私たちはインターネットとワイヤレス接続(internet and wireless connections)の時代に生きており、ほとんどの人が自宅にワイヤレスルーターを持っています。(wireless router)Wi-Fiは私たちの語彙で一般的な用語になっていますが、ワイヤレスネットワークの標準は理解しやすく、発音しさえしません。それは、ネットワークエンジニアや企業によって発明された複雑な名前を持っているためです。802.11axとは何か知っていますか?802.11ad、または802.11acはどうですか?これらの名前がWi-Fi6 (Wi-Fi 6)、(Did) Wi -Fi(Wi-Fi) 5、Wi-Fi 4などのより単純な用語に変更されているというニュースを聞いたことがありますか?それが何を意味し、なぜそれが重要なのかを理解したいですか?この記事を読んで、必要な情報を見つけてください。
Wi-Fi Allianceは、ワイヤレスネットワーク標準の開発を担当しています
Wi-Fi Allianceは、Wi-Fiネットワーク標準を開発および公開している世界中のコンピューティングメーカーの同盟です。テクノロジー業界(tech industry)全体がそれらに従い、Wi-Fi標準の助けを借りて相互に互換性のあるワイヤレスデバイスを開発しています。

Wi-Fi Allianceがなければ、ワイヤレスルーターと(Alliance)ラップトップやスマートフォン(laptop and smartphone)などのワイヤレスデバイスとの相互運用性は高くありません。Wi-Fi Allianceは、この記事で取り上げているすべての標準を公開しています。それらについて1つずつ説明しましょう。
Wi-Fi 4とも呼ばれる802.11nとは何ですか?
802.11nは、そのフルネームIEEE 802.11n-2009(name IEEE 802.11n-2009)で、2009年に公開されたワイヤレスネットワーク規格です。Wi-Fi802.11nはWi-Fi4とも呼ばれ(Wi-Fi 802.11n is also referred to as Wi-Fi 4)ます。802.11nでは、2.4GHz(GHz)と5GHzの2つの(GHz)無線周波数(radio frequency)帯域を使用でき、最大600Mbps(Mbps)のデータ転送速度を実現できます。Wi-Fi 802.11nは、MIMO(多入力多出力)のサポートを提供した最初のワイヤレス規格でもありました。MIMOは、複数のアンテナを使用して、独立したデータストリームを組み合わせることにより、より多くのデータを送信できるようにするテクノロジーです。

最新の無線ルーターは、 (Modern wireless)2.4GHz帯域(GHz band)でWi-Fi4標準を使用しています。Wi-Fi 4は、古いデバイスをネットワークに接続するため、またはスマートプラグ、スマート電球、センサーなどのスマートホームデバイスを接続するために使用されます。
Wi-Fi 5とも呼ばれる802.11acとは何ですか?
802.11acまたはIEEE802.11acは、2013年後半に公開されたワイヤレスネットワーク規格です。Wi-Fi802.11acは、Wi-Fi5とも呼ばれ(Wi-Fi 802.11ac is also known as Wi-Fi 5)ます。過去数年間に販売されたほとんどのルーターは802.11acと互換性があるため、802.11acは今日最も一般的なワイヤレス規格です。(standard today)この規格は、以前の802.11nと同様に、MU-MIMOをサポートしていますが、最大(MU-MIMO)2.3Gbps(Gbps)の最大データ転送速度を提供できます。802.11ac規格は5GHz周波数帯でのみ機能しますが、802.11ac規格をサポートするほとんどの無線ルーターは、 (GHz frequency)2.4GHz周波数(GHz frequency)帯での802.11n規格もサポートしています。

