今日の初めに、クライアントコンピュータ(client computer)をセーフモードで起動し、 コマンドプロンプトからウイルスを削除する必要がありました。これは、 (command prompt)Windowsが読み込まれるたび にファイルがロックされ、削除できなくなるためです。人生でコマンドプロンプト(command prompt)を使用しなければならない理由は他にもいくつかあります(めったにありませんが)。そのため、ナビゲートする方法を知っておくとよいでしょう。
Windowsで(Windows)コマンドプロンプト(command prompt)を使用する方法を学ぶつもりなら、最も頻繁に実行される基本的なコマンドのいくつかを見ていきます。全員が同じ(Just)ページにいるので、 [スタート]に移動し、[ファイル名を指定して(Start)実行(Run)]をクリックして、 CMDと入力すると、コマンドプロンプト(command prompt)が表示されます。Windows 7では、[スタート(Start)]をクリックして、cmdと入力し始めます。Windows 8では、 [スタート]ボタン(Start button)を右クリックして、 [コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt.)]を選択するだけです。


これで、 C:\Documents and Settings\UsernameまたはC:\Users\Usernameユーザープロファイル(user profile)へのパスの最後にカーソルが置かれた大きな黒いウィンドウが表示されます。だから今何をすべきか!?さて、私はすべてを説明することはできないので、おそらく(explain everything)ヘルプ(HELP)を入力してEnterキーを押すことにより、 MSDOS自体で提供されるヘルプガイドのいくつかを使用することになるでしょう。(Enter.)
これを行うと、 MS DOS(MS DOS)で使用できるすべてのコマンドのリストと、それらの機能の簡単な説明が表示されます。

また、コマンド名(command name)の後に/?を入力すると、パラメーターと各コマンドの使用方法に関する詳細情報を確認できます。。たとえば、CD /?,CDコマンド(CD command)の使用方法に関する簡単なチュートリアルが表示されます。
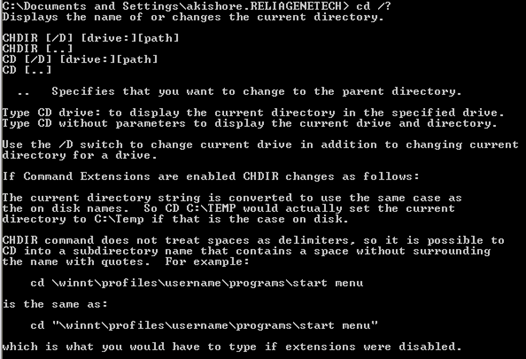
上からわかるように、MS DOS コマンドCD(command CD)は、現在のディレクトリの名前を表示するか、現在のディレクトリを変更します。したがって、デフォルトのユーザープロファイルディレクトリ(default user profile directory)からWindows System32ディレクトリに変更して(Windows System32 directory)ウイルスファイル(virus file)を削除する場合は、次のように入力してそのディレクトリに移動します。
cd c:\window\system32 and press Enter
プロンプトの現在のディレクトリは次のように変更されます。

そのディレクトリにいるので、最初にすべてのファイルとディレクトリを表示したい場合があります。そのため、コマンドDIRを入力して、 (DIR)Enterキー(Enter)を押します。これで、そのディレクトリ内のすべてのファイルとフォルダの巨大なリストが表示されます。DIR /?と入力できます。渡すことができるパラメータを確認してください。

ご覧のとおり、DIR /Pと入力して、ゆっくりと閲覧できるページ形式でリストを表示できます。または、DIR /Wと入力して、単一の列ではなくワイド形式でリストを取得することもできます。DOSの優れた点は、コマンドごとに複数のパラメーターを含めることができるため、DIR /P /Wと入力して、ワイドフォーマットとともにページごとのビューを取得できることです。

ファイルとフォルダのリストができたので、ウイルスの例(virus example)を削除していきましょう。ファイルを削除する場合は、DELコマンドを使用します。もう一度DEL /?コマンドに関するいくつかの有用な情報を提供します。

ファイルを削除するには、 DELファイル名(DEL filename)を入力するだけでファイルが削除されます。この方法でコマンドを使用すると、ファイルを削除する前に確認を求めるプロンプトが表示されないため、正しいファイル名(correct file name)を入力したことを確認してください。また、拡張子を付けてファイル名(file name)を入力する必要があるため、そのファイルを削除するにはDELTest.txtになります。(DEL Test.txt)また、名前にスペースが含まれているファイルを削除する必要がある場合は、DEL「Thisisatest.txt」の(DEL “This is a test.txt”)ような引用符を使用する必要があります。

