新しいWindows電卓(Windows Calculator)は、これまでになく正確な計算を提供し、新しく強力なインターフェイスも備えています。現在、基本的な標準計算をプログラミング、科学計算、統計と統合しています。これに加えて、非常に便利な他の機能もあります。住宅ローンの計算(mortgage calculation)、多機能コンバーター、注目に値するいくつかのオプションなどです。この記事では、それらを1つずつ紹介し、いくつかの可能な使用シナリオを共有します。
Windows7およびWindows8で(Windows 8)電卓(Calculator)を見つける場所
Windows 7では(Windows 7)、Start Menu - > Accessories -> Calculatorに移動してアクセスできます。
電卓(Calculator)を開くには、[スタート]メニューの(Start Menu)検索ボックス(search box)(Windows 7の場合)または[スタート](Start)画面(Windows 8の場合)に(Windows 8)calculatorまたはcalcと入力し、適切な(calc)検索結果(search result)を開きます。
その実行可能ファイルは、次の場所にあります"C:WindowsSystem32calc.exe"。
計算モード
Windows8ではWindows7(Windows 8)と(Windows 7)はバージョンが異なりますが、電卓(Calculator)は両方のオペレーティングシステムで同じです。インターフェイスはまったく同じように見え、その機能は同じです。
電卓(Calculator)には、計算を実行できる4つの主要なモードがあります。
- 標準モード。
- 科学モード。
- プログラミングモード。
- 統計モード。
以下のセクションでは、それぞれについて説明し、それらの機能と使用方法について説明します。
標準モード
電卓(Calculator)を最初に開いたとき、デフォルトで標準(Standard)モードが選択されています。このモードは、通常のポケット電卓(pocket calculator)と同等です。キーボード(keyboard number)の数値、キーパッド(Numキーがアクティブになっている)、またはマウスを使用して計算を行うことができます。
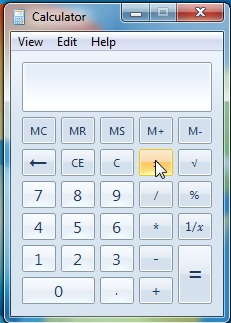
例:(Example:)計算を行う数値とそれらの数値の演算を選択する必要があります。したがって、単純な乗算を行う場合は、最初の数値、演算(*乗算記号)、および2番目の数値をクリックします。計算プロセス(calculation process)の最後に、その結果に新しい操作を追加し続けるか、等号をクリックして(result or click)最終結果(end result)を取得することができます。
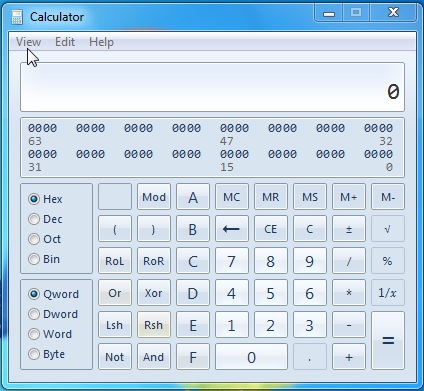
プログラマーモード
このモードでは、基数(2進数、8進数、16進数、10進数)で操作を実行できます(bases)。あるベースから別のベースに値を変換できます。たとえば、2進(base two) 数のシステム(number system)(2進数-0、1)から10進数のシステム(base ten number system)(10進数の0-9)に変換できます。また、このモードは、論理ビット演算(XOR、OR、ANDなど(AND etc))を支援します。
このモードにアクセスするには、[表示(View)]メニューをクリックして、[プログラマー(Programmer)]オプションを選択します。

