ほとんどの人がデータ分析について考えるとき、彼らはMicrosoftExcelのような(like Microsoft Excel)ツールでデータを操作して分析することを考えます。現実には、データ分析には、データが伝えるストーリーを操作および理解するためのさまざまなツールとさまざまな方法が含まれます。
データ分析とは何ですか?ビジネスデータ、製造データ、マーケティングデータ、または事業を行っている業界やビジネスに固有のデータについて話している場合、データ分析の使用方法は大きく異なります。(Data)

この記事では、データ分析のさまざまな側面、それらの意味、およびそれらが全体的にどのように一般的に使用されているかについて学習します。
データ収集(Data Collection)
データ分析の最初の段階はデータ収集です。これは単に、必要な情報を保持しているすべてのソースからデータを収集することを意味します。
データには、次のいずれか以上を含めることができます。
- 製造機械コントローラー
- 誰かが手動でコンピューターにデータを入力している
- 温度や圧力などを測定するセンサー
- クラウドベース(Cloud based)のデータソース
- 天気や政府のデータベースなどのインターネットからの情報
- (Databases)会社のネットワークに格納されているデータベース
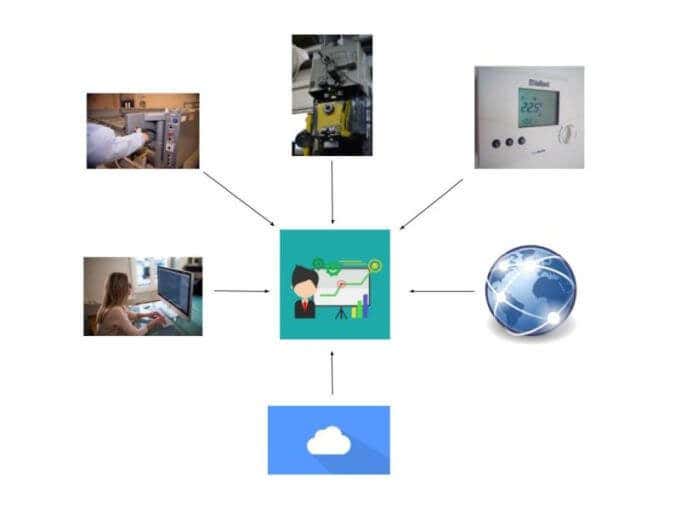
多くの組織にとっての主要な課題は、その情報を収集するために利用できる技術ツールを把握することです。ほとんどの場合、ソフトウェアはそのリモートデバイスまたはデータソースに接続し、それらを内部データベースまたはデータ履歴システムにプルする必要があります。
これらのストレージ領域は、「データウェアハウス」と呼ばれることがよくあります。
組織内のデータウェアハウスに情報が収集されると、さまざまなツールを使用して実際のデータ分析を実行できます。
ビジネス・インテリジェンス(Business Intelligence)
データが収集されたら、次のステップはそのすべてのデータをどう処理するかを決定することです。ビジネスインテリジェンスに関しては、必要なデータは組織がより良いビジネス上の意思決定を行うのに役立つはずです。
ビジネスインテリジェンス(Intelligence)(BI)レポートとダッシュボードは、マネージャーやその他のビジネスリーダーが傾向をよりよく理解し、ビジネスのさまざまな側面について洞察を得るのに役立ちます。