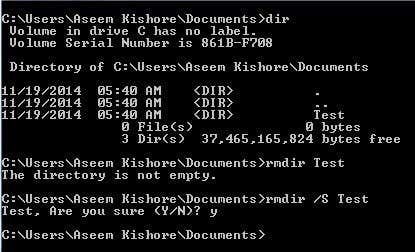
フォルダを作成または削除する必要がある場合は、MKDIR およびRMDIR コマンドを使用します。空でないディレクトリを削除しようとすると、エラーメッセージが表示(error message)されることに注意してください。ただし、ディレクトリとその中のすべて(directory and everything)を削除したい場合は、 RMDIR /S foldernameコマンドを使用できます。
ファイルのコピー、テキストファイルの印刷、(print text)ファイルのアクセス許可の変更(change file)など、あらゆる種類の操作を実行するために使用できるコマンドは他にもたくさんあります。したがって、 GUIインターフェイス(GUI interface)を使用してWindowsでこれらの操作のほとんどを実行できるのであれば、なぜわざわざDOS、そうですか?
まず、 Windows(Windows)に何か問題が発生する時期がわからず、他に何も読み込まれないため、コマンドプロンプト(command prompt)でスタックします。また、上記のようにコマンドプロンプト(command prompt)に入力したコマンドは、拡張子が.BATのファイルに保存して、ファイルをクリックするだけでいつでも実行できます。または、Windowsの[スケジュールされたタスク]コントロールパネルアプレット(Windows Scheduled Tasks Control Panel applet)を使用して実行をスケジュールすることもできます。 。
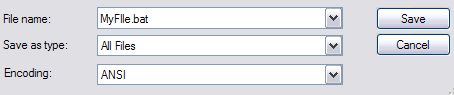
したがって、あるフォルダから別のフォルダにファイルをコピーするなど、コンピュータで日常的にいくつかの簡単なアクションを実行できるようにする場合は、メモ帳にコマンドを入力し、(Notepad)テキストファイル(text file)ではなく.BAT拡張子を付けてファイルを保存します。基本的に、 (Basically)[ファイルの種類]オプション(File Type option)で[すべてのファイル]を選択し、引用符を含めて「MyFile.bat」のような名前を入力する必要があります。
非常に頻繁に役立つことが証明されている他のいくつかのコマンドについて説明します。
IPCONFIG
IPCONFIGコマンド(IPCONFIG command)は、ネットワークカード、IPアドレスに関する情報を提供し、IP(IP address)アドレス(IP address)を更新することもできます。私のお気に入りは ipconfig /all,ネットワークアダプター(network adapter)に関する詳細情報を提供します。次に、この情報を使用して、ルーターのIPアドレス(デフォルトゲートウェイ)と、 (IP address)DHCPサーバー(DHCP server)からIPアドレス(IP address)を取得しているかどうかを確認できます。

DISKPART
繰り返しになりますが、ハードドライブの問題が発生した場合、このコマンドは非常に便利です。DISKPARTを使用すると、コンピュータにインストールされているハードディスクを管理できます。パーティションをアクティブパーティションに設定する、ドライブ文字をパーティションに割り当てる、ディスクを縮小する、ディスクをオフラインまたはオンライン(disk offline or online)にするなどの操作を実行できます。

SFC
システムファイルチェッカー(System File Checker)は、保護されているすべてのシステムファイルをスキャンし、誤ったバージョンを正しいファイルバージョンに置き換えるため、非常に便利です。Windowsの特定のシステムファイルが破損し、システムファイルチェッカー(system file checker)がそれらを簡単に修正することがよくあります。sfc /scannowを実行するだけで、スキャンが実行され、問題が修正されます。かなりの時間がかかりますが、何らかの破損の問題が発生している場合は、それだけの価値があります。
最終的に使用しなければならない可能性のあるその他の非常に便利なコマンドを以下に示します。
- chkdsk –ファイルシステムの整合性(file system integrity)についてハードディスクまたはフロッピーディスクを検証します。
- コピー(copy)–ある場所から別の場所にファイルをコピーします。宛先はデフォルトで現在のディレクトリになります。複数のソースファイルがある場合、宛先はディレクトリである必要があります。そうでない場合、エラーが発生します。
- fc – 2つのファイルまたはファイルのセットを比較し、それらの違いを表示します
- fdisk –ハードディスクパーティション(disk partition)テーブルを操作します。(Manipulates)コマンドライン(command line)から実行すると、さまざまなパーティショニング操作のメニューが表示されます。
- format –ディスク上のすべてのファイルを削除し、 (Delete)MS-DOS用に再フォーマットします。主にフロッピーディスクまたはその他のリムーバブルディスクのフォーマットに使用します。(Use)
- scandisk –CHKDSK(scandisk)ユーティリティの代わりとなるディスク(Disk)診断ユーティリティ(CHKDSK utility)。
- netstat –ローカルコンピューターから外部への現在の接続をすべて表示します。(Shows)
これで、 MSDOSコマンド(MS DOS command)プロンプトでの使用方法とナビゲート方法を理解できるようになるはずです。コマンドプロンプト(command prompt)で使用できるすべてのコマンド(all commands)のリストがあるこのサイトをチェックアウトすることもできます。ご不明な点がございましたら、コメントを投稿してください!楽しみ!
Beginner’s Guide to the Windows Command Prompt
Earlier today I had to bоot a сlient computer into safe mode and delete a virus via the command prompt because whenever Windows would load, the file would become loсked and hence undeletable! There are several other reasons why you mаy have to use the command prompt in your life (though rarely), so it’s gоod to know how to navigate your way around!
If you have been meaning to learn how to use the command prompt in Windows, I’ll go through some of the basic commands that are performed most often. Just so everyone’s on the same page, you can get to the command prompt by going to Start and then click on Run and typing in CMD. In Windows 7, just click on Start and begin typing cmd. In Windows 8, you can just right-click on the Start button and choose Command Prompt.


