多くのWindowsおよびMacユーザーは、ほとんどの時間をWebブラウザーで開いているタブを見つめています。これはアクティビティの中心であり、メールへの返信、ゲームのプレイ、ソーシャルメディアのチェック、ビデオの視聴などを行うことができます。可能性は無限大ですが、残念ながら、システムリソースは無限大ではありません。
Mozilla Firefoxのようなブラウザは、使用するほど利用可能なシステムメモリを使い果たす可能性があります。これにより、特に原因を特定できない場合に、コンピューターの速度が低下し、応答が停止する可能性があります。Firefoxが一般的な使用中に大量のメモリを使用している場合は、これらの修正を試して、問題が解決するかどうかを確認する必要があります。

Firefoxを再起動します(Restart Firefox)
FirefoxやChromeを含め、すべてのWebブラウザでメモリリークの問題が発生します。メモリリークは通常、複数のタブが実行されているブラウザが長期間実行されたままになっている場合に発生します。しばらくすると、開いているタブが使い果たされ、利用可能なシステムリソースのほとんどが要求され始め、PCの応答に苦労します。
それが発生し、 Firefox(Firefox)が原因だと思われる場合、簡単な解決策はFirefoxを再起動することです。ただし、Firefoxを閉じても、実行中の(Closing Firefox)Firefoxプロセスが完全に終了しない場合があります。Windowsを実行している場合は、実行中のすべてのFirefoxプロセスが(Firefox)Windowsタスクマネージャー(Windows Task Manager)で閉じられていることを確認する必要があります。
- これを行うには、タスクバーを右クリックして、[タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)]オプションを選択します。

- タスクマネージャ(Task Manager )ウィンドウで、実行中のFirefoxプロセスを見つけます。それらを終了するには、エントリを右クリックして、[タスクの終了(End Task)]オプションを選択します。これにより、 Firefox(Firefox)が強制的に閉じられます。
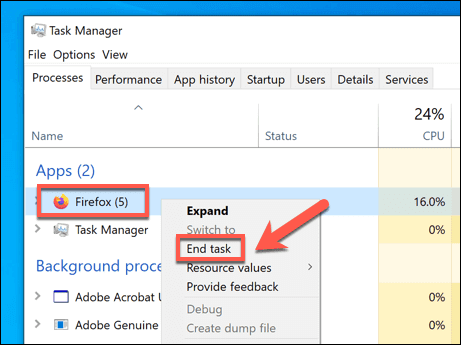
- Macを使用している場合は、DockのFirefoxアイコン(Firefox icon)を右クリックし、[終了]を選択することで、実行中のFirefoxウィンドウを(Quit)強制的に終了できます(Firefox)。Firefoxが閉じず、完全に応答しなくなった場合は、プロセスを繰り返し、代わりに[強制終了](Force Quit)を選択します。