802.11acデバイスは、802.11acWave1とWave2(Wave 1)と呼ばれる2(Wave 2)つのカテゴリに分けられます。802.11ac Wave 1の一部として販売されている製品は、2013年に市場に導入され、Wave (Wave 2)2(Wave 2)の製品は2016年に導入されました。Wave2は、標準の改良版です。802.11ac Wave 2ワイヤレス(Wave 2)ルーターはスループットが高く、MU-MIMOの(MU-MIMO)サポートが追加されています。Wave1ルーターは最大1.3 Gbpsの速度を提供できますが、Wave2のルーターは最大(Wave 1)2.3Gbps(Gbps)の速度を提供できます。したがって、今日ワイヤレスルーター(wireless router today)を購入した場合、ワイヤレス速度とカバレッジ(wireless speed and coverage)の向上の恩恵を受けるため(Wave 2)に、802.11acWave2のサポートを提供しているかどうかを確認することをお勧めします。
802.11axとは何ですか?
802.11axまたはIEEE802.11axは、まだ作業中であり、まだ承認されていないワイヤレスネットワーク標準です。ZDNet:次世代802.11ax wi-fi:高密度、高速、遅延で(Next-generation 802.11ax wi-fi: Dense, fast, delayed)共有されているように、2019年後半に最終化および承認される予定です。
802.11axはWi-Fi6とも呼ばれ(802.11ax is also referred to as Wi-Fi 6)ます。これは、高効率ワイヤレス(High-Efficiency Wireless)(HEW )とも呼ばれ、これまでに説明した標準と同じ2.4GHz(GHz)および5GHzの周波数(GHz frequency)帯域で動作するように設計されています。利用可能になると、 1〜7GHz(GHz)の追加帯域でも動作できるようになります。802.11axワイヤレスネットワーク規格は、802.11ac規格の最大4倍の平均データ転送速度を向上させることを目的としています。特に空港、駅、レストラン、コーヒーショップなどの混雑した場所では、速度が大幅に向上するはずです。

Wi-Fi6を搭載したワイヤレスルーターとメッシュWi-Fiシステムはすでに市場に出回っています。しかし、彼らはプレミアム価格を持っている傾向があり、ほとんどの人はそれらを買う余裕がありません。標準が承認されて完成したらすぐに、より手頃なWi-Fi機器が発売されることを期待してください。
802.11adとは何ですか?
IEEE 802.11adは、 (IEEE 802.11ad)WiGigまたは60GHzWi-Fi(WiGig or 60 GHz Wi-Fi)とも呼ばれるワイヤレスネットワーク標準です。これは、 2.4GHz(GHz)や5GHz(GHz)などの従来のワイヤレス周波数(wireless frequency)帯域を使用する代わりに、約60GHzで動作する(GHz)無線スペクトル(radio spectrum)のマイクロ波セクションを使用するWi-Fiの形式です。最大7Gbps(Gbps)の信じられないほど高速なデータ転送速度を可能にします。ただし、マイクロ波範囲の周波数で動作するため(microwave range frequency)、壁を通過できないという重大な欠点があり、範囲はわずか3〜32フィート(1〜10メートル)です。「超高速」ですが、壁や障害物が邪魔にならない場合は、1つの部屋だけをカバーするように設計されています。
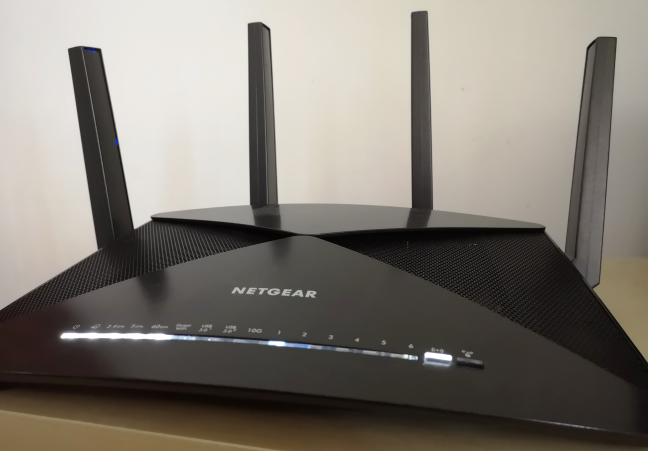

