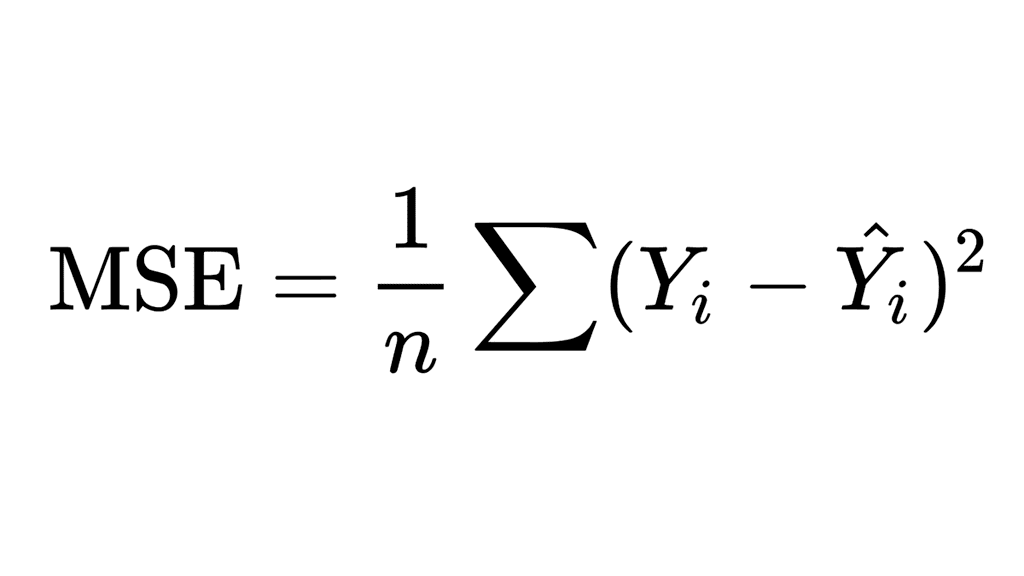統計学では、平均二乗誤差 ( MSE ) は、統計モデルの誤差の量を測定する重要な指標です。これは、将来の値を予測するために使用されるモデルの精度を評価するためによく使用されます。
このチュートリアルでは、 MSE と(MSE)は何かをさらに詳しく説明し、 ExcelでMSE を(MSE)計算する方法を示します。

平均二乗誤差とは何ですか?
平均二乗誤差 ( MSE ) は、データセット内の推定値と実際の値の間の平均二乗差を測定する計算です。言い換えれば、統計モデルの誤差の量を推定します。統計マニアのために、回帰直線が一連のデータ ポイントにどれだけ近似しているかを計算します。
たとえば、ソフトウェア会社として 1 年間に受け取るであろう売上高を予測するモデルがあるとします。年末に、生成した実際の売上高を入力します。次に、MSEを計算して、モデルが結果をどの程度正確に予測したかを確認できます。
MSE は、(MSE)ターゲット変数の予測値と実際の値の間の二乗差の平均を取ることによって計算されます。
MSE の式は次のようになります。
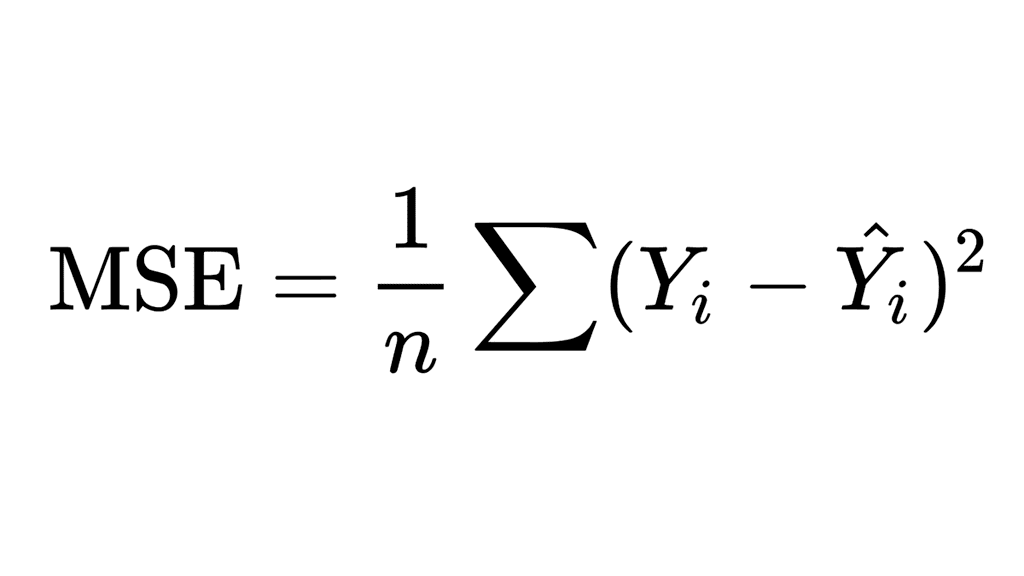
どこ:
- Σ は値の合計を意味します。
- n はサンプルサイズまたは観測値の数です。
- Yi は観測値であり、
- Ŷi は予測値です。
誤差値が低いほど、モデルの標準誤差が小さく、ターゲット変数の予測が優れていることを示します。MSEは統計回帰やデータ分析で広く使用されており、さまざまなモデルを比較したり、パラメーターを調整して予測の精度を向上させるのに役立ちます。