You’ll now see a large black window with the cursor at the end of the path to your user profile in C:\Documents and Settings\Username or C:\Users\Username. So what to do now!? Well, since I can’t explain everything, you’ll probably want to end up using some of the help guides that are provided in MS DOS itself by typing in HELP and pressing Enter.
When you do that, you’ll get a list of all the commands you can use in MS DOS and a short description of what they do:

You can also find out more detailed information about the parameters and how to use each command by typing in the command name followed by a /?. For example, typing in CD /?, will present you with a quick tutorial on how to use the CD command:

As you can see from above, the MS DOS command CD displays the name of or changes the current directory. So if you wanted to change from the default user profile directory to the Windows System32 directory to delete a virus file, you would type in the following to navigate to that directory:
cd c:\window\system32 and press Enter
You current directory at the prompt will now change to:

Now that you are in that directory, you may want to view all of the files and directories first, so you can type in the command DIR and press Enter. You’ll now get a giant list of all of the files and folders in that directory. You can type in DIR /? and see what parameters you can pass to it.

As you can see, you could type in DIR /P to give the list in a paginated format that you can browse through slowly. Or you could type in DIR /W to get the list in a wide format rather than one single column. The cool thing about DOS is that you can include several parameters for each command, so you could type in DIR /P /W and get a page-by-page view along with wide format:

So now that we have a list of files and folders, let’s continue with our deleting a virus example. If you want to delete a file, you would use the DEL command. Again typing in DEL /? will give you some useful info on the command.

To delete a file, we can simply type in DEL filename and that will delete the file. When you use the command this way, it won’t prompt you to confirm before deleting the file, so make sure you have typed in the correct file name. Also, you have to enter the file name with the extension, so it would be DEL Test.txt to delete that file. Also, if you need to delete a file that has spaces in the name, you have to use quotes like DEL “This is a test.txt”.

If you need to create or delete folders, you would use the MKDIR and RMDIR commands. It’s worth noting that if you try to delete a non-empty directory, you will get an error message. However, if you are sure you want to delete the directory and everything inside, you can use the RMDIR /S foldername command.

There are lots of other commands that you can use to do all sorts of stuff like copy files, print text files, change file permissions, etc. So if you can do most of this stuff in Windows using the GUI interface, then why bother with DOS, right?
Firstly, you never know when something bad will happen to Windows and you’re stuck in the command prompt because nothing else will load. Also, any command you type in the command prompt, like we showed above, can be saved into a file with a .BAT extension and run anytime by just clicking on the file or can be scheduled to run using the Windows Scheduled Tasks Control Panel applet.
So if you want to be able to routinely perform some simple actions on your computer, like copying files from one folder to another, just type the commands into Notepad and save the file with a .BAT extension instead of as a text file. Basically, you have to choose All Files for the File Type option and then type in the name like “MyFile.bat” with the quotes included.

Let me mention a couple of other commands that prove to be very useful very often.
IPCONFIG
The IPCONFIG command gives you information about your network cards, IP addresses and also lets you renew your IP address. My favorite is ipconfig /all, which will give you detailed information about each network adapter on your computer. You can then use this info to figure out your router IP address (default gateway) and whether or not you’re getting an IP address from a DHCP server.

DISKPART
Again, when you end up with hard drive problems, this command can prove to be very useful. DISKPART lets you administer the hard disks installed on your computer. You can do things like set a partition to be the active partition, assign a drive letter to a partition, shrink a disk, take a disk offline or online, etc.

SFC
System File Checker is really useful because it scans all protected system files and replaces incorrect versions with correct file versions. There will be a lot of times when certain system files in Windows have become corrupt and system file checker will fix them for you easily. You just run sfc /scannow and it will perform a scan and fix any issues. It does take quite a bit of time, but worth it if you’re having any kind of corruption issues.
A couple of other very useful commands that you might have to end up using are listed below:
- chkdsk – Verifies a hard disk or a floppy disk for file system integrity.
- copy – Copies files from one location to another. The destination defaults to the current directory. If there are multiple source files, the destination must be a directory or else you will get an error.
- fc – Compares two files or sets of files and displays the differences between them
- fdisk – Manipulates hard disk partition tables. When run from the command line, it displays a menu of various partitioning operations.
- format – Delete all the files on the disk and reformat it for MS-DOS. Use mostly for formatting floppy disks or other removable disks.
- scandisk – Disk diagnostic utility that is a replacement for the CHKDSK utility.
- netstat – Shows you all the current connections from your local computer to anything external.
That should hopefully get you up and running on how to use and navigate in the MS DOS command prompt! You can also check out this site that has a list of all commands you can use at the command prompt. If you have a question, please post a comment! Enjoy!