Firefoxの拡張機能、プラグイン、テーマを無効にする(Disable Firefox Extensions, Plugins, and Themes)
Firefoxは、テーマから拡張機能まで、その機能を拡張できるさまざまなアドオン(add-ons)を備えたカスタマイズ可能なブラウザです( Chrome拡張機能(Chrome extensions)の動作と同様)。残念ながら、アドオンを追加しすぎると、特に低電力のPCで実行している場合に、ブラウザのパフォーマンスに悪影響を与えることがあります。
Firefoxのテーマ、プラグイン、または拡張機能がFirefoxのメモリ使用量を増やしているのではないかと疑問に思っている場合は、それらを無効にする必要があります。方法は次のとおりです。
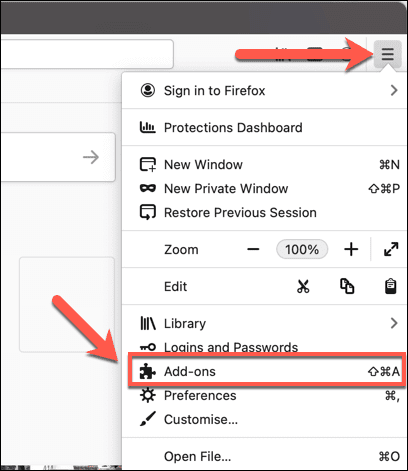
- Firefoxアドオンを無効にするには、 Firefoxを開き、右上のハンバーガーメニューアイコン(hamburger menu icon)を選択します。メニューから、[アドオン(Add-ons )]オプションを選択します。
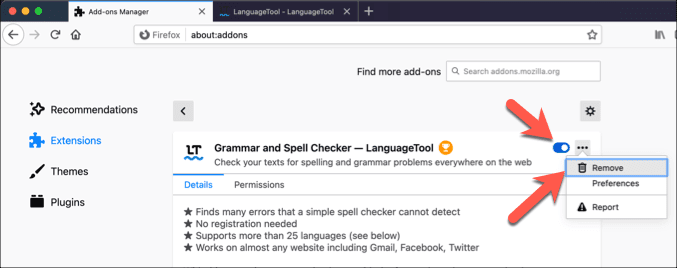
- アドオン(Add-ons )メニューの左側に、拡張機能(Extensions)、テーマ(Themes)、プラグイン(Plugins)のオプションが表示されます。[拡張機能](Extensions)で、有効な拡張機能の横にあるスライダーを選択して無効にします。削除するには、横にある3つのドットのメニューアイコンを選択し、メニューから[(three-dots menu icon )削除(Remove)]を選択します。
- カスタムFirefox(Firefox)テーマを使用している場合は、 Add-ons > Themes有効(Enable)にする]ボタンを選択して、デフォルト(Default )のテーマに戻します。デフォルトのFirefoxテーマとして、不要なメモリ使用を引き起こす可能性が最も低くなります。

- Firefoxプラグイン(メディア再生プラグインなど)が問題の原因であることが心配な場合は、[Add-ons > Plugins 3つのドットのメニュー(three-dots menu )アイコンを選択します。メニューから、[アクティブ化しない(Never Activate )]オプションを選択して無効にします。

Firefoxのアップデートを確認する(Check For Firefox Updates)
Firefoxの新しいリリースごとに、不要なメモリ使用量などの既知の問題の影響を軽減するのに役立つ新機能とバグ修正が提供されます。Firefoxが古くなっている場合は、重大なバグ修正が欠落している可能性があります。
- Firefoxの新しいアップデートを確認するには、右上のハンバーガーメニューアイコンを選択します。(hamburger menu icon )メニューから、[設定](Preferences)オプションを選択します。

- [設定]メニューで、[ (Preferences)Firefoxの更新(Firefox Updates)]セクションまで下にスクロールします。新しい更新を確認するには、[更新の確認(Check for updates)]オプションを選択します。Firefoxはアップデートをチェックし、アップデートが利用可能な場合は、設定に応じて自動的にアップデートするか、インストールを求めるプロンプトを表示します。

about:memoryメニューを使用して、メモリ使用量を最小限に抑えます(Use The about:memory Menu to Minimize Memory Usage)
Firefoxのような最新のブラウザは、常に機能するとは限らない場合でも、メモリフットプリントを最小限に抑えるように設計されています。Firefoxが大量のメモリを使用している場合は、 about:memoryと呼ばれる非表示の設定メニューを利用して、アクティブなメモリ使用量をすばやく減らすことができます。
- これを行うには、アドレスバーに about:memoryと入力し、Enterキーを押します。(about:memory )

- about:memory設定メニューの使用可能なオプションのリストから、[メモリ使用量の最小(Minimize memory usage)化]オプションを選択します。成功すると、オプションの下にメモリ最小化完了(Memory minimization completed )メッセージが表示されます。このプロセスはいつでも繰り返すことができます。