これは混乱しているように見えますが、次のセクションで詳しく説明すると、理解するのはそれほど難しくありません。
Microsoft Excelで平均二乗誤差(Mean Squared Error)を計算する方法
Microsoft ExcelでMSE を(MSE)計算するには、主に 2 つの方法があります。それは、 SUMSQ関数、AVERAGE 関数(AVERAGE function)、およびMSE式です。以下の例を使用して、これらの各関数を使用して
MSE を(MSE)計算する方法を示します。
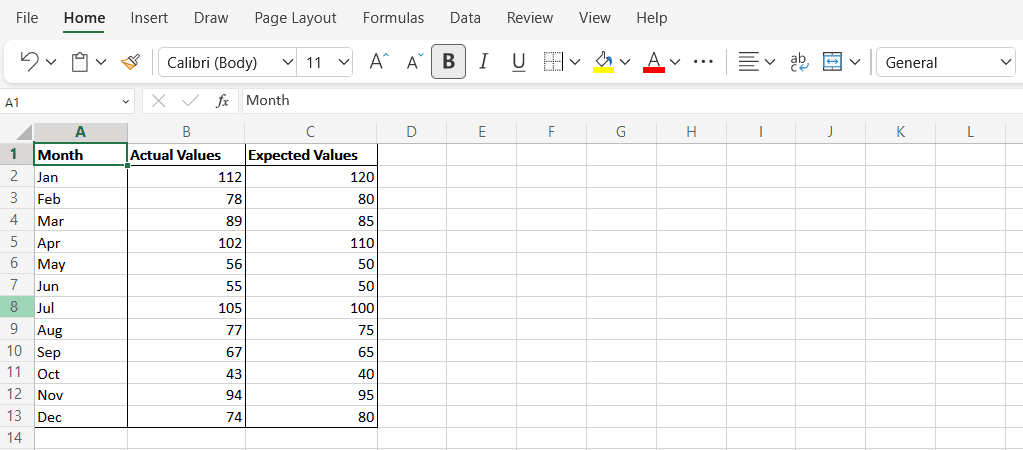
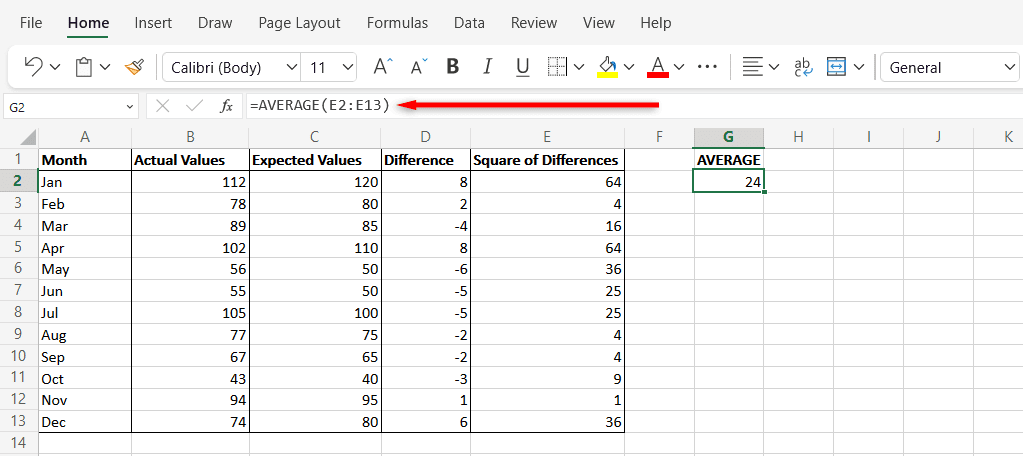
この単純化された例では、各月の架空の売上高 (列 A(Column A) )を見ていきます。推定値は列 B(Column B)に示され、実際の値は列 C(Column C)に示されます。
(Calculate MSE)SUMSQ 関数(SUMSQ Function)を使用してMSE を計算する
ExcelのSUMSQ関数は、範囲内の数値の二乗和を計算するために使用されます。これを使用してMSE(MSE)を計算する方法は次のとおりです。
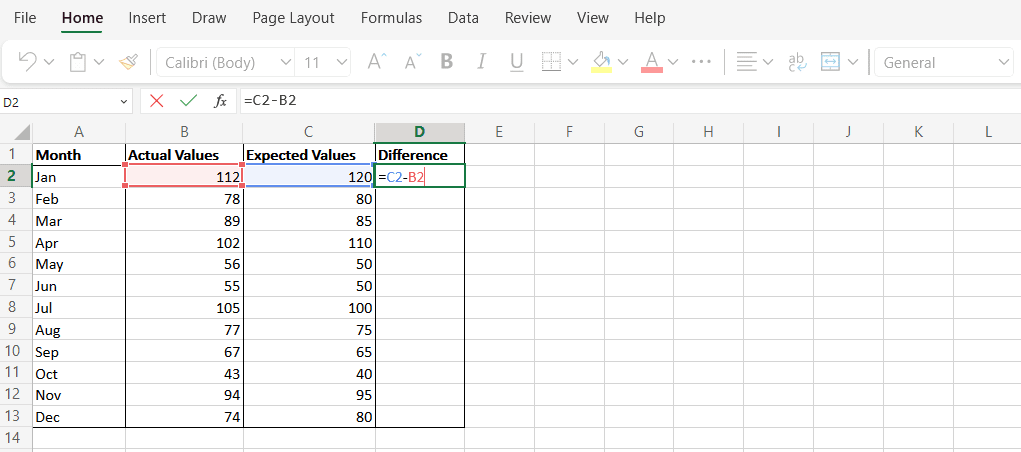
- 列D(Column D)に「Difference 」という新しい列を作成します。これは、期待値と実際の値の差を表します。