これらの側面は次のとおりです。
- サプライチェーンのニーズまたは制限
- コスト削減
- 売上の向上
- 顧客のニーズと行動
- 将来の売上または市場の需要を予測する
- ロジスティクスと配送
組織全体のこれらのさまざまなシステムすべてからデータを収集することで、これまで不可能だった可能性のある情報間の接続を構築できます。
マニュファクチャリングインテリジェンス(Manufacturing Intelligence)
製造プロセスからデータを収集する場合の難しさは、通常、データが非常に多いことです。
典型的な製造施設について考えると、製造現場のすべてのマシンは、次のような数十から数百のデータポイントを収集します。
- 温度と圧力
- 製造された部品または製品
- 使用した原材料
- 不良部品の廃棄
- 誤動作のカウントとアラーム
ほとんどの場合、製造装置はプログラマブルロジックコントローラー(PLC)を使用して自動化されています。これらのデバイスは、プログラムされた方法に従って機器を実行するだけでなく、その機器からデータを収集および収集します。
これらのPLC(PLCs)からデータを取得するには、それらのPLC(PLCs)と同じネットワーク上のサーバーで実行されるソフトウェアが必要です。これらのコントローラーからデータヒストリアンまたはデータベースにデータを取得するためのソフトウェアを作成したベンダーはたくさんあります。

この分野のデータ歴史家のリーダーは次のとおりです。
- OSIsoft:この会社は何十年も前から存在しており、ほぼすべての種類のプロセッサ、センサー、またはデータベースからデータを取得できる「インテグレータ」またはドライバが含まれています。
- Factorytalk:長年の自動化リーダーであるロックウェル・オートメーション(Rockwell Automation)は、顧客がマシンプロセッサからデータを収集するのを支援するために、 Factorytalkと呼ばれる独自のデータヒストリアンを作成しました。
- Aveva:以前はWonderwareとして知られていたAVEVA Historianは、プロセスデータ、アラーム、イベントなどのマシンデータへの「オープンアクセス」を提供することを約束します。
- Iconics:データヒストリアンマーケットプレイスの小規模なプレーヤーであるIconicsのメーカーは、保存されたデータ解像度がマシンで最初に発生したものと一致するように「高速アーカイブ」を提供することを約束します。
これらのソフトウェアプロバイダーのほぼすべてに、データヒストリアンソリューションに対応するデータ分析ツールが含まれています。製造施設に適したデータ収集および分析ソリューションの選択は、実際には、使用するコントローラー、データの保存方法、および使用する金額によって異なります。
データの視覚化
ビジネスデータを収集、分析、および視覚化するための最も一般的なツールは、MicrosoftPowerBIです(Microsoft PowerBI)。
PowerBIは、 (PowerBI)Microsoftが提供する強力な視覚化ツールであり、さまざまなデータソースからデータを取り込むことができます。次に、さまざまな円グラフや棒グラフ、線グラフ、表などでデータをスライスおよびダイシングできます。
さまざまなデータソースからの情報を組み合わせる機能により、以前は不可能だった相関関係を見つけることができます。これが現代のデータ分析の魔法です。これにより、多くのソースからのデータを視覚化できるツールではこれまで不可能だった洞察を得ることができます。
(PowerBI)この方法でデータを操作および視覚化する機能を備えたアプリは、PowerBIだけではありません。実際、これらのタイプのツールだけの市場が成長しています。
今日の主要なデータ視覚化ツールには、次のものがあります。
- Metabase:組織内の人々が「質問をしてデータから学ぶ」ことができると自慢するオープンソース(無料)ソリューション。
- Tableau:さまざまな業界で使用されている人気のあるデータ視覚化プラットフォーム。多くの異なるデータソースとの接続が利用可能です。(Connectivity)
- Whatagraph:わかりやすいレポートを作成しやすいため、マーケティングエージェンシーの間で人気があります。このツールには自動レポート生成が含まれており、それらを誰にでも自動的に電子メールで送信できます。
- JasperReports:これは別のオープンソースレポートソリューションです。その力は、印刷されたドキュメント、PDF(PDFs)、Webベースのレポートなどのさまざまな形式でレポートを出力する機能にあります。
どちらを選択するかは、実際には、あなたまたはあなたの組織が行いたい投資によって異なります。ありがたいことに、そこから始める必要がある場合は、優れたオープンソースオプションを利用できます。
データマイニング
最も強力な新しいデータ分析手法の1つは、データマイニングと呼ばれるものです。
データ(Data)マイニングは、将来の傾向を予測するために、統計モデリングを使用して大量のデータからパターンと傾向を引き出すことに重点を置いています。
データマイニング統計分析を実行できるアプリケーションは高度に専門化されており、多くの場合、手元のアプリケーションや状況に合わせてカスタマイズする必要があります。
データマイニング分析の種類は次のとおりです。
- 探索的データ分析(Exploratory Data Analysis)(EDA):これには、新しい傾向を特定したり、新しい情報を学習したりするために、データのパターンを検索することが含まれます。
- 確認データ分析(Confirmatory Data Analysis)(CDA:これには、収集されたすべてのデータを使用して、疑わしい相関が真であるかどうかを判断することが含まれます。
現在市場に出回っている主要なデータマイニングソフトウェアツールには、次のものがあります。
- Rapid Miner : Javaで記述された優れたオープンソースの予測分析システム。機械学習、予測分析、テキストマイニングが可能です。
- Sisense:ビジネスインテリジェンス向けに調整されたライセンスソフトウェアで、大規模な組織向けにスケールアップできます。優れたレポートモジュールが含まれています。
- Oracle:データ業界の主要な名前の1つであるOracleは、 (Oracle)SQL内にデータマイニング機能を提供し、組織がOracleデータベースに格納されているデータを使用できるようにします。
- IBM Cognos:このソフトウェアは、重要な傾向を特定するために大量のデータを処理することができます。これらは、管理者またはその他の人のためのレポートを生成するために使用できます。
- SAS:データ業界のもう1つの有名な統計分析システム(Statistical Analysis System)(SAS)は、分析結果に基づいてデータをマイニング、管理、さらには更新するために特別に設計されました。
ご覧のとおり、データ分析には多くの側面があり、使用する必要のあるツールは、そのデータから何を学びたいかによって異なります。
データ分析の進歩は毎年進歩し続けており、業界で先を行くことを望む企業や組織は、利用可能なデータ分析ツールを常に把握し、それらを最大限に活用する必要があります。
What Is Data Analysis And The Best Tools To Use
When most people think of data analysis, they think of manipulating and analyzing data in a tool like Microsoft Excel. The reality is that data analysis encompasses a wide range of tools and a lot of different methods to manipulate and understand the story that the data tells.
What is data analysis? Data analysis is used very differently if you’re talking about business data, manufacturing data, marketing data, or data specific to the industry and business that you operate.