以前のバージョンと同様に、使用するキーはベースに関連しています。たとえば、A〜Fボタンは、16進値で動作するようにチェックした場合にのみアクセスできます。他のボタンは、プログラマーにとってすでに一般的であるか、またはすでに一般的であるはずです。パレットXORテーブル(XOR table)の範囲、%-モジュラス、シフトおよび10進数から16進数または2進数の結果への変更。また、取得する値は整数として表示されます(自然数、つまり16/3は5に等しくなります)。
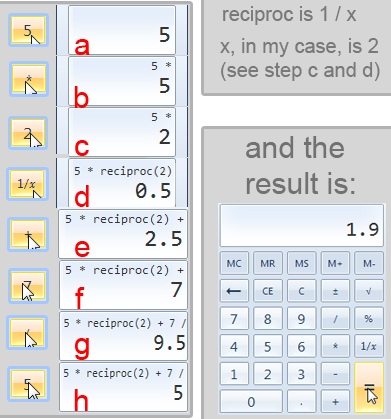
例:(Example:) 1011のような2進値をその10進値に変換する必要がある場合は、数値を入力して、10進ラジオボックス(radio box)をクリックするだけです。手動では、このプロセスはかなり長くなり、概念を完全に理解していないと、おそらくエラーの問題が発生します。

科学モード
このモードは、数学または他の科学的な計算を追求する人に少し笑顔を提供します。オファリングは、基本的なXから(X to the power of)、より便利なcos、sin、またはpi関数のパワーまで多岐にわたります。
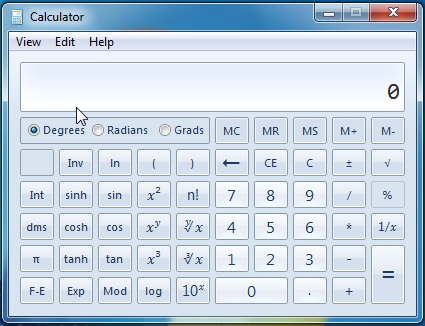
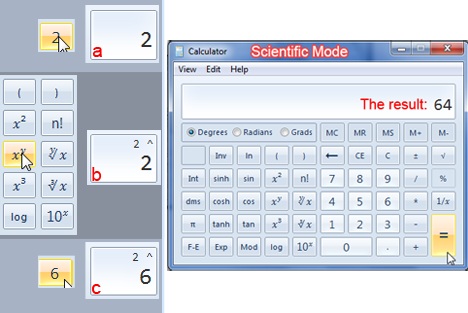
例:(Example:)前に標準モードで行ったように、操作を行うには、数字をクリックしてから操作を行い、2番目の数字を入力します。
統計モード
このモードでは、統計に関連するオプションが表示されます。他のモードのような機能はあまりありませんが、大歓迎です。数値の合計、数値の合計などの関数を使用して、統計を計算することができます。
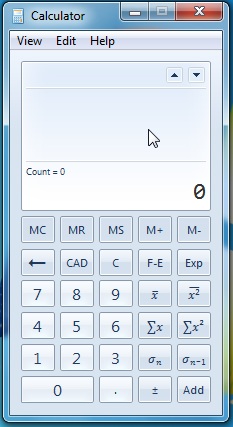
統計モードの場合のみ、 C(C)を押すと、表現されている現在の値が削除されます。CADはデータセットからすべての値をクリアします。データセットは、追加された番号のリストです。データセットは、さまざまな操作を実行するためのリストです。
例:(Example:)統計モードで操作を行うには、値を配置する必要があります。入力された後の各値は、[追加]ボタンをクリックしてデータセットに配置されます(ADD)。必要なすべての値をデータセットリスト(dataset list)に配置したら、目的の操作をクリックできます。

計算モード(Calculation Modes)での履歴(History)の使用
このオプションは、メモリに保持されている有用な値を超えています。File -> Historyに移動して使用でき、統計モードを除くすべてのモードで使用できます。名前はそれをすべて言います、しかしそれはそれが思っているより強力です。複雑な数式をいじるのは簡単です。計算を行うことができ、完了したら、等しいをクリックして結果を取得します。これにより、結果が履歴(History)リストに入力されます。別の計算を行い、前の結果または(result or values)その結果の値が必要な場合は、リストを調べてそれらの値を確認するだけです。これは、以前の計算をすばやく再編集できるという事実と相まって、計算機が他のオンライン計算機製品を(calculator offering)凌駕するようにします(calculator surpass)商品に使用する可能性があります。このオプションにアクセスするには、有効なモード(統計モードを除くすべて)になっていることを確認してください。

