PerfMon.exeまたはPerfMon.mscとしても知られるパフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)について聞いたことがありますか?これは、 Windowsコンピューターまたはデバイス(Windows computer or device)のパフォーマンスを監視するために使用できる洗練されたツールです。これを使用すると、コンピューターがリソースをどのように管理しているかを確認できます。それが提供する情報は、特にコンピューターのパフォーマンスが期待を下回っている場合に、ソフトウェアとハードウェアの選択(software and hardware choices)について決定を下すのに役立ちます。トラブルシューティングを行う場合にも役立ちます。パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)を使用して、プロのようにシステムのパフォーマンスを分析する方法は次のとおりです。
注:(NOTE:)このガイドは、Windows 10、Windows 7、およびWindows8.1で機能します。
Windowsで(Windows)パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)を起動する方法
パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)を起動する方法はたくさんあります。Windowsのすべてのバージョンで機能するのは、検索を使用することです。たとえば、Windows 10では、タスクバーの検索ボックスに(search box)「パフォーマンスモニター」("performance monitor")と入力し、適切な結果をクリックまたはタップします。

Windowsバージョンで(Windows version)パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)を開く他の方法については、次の記事を確認してください: Windows(すべてのバージョン)でパフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)を起動する11の方法。
パフォーマンスモニターを使用して(Performance Monitor)システムパフォーマンス(system performance)を分析する方法
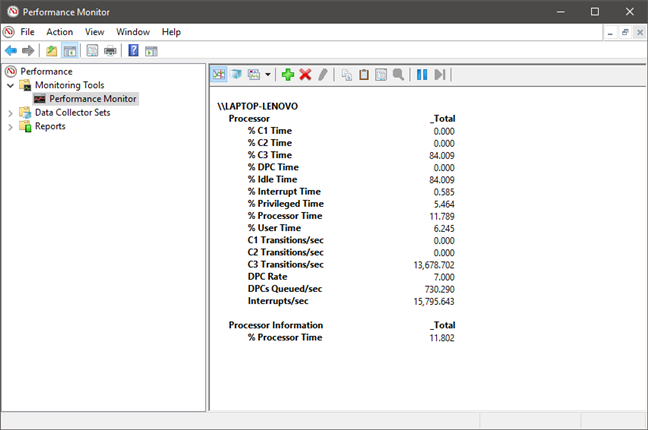
コンピュータの現在のパフォーマンスの分析を開始するには、以下に示すように、プログラムのメインパネルの[監視ツール(Monitoring Tools)]の下にある[パフォーマンスモニター]を(Performance Monitor)クリックまたはタップ(click or tap)します。

注:特定の(NOTE:)アプリやプログラム(apps and programs)のセットを使用しているときにコンピューターがどのように動作するかを確認したい場合は、グラフがシステムのリソースへの影響を記録できるように、今すぐそれらを開いてください。
デフォルトでは、パフォーマンスモニターによって表示されるグラフは、(Performance Monitor)プロセッサー(Processor)時間を測定します。これは、プロセッサーがアクティブなプログラムの実行でビジー状態になっている時間です(パーセンテージで表示)。これにより、プロセッサの動作の基本的な測定値が得られます。

このグラフは、追加の列やその他のいくつかのオプションを使用してカスタマイズできます。より詳細な分析のために、他のデータを詳細に示すことができるカウンターをグラフに追加することもできます。これを行うには、グラフの上にある緑色のプラス記号を押します。

開いた[カウンターの追加](Add Counters)ウィンドウで、リアルタイムで監視するカウンターを選択できます。それらはタイプ別に整理されており、たくさんあります。カウンターの名前をダブルクリック(ダブルタップ)すると、いくつかの個別のオブジェクトが表示され、それらのいずれか、およびすべてを監視するように選択できます。
監視するカウンターとオブジェクトの選択が完了したら、[追加(Add)]ボタンをクリックまたはタップします。追加されたカウンターは、ウィンドウの右側に表示されます。[ OK ]をクリックまたはタップすると、パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)からグラフに追加されます。

たとえば、次のグラフでは、プロセッサ(Processor) カウンタセット(counter set)を使用しました。Interrupts/sec(プロセッサが応答するように求められた割り込みの数。ハードディスクコントローラ(disk controller)アダプタやネットワークインターフェイス(network interface)カードなどのハードウェアコンポーネントによって生成されます)や%User (total amount)%User Time(-ユーザーモード操作に費やされたアイドル時間)。

