Windowsが起動すると、多くのプロセスやアプリケーションのロードなど、多くのことが起こります。これらのプロセスのいずれかがスタックした場合、Windowsはロードに失敗するか、ロードが非常に遅くなります。そこで、Windowsの組み込みツールであるMSConfigまたはシステム構成ユーティリティ(System Configuration Utility)が機能します。この投稿では、Windows 11/10/8/7でMSConfigを開いて使用する方法Windows 11/10/8/7、(MSConfig)スタートアップアイテム、起動オプション、サービス(Services)、セーフモード(Safe Mode)での起動などを管理する方法について説明します。
Windows11/10のMSConfigとは何ですか
MSCONFIGまたはシステム構成ユーティリティは、ユーザーが(System Configuration)Windowsの起動(Windows Startup)に関する問題をトラブルシューティングするのに役立ちます。スタートアップの選択、セーフブートの管理、 (Safe Boot)Windows サービス(Services)の有効化または無効化、パフォーマンスモニター(Performance Monitor)、リソースモニター(Resource Monitor)などのシステムツールの検索と起動を行うことができます。システム構成(System Configuration)ユーティリティは、より多くの診断ツールであり、システムの起動を構成するためのいくつかの優れたコントロールを提供します。
MSConfigユーティリティを開く方法
実行プロンプト(Win + R)を開き、msconfigと入力します。Enterキーを押します。システム構成(System Configuration)ユーティリティが起動します。5つのタブが表示されます。
- 一般(General):必要に応じて、診断モードまたは選択モードでWindowsを起動できます
- 起動(Boot):セーフモードを含む、Windowsの起動に関連するすべてを管理します。
- サービス(Services):Windowsおよびその他のサービスを有効または無効にします
- スタートアップ(Startup):スタートアップセクションは、タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)を介して管理されるようになりました。
- ツール(Tools):ここから人気のあるシステム(System)サービスを起動します。
機能を詳しく見ていきましょう。
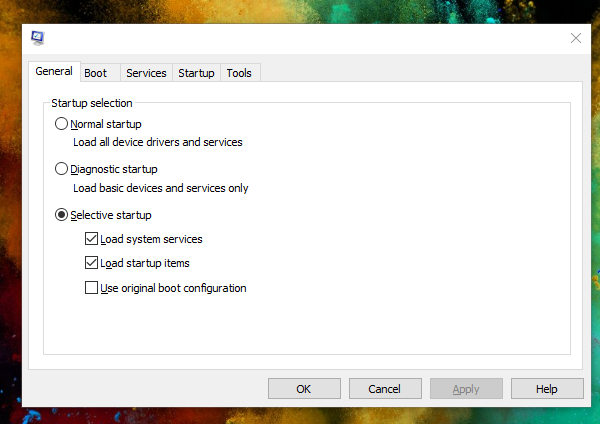
1]一般/スタートアップの選択
スタートアップ(Startup)の選択には3つのタイプがあります。1つ目は通常(Normal)の起動で、起動プロセスにどの広告を表示するかについてほとんど制限がありません。2つ目は診断(Diagnostic)です。これは最小限のサービスでトラブルシューティングを行うのに役立ちますが、選択機能は(Selective)Windows 11/10で何を開始するかを決定する場所です。
- 通常(Normal):診断サービスなしでシステムを起動します。問題を診断しようとしている場合は、他の2つのオプションのいずれかを選択する必要があります。問題が解決したことを確認したら、この設定をクリックして、システムを通常どおりに再起動します。
- 診断—(Diagnostic —)これにより、Windowsがコンピューターを起動するのに十分な重要なサービスとドライバーで起動することが確認されます。問題の原因となっている悪名高いサードパーティのサービスやソフトウェアを確実に見つけるのに役立ちます。
- 選択的—(Selective —)このセクションを使用して、コンピューターの起動を高速化します。Windowsで起動する必要のないサービスやプログラムを無効にすることを選択できます。
選択的スタートアップモード(Selective Startup mode)では、システムを重要なサービスとドライバー(診断と同じように)で起動できるだけでなく、追加のサービスとスタートアップアプリケーションの使用を正しく構成できるため、問題の原因をゆっくりと特定できます。ブートプロセス。[サービス(Service)]タブまたは[スタートアップ](Startup)タブから一度に1つずつ項目を確認してオンにし、再起動したときにシステムがどのように反応するかを確認できます。