802.11adをサポートするワイヤレスルーターは市場にほとんどなく、802.11adをサポートするネットワークデバイスもほとんどありません。802.11adでテストしたルーターの1つは、NetgearNighthawkX10です(Netgear Nighthawk X10)。
Wi-Fi 6、Wi-Fi 5、Wi-Fi 4などとは何ですか?
2018年10月3(October 3)日、Wi-Fi Allianceは、人々が簡単に識別できるように、ワイヤレスネットワーク標準に(wireless networking)新しい名前(new naming)を追加したことを発表しました。結局のところ、802.11ax、802.11ad、802.11ac、802.11n、および他のすべての同様の名前は覚えるのが簡単ではなく、ほとんどの人はそれらが何を意味するのかわかりません。彼らの考えは、Wi-Fiの後に数字が続くのは覚えやすいということです。ルールは、数値が大きいほど、標準が新しく、優れているということです。Wi-Fi 6、Wi-Fi 5、およびWi-Fi4の(Wi-Fi)意味はすでにご存知でしょう。ただし、要約すると、次のようになります。
- Wi-Fi 6は、 (Wi-Fi 6)802.11axワイヤレスネットワーク規格をサポートするデバイスを識別します
- Wi-Fi 5は、 (Wi-Fi 5)802.11acWave2を含む(Wave 2)802.11acワイヤレスネットワーク規格をサポートするデバイスを識別します
- Wi-Fi 4は、 (Wi-Fi 4)802.11nワイヤレスネットワーク規格をサポートするデバイスを識別します
最新のWi-Fiネットワーク(Wi-Fi networking)標準のそれぞれが提供するものを理解しやすくするために、それらの周波数帯域と最大理論速度を比較する表を作成しました。

Wi-Fi 1、Wi-Fi 2、およびWi-Fi3はブランド化されていません。これは、Wi-FiAllianceが(Alliance)古いWi-Fi規格の使用をあまり考慮していなかったためと考えられます。ただし、完成させるために、正しいブランディングは次のようになっていると考えています。
- Wi-Fi1は802.11bである必要があります。この規格は1999年にリリースされ、2.4 GHz帯域(GHz band)を使用し、最大11Mbpsの(Mbps)データレート(data rate)を備えています。
- Wi-Fi2は802.11aである必要があります。1999年にリリースされ、5 GHz帯域(GHz band)を使用し、最大54Mbpsの(Mbps)データレート(data rate)を備えています。
- Wi-Fi3は802.11gである必要があります。この規格は2003年にリリースされ、2.4 GHz帯域(GHz band)を使用し、最大54Mbpsの(Mbps)データレート(data rate)を備えています。
802.11ax vs 802.11acvs802.11nまたはWi- Fi6vs(vs 802.11n) Wi-Fi 5 vs Wi-Fi 5、および実際の速度
各Wi-Fi規格(Wi-Fi standard)の仕様と、それぞれが達成できる最大理論速度を読むと、感動することでしょう。ただし、実際には、取得する速度ははるかに遅くなります。このテーマの詳細については、この記事を参照してください:AC1200、AC1750、AC1900以上とはどういう意味で、違いは何ですか?
利用可能なさまざまな標準から得られる実際の速度について現実的な視点を提供するために、最も強力なワイヤレスルーターの1つであるASUS ROG Rapture GT-AX11000を使用し、SpeedTestを使用していくつかの測定を行いました。 Intel Wi- (Intel Wi-Fi 6) Fi6AX200ネットワーク(AX200 network)カード。私たちのインターネット接続は、1Gbpsの(Gbps)ダウンロード速度(download speed)と500Mbps(Mbps)のアップロード速度を提供します。
最初に、802.11n(Wi-Fi 4)標準を使用して、ルーターから発信される2.4 GHz帯域の(GHz band)Wi-Fiに接続しました。測定した最大(Wi-Fi)ダウンロード速度(download speed)は、221.28Mbpsです(Mbps)。
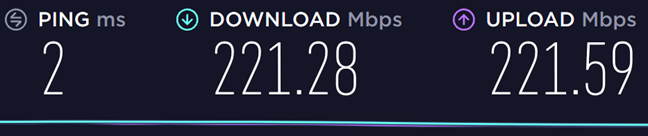
次に、802.11ac( Wi-Fi 5(Wi-Fi 5))規格を使用して、ルーターから放出される2つの最初の5GHz帯域(GHz band)に切り替えました。到達した最大ダウンロード速度(download speed)は630.10Mbpsです(Mbps)。このワイヤレスルーター(wireless router)を使用すると、Wi-Fi5規格はWi-Fi4規格より2.8倍高速になります(Wi-Fi 5)。
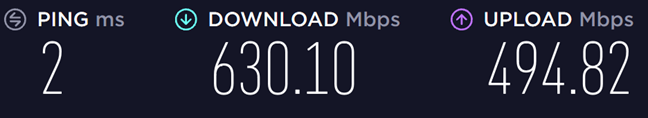
最後に、802.11ax(Wi-Fi 6)規格を使用する2番目の5GHz帯域(GHz band)に切り替えました。今回は最大ダウンロード速度(download speed)762.03Mbpsに達し(Mbps)ました。これはWi-Fi5よりも20%高速であり、大幅な改善ですが、Wi-Fi6規格で約束されている理論上の最大速度からはほど遠いものです。