電卓の他のオプション
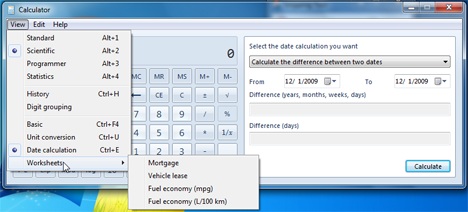
電卓計算(Calculator)機には、計算モードの範囲を超える他のツールが含まれるようになりました。彼らはより日常の必需品に関連しています。軽量変換や、特定の日から別の日までの距離の計算など。計算機から通常必要となるものよりも少し進んで、住宅ローンの値、カーリース、車の消費量(vehicle lease and car consumption)を計算するのに役立ちます。
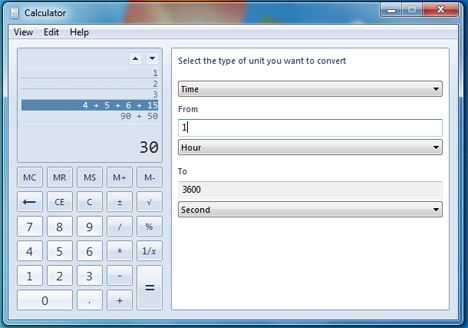
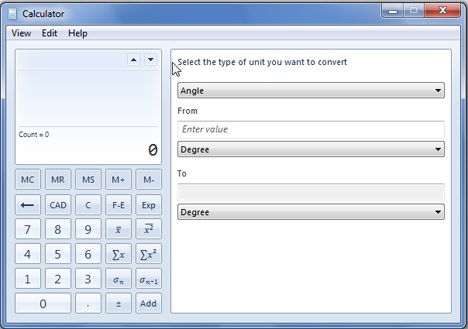
変換のタイプ(例:時間)、From 単位の測定(unit measurement)(Hourなど)、およびTo測定単位(Secondなど)を選択する必要があります。
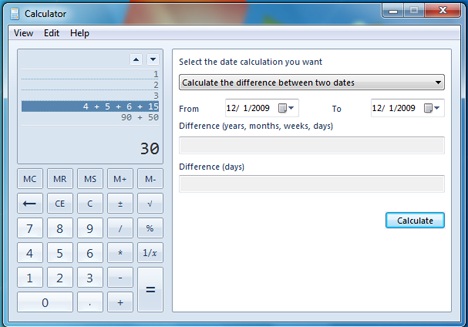
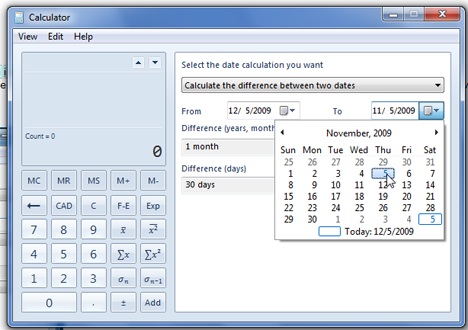
日付(開始日と終了日)を選択して、それらの違いを確認します。日数、月数(など)を手動で入力して、日付から減算(または加算)し、最終結果を確認することもできます。これは、「2つの日付の差を計算する」('Calculate the difference between two dates')をクリックし、2番目に指定されたオプションを選択することによって行われます。
Worksheets - These are options offered for real life calculations. Whether you want to calculate mortgage, vehicle lease or car consummation (American or European measurement), the calculator offers it all in the worksheets place.
ヒントとコツ
いくつかのユーティリティが通常の計算機からどれほど未使用であるかに私はしばしば驚いています。私が言及している主題は、電卓に含まれているメモリやその他の便利な機能です。
MC (Memory Clear or Clean) - clears the memory of any stored number leaving only the null or zero number in memory.
MR (Memory Reminder or Recalled) - tells the calculator to show the number present in memory.
MS (Memory Store or Set) - this takes the number present in the results and stores it in the memory. Previous calculation stored in memory will be deleted.
M+ (Add to memory) - formula> value stored in memory + current value = new value stored.
M- (Subtract from memory) - formula> value stored in memory - current value = new value stored.
C - Clear all calculations that are currently made.

