MnLmd0KwZo4qU3vaO3OQOutgpXWW1yHWLDsgvUWG4wybPqFh4idUvTQRR786lrgNYjAwlqDdkQY/s0/MtDu3Lfk-rlI-bsd--9arREBGnk.png)
![フルバージョンのタスクマネージャの[プロセス]タブ](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-wlaTiGkiqfw/YjcH28vxX3I/AAAAAAAAm5I/2NtPv8khqWsj61a9VpIY9egJnMpAPGnkQCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhz5DZ-hz5cO1PBItFuqMt-Vmf8q6HMW3ErIDpIKqiIjAdYSAk3FM5AHzJHByJ7ls2gNEmwAwFU0Ofl7XtDrldpz8Od3Xgk0E1vJj4Vjlb1vj9nKSLQ3vEyxx8CWS_pOrSgwx-a_C6rBAJXLmyBISO27kOBOVup524UvkN6du6YslurFWA0meGuI6sSMlM8REHDlcVzWZTKdf3agRkJ_O4LULbX1kdOJnkXJAEf0WDef8yqF09q5K4ltEDf35w9NWKYrfoc04zjDgLzbORLLq7BinuKlY5z2_dx11uMMcsSCJpg79IOuVfy7HqpZNHwtw-Va1KN9Z8dIISY5TsfDcorwAZtCGvvmsSd-VwceZrJDYuOOZmeJBK4TG7cF42ZjeugI7rq3Y76ZavRUVtMNjWJrhJ00z90G1JFKrEmL4RW9zBZpSo5l8mIGEpwxjqPsRMrt1R9i6ii8F_GVFwEOsU_6J6LE8SL8Jfd_oZtVwv5Tx6mqKpXstTllxBWWZdVkT0QMSpOTfTyALG4uBghJWAlDIGBuZYMmHOdWDrjlbCdOJGjS7nLJumJiVzeMGZNca53dSx2ID3UI8kB3a_Sb0TqkADaww2cVzPB484fwe7MVoGbqjzeV0EV5cznHnTsy3uPhCtQn5zCRz9yRBg/s0/6GrQipy4h1nmoEsC7esPtqH37Lo.png)
![[プロセス]タブで使用できるオプションの列は14個あります](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-zi854JoF6m0/Yjc69jPQ3VI/AAAAAAAAr4Q/rjBAKEZVXUoifdt3dUyp64M9Y-czQ_xJwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwCXdzMJo7Wy553Aab3IZfOcw-mLQTdmC4hM2tdUzSWs4kfq4JkoKacm2dcmiXk_lz8R0wls265Moyy3wuNaVsnq-WRgFjO_g6jIIA0z4UcLfbp5OSpexjAMt1MPlFLsqd11iAcc2q3-vnx2pbUltMYmtCvDHn8913LB0YagLYUztW6LL99jHPxoNDfJV-VRQw1VU6BzKNgZigC1RnuEe_Z1OKbhBf5_Os7MrqGIJN8PSviPXrUAxQVJPkJV0J9TYOsa0KL5Y5KDXH5I0JOltaY5xDdlJq0pSEUYuMc34yqT9IZHXVxomR9MPmvM0KXWAOVQMvqqCuV0YaEOlvZakcX5oQ_f7-rpZXL2VMObbH-GM4TiplrfKmfFxHplCqA6PaiKPNwpIKRY6yejrQRKB7wrgbFZz6rLPDaNHbT2uVjnNMrdL5H-gWEn3XTzoL1Qn51kZCcfLC5L1qmSoK0uQK7ZDR3eT3dAaqQHSI0aPeKW3GcnREgQYRdljNChhFutZpWHKZvIzbesmhsvphyR609wQ9kmts6IC_BuC_O7TMsj35HzoCsCP9QlXujZLExO7mrwLuBQjCqqtuxizkyA9_9mgzkeDk8xyBwzVKh8C4GTmKyzd-LbNX_CUazBZpV4bWInTWPlDCFoN2RBg/s0/j1IhUO4xCd3UFWQ4OjEtmE7s5kI.png)
![[タイプでグループ化]オプションは、アプリとプロセスの並べ替え方法を変更します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-YPYxnedQ0ik/YjdGavNcZsI/AAAAAAAAuwI/Se2Prg-8S481Wh-bLaZ0Pyg4rTew5NU-QCEwYBhgLKu8DABHVOhxcrfjNL0kpApMdsYcrhR6ibP9yFPgid8tif1XJf590Y_S6I5KKOmSt3l5FGY4xSNyvZdonIyhAy17tqtmX612OyJ04O3L0FlnNcNc0C54eOcYAIPck3FI_krYDif6TAC-yzKxFLqijseiFajZsn5zZb5ikZDEoD98WADPb77Q8xJjOH9YzrQe3CB3fICtjnubLwJfl_5qf96x98EvSIMovAxNksn1luuo0