Firefoxのセーフモードに切り替えます(Switch to Firefox Safe Mode)
Firefoxセーフモード(Firefox Safe Mode)は、ブラウザの問題を特定して修正するのに役立つ特別なブラウザモードです。Firefoxのアドオンまたは設定の問題が不要なメモリ使用量を引き起こしていると思われる場合は、セーフモード(Safe Mode)に切り替えると問題の診断に役立ちます。
- Firefoxのセーフモード(Firefox Safe Mode)に切り替えるには、右上のハンバーガーメニューアイコン(hamburger menu icon )を選択します。メニューから、[Help > Restart with add-ons disabled]を選択します。
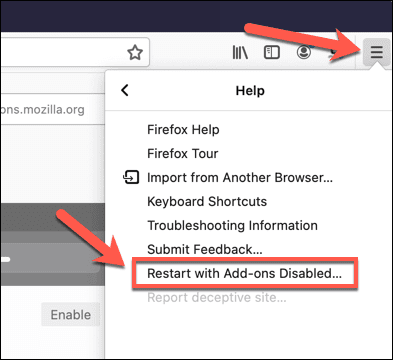
- (Confirm)ポップアップで[再起動(Restart)]オプションを選択して、Firefoxをセーフモードで再起動することを(Safe Mode)確認します。
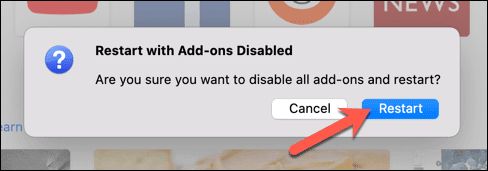
- Firefoxが再起動し、(Firefox)セーフモード(Safe Mode)を開くかFirefoxを完全にリセットするかを選択できます。[セーフモードで開始]を選択して、セーフモード(Start in Safe Mode)を起動します。
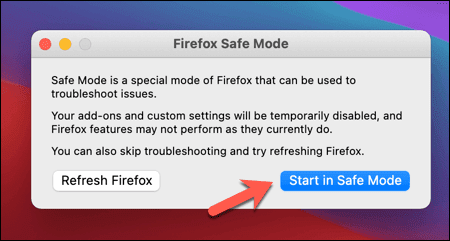
Firefoxウィンドウは通常どおり起動しますが、すべての拡張機能、テーマ、およびプラグインが無効になっています。システムリソースの使用状況を監視しながら、通常どおりブラウザを使用します。大量のメモリを使用していない場合、これは通常の使用中にFirefoxに問題があることを示しているため、さらに調査する必要があります。
ハードウェアアクセラレーション設定の変更(Change Hardware Acceleration Settings)
システムリソースの能力を最大化するために、Firefoxはハードウェアアクセラレーションを使用して、実行中のさまざまなタブやサービスの要求のバランスを取ります。これにより、システムリソースに対する需要が増加し、実行中の他のアプリの速度が低下したり、クラッシュしたりする可能性があります。
その場合は、Firefoxのハードウェアアクセラレーション設定を変更し、必要に応じて完全に無効にする必要があります。
- 開始するには、hamburger menu icon > PreferencesFirefox設定メニューを開きます。

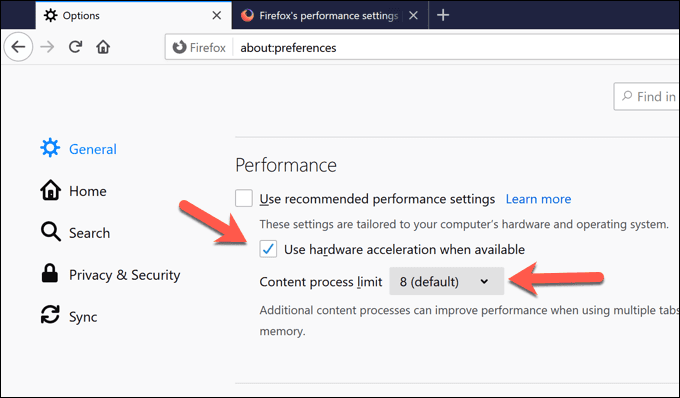
- [設定(Preferences)]タブの[General > Performance]セクションで、 [推奨されるパフォーマンス設定を使用する(Use recommended performance settings)]オプションをオフにして、追加の設定を表示します。そこから、コンテンツプロセスの制限(Content process limit )値を減らして、実行中の追加のFirefoxプロセスの数を制限し、プロセスのメモリ使用量を減らします。または、[使用可能な場合はハードウェアアクセラレーションを使用(Use hardware acceleration when available )する]オプションをオフにして、ハードウェアアクセラレーションを完全に無効にします。
Firefoxをデフォルト設定にリセット(Reset Firefox to Default Settings)
他のすべてが失敗し、Firefoxの設定、アドオン、または機能の問題を診断できない場合は、デフォルト設定にリセットすると、Firefoxが大量のメモリを使用している問題の解決に役立つ場合があります。
- これを行うには、Firefoxを開き、hamburger menu icon > Help > Troubleshooting Informationを選択します。