うまくいけば、この簡単な比較により、さまざまなWi-Fi標準を使用したときに実際に達成できる速度のより現実的な視点が得られます。
ワイヤレス(Do wireless)ルーターは1つ以上のWi-Fi規格を使用していますか?
はい、それらのほとんどはそうです!メーカーは、各帯域で異なる無線規格をサポートしながら、1つ、2つ、または3つの帯域で同時に動作できる無線ルーターを製造しています。今日のほとんどのワイヤレスルーターは、さまざまなデバイスとの速度と互換性(speed and compatibility)が高いため、デュアルバンドまたはトライバンドルーターです。現在販売されているすべてのワイヤレスルーターは、802.11n標準(通常は2.4 GHz帯域(GHz band))をサポートし、802.11ac標準(5 GHz帯域(GHz band))もサポートしています。ハイエンドのワイヤレスルーターはそれをすべて行いますが、 802.11ac Wave(Wave 2) 2、802.11ax、802.11adなどの新しい規格に使用される3番目の帯域( 5GHz(GHz)または60GHz )を含めることもできます。(GHz)
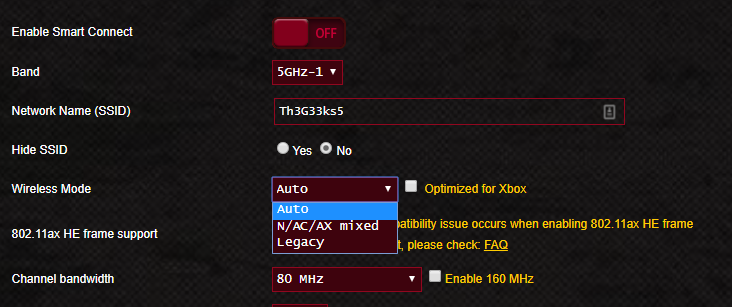
シングルバンド、デュアルバンド、またはトライバンドルーター(tri-band router)のいずれを使用している場合でも、ファームウェアを使用して、有効にして使用するWi-Fi標準と帯域を選択できるようにする必要があります。2.4 GHz帯域(GHz band)とそれにサポートされている無線規格のみをアクティブにするか、5GHz帯域とそれにサポートされている無線規格のみをアクティブにするかを選択できます(GHz band)。さらに、ルーターで利用可能なすべての帯域とすべてのワイヤレス標準を有効にして、すべてを混合してネットワークに望ましい結果を得ることができます。
新しいWi-Fi標準をサポートする新しいデバイスを入手する予定はありますか?
Wi-Fi 5互換デバイスを使用していますか(Are)?最新のWi-Fi6規格にアップグレードする価値があると思いますか、それとも投資するのが早すぎますか?以下にコメントし、すべての(Comment) ワイヤレスネットワーク(wireless networking)標準、それらの命名規則、および機能についての意見を共有してください。(below and share)
What is 802.11ax, 802.11ad, 802.11ac, and 802.11n? What is Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5 and so on?
We are living іn the age of thе internеt and wireless connections, and most people have a wіreless router in theіr homes. Wi-Fi has become a common term in our vocabulary, but wireless networking standards are not easy to understand or even pronounce. That is because they have complicated names, invented by network engineers and corporations. Do yoυ know what 802.11ax is? What about 802.11ad, or 802.11ac? Did you heаr the news that thеse names are сhanging into ѕimpler terms like Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5, or Wi-Fi 4? Do you want to understand what all that means and why it matters? Read thіs аrticle to find the information you need:
The Wi-Fi Alliance is in charge of developing wireless networking standards
The Wi-Fi Alliance is an alliance of computing manufacturers from all over the world that develops and publishes the Wi-Fi networking standards. The entire tech industry follows them and develops wireless devices that are compatible with each other, with the help of Wi-Fi standards.