L_dnicCPkBgBf5wN0-gtGg1mLEXM8O7RQ9uZx49lRm7ceAFzzMt_6Cq2w-eXXuubN_kNKoT7juKeFa2-L0zW6YGXdHX_H-uPut3z-kosp-leDwO3y29zBsAOH0aOENAJ-JGeAnRJ7TKv4t2I6l2cfc-lF9kRTKX6aYwsM79CQqNoNt61sae4bD0zEcPXA9px0izvU6TWFBY_0eJV8U_jRs_hFuQGd3mv42XGA9AF9USp0pq4reDvfzEUbUScBDJxV2FH0gc74fjQOnfl4a2FntrUFG4TIrLZdM1piJaWyZ1PgX8v43nHC1Hi9uMmXsWiYFo5NX1MHFRWVJnhLyCAzaIwxq_hg3o27aMIgAeS-fQ5cwlLgvZliezsqr04t33qG12AvR8NX8glkuNvFAGVed6Q_NgxRGKhvGXPVRSd4G8WMKKg3ZEG/s0/rbk3b91O-FsK-Hiy-bufP6n4x4M.png)

![サブプロセスの詳細については、左側の矢印を使用するか、[展開]をクリックまたはタップしてください](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-So9wuMnuhgg/YjctbafvKbI/AAAAAAAAsCw/CJ8On6-AkcEaOmR71OdWfN0XLN1AhbNIwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhwCXdzMJo7Wy553Aab3IZfOcw-mLQTdmC4hM2tdUzSWs4kfq4JkoKacm2dcmiXk_lz8R0wls265Moyy3wuNaVsnq-WRgFjO_g6jIIA0z4UcLfbp5OSpexjAMt1MPlFLsqd11iAcc2q3-vnx2pbUltMYmtCvDHn8913LB0YagLYUztW6LL99jHPxoNDfJV-VRQw1VU6BzKNgZigC1RnuEe_Z1OKbhBf5_Os7MrqGIJN8PSviPXrUAxQVJPkJV0J9TYOsa0KL5Y5KDXH5I0JOltaY5xDdlJq0pSEUYuMc34yqT9IZHXVxomR9MPmvM0KXWAOVQMvqqCuV0YaEOlvZakcX5oQ_f7-rpZXL2VMObbH-GM4TiplrfKmfFxHplCqA6PaiKPNwpIKRY6yejrQRKB7wrgbFZz6rLPDaNHbT2uVjnNMrdL5H-gWEn3XTzoL1Qn51kZCcfLC5L1qmSoK0uQK7ZDR3eT3dAaqQHSI0aPeKW3GcnREgQYRdljNChhFutZpWHKZvIzbesmhsvphyR609wQ9kmts6IC_BuC_O7TMsj35HzoCsCP9QlXujZLExO7mrwLuBQjCqqtuxizkyA9_9mgzkeDk8xyBwzVKh8C4GTmKyzd-LbNX_CUazBZpV4bWInTWPlDCFoN2RBg/s0/J21oHlprEXBU7plWDmkYMPXVW5I.png)
![左側の矢印を使用するか、[折りたたみ]をクリックまたはタップして詳細を非表示にします](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-E7upTPJfsyw/YjdR1vKmWgI/AAAAAAAAxSg/cWoVaG1MTOEvim1TgrCCQeNLahiTKo-tgCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCd4d2RBg/s0/SV9KENhtr2Gs-iAM2Y0At34mLFI.png)
![[すべて展開]をクリックまたはタップして、すべてのプロセスを展開します](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Ejwl7nBsTpw/YjcX0OLX-EI/AAAAAAAAC_Q/QFvknDpIlVwTf2AFbDX1vG72KeNfteZJQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxeSqmKu1BtuATYSULyy9OK0vUZJMh4EEreX9rzJid57_Lr5itgoyxzXecCdHil_kcjllNp636SB8ECcTxmI--8us7mIs7_4fcnjy5EcSKFLsehZVlA79dQvMROYqrbbfCkZz25BePPjbkt5vMp0a-Ffrw5A99b5RlKddBRMXeM9g_FOe-xFzRbvRW7TYY6HykLA9PekQsEvOV8jpg0SHFKFaAgGIgHmS8N7Z4b0t8oAyxaq09z-wMB1q859mpaUbsnf4wcrBa-aLiovkCSe0-odM-A-9luIU_P030lCRFTGU9BY0zVaY2-1KUD4qSF0CxrUZ63BI5AN1rY-GLaYkrr6q6sLymszIx_5ReHwutHRLMCol2Y3bqo8_EmWqm1xKORC4FaaCfGnEFVJB_wg7045IZzS73d4lf5GevtJPILvrX6AAn4MdBndWPI54Il_GyriQm-PvgqlWRU8VIZSbskQDSr606f1DhUT0lFbEm55jRTZO5fxh4ah9Me-2zfxCotjHRzCLkIkXarR56jt-M2SgQLbI-FEfyKwUTPXJ4v_RR4iPWc90tJKVi01D3pbDGX5WGBgfwItEcVTJrbT3YKakmk0mweSX3-I0kynawDx1NIRHydgBsBNyU99ZZWyYdyYcFCu2SsV1d5Oa8w3dXckQY/s0/bBrDTsmvprcHSCdPrUbknkuMqmg.png)