これで、選択したカウンターを使用して、監視したいアクティビティを実行し、それらがリアルタイムでどのように変化するかを確認できます。
パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)でのデータの表示方法をカスタマイズする方法
[グラフの種類("Change graph type")の変更]ボタンをクリックまたはタップして(またはキーボードのCTRL + Gヒストグラムバー(Histogram bar)またはレポート(Report)オプションを選択して、他の形式のデータを表示することもできます。

この写真は、ヒストグラム(Histogram)形式のデータを示しています。

ここに、レポート(Report)オプションのデータ表示の例があります。
下で強調表示されている[プロパティ]ボタンをクリックするか、キーボードの(Properties)CTRL + Qを押すと、データの表示方法をさらに変更できます。

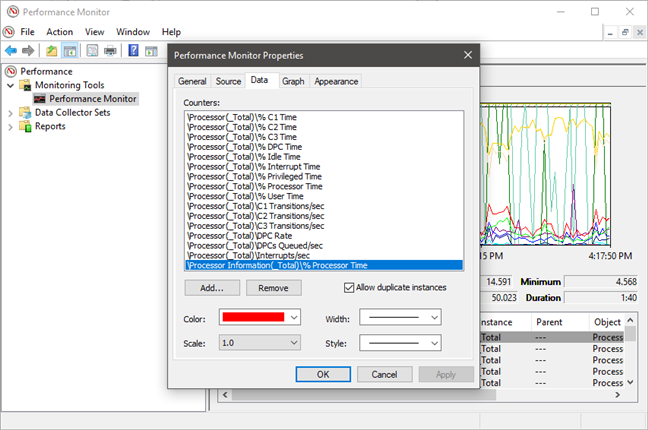
これにより、[パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor Properties)のプロパティ]ウィンドウが開きます。このウィンドウでは、各カウンターの表示方法、色、線の種類などをカスタマイズできます。このタイプのパーソナライズには、[データ(Data)]タブと[グラフ](Graph)タブの両方を使用できます。
![[パフォーマンスモニターのプロパティ]ウィンドウ](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Ayg7tmukMqA/Yjc15FsI5rI/AAAAAAAAKuI/QGG7qCngYBAAuh23-MDm-XnFUNnRjdoIQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxqHo63eC-w2z6yviSn9DYRDJuWMKm_sPX6g-BI1OEFwv6L01SgCY8x7NMPafCADWrqG-5bpVDJ9v1dX5VJUMKLtB4dJOAcVJsEhFbbXtL-XEojuNI5AruC6OEcs4cjQnBRmHxiidG_bT2PUln-JyMDeM9aSWLAKSXNGv7-yc7yQmIvhyUYhbDkEh81nfEAWmrpABM29e2_Sw9E50aw52PTBbSFGr-9f2F_zVQ6X8hhfsueD2Q3TAAeasc4-YpuzFdw2-e8Er4zY_PbIim0s6V3-GMF_pNVuXyk43N0cVPAQ4d5EcEKzOSQZl94Dd4hs_80k2TqFQdbSNhpq9D9NQyskK8FU-cfokIaFU0zhsWLLuGZVsuH1NRNGn4YNiKEV3QCAPqc9kzi1dPCRqXGd--4GOATbeSeKcQVgEuAwUTG5knE2W6mc6eg3LAB05feSMp5RK6QTKY72osxAAWsYKriaD-cjcVT3-YNVM5UanAfvczKJd_aCqsMi7kY2O-rOOq_hTYACxmVLcoKulU2T9PDKqZObOmLUWvpw1LFqfbIcIgdTfhTJx2pOU5yBgXu92TP53dU475DxGW5MnLmd0KwZo4qU3vaO3OQOutgpXWW1yHWLDsgvUWG4wybPqFh4idUvTQRR786lrgNYjAwl6DdkQY/s0/Ne1m2kzjhhA3pvUNGWyI790zmhA.png)
必要に応じてすべてをパーソナライズし終えたら、OKボタンを押すことを忘れないでください。
最も便利なパフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)カウンターはどれですか?
パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)のグラフィカルレポートに含まれるデータは非常に技術的であり、カジュアルユーザーが理解するのは困難です。ただし、少なくとも自分の机にWindowsコンピューターを持っている通常のユーザーにとっては、他のカウンターよりも便利なカウンターがいくつかあります。(Windows computer)何かが正しく機能していないかどうかを確認するのに役立つパフォーマンスカウンターの選択を次に示します。
-
Processor -> % Processor Time:カウンタのプロセッサ(Processor)リストで見つけることができます。プロセッサがさまざまなタスクに費やした時間を示します。その値が常に80%を超えている場合は、プロセッサがコンピュータで行うすべてのことを維持するのに十分な能力を備えていないことを意味するため、ボトルネックになります。この問題の解決策は、コンピューターで要求の少ないアプリを使用することですが、長期的な解決策は、プロセッサーをアップグレードすることだけです。
-
Memory -> Available MBytes数:カウンタのメモリリストにあります。(Memory)このカウンターをグラフに追加して、システムに使用可能な十分なメモリがあるかどうかを確認できます。グラフに、使用可能なメモリが合計量の10%未満であることが示されている場合は、十分なRAMがインストールされていない可能性があります。その場合は、さらに追加することを検討してください。
-
PhysicalDisk -> Current Disk Queue LengthとPhysicalDisk -> % Disk Time:これらの2つのカウンターは両方ともPhysicalDiskリストにあります。現在のディスクキューの長さ(Current Disk Queue Length)が2より長く、ディスク時間(Disk Time)が100%で閉じている場合は、監視しているハードドライブが遅すぎるか、故障している可能性があります。その場合は、ハードドライブのアップグレードを検討することをお勧めします。

パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)で利用可能なすべてのデータを理解する方法
残念ながら、パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)で使用できるカウンターのリストは非常に長く、1つの記事ですべてを網羅することはできません。%DPC TimeやPage Faults/secなどの厄介な用語を説明する優れた知識ベース(knowledge base)を探している場合は、MicrosoftのTechNet:パフォーマンスモニターカウンター(Performance Monitor Counters)でこのエントリを読んでください。そこには、レポートの標準リストにある各カウンターに関する完全な情報があります。
パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)を使用して、システムのボトルネックを見つけますか?
この記事では、パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)のレポートを開いて読み上げる方法と、カウンターセットを適用してシステムのアクティビティをさらに監視する方法について説明しました。また、 Windowsコンピューター(Windows computer)の主要なハードウェアパーツの分析を実行するのに役立ついくつかの便利なカウンターも示しました。PCのトラブルシューティングにパフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)を使用しましたか?(Did)このツールの使用方法と、目的に役立ったかどうかをお知らせください。
How to work with the Performance Monitor in Windows
Have you heard about the Performance Monitor, also known as PerfMon.exe or PerfMon.msc? It is a sophisticated tool that can be used to monitor the performance of your Windows computer or device. Using it, you can see how your computer manages its resources. The information it gives you can help you make decisions about software and hardware choices, especially when your computer's performance is below expectations. It is also useful when you want to do some troubleshooting. Here is how to use the Performance Monitor to analyze your system's performance like a pro:
NOTE: This guide works in Windows 10, Windows 7 and Windows 8.1.
How to start the Performance Monitor in Windows
The are many ways to start the Performance Monitor. One that works in all versions of Windows is to use the search. For example, in Windows 10, type "performance monitor" in the search box on the taskbar and then click or tap the appropriate result.

For other ways to open the Performance Monitor in any Windows version, check this article: 11 ways to start Performance Monitor in Windows (all versions).
How to analyze system performance with Performance Monitor
To begin an analysis of your computer's current performance, click or tap on Performance Monitor under Monitoring Tools on the program's main panel, as indicated below.

NOTE: If you want to see how your computer performs while using a particular set of apps and programs, make sure to open them now so that the graphs can take note of their impact on your system's resources.
By default, the graph shown by Performance Monitor measures Processor time, which is the amount of time that the processor is busy working on running active programs (shown in percentages). This gives you a basic measure of how hard your processor is working.

This graph can be customized with additional columns and several other options. For a more in-depth analysis, you can also add counters to the graph that can detail other data. To do this, hit the green plus sign above the graph.

In the Add Counters window that opens, you can select the counters that you want to monitor in real time. They are organized by type and they are many. If you double-click (double-tap) on the name of a counter, you should see several individual objects and you can select to monitor any of them, as well as all of them.
When you are done selecting the counters and the objects that you want to monitor, click or tap the Add button. The added counters are shown on the right side of the window. When you click or tap OK, they are added to the graph from the Performance Monitor.

For example, in the graph below, we used the Processor counter set. It shows technical but useful data such as Interrupts/sec (the numbers of interrupts your processor was asked to respond to. They are generated by hardware components like hard disk controller adapters and network interface cards) or %User Time (the total amount of non-idle time that was spent on user mode operations).

Now you can go ahead and perform the activities that you want to be monitored, using the selected counters and see how they change in real time.
How to customize the way data is displayed in Performance Monitor
You can also look at the data in other formats by clicking or tapping on the "Change graph type" button (or by hitting CTRL + G on your keyboard) and choosing the Histogram bar or Report options.