読む(Read):MSConfigスタートアップリストから無効なアイテムを削除する(remove disabled items from the MSConfig startup list)方法。
2]起動オプション
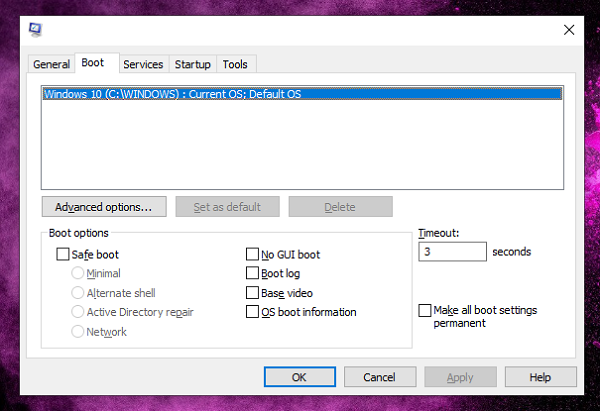
セーフブートのオプションは次のとおりです。
- セーフブート:最小:(Safe Boot: Minimal:)Windows GUI を起動しますが、重要なサービスのみを実行します。ネットワーク機能も無効になります。システムがこのレベルで機能していることがわかった場合は、サービスをオンにして、さらに問題が発生するかどうかを確認することをお勧めします。
- セーフブート:代替シェル:(Safe Boot: Alternate Shell:)このオプションを使用して、コマンドプロンプトで起動します。重要なサービスは実行され続けますが、ネットワークとGUIは無効になります。
- セーフブート:Active Directoryの修復:(Safe Boot: Active Directory Repair:)重要(Active Directory)なサービスとActiveDirectoryを実行し(Windows GUI) ているWindowsGUIを起動します。
- セーフブートネットワーク:(Safe Boot Network:)このオプションを使用して、Windows GUIを起動し、重要なサービスとネットワークを実行します。問題がネットワークサービスにあると思わない場合は、システムのネットワークをオンにしておくと役立ちます。これにより、診断のためにネットワークまたはインターネット上(Internet)で必要になる可能性のあるリソースにアクセスできるようになります。
その他のオプションは次のとおりです。
- GUI起動なし:起動時に(No GUI Boot:)WindowsVistaのスプラッシュ画面を 表示しません。代わりに、前述のように、Aurora画面が表示されます。
- (Boot Log)ブートログ。 :ブートプロセスからの情報を、 ntbtlog.txt(Stores)と呼ばれる%systemroot%にあるログに保存します。他の技術者はこれらのログを読んで、システムがクラッシュする原因を見つけることができます。
- ベースビデオ:(Base Video:)過去のVGAモード と同様に、このモードでは、ハードウェアに特に関連するものではなく、標準のVGAドライバーがシステムにロードされます。(VGA)このオプションは、ビデオドライバの問題を解消するのに適しています。このモードでは、Windowsは640 X 480の解像度で実行され、メモリの消費量が少なくなります。
- OSブート情報:(OS Boot Information:) ロード中のブートプロセス中のすべてのドライバーを表示します。
- すべての起動設定を永続化する: (Make All Boot Settings Permanent: )変更が完了し、永続化する場合は、このオプションを選択します。ただし、これを投稿すると、以前の設定に戻す簡単な方法がないことを忘れないでください。すべてを手動で変更する必要があるため、このオプションは慎重に使用するように注意してください。
- タイムアウト設定:(Timeout Settings:)マルチブートシステムにさまざまなカウントダウンを構成できます。好きなものを入力してみることができますが、3秒から999秒の間の数字を要求されます。
- 詳細設定:(Advanced Settings:)これらの詳細オプションを使用すると、プロセッサの数、メモリの量、グローバルデバッグ(Global Debug)設定などを構成できます。これらのオプションは、システムを診断するための最後の手段であることに注意してください。Microsoftサポートサービスの指示の下で使用してください。
読む(Read):MSCONFIGのブート詳細オプション(Boot Advanced Options in MSCONFIG)とは何ですか?