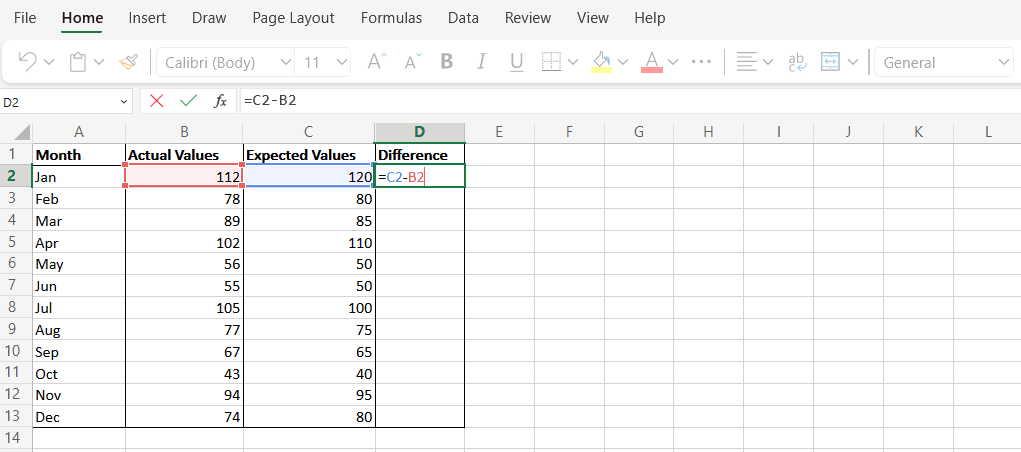
- 式「C2-B2」を使用して、各行のデータ ポイントの差を計算します。
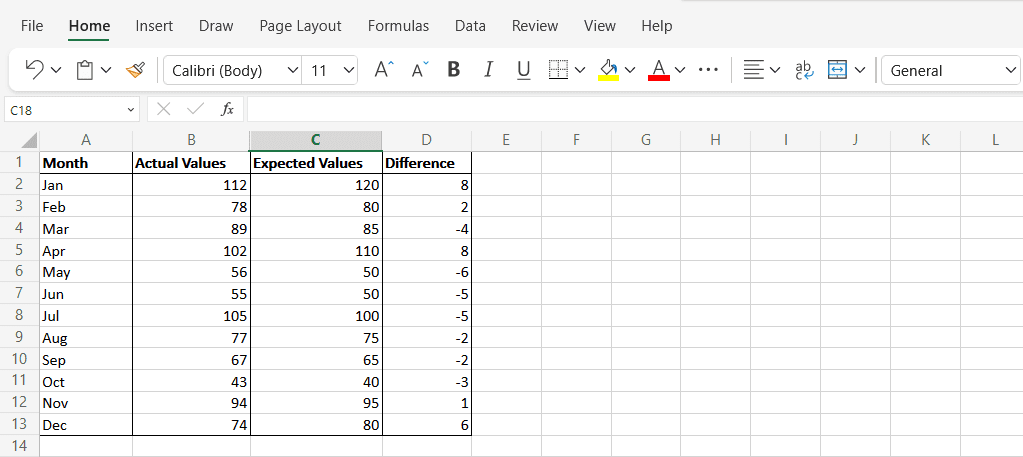
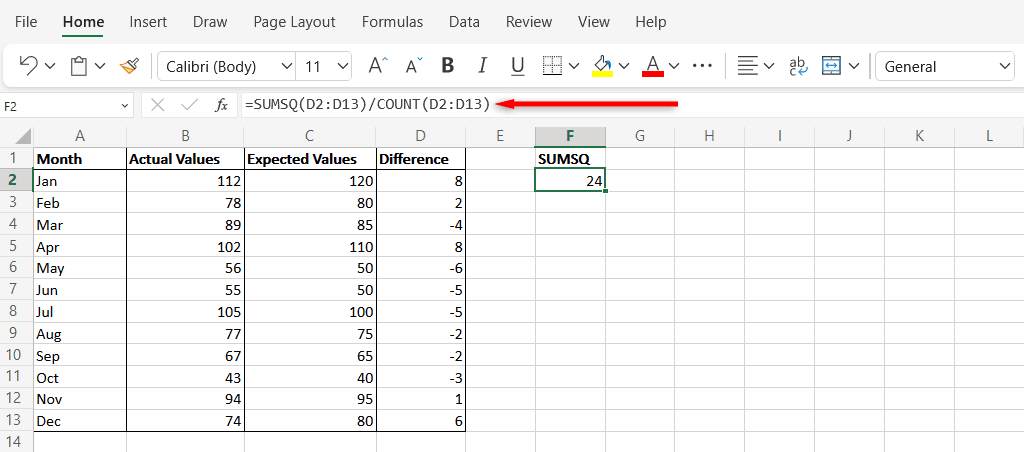
- 新しいセルを選択し、次の構文を入力します: “=SUMSQ(D2: D13/COUNT (D2: D13 )”。数式内のセルを(D13)Excelスプレッドシートの正しいセルに置き換えます。このセルの最終結果がMSEです。 。
(Calculate MSE)AVERAGE関数
を使用してMSE を計算する
MS Excelの AVERAGE 関数は、数値範囲(AVERAGE)の平均を計算するために使用されます。このメソッドはSUMSQ(SUMSQ)関数と同じ結果を返しますが、各ステップは手動で実行されます。
- (Perform)SUMSQメソッドで説明されている手順 1 と 2を実行します。これにより、予測値と実際のデータの差が返されます。
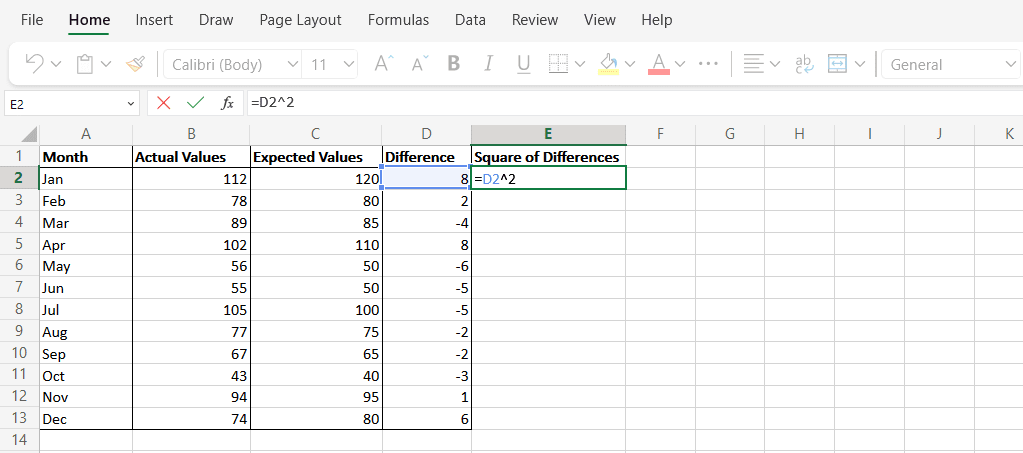
- 列 E に「差の二乗」という名前を付け、式「=D2^2」を使用して列 D(Column D)の各値の差の二乗を計算します。
- 新しいセルを選択し、列 E(Column E.)の平均値を計算します。これにより、以前に計算した二乗値の平均が返されます。これを行うには、「=AVERAGE(E2:E12)」と入力してEnterを押します。必ずセルをワークシート(worksheet)で使用したセルに置き換えてください(Make)。結果として得られるデータ値がMSEです。