In this article, you’ll learn about the different aspects of data analysis, what they mean, and how they’re generally used across the board.
Data Collection
The first stage of any data analysis is data collection. This simply means gathering data from all of the sources that hold information you need.
Data can include any of the following and more:
- Manufacturing machinery controllers
- Someone manually entering data into a computer
- Sensors that measure temperature, pressure, and more
- Cloud based data sources
- Information from the internet like weather or government databases
- Databases housed on your company network

A major challenge for a lot of organizations is figuring out what technical tools are available to gather that information. Most of the time software is required to connect to that remote device or data source and then pull them into an internal database or data historian system.
These storage areas are often referred to as a “data warehouse”.
Once information is collected into a data warehouse inside an organization, various tools can be used to conduct the actual data analysis.
Business Intelligence
Once data is collected, the next step is deciding what to do with all that data. When it comes to business intelligence, the required data should help an organization make better business decisions.
Business Intelligence (BI) reports and dashboards help managers and other business leaders better understand trends and gain insights into various aspects of the business.

These aspects include:
- Supply chain needs or limitations
- Reducing costs
- Improving sales
- Customer needs and behaviors
- Predicting future sales or market demands
- Logistics and shipping
Gathering data from all of these different systems throughout your organization lets you build connections between information that may never have been possible before.
Manufacturing Intelligence
The difficulty when it comes to gathering data from manufacturing processes is that usually there’s just so much of it.
If you think about a typical manufacturing facility, every single machine on the shop floor collects dozens to hundred of data points that include:
- Temperatures and pressures
- Parts or product made
- Raw material used
- Bad parts scrapped
- Malfunction counts and alarms
In most cases, manufacturing equipment is automated by the use of a programmable logic controller (PLC). These devices not only run the equipment according to how they’re programmed, but they also collect and gather data from that equipment.
Getting data out of those PLCs involves software that runs on a server on the same network as those PLCs. There are many vendors that have written software to get data out of those controllers and into a data historian or a database.