Without the Wi-Fi Alliance, we would not have good interoperability between wireless routers and wireless devices, such as your laptop and smartphone. The Wi-Fi Alliance publishes all the standards covered in this article. Let's discuss them one by one:
What is 802.11n, also known as Wi-Fi 4?
802.11n, under its full name IEEE 802.11n-2009, is a wireless networking standard that was published in 2009. Wi-Fi 802.11n is also referred to as Wi-Fi 4. 802.11n allows the use of two radio frequency bands, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz, and can deliver data transfer speeds of up to 600 Mbps. Wi-Fi 802.11n was also the first wireless standard that offered support for MIMO (multiple-input-multiple-output). MIMO is a technology that allows the use of multiple antennas to transmit more data by combining independent data streams.

Modern wireless routers use the Wi-Fi 4 standard on the 2.4 GHz band. Wi-Fi 4 is used to connect older devices to the network, or smart home devices like smart plugs, smart bulbs, sensors, and so on.
What is 802.11ac, also known as Wi-Fi 5?
802.11ac or IEEE 802.11ac is a wireless networking standard that was published in late 2013. Wi-Fi 802.11ac is also known as Wi-Fi 5. The 802.11ac is the most common wireless standard today, as most routers sold during the last few years are 802.11ac-compatible. This standard, just like the 802.11n before it, supports MU-MIMO, but it can offer maximum data transfer speeds of up to 2.3 Gbps. The 802.11ac standard works only on the 5 GHz frequency band but most of the wireless routers that support it also offer support for the 802.11n standard on the 2.4 GHz frequency band.

802.11ac devices are split into two categories, called 802.11ac Wave 1 and Wave 2. The products that are sold as part of the 802.11ac Wave 1 were introduced to the market in 2013, while the ones in Wave 2 were introduced in 2016. Wave 2 is an improved version of the standard. The 802.11ac Wave 2 wireless routers have higher throughput and add support for MU-MIMO: while the Wave 1 routers can provide speeds of up to 1.3 Gbps, the ones in Wave 2 can deliver speeds of up to 2.3 Gbps. Therefore, if you buy a wireless router today, it is a good idea to check whether it offers support for 802.11ac Wave 2, to benefit from improved wireless speed and coverage.
What is 802.11ax?
802.11ax or IEEE802.11ax is a wireless networking standard that is still in the works and has not yet been approved. It is expected that it will be finalized and approved sometime during late 2019, as shared by ZDNet: Next-generation 802.11ax wi-fi: Dense, fast, delayed.
802.11ax is also referred to as Wi-Fi 6. It is also known as High-Efficiency Wireless (HEW) and is designed to work in the same 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz frequency bands as the standards that we mentioned so far. It appears that it will also be capable of working with additional bands between 1 and 7 GHz, when they become available. The 802.11ax wireless networking standard aims to improve the average data transfer speeds by up to four times more than the 802.11ac standard. It should offer significantly improved speeds, especially in crowded places such as airports, train stations, restaurants, or coffee shops.

Wireless routers and mesh Wi-Fi systems with Wi-Fi 6 have already shown up on the market. However, they tend to have a premium price, and most people can't afford them. As soon as the standard is approved and finalized, expect more affordable Wi-Fi equipment to be launched.
What is 802.11ad?
IEEE 802.11ad is a wireless networking standard that is also known as WiGig or 60 GHz Wi-Fi. It is a form of Wi-Fi that, instead of using traditional wireless frequency bands such as 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, uses a microwave section of the radio spectrum, running at about 60 GHz. It allows for incredibly fast data transfer speeds of up to 7 Gbps. However, because it works on a microwave range frequency, it has the significant disadvantage of not being able to pass through walls and has a range of only 3 to 32 feet (1 to 10 meters). It is "lightning fast," but it is designed to cover only one room when no walls or obstacles stand in the way.