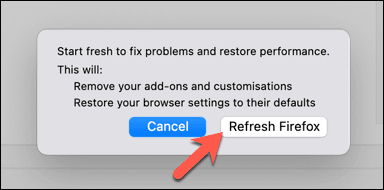
- [トラブルシューティング情報(Troubleshooting Information )]メニューで、右上隅にある[ Firefoxの更新]オプションを選択します。(Refresh Firefox)

- Firefoxは、これによりブラウザの設定、アドオン、およびカスタマイズが消去されることを警告します。ただし、ブックマークと閲覧履歴は削除されません。確認するには、[ Firefoxの更新(Refresh Firefox)]オプションを選択してプロセスを開始します。
- リセットプロセスが完了すると、Firefoxが再起動します。成功(Success )メッセージが表示され、以前のタブとウィンドウを復元できます。選択を確認してから、[ Firefoxの使用を再開しましょう(Let’s go )]を選択します。

Firefoxを効果的に使用する(Using Firefox Effectively)
Firefoxが大量のメモリを使用している場合、上記の修正はほとんどの場合問題の解決に役立つはずです。そうでない場合は、別のブラウザに切り替える、ハードウェアをアップグレードする(upgrading your hardware)など、別の解決策を検討する必要があります。遅いブラウザは、識別と修正に役立つ診断ツールを必要とする可能性のある他の問題を指摘する可能性があります。(diagnostic tools)
Firefoxが適切に機能すると、プライバシーに重点を置いた多くの機能を利用できるようになります。たとえば、追加のセキュリティ設定でFirefoxをより安全(make Firefox safer)に使用できるようにしたり、 Firefox Monitorを使用してプライバシー侵害(privacy breaches)を警告したり、FirefoxPrivateNetworkを使用(use Firefox Private Network)して匿名のオンラインを維持したりできます。
Firefox Using Too Much Memory? 7 Ways to Fix
There are many Windows and Mac users who spend most of their time staring at open tabs in theіr web browser. It’s the center poіnt of activity, allowing yоu to respond to emailѕ, play games, check social media, watch videos, and more. Τhe possibilities are endleѕs, but, unfortunately, yoυr system reѕources are not.
Browsers like Mozilla Firefox can and will use up available system memory the more you use them. This can cause your computer to slow down and stop responding, especially if you can’t figure out the cause. If Firefox is using too much memory during general usage, you’ll need to try these fixes to see if they resolve the problem.

Restart Firefox
All web browsers suffer from memory leak issues, including Firefox and Chrome. Memory leaks are usually caused when a browser, with multiple running tabs, is left running for a long period of time. After a while, the open tabs begin to eat up and claim most of the available system resources, leaving your PC struggling to respond.
If that happens, and you think Firefox is the cause, an easy solution is simply to restart Firefox. Closing Firefox may not fully end any running Firefox processes, however. If you’re running Windows, you’ll need to check that all running Firefox processes have closed in Windows Task Manager.
- To do this, right-click the taskbar and select the Task Manager option.

- In the Task Manager window, find any running Firefox processes. To end them, right-click the entry and select the End Task option. This will force Firefox to close.

- If you’re on Mac, you can force quit a running Firefox window by right-clicking the Firefox icon on the Dock and selecting Quit. If Firefox doesn’t close and stops responding entirely, repeat the process, selecting Force Quit instead.

Disable Firefox Extensions, Plugins, and Themes
Firefox is a customizable browser with various add-ons that can extend its functionality, from themes to extensions (similar to how Chrome extensions work). Unfortunately, adding too many add-ons can occasionally have a detrimental impact on your browser performance, especially if you’re running on a lower-powered PC.
If you’re wondering whether a Firefox theme, plugin, or extension is causing Firefox to use too much memory, you’ll need to disable them. Here’s how.
- To disable Firefox add-ons, open Firefox and select the hamburger menu icon in the top-right. From the menu, select the Add-ons option.

- In the Add-ons menu, you’ll see options for Extensions, Themes, and Plugins on the left. In Extensions, select the slider next to an enabled extension to disable it. To remove it, select the three-dots menu icon next to it, then select Remove from the menu.