Microsoft Excelでの統計分析
Microsoft Excel は(Microsoft Excel)長い間、データ分析のための最も強力なツールの 1 つです。このチュートリアルにより、Excelを使用して(Excel)MSE を(MSE)簡単に計算できるようになることを願っています(Hopefully)。また、これらは非常に似ているため、 Google スプレッドシート(Google Sheets)でも同じ計算を実行できるはずです。
How to Calculate Mean Squared Error (MSE) in Microsoft Excel
In statistics, the mean squared error (MSΕ) is an important metric that measures the аmount of error in a statistical model. It’s often used to aѕsesѕ the acсuracy of a model that’s used to predict future values.
In this tutorial, we’ll explain what MSE is in more detail and then show you how to calculate MSE in Excel.

What Is Mean Squared Error?
The mean squared error (MSE) is a calculation that measures the average squared difference between estimated and actual values in a dataset. In other words, it estimates the amount of error in a statistical model. For the statistics geeks out there, it calculates how closely a regression line fits a set of data points.
For example, say you have a model that predicts the value of sales you’ll receive as a software company over a year. At the end of the year, you plug in the actual sales values that you generated. You can then calculate the MSE to see how well your model predicted the outcome.
MSE is calculated by taking the average of the squared differences between the predicted and actual values of the target variable.