3]サービス
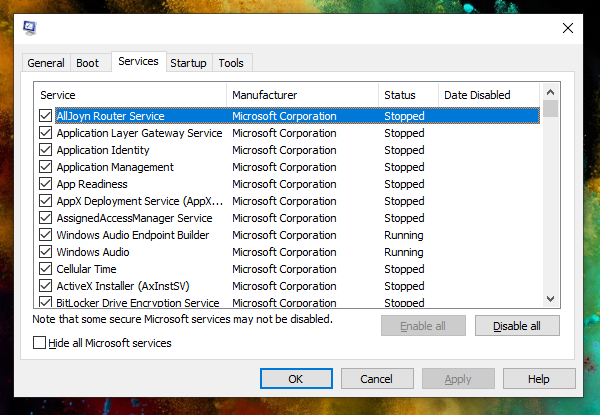
いずれかのWindowsサービス(Windows Services)が問題の原因であると思われる場合は、このセクションで選択を解除し、把握するのに役立ちます。ブートで開始するすべてのサービスが一覧表示されます。チェックボックスをオフにして、次にシステムを起動したときにそのサービスが起動しないようにすることもできます。
サービスの選択を解除することを選択すると、スタートアップモードが選択的スタートアップ(Selective Startup)に変わります。Windowsシステムサービスを無効にしないようにするには、チェックボックスをオンにして、Windowsでサービスを非表示にするを選択します。
元の問題の原因となっているサービスを検索しようとすると、他の問題が発生する可能性があるため、サービスを無効にする場合は注意してください。一部のサービスは、システムが正しく動作するために必須です。他のサービスを無効にすると、OSの他の側面に影響を与える可能性があるため、診断アプローチが失敗する可能性があります。
つまり、サービスを無効にする前に、そのサービスを無効にする理由を理解し、そのサービスが他のサービスやシステムの機能にどのように影響するかを理解してください。( impact other services or features of your system.)
ヒント(TIP):Autostart Explorerを使用すると、最もあいまいな起動場所でも探索できます。
4]スタートアップ
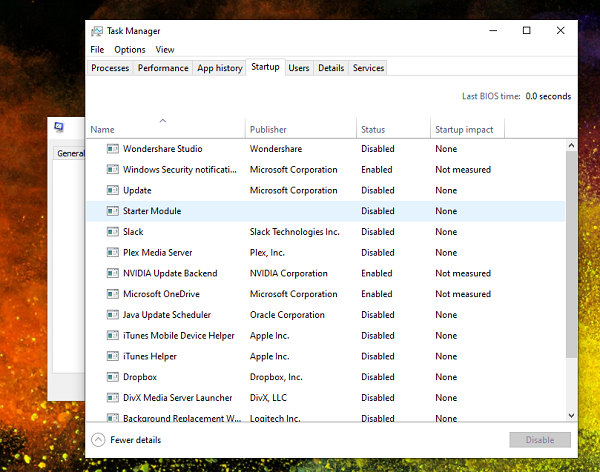
Windows 10では、スタートアップアイテムを管理するセクションが(manage Startup items)タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)で利用できるようになりました。Windowsで起動するアプリケーションを有効にするか無効にするかを選択できます。これを使用して、 Windows(Windows)で起動するように登録されている特定のアプリケーションを削除できるようにします。それは私の全体的な起動タイミング(boot timing)を改善しました。
5]ツール
[ツール(Tools)]タブには、診断ツールと情報ツールのリストが表示され、これらのツールの場所が表示されます。このタブ内から、任意のシステムツールを文字通り「起動」するか、ツール自体の場所または名前をメモすることができます。これの優れている点は、あらゆる種類のツールと、いくつかの事前構成されたコマンドラインオプションの中心的な場所であるということです。例えば:
C:\WINDOWS\System32\cmd.exe /k %windir%\system32\ipconfig.exe
ただし、特定のスパイウェアやマルウェアアプリケーションなど、[スタート]メニューの特定のアプリケーションを無効にする場合は、 MSCONFIG(Startup)クリーンアップツール(MSCONFIG Cleanup tool)を試してください。また、レジストリ(Registry)からそのエントリを削除し、これらのアイテムを削除するのに役立ちます。
次を読む(Read next):MSConfigを使用して、システムの復元、RegeditなどのWindowsツールを起動します。
What is MSConfig or System Configuration Utility in Windows 11/10
When Windows boоts up, a lot of things happen, including the loading of a lot of processes аnd applications. If any of these processes get stuck, Windоws will either fail to load or load very slowly. That’s is where the Windows inbuilt tool MSConfig or System Configuration Utility comes into action. In this post, we will see how to open & use MSConfig in Windows 11/10/8/7 and how to manage startup items, boot options, Services & boot in Safe Mode, etc.

What is MSConfig in Windows 11/10
MSCONFIG or System Configuration utility helps users troubleshoot Windows Startup issues. It allows you to manage startup selection, Safe Boot, enable or disable Windows Services, find & launch system tools like Performance Monitor, Resource Monitor, and more. The System Configuration utility is more of a diagnostics tool and offers some great controls for configuring the startup of your system.
How to open MSConfig utility
Open Run Prompt (Win+R), and type msconfig. and press the Enter key. It will launch the System Configuration utility. It will display five tabs:
- General: Allows you to boot Windows in diagnostic or selective mode when necessary
- Boot: Manage everything related to Windows boot, including Safe mode.
- Services: Enable or disable Windows and other services
- Startup: The startup section is now managed via Task Manager.
- Tools: Launch popular System services from here.
Let us take a look at the features in detail.
