Windows 10を使用する場合、PCの内部ストレージは時間の経過とともに徐々にいっぱいになります。これは、大容量HDDやSSD(capacity HDDs and SSDs)では大きな問題ではありません。しかし、最初から十分な余裕(t offer)が(breathing room)ないドライブで、スペース関連の問題が発生する可能性があります。
Windows 10のディスク領域を解放するには、いくつかの方法に頼ることができます。それらの中には、数十ギガバイト(数百ではないにしても)を解放するのに役立つものもあれば、ほんの数メガバイト余分にネットするものもあります。

1.ごみ箱を解放します
コンピューター上のファイルを削除しても、Windows10はそれらを完全に削除しません。代わりに、ごみ箱(Recycle Bin)にそれらを隠します。これにより、後で気が変わった場合に削除されたファイルを復元(restore deleted files if you change your mind)できます。しかし、あなたは便宜のためにディスクスペース(disk space)を交換することになります。
削除されたファイルを復元する予定(t plan)がない場合は、ごみ箱(Recycle Bin)を空にすることを選択できます。これを行うには、デスクトップのごみ箱(Recycle Bin)アイコンを右クリックして、[ごみ箱を空にする(Empty Recycle Bin)]を選択します。または、ごみ箱(Recycle Bin)を開いて、その中の選択したファイルを削除することもできます。

ファイルを選択してShift(Shift ) + Deleteを押すと、ファイルをごみ箱(Recycle Bin)に送信せずに完全に削除することもできます。
2.ダウンロードフォルダをクリアします
Windows 10 PCのダウンロードフォルダー(Downloads folder)は、めったに再利用されないジャンクファイルやプログラムインストーラーのホットスポットです。
ファイルエクスプローラーを開き、サイドバーで[このPC](This PC) >[ダウンロード(Downloads )]を選択します。次に、不要なファイルを削除します。フォルダをリスト(List )ビューに切り替え、ファイルをサイズ(Size )でフィルタリングして、スペースを最も多く使用しているアイテムを見つけて削除することもできます。
3.不要なアプリを削除します
コンピューターから不要なアプリやプログラム(apps and programs)を取り除くことは、Windows10コンピューターで使用されているストレージの量を減らすもう1つの簡単な方法です。
これを行うには、[スタート(Start )]メニューを開き、 [設定](Settings ) >[アプリ(Apps )] >[アプリと機能(Apps & Features)]に移動します。次に、リストをスクロールして、使用し(t use)なくなったアプリを選択し、[アンインストール(Uninstall)]を選択してそれらを削除します。

4.OneDriveでファイルをオンデマンドで使用する
OneDriveはWindows10(Windows 10)に組み込まれており、ドキュメントや写真をクラウドに簡単にバックアップ(back up documents and photos)できます。また、Files On-Demand機能(On-Demand functionality)もサポートしているため、必要な場合にのみバックアップファイルをローカルストレージにダウンロードできます。
OneDriveでファイルオンデマンド(On-Demand)を有効にするには、タスクバーのOneDriveアイコンを選択し、[ヘルプと設定](Help & Settings ) > [設定(Settings)]を選択します。次に表示される[MicrosoftOneDrive]ダイアログボックスで、 (Microsoft OneDrive dialog)[設定(Settings )]タブに切り替えます。続いて、[スペースを節約し、ファイルを使用しながらダウンロードする](Save space and download files as you use them)の横にあるチェックボックスをオンにします。
Files On-Demandをアクティブにすると、右クリックして[(right-clicking and selecting) 空き容量(Free up space)を増やす]を選択することで、バックアップしたファイルとフォルダーをいつでも直接オフロードできます。アイテムのプレースホルダーアイコンが引き続き表示されます。オフロードされたファイルにアクセスしようとすると、OneDriveにローカルでダウンロードするように求められます。

