グラフとExcel チャートは(Excel charts)複雑なデータセットを視覚化する優れた方法であり、ベル(Bell)曲線も例外ではありません。これらを使用すると、正規分布を簡単に分析でき、 Excel(Excel)で簡単に作成できます。その方法を見てみましょう。
ベルカーブの目的は、単にデータをきれいにすることだけではないことに注意してください。このようなグラフに対して実行できるデータ分析にはさまざまな形式があり、データセットの多くの傾向や特徴が明らかになります。ただし、このガイドでは、分析ではなく、釣鐘曲線の作成にのみ焦点を当てます。

正規分布(Normal Distribution)の概要
ベル(Bell)カーブは、正規分布したデータセットを視覚化する場合にのみ役立ちます。したがって、釣鐘曲線に入る前に、正規分布が何を意味するのかを見てみましょう。
基本的に、値が平均値の周囲に大きく集まっているデータセットは、正規分布 (またはガウス分布と呼ばれることもあります) と呼ぶことができます。従業員の業績数値から週ごとの売上高に至るまで、自然に収集されたデータセットのほとんどはこのような傾向があります。
ベルカーブ(Bell Curve)とは何ですか?なぜそれが役立つの(Useful)ですか?
正規分布のデータ ポイントは平均の周囲に集まっているため、絶対値よりも中心平均からの各データ ポイントの分散を測定する方が便利です。これらの分散をグラフの形でプロットすると、ベル曲線(Bell Curve)が得られます。
これにより、異常値を一目で特定できるだけでなく、平均に対するデータ ポイントの相対的なパフォーマンスを確認することもできます。これにより、従業員の評価や学生の成績などで、成績の悪い人を区別できるようになります。
ベルカーブの作成方法
Excel の(simple charts in Excel)多くの単純なグラフとは異なり、データセットに対してウィザードを実行するだけでは釣鐘曲線を作成できません。データには最初に少しの前処理が必要です。行う必要があるのは次のとおりです。
- データを昇順に並べ替えることから始めます。これは、列全体を選択し、Data > Sort Ascendingに進むことで簡単に行うことができます。

- 次に、Average 関数を使用して平均値 (または Mean) を計算します。(calculate the average value (or Mean))結果は小数で表示されることが多いため、 Round(Round)関数と組み合わせることをお勧めします。
サンプル データセットの場合、関数は次のようになります:
=ROUND(AVERAGE(D2:D11),0)

- これで、標準偏差(Standard Deviation)を計算するための 2 つの関数ができました。STDEV.S は(STDEV.S)母集団のサンプルしかない場合 (通常は統計調査) に使用され、STDEV.P は(STDEV.P)完全なデータセットがある場合に使用されます。
ほとんどの実際のアプリケーション (従業員の評価、学生の成績など) には、STDEV.Pが最適です。もう一度、Round関数を使用して整数を取得できます。
=ROUND(STDEV.P(D2:D11),0)

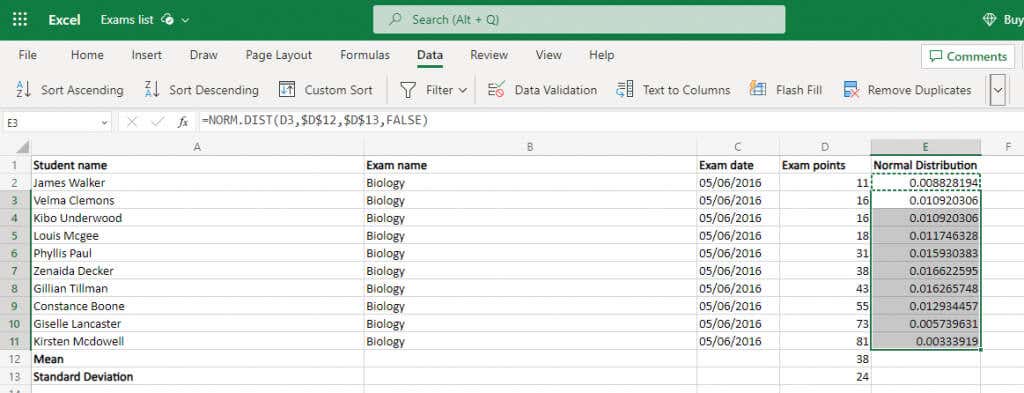
- これらはすべて、必要な実際の値、つまり正規(Normal)分布のための準備作業にすぎませんでした。もちろん、Excelにも専用の関数がすでに用意されています。
NORM.DIST関数は、データ ポイント、平均、標準偏差、および累積分布を有効にするブール フラグの 4 つの引数を受け取ります。(NORM.DIST)最後の値は無視しても問題ありません ( FALSE(FALSE)を入力します)。すでに平均と偏差が計算されています。つまり、セル値を入力するだけで結果が得られます。
=NORM.DIST(D2,$D$12,$D$13,FALSE)
1 つのセルに対してこれを実行し、数式を列全体にコピーするだけです。Excel は(– Excel)新しい位置に一致するように参照を自動的に変更します。ただし、最初に $ 記号を使用して平均と標準偏差のセル参照をロックしてください。
- 元の値とともにこの正規分布を選択します。分布は Y 軸を形成し、元のデータ ポイントは X 軸を形成します。