![[すべて折りたたむ]をクリックまたはタップして、すべてのプロセスを折りたたむ](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-AZpqJ9tIsb0/YjdRrRmfGzI/AAAAAAAAxQs/eBK-P6WxrMQjFhuhbCrh9BF5wKuc5OdAwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCd4d2RBg/s0/SU-iCulYdcyWlnogwq9Pb9xJ96Q.png)






![[詳細]タブが開き、対応する実行可能ファイルが強調表示されます](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-3NAvUkzAw9g/YjdkUAu67zI/AAAAAAAAP3Y/lJEBrYqx3lo4h8rQbc36OwmFLHlWNMaawCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhyU0JW91iiU4HdUNyWpEBsKLTw-6rQ88JJcf3GF8lMk7uR2vURQvSrLKx3HPJ-0bFTSQRDYtFiF0xXMnzMqjkeinj0p4_6R1kO7c7YxY5qQhApZ0W4keaxtQNkUgY3tkRT5-ypFY9VCwWOdWlQjQXqnqqmUhUOHojDHDyRxOdzXgn83uL9cUhyZQAyqoLNXwTuyPI3w7jMVLY_X3G_jMusEXoZHkAYQKZqBgUhPxBxFlPwhH-2DdZDXsVjKZqfavx4quKoI8Dn5vbKBw1fBP2LP-TMONu3R7eOkf34NH9fhPJJ8dtB0a9Nr9Lbun4wsDt2UkPoVWdXK-T5WEyqL8jtJIZzuNmeYS32rgbNJxt2MkVJe0ECNAjwjXY1oCKwCAja-lwWv2MG2WdS5jNcBqq8uNpsf5TXfjQaewupijbNsp_viGHOdMXhU68bv9CYzh3Jg897TZj113lNc9x2yiPm9ZLpb68caNxrHKk6kQvdPMHMRzJzCFsHGdrcsGW8UUQ6Ht3UrJUSKHvNnPH9C-EavJf8LBHVfter4gT7dO0uaIhreDldhomF7fI1DE1HmW7QFlecOcn2MqpmjESsYDZlEqVL_O7bu6l5iDcDGvhsDH0Fhqz9rIOYRCpkWkIV1yugxhdBnKN3LY3H2ntww_OXdkQY/s0/vooj14PM6EQAkqAB4jlXrWwe6uk.png)




![[プロパティ]を押すと、アプリまたはプロセスに関する詳細情報が表示されます](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-nUbE8sXk23A/YjdSQDKNv8I/AAAAAAAAxQc/Q7Rh-95fk6wXoUuoDEQ_rvf1n7nwtmOfwCEwYBhgLKuoDABHVOhyA7Kl1nmuuE8YbfjpS9M3y-4uTVj7wwni_pQolcgJ95qTiO-uLPhHKnju5WtDUoCrh2GRhIuYn7H3A46WuR-NxwSiz3saC40lwEhLnEYSN1u049dY0D67l2CYyjg9Y07wRfnE24PF602JMWQ1tdO-7rwnXCbH-aen2ea7CQo1ODnAY1BCnUqtOf3xImHqFiNG3S8Q2NwO2TMd0tE1PbEUe3d5YJbd5HYjzbMmBiGMhVyvwZzVxKv1vF6EyEneYOXYpGLPPH2NpymJra9dKyL2eURnGuZzKwpReiu5BpQLzp-hh87uSJSlyCQ7ayU5pcMdJssGrsEJh5C-WsErMEJ0tE_FqLyDYX9EQ_MunDF7n3WJGQfXpQv5pjBA8MziUg9apzX0jdHDVVZJig8mgsk-81NqKeyDpZur2nn6PNvOlsduvCBq6Pgr51EQrrqOG5FNe5uiW36h5-u_yykFWzomxUoJ5SZkrxNrRvDqgntZvuPVxqE97MLOzC2UMF7kEWnA8HOkgWS4DRgY5vw2HYe0vwyFUDZbgDKOdbw0wn573JdoDAEeF7eTzjYqswz6pOpZDT0yyKKczaWxJPtWMgZ6yH18L_euilSbnLknCwvQX6JL3-DCrNUOD7sWAloZMYvFekGONPDCd4d2RBg/s0/SZbfu781jOeBVIldgnQ6iSNOwfQ.png)