The Back Arrow or Backspace - present on Windows Calculator but not present on a pocket calculator. This option deletes the last typed number from the current value. This option can be used by clicking on the Back Arrow or by pressing the Backspace key.
Using numerical values from the keyboard makes the calculation faster. You can also use the * key to quickly multiple, the minus key "-", the plus key "+", the divisible by "/" or the equal key "=".
Although this has nothing to do with notations, you can click on the Edit-> Copy to copy the value to clipboard.
Going to the help page for calculator reveals useful keyboard shortcuts for use with functions or options.
結論
外観とオプションの変更により、電卓(Calculator)は迅速で軽量な機能を念頭に置いて構築されたように感じられます。すべての機能が連携して機能し、オプション間の移行は非常に簡単に行われます。最後に、問題や質問がある場合、またはこのツールに関するいくつかの優れたヒントやコツを知っている場合は、コメントでそれらを共有することを躊躇しないでください。
The Calculator in Windows 7 & Windows 8 - A Tool for the Geek in You!
The new Windows Calculator offers more precise calculations than ever and it also has a new and powerful interface. It now integrates the basic standard calculations with programming, scientific calculations and statistics. Beyond this, there are also other features which are very useful: things like mortgage calculation, a multifunctional converter and a few more options which deserve their share of attention. In this article I will present them one by one and also share some possible usage scenarios.
Where to Find the Calculator in Windows 7 & Windows 8
In Windows 7 you can access it by going to Start Menu - > Accessories -> Calculator.

The Calculator can be opened also by typing calculator or calc in the Start Menu search box (in Windows 7) or in the Start screen (in Windows 8) and opening the appropriate search result.
Its executable can be found in this location: "C:WindowsSystem32calc.exe".
Calculation Modes
Even though it has a different version in Windows 8, compared to Windows 7, the Calculator is the same in both operating systems. The interface looks just the same and its features are identical.
The Calculator has 4 main modes with which you can do calculations:
- The Standard Mode.
- The Scientific Mode.
- The Programming Mode.
- The Statistics Mode.
In the sections below I will describe each of them and explain what they do and how to use them.
The Standard Mode
When you first open the Calculator, the Standard mode will be selected by default. This mode is the better equivalent of the normal pocket calculator. You can use the keyboard number values, the keypad (with the Num key activated) or the mouse to make calculations.

Example: You need to choose the numbers with which you want to do calculations and the operation on those numbers. So, if you were to do a simple multiplication you would click on the first number, the operation ( * multiply sign ) and the second number. At the end of the calculation process you can either continue to add a new operation to that result or click on the equal sign to get the end result.

The Programmer Mode
This mode offers the possibility to do operations with bases (binary, octal, hexadecimal, decimal). You can convert values from one base to another. For example, you can convert from a base two number system (binary - 0, 1) to a base ten number system (decimal 0-9). Also, this mode offers to help with logical bit operations (XOR, OR, AND etc).
To access this mode click on the View menu and select the Programmer option.

Like previous versions, the keys you use are related to the base. For example, the A - F buttons are only accessible if you check to work in hexadecimal values. The other buttons are or should be already common for a programmer. Ranging through the palette XOR table, % - modulus, shifting and changing from decimal to hexadecimal or binary results. Also, the values you get are shown as integers (natural numbers, meaning 16/3 will equal to 5).