- [挿入](Insert)メニューに移動し、散布図に移動します。「滑らかな線(Smooth Lines)で散布」(Scatter)オプションを選択します。

MS Excelでベルカーブチャート(Bell Curve Chart)を作成する最良の方法は何ですか?
ベル(Bell)カーブ チャートは複雑に見えるかもしれませんが、実際には作成するのは非常に簡単です。必要なのは、データセットの通常の配布ポイントだけです。
まず、組み込みのExcel(Excel)式を使用して平均と標準偏差を決定します。次に、これらの値を使用して、データセット全体の正規分布を計算します。
釣鐘曲線グラフは、x 軸に元のデータ ポイント、y 軸に正規分布値を使用した、滑らかな線を持つ散布図プロットです。(Smooth Lines)データセットが正規分布していれば、 Excel(Excel)では滑らかな釣鐘曲線が得られます。
How to Create a Bell Curve Chart in Microsoft Excel
Graphs and Excel charts are a great way to visualize complex datasets, and Bell curves are no exception. They let you analyze a normal distribution easily and can be easily created in Excel. Let’s find out how.
Keep in mind that the purpose of a bell curve goes beyond simply prettifying the data. There are many forms of data analysis that can be performed on such a chart, revealing many trends and characteristics of the dataset. For this guide, though, we will be only focusing on creating a bell curve, not analyzing it.

Introduction to a Normal Distribution
Bell curves are only useful to visualize datasets that are distributed normally. So before we dive into bell curves, let us take a look into what a normal distribution even means.
Basically, any dataset where the values are largely clustered around the mean can be called a normal distribution (or a Gaussian distribution as it is sometimes called). Most naturally collected datasets tend to be like that, from employee performance numbers to weekly sales figures.
What Is a Bell Curve And Why Is It Useful?
Since the data points of a normal distribution are clustered around the mean, it is more useful to measure the variance of each data point from the central mean rather than its absolute value. And plotting these variances in the form of a graph yields a Bell Curve.
This allows you to spot the outliers at a glance, as well as see the relative performance of the data points with respect to the average. For things like employee appraisals and student scores, this gives you the ability to tell the underperformers apart.
How to Create a Bell Curve
Unlike many simple charts in Excel, you cannot create a bell curve by simply running a wizard on your dataset. The data needs a bit of pre-processing first. Here is what you need to do:
- Begin by sorting the data in ascending order. You can do this easily by selecting the whole column and then heading to Data > Sort Ascending.

- Next, calculate the average value (or Mean) using the Average function. As the result is often in decimals, it is a good idea to pair it with the Round function as well.
For our sample dataset, the function looks something like this:
=ROUND(AVERAGE(D2:D11),0)

- Now we have two functions for calculating the Standard Deviation. STDEV.S is used when you only have a sample of the population (usually in statistical research) while STDEV.P is used when you have the complete dataset.
For most real-life applications (employee appraisal, student marks, etc.) the STDEV.P is ideal. Once again, you can use the Round function to get a whole number.
=ROUND(STDEV.P(D2:D11),0)

- All of this was just prep work for the real values we need – the Normal distribution. Of course, Excel already has a dedicated function for that as well.
The NORM.DIST function takes in four arguments – the data point, the mean, the standard deviation, and a boolean flag to enable cumulative distribution. We can safely ignore the last one (putting in FALSE) and we already calculated the mean and the deviation. This means we just need to feed in the cell values and we will get the result.
=NORM.DIST(D2,$D$12,$D$13,FALSE)
Do it for one cell and then just copy the formula over to the whole column – Excel will automatically change the references to match the new locations. But make sure to lock the mean and standard deviation cell references first by using a $ symbol.

- Select this normal distribution along with the original values. The distribution will form the y-axis while the original data points form the x-axis.

- Head to the Insert menu and navigate to the scatter diagrams. Select the Scatter with Smooth Lines option.

What Is the Best Way of Creating a Bell Curve Chart in MS Excel?
Bell curve charts might seem complicated, but are actually pretty simple to create. All you need is the normal distribution points of your dataset.
First, determine the mean and the standard deviation using built-in Excel formulas. Then use these values to calculate the normal distribution of the entire dataset.
The bell curve chart is just a Scatter with Smooth Lines plot using the original data points for the x-axis and the normal distribution values for the y-axis. If your dataset was normally distributed, you will get a smooth bell curve in Excel.