The MSE formula looks like this:
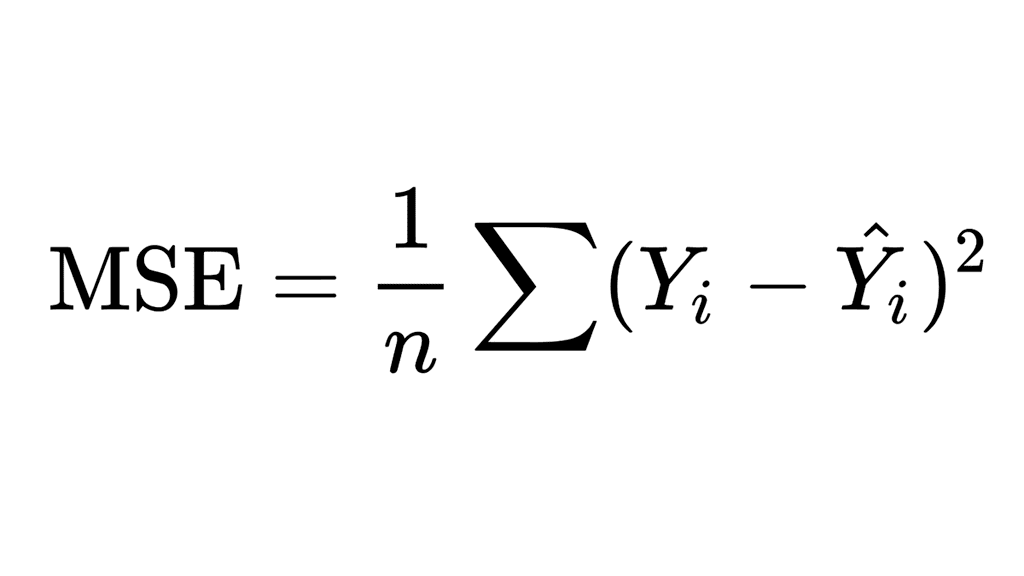
Where:
- Σ means the sum of values;
- n is the sample size or number of observations;
- Yi are the observed values, and;
- Ŷi are the predicted values.
A lower error value indicates that the model has a smaller standard error and is better at predicting the target variable. MSE is widely used in statistical regression and data analysis and can be helpful in comparing different models or tuning parameters to improve the accuracy of predictions.
This looks confusing, but it isn’t too hard to follow when we break it down in the following sections.
How to Calculate Mean Squared Error in Microsoft Excel
There are two main ways you can calculate MSE in Microsoft Excel: the SUMSQ function, the AVERAGE function, and the MSE formula. We’ll use the example below to show you how to calculate MSE using each of these functions:
In this simplified example, we’ll look at fictional sales values for each month (Column A). The estimated values are represented in Column B and the actual values in Column C.

Calculate MSE Using the SUMSQ Function
The SUMSQ function in Excel is used to calculate the sum of the squares of numbers in a range. Here’s how to use it to calculate MSE:
- Create a new column in Column D called “Difference”. This will represent the difference between the expected and actual values.

- Use the formula “C2-B2” to calculate the difference for the data points in each row.

- Select a new cell and type the following syntax: “=SUMSQ(D2:D13/COUNT(D2:D13)”. Replace the cells in the formula with the correct cells from your Excel spreadsheet. The final result in this cell is your MSE.

Calculate MSE Using the AVERAGE Function
The AVERAGE function in MS Excel is used to calculate the average of a range of numbers. This method returns the same result as the SUMSQ function, but each step is performed manually.
- Perform Steps 1 and 2 described in the SUMSQ method. This will return the differences between the forecasted values and actual data.

- Name Column E “Square of Differences”, then use the formula “=D2^2” to calculate the square of the difference of each value in Column D.

- Select a new cell and calculate the average value of Column E. This will return the mean of the squared values that you previously calculated. To do so, type “=AVERAGE(E2:E12)” and press Enter. Make sure to replace the cells with the cells you used in your worksheet. The resulting data value is your MSE.

Statistical Analysis in Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel has long been one of the most powerful tools for data analysis. Hopefully, with this tutorial, you can now use Excel to calculate MSE easily. And, since they’re so similar, you should be able to perform the same calculations in Google Sheets.