The data historian leaders in this area include:
- OSIsoft: This company has been around for decades, and includes “integrators” or drivers that can get data out of almost any kind of processor, sensor, or database.
- Factorytalk: Long time automation leader Rockwell Automation produced their own data historian called Factorytalk to help their customers collect data from machine processors.
- Aveva: Formerly known as Wonderware, the AVEVA Historian promises to provide “open access” to machine data like process data, alarms, events, and more.
- Iconics: A smaller player in the data historian marketplace, the makers of Iconics promise to provide “high-speed archiving” so the stored data resolution matches what originally occurred on the machine.
Nearly all of these software providers include data analysis tools to go along with their data historian solution. Choosing the right data collection and analytics solution for your manufacturing facility really depends on the controllers you use, how you want to store the data, and how much you are willing to spend.
Data Visualization
The most popular tool for collecting, analyzing, and visualizing business data is Microsoft PowerBI.
PowerBI is a powerful visualization tool offered by Microsoft that lets you bring in data from many different data sources. You can then slice and dice the data across various pie and bar charts, line graphs, tables, and more.
The ability to combine information from various data sources lets you find correlations that wouldn’t have been possible before. This is the magic of modern data analysis. It provides the ability to gain insights that were never before possible before tools that let you visualize data from many sources.
PowerBI isn’t the only app with the ability to manipulate and visualize data in this way. In fact, there’s a growing market for just these types of tools.

The leading data visualization tools today include:
- Metabase: An open-source (free) solution that touts itself as letting people in your organization “ask questions and learn from data”.
- Tableau: A popular data visualization platform used across many different industries. Connectivity with many different data sources is available.
- Whatagraph: Popular among marketing agencies because it’s easy to produce easy-to-understand reports. The tool includes automated report generation and can automatically email those to anyone.
- JasperReports: This is another open-source reporting solution. It’s power comes from the ability to output reports in many different formats like printed documents, PDFs, and web-based reports.
The option you decide to go with really depends on the investment you or your organization wants to make. Thankfully there are excellent open-source options available if that’s where you need to start.
Data Mining
One of the most powerful new data analysis techniques is something called data mining.
Data mining focuses on using statistical modeling to pull patterns and trends out of a large volume of data in order to predict future trends.
The applications that can perform data mining statistical analysis are highly specialized and often need to be customized to the application or situation at hand.
Types of data mining analysis include:
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA): This involves searching for patterns in data in order to identify new trends or learn new information.
- Confirmatory Data Analysis (CDA: This involves using all of the collected data to try and determine whether suspected correlations are true.

Some of the leading data mining software tools available on the market today include:
- Rapid Miner: An excellent open-source predictive analysis system written in Java. It’s capable of machine learning, predictive analysis, and text mining.
- Sisense: Licensed software tailored for business intelligence, with the ability to scale up for large organizations. It includes an excellent reporting module.
- Oracle: One of the leading names in the data industry, Oracle offers data mining feature within SQL that lets organizations use data stored in an Oracle database.
- IBM Cognos: This software is capable of processing large volumes of data to identify important trends. These can be used to generate reports for management or others.
- SAS: Another big name in the data industry, Statistical Analysis System (SAS) was specifically designed to mine, manage, and even update data based on analytical results.
As you can see, there are many facets to data analysis and the tools you need to use really depends on what you hope to learn from that data.
Advancements in data analysis continue to advance every year, and any company or organization that hopes to stay ahead in their industry needs to stay on top of what data analysis tools are available and to use them to their fullest potential.