There are few wireless routers on the market with support for 802.11ad, and few network devices that have support for it. One of the routers that we tested with 802.11ad is Netgear Nighthawk X10.
What is Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 4, and so on?
On October 3, 2018, the Wi-Fi Alliance announced that it added a new naming for the wireless networking standards, to make it easier for people to identify them. After all, 802.11ax, 802.11ad, 802.11ac, 802.11n, and all the other similar names are not easy to remember, and most people have no idea what they mean. Their thinking is that Wi-Fi, followed by a number, is easy to remember. The rule is that the higher the number, the newer and the better the standard. You already know by now what Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 5, and Wi-Fi 4 mean. However, to summarize, here is what they are:
- Wi-Fi 6 identifies devices that support the 802.11ax wireless networking standard
- Wi-Fi 5 identifies devices that support the 802.11ac wireless networking standard, including 802.11ac Wave 2
- Wi-Fi 4 identifies devices that support the 802.11n wireless networking standard
To help you understand what each of the modern Wi-Fi networking standards offers, we made a table which compares their frequency bands and maximum theoretical speed:

Wi-Fi 1, Wi-Fi 2, and Wi-Fi 3 are not branded. That is likely because the Wi-Fi Alliance did not consider older Wi-Fi standards to be used much. However, for the sake of completion, we believe that the correct branding would have been:
- Wi-Fi 1 should have been 802.11b. This standard was released in 1999, it uses the 2.4 GHz band, and it has a data rate of up to 11 Mbps.
- Wi-Fi 2 should have been 802.11a. It was released in 1999, it uses the 5 GHz band, and it has a data rate of up to 54 Mbps.
- Wi-Fi 3 should have been 802.11g. This standard was released in 2003, it uses the 2.4 GHz band, and it has a data rate of up to 54 Mbps.
802.11ax vs 802.11ac vs 802.11n or Wi-Fi 6 vs Wi-Fi 5 vs Wi-Fi 5, and real-life speeds
If you read the specifications of each Wi-Fi standard, and the maximum theoretical speed that each can achieve, you are going to be impressed. However, in real life, the speeds you get are much lower. You can find out more about this subject, in this article: What does AC1200, AC1750, AC1900 or more, mean and what's the difference?
To give you a realistic perspective on the real-life speed you get from the different standards that are available, we took one of the most powerful wireless routers - ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AX11000 - and made some measurements with SpeedTest, on a laptop with an Intel Wi-Fi 6 AX200 network card. Our internet connection offers a download speed of 1 Gbps, and an upload speed of 500 Mbps.
We first connected to the Wi-Fi emitted by the router, on the 2.4 GHz band, using the 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) standard, and the maximum download speed we measured is of 221.28 Mbps.

We then switched to the first 5 GHz band of the two emitted by the router, using the 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) standard. The maximum download speed that we reached is 630.10 Mbps. The Wi-Fi 5 standard is 2.8 times faster than the Wi-Fi 4 standard when using this wireless router.

Lastly, we switched to the second 5 GHz band, which used the 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) standard. This time we reached a maximum download speed of 762.03 Mbps. That is 20% faster than Wi-Fi 5, which is a substantial improvement, but far from the maximum theoretical speeds that are promised by the Wi-Fi 6 standard.

Hopefully, this quick comparison has given you a more realistic perspective of the speeds you can achieve, in real life, when using different Wi-Fi standards.
Do wireless routers use one or more Wi-Fi standards?
Yes, most of them do! Manufacturers make wireless routers that can work on one, two, or even three bands simultaneously, while supporting different wireless standards on each band. Most wireless routers today are dual-band or tri-band routers because they offer more speed and compatibility with various devices. All the wireless routers sold today have support for the 802.11n standard (usually on the 2.4 GHz band), and also add support for the 802.11ac standard (on the 5 GHz band). High-end wireless routers do all that, but can also include a third band (5 GHz or even 60 GHz), that is used for newer standards such as 802.11ac Wave 2, 802.11ax or 802.11ad.

Whether you have a single-band, dual-band, or tri-band router, the good thing is that the firmware should let you choose what Wi-Fi standards and bands you want to enable and use. You can select whether to activate only the 2.4 GHz band and the wireless standards supported on it, or you can choose to activate only the 5 GHz band and the wireless standards supported on it. Furthermore, you can also enable all the bands and all the wireless standards available on your router, mixing everything to get the desired results for your network.
Do you plan on getting new devices that support newer Wi-Fi standards?
Are you using Wi-Fi 5 compatible devices? Do you believe that it is worth upgrading to the latest Wi-Fi 6 standard, or is it too soon to invest in it? Comment below and share your opinion about all the wireless networking standards, their naming conventions, and features.