1] General/Startup Selection
There are three types of Startup selection. The first is the Normal boot where there is almost no restriction on what ads to the boot process. The second is Diagnostic, which is useful to troubleshoot with minimal service while Selective is where you decide what starts with Windows 11/10.
- Normal—Boots the system without any diagnostic services. If you are trying to diagnose a problem, you should select one of the other two options. When you are sure the issue is resolved, click this setting to boot your system normally again.
- Diagnostic — This will make sure Windows boots with essential services and drivers enough to start the computer. It helps you to make sure to find out notorious third-party services and software causing the problem.
- Selective —Use this section to speed up computer startup. You can choose to disable services and programs which need not start with Windows.
The Selective Startup mode not only allows you to start your system with essential services and drivers (just like diagnostic), but it also allows you to correctly configure the use of additional services and startup applications so you can slowly determine what is causing the problem in your boot process. You can go through and turn on items one at a time from the Service or Startup tabs and see how your system reacts when you reboot.
Read: How to remove disabled items from the MSConfig startup list.
2] Boot Options

The options for Safe Boot are:
- Safe Boot: Minimal: Boots to the Windows GUI but only running critical services. Networking functions are also disabled. If you find your system is working at this level, then you might want to try turning on services to see if they cause any further issues.
- Safe Boot: Alternate Shell: Use this option to boot to a command prompt. It will keep the critical services running, but networking and the GUI are disabled.
- Safe Boot: Active Directory Repair: Boots to the Windows GUI running critical services and Active Directory.
- Safe Boot Network: Use this option to boot to the Windows GUI, running critical services and networking. If you don’t think your problem is in the networking services, then having the network turned on for your system will help. It will allow you to access resources you might need on the network or the Internet for diagnosis.
The other options are:
- No GUI Boot: Does not display the Windows Vista splash screen when you are booting. Instead, as mentioned earlier, the Aurora screen appears.
- Boot Log.: Stores information from the boot process in a log located in %systemroot% called ntbtlog.txt. Other technicians can read these logs to find what might be causing your system to crash.
- Base Video: Just like VGA mode in times past, this mode loads the system with standard VGA drivers instead of those that specifically relate to your hardware. This option is suitable for eliminating problems with video drivers. When in this mode, Windows runs at 640 X 480 resolution at which it will consume less memory.
- OS Boot Information: Shows all the drivers during the boot process as they load up.
- Make All Boot Settings Permanent: Once you are done with the changes, and want to make it permanent, select this option. However, do remember that post this, there is no easy way to revert to the previous settings. You will have to change everything manually, and hence we caution to use this option carefully.
- Timeout Settings: You can configure different countdowns for your multi-boot systems. You can try to type in what you like, but it will ask for a number between 3 seconds and 999 seconds.
- Advanced Settings: These advanced options enable you to configure such things as the number of processors, the amount of memory, and Global Debug settings. Keep in mind that these options are last-resort choices to diagnose your systems. Use it under the direction of Microsoft support services.
Read: What are Boot Advanced Options in MSCONFIG?
3] Services

If you believe that any of the Windows Services is causing an issue, then this section lets you deselect, and help you figure. It lists all the services which start with the boot. You can also uncheck the checkbox to prevent that service from starting up the next time you boot the system.
When you choose to deselect services, the startup mode will change to Selective Startup. To make sure not to disable any of the Windows system services, check the box to select hide services in Windows.
Be careful when you decide to disable a service because you might cause other problems while attempting to search for the one causing your original problem. Some services are compulsory for your system to operate correctly. Other services, if disabled, may throw off your diagnostic approach because you may be affecting other aspects of your OS.
In other words, know why you are disabling a service before you do it, and understand how that service may impact other services or features of your system.
TIP: Autostart Explorer lets you explore EVEN the most obscure start up locations.
4] Startup

In Windows 10, the section to manage Startup items is now available with the Task Manager. You can choose to enable or disable applications to start with Windows. I use it to make certain applications that register themselves to start with Windows can be removed. It improved my overall boot timing.
5] Tools
The Tools tab provides a list of diagnostic and informational tools and shows the location of these tools. From within this tab, you can literally “Launch” any system tool, or you can note the location or name of the tool itself. What’s great about this is that it’s a central location to all sorts of tools and even a few preconfigured command-line options. E.g:
C:\WINDOWS\System32\cmd.exe /k %windir%\system32\ipconfig.exe
That said if you want to disable specific applications in the Startup menu, such as certain spyware and malware applications you find, then you should try the MSCONFIG Cleanup tool. It can also help you get rid of its entry from the Registry and remove these items.
Read next: Use MSConfig to launch Windows tools like System Restore, Regedit, etc.