Example: If you have to transform a binary value like 1011 to its decimal value you would type the number and simply click on the decimal radio box. Manually, this process would be rather lengthy and probably bring error problems if you don't fully grasp the concept.

The Scientific Mode
This mode offers a bit of a smile to any person who pursues mathematical or other scientific calculations. The offering ranges from your basic X to the power of to the more useful cos, sin or pi functions.

Example: Like you did before in the standard mode, to do an operation, click on a number, followed by an operation then put the second number.

The Statistics Mode
This mode presents options related to the statistics. Although it doesn't have many functions like other modes, they are more than welcomed. You can use functions like sum of numbers, sum of numbers to the power to make statistics calculus.

Pressing the C, in the sole case of statistics mode, deletes the current value expressed. The CAD clears all the values from the dataset. The dataset is the list of added numbers. The dataset is the list with which you will perform different operations.
Example:To do an operation in the statistics mode, you have to place the values. Each value after has been typed will be placed in the dataset by clicking the ADD button. After you have placed all the needed values in the dataset list, you can click on the wanted operation.

Using History with Calculation Modes
This option goes beyond the useful values kept in memory. It can be used by going to File -> History and it is available for all the modes except the statistics one. The name says it all, however it is more powerful than it sounds. Playing around with complex formulas is made simple. You can do a calculation and, when done, click on the equal to have the result. This will make the result to enter into the History list. If you do another calculation and need the previous result or values from that result you just look up into the list and see those values. This coupled with the fact that you can quickly reedit former calculations makes the calculator surpass any online calculator offering that one might use for commodity. To access this option, make sure you are in a valid mode (all except statistics mode).

Other Options in the Calculator
The Calculator calculator now includes other tools that are beyond the scope of the calculation modes. They are more related to everyday necessities. Things like light weight conversion or calculating the distance from one specified day to another one. Going a little further than what you would normally need from a calculator, it also offers to help you with calculating mortgage values, vehicle lease and car consumption.




You have to select the type of transformation (example: Time), the From unit measurement (like Hour), and the To measurement unit (like Second).

Select the dates (from and to) to see the difference between them. You can also manually type a number of days, months (etc.) to subtract (or add) from a date and to see the final result. This is done by clicking on the 'Calculate the difference between two dates' and selecting the second given option.
Worksheets - These are options offered for real life calculations. Whether you want to calculate mortgage, vehicle lease or car consummation (American or European measurement), the calculator offers it all in the worksheets place.
Tips and tricks
I am often surprised of how unused some utilities are from a regular calculator. The subject I am referring to is the memory and other useful functions included in a calculator.
MC (Memory Clear or Clean) - clears the memory of any stored number leaving only the null or zero number in memory.
MR (Memory Reminder or Recalled) - tells the calculator to show the number present in memory.
MS (Memory Store or Set) - this takes the number present in the results and stores it in the memory. Previous calculation stored in memory will be deleted.
M+ (Add to memory) - formula> value stored in memory + current value = new value stored.
M- (Subtract from memory) - formula> value stored in memory - current value = new value stored.
C - Clear all calculations that are currently made.

The Back Arrow or Backspace - present on Windows Calculator but not present on a pocket calculator. This option deletes the last typed number from the current value. This option can be used by clicking on the Back Arrow or by pressing the Backspace key.
Using numerical values from the keyboard makes the calculation faster. You can also use the * key to quickly multiple, the minus key "-", the plus key "+", the divisible by "/" or the equal key "=".
Although this has nothing to do with notations, you can click on the Edit-> Copy to copy the value to clipboard.
Going to the help page for calculator reveals useful keyboard shortcuts for use with functions or options.
Conclusion
The changes in the way it looks and the options it has, make the Calculator feel like it has been built with quick lightweight functionality in mind. All features work well together and the transitions between options are done very easily. In the end, if you have problems, questions or you just know some great tips and tricks about this tool, don't hesitate to share them with us in a comment.

