This picture shows the data in Histogram format.

And here we have an example of the data display for the Report option.

You can further change how the data is displayed, by clicking the Properties button highlighted below or by pressing CTRL + Q on your keyboard.

This opens the Performance Monitor Properties window, where you can customize how each counter is displayed, in what color, using which type of lines and so on. You can use both the Data and the Graph tabs for this type of personalization.
When you are done personalizing everything as you wish, do not forget to press the OK button.
Which are the most useful Performance Monitor counters?
The data included in the Performance Monitor's graphical reports are highly technical and difficult to understand by casual users. However, there are a few counters that are more useful than others, at least for the regular user with a Windows computer in his or her desk. Here is a selection of performance counters that can help you see whether something is not working right:
-
Processor -> % Processor Time: you can find it in the Processor list of counters. It shows you the time spent by the processor on various tasks. If its value is consistently above 80%, it means that your processor is not powerful enough to sustain everything you do on your computer, so it becomes a bottleneck. Although a solution to this issue would be to use less demanding apps on your computer, the only long-term solution is to upgrade your processor.
-
Memory -> Available MBytes: is found in the Memory list of counters. You can add this counter to your graph to see whether your system has enough memory available to use. If the graph shows you that the available memory is somewhere less than 10 percent of your total amount, it could mean that you do not have enough RAM installed. In that case, consider adding some more.
-
PhysicalDisk -> Current Disk Queue Length and PhysicalDisk -> % Disk Time: these two counters are found both in the PhysicalDisk list. If the Current Disk Queue Length is higher than 2 and the Disk Time is closing on 100%, it is likely that the hard drive that you are watching is too slow or even faulty. In that case, you might want to consider upgrading your hard drive.

How to make sense of all the data that is available in Performance Monitor
Unfortunately, the list of counters available in Performance Monitor is exceptionally long and we cannot cover everything in just one article. However, if you are looking for a good knowledge base, explaining all the gibberish terms like %DPC Time or Page Faults/sec, read this entry on Microsoft's TechNet: Performance Monitor Counters. There you will find complete information about each counter found in the standard list of reports.
Do you use the Performance Monitor to find the bottlenecks in your system?
This article has shown you how to open and get an essential reading of Performance Monitor reports and how to apply counter sets to monitor the activity of your system further. We have also shown a few useful counters that can help you perform an analysis of the main hardware parts in your Windows computer. Did you use the Performance Monitor for troubleshooting your PC? Let us know how you use this tool and whether it was helpful for your purposes.










![[パフォーマンスモニターのプロパティ]ウィンドウ](https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/-Ayg7tmukMqA/Yjc15FsI5rI/AAAAAAAAKuI/QGG7qCngYBAAuh23-MDm-XnFUNnRjdoIQCEwYBhgLKvEDABHVOhxqHo63eC-w2z6yviSn9DYRDJuWMKm_sPX6g-BI1OEFwv6L01SgCY8x7NMPafCADWrqG-5bpVDJ9v1dX5VJUMKLtB4dJOAcVJsEhFbbXtL-XEojuNI5AruC6OEcs4cjQnBRmHxiidG_bT2PUln-JyMDeM9aSWLAKSXNGv7-yc7yQmIvhyUYhbDkEh81nfEAWmrpABM29e2_Sw9E50aw52PTBbSFGr-9f2F_zVQ6X8hhfsueD2Q3TAAeasc4-YpuzFdw2-e8Er4zY_PbIim0s6V3-GMF_pNVuXyk43N0cVPAQ4d5EcEKzOSQZl94Dd4hs_80k2TqFQdbSNhpq9D9NQyskK8FU-cfokIaFU0zhsWLLuGZVsuH1NRNGn4YNiKEV3QCAPqc9kzi1dPCRqXGd--4GOATbeSeKcQVgEuAwUTG5knE2W6mc6eg3LAB05feSMp5RK6QTKY72osxAAWsYKriaD-cjcVT3-YNVM5UanAfvczKJd_aCqsMi7kY2O-rOOq_hTYACxmVLcoKulU2T9PDKqZObOmLUWvpw1LFqfbIcIgdTfhTJx2pOU5yBgXu92TP53dU475DxGW5MnLmd0KwZo4qU3vaO3OQOutgpXWW1yHWLDsgvUWG4wybPqFh4idUvTQRR786lrgNYjAwl6DdkQY/s0/Ne1m2kzjhhA3pvUNGWyI790zmhA.png)