- If you’re using a custom Firefox theme, switch back to the Default theme by selecting the Enable button in the Add-ons > Themes menu. As the default Firefox theme, it offers the least likelihood of causing unnecessary memory usage.

- If you’re worried that a Firefox plugin (such as a media playback plugin) is causing issues, select the three-dots menu icon next to a plugin in the Add-ons > Plugins menu. From the menu, select the Never Activate option to disable it.

Check For Firefox Updates
Each new Firefox release brings new features and bug fixes that can help to reduce the impact of known issues, including unnecessary memory usage. If Firefox is out of date, you might be missing a crucial bug fix.
- To check for new Firefox updates, select the hamburger menu icon in the top-right. From the menu, select the Preferences option.

- In the Preferences menu, scroll down to the Firefox Updates section. To check for new updates, select the Check for updates option. Firefox will check for updates and, if an update is available, it will update automatically or prompt you to install it, depending on your settings.

Use The about:memory Menu to Minimize Memory Usage
Modern browsers like Firefox are designed to try and minimize their memory footprint, even if it doesn’t always work. If Firefox is using too much memory, you can take advantage of a hidden settings menu called about:memory to force it to quickly reduce active memory usage.
- To do this, type about:memory in the address bar and press enter.

- From the list of available options in the about:memory settings menu, select the Minimize memory usage option. If successful, a Memory minimization completed message will appear beneath the options. You can repeat this process at any point.

Switch to Firefox Safe Mode
Firefox Safe Mode is a special browser mode that helps you to identify and fix issues with the browser. If you suspect that a problem with a Firefox add-on or setting is causing unnecessary memory usage, switching to Safe Mode can help to diagnose the problem.
- To switch to Firefox Safe Mode, select the hamburger menu icon in the top-right. From the menu, select Help > Restart with add-ons disabled.

- Confirm you want to restart Firefox in Safe Mode by selecting the Restart option in the pop-up.

- Firefox will restart, giving you the option to open Safe Mode or reset Firefox entirely. Select Start in Safe Mode to launch Safe Mode.

The Firefox window will launch as normal, but with all extensions, themes, and plugins disabled. Use your browser as normal while monitoring system resource usage. If it isn’t using a huge amount of memory, this would indicate a problem with Firefox during normal usage, and you’ll have to investigate further.
Change Hardware Acceleration Settings
To maximise the power of your system resources, Firefox uses hardware acceleration to balance out the demands of various running tabs and services. This can cause an increased demand on your system resources which can cause other running apps to slow down or crash.
If that’s the case, you’ll need to change Firefox’s hardware acceleration settings and, if necessary, disable it entirely.
- To start, open the Firefox settings menu by selecting the hamburger menu icon > Preferences.

- Under the General > Performance section of the Preferences tab, uncheck the Use recommended performance settings option to view additional settings. From there, reduce the Content process limit value to limit the number of additional running Firefox processes and reduce memory usage in the process. Alternatively, disable hardware acceleration completely by unchecking the Use hardware acceleration when available option.

Reset Firefox to Default Settings
When all else fails, and you can’t diagnose a problem with Firefox’s settings, add-ons, or features, you may find that resetting it to default settings can help to resolve a problem where Firefox is using too much memory.
- To do this, open Firefox and select the hamburger menu icon > Help > Troubleshooting Information.

- In the Troubleshooting Information menu, select the Refresh Firefox option in the top-right corner.

- Firefox will warn you that this will erase any browser settings, add-ons, and customization. It won’t, however, remove your bookmarks and browsing history. To confirm, select the Refresh Firefox option to begin the process.

- Once the reset process is complete, Firefox will restart. You’ll see a Success message, allowing you to restore previous tabs and windows. Confirm your choice, then select Let’s go to resume using Firefox.

Using Firefox Effectively
If Firefox is using too much memory, the fixes above should help to resolve the problem in most cases. If they don’t, you may need to consider alternative solutions, such as switching to another browser or upgrading your hardware. A slow browser could point to other issues that might require diagnostic tools to help identify and fix.
Once Firefox is working properly, you can take advantage of its many privacy-focused features. For instance, you can make Firefox safer to use with extra security settings, use Firefox Monitor to alert you to any privacy breaches, or you can use Firefox Private Network to stay anonymous online.





