5.設定でストレージペインを使用する
Windows 10の設定アプリ(Settings app)には、PCのストレージを最も多く使用しているデータの種類を特定するのに役立つ [ストレージ]ペイン(Storage pane)が付属しています。
[スタート](Start ) > [設定](Settings ) >[システム(System )] >[ストレージ(Storage)]に移動してアクセスできます。次に、アプリと機能(Apps & Features)、一時ファイル(Temporary Files)、画像(Pictures)、音楽(Music)などのカテゴリのリストが表示されます。これらはすべて、スペースを消費するプログラムやファイルに飛び込んで削除できます。
ただし、最も重要なのは一時ファイル(Temporary Files)です。これを選択すると、ダウンロードフォルダー(Downloads folder)、ごみ箱(Recycle Bin)、Windows Updateキャッシュ(Windows Update cache)など、一時ファイルを保持する領域のリストがすぐに表示されます。次に、削除するものを選択し、[(Next)ファイル(Remove files)の削除]を選択します。

6.StorageSenseを実行またはアクティブ化する
上の[ストレージ]ペインには、 (Storage pane)StorageSenseと呼ばれる機能もあります。これをアクティブにすると、コンピューター上の一時ファイルを自動的に削除するためのWindows10のアクセス許可が付与されます。
[スタート](Start ) > [設定](Settings ) >[システム(System )] >[ストレージ(Storage )] > [StorageSenseの構成]に移動するか、今すぐ実行して(Configure Storage Sense or run it now)StorageSense設定にアクセスします。
次に、 StorageSense(Storage Sense)の下のスイッチをオンにして機能をアクティブにします。その後、設定を微調整して、コンピューターでStorageSenseを実行する方法を決定します。たとえば、実行するタイミング(たとえば、ディスク容量が少ないとき)、(disk space)ごみ箱とダウンロードフォルダ(Recycle Bin and Downloads folder)内のコンテンツを削除する頻度などを指定できます。

必要に応じて、 StorageSense(Storage Sense)を手動で実行することもできます。画面(screen and select)の一番下までスクロールして、[(Just scroll)今すぐクリーン](Clean now)を選択します。
7.ディスククリーンアップを使用する
設定アプリ(Settings app)のストレージ画面(Storage screen)よりもコンパクトなビューが必要な場合は、代わりに従来のディスククリーンアップユーティリティ(legacy Disk Cleanup utility)を選択できます。同様の機能を提供し、一時ファイルのロードをすばやく削除できます。[スタート]メニューで[ディスククリーンアップ(Disk Cleanup)]を検索すると、起動できます。
次に、削除するデータの種類( (Follow)Windows Updateのクリーンアップ(Windows Update Cleanup)、インターネット一時ファイル(Temporary Internet Files)、システムエラーメモリダンプファイル(System error memory dump files)など)の横にあるチェックボックスをオンにします。次に、[ OK]を選択します。
[システムファイルのクリーンアップ(Clean up system files)]オプションを選択して、追加の一時ファイルタイプを表示することもできます。

8.より多くの一時ファイルを削除します
Windows 10には、安全に削除できる他の一時ファイルも大量に含まれています。完全なステップバイステップのウォークスルーについて(step-by-step walkthrough)は、Windows10での一時ファイルの削除(removing temporary files in Windows 10)に関するこのガイドを確認することをお勧めします。しかし、ここに簡単なプロセスがあります。
まず、 Windows(Windows ) + Rを押して、[実行]ボックスを開きます。次に、%temp%OK ]を選択します。
続い(Follow)て、表示されるディレクトリ内のすべてのファイルとフォルダを削除します。次に、別の[実行]ボックスにtempと入力し、[ (temp )OK ]を選択して、そのディレクトリ内のすべてのファイルも削除します。最後に、コンピュータを再起動して終了します。

9.ブラウザキャッシュをクリアする
インターネットを閲覧すると、ブラウザはデータをキャッシュして、その後のWebサイトへのアクセスを高速化することになります。ただし、ストレージが不足している場合は、ブラウザのキャッシュ(browser cache)をクリアすることで、約500メガバイトを1ギガバイトのストレージにすばやく解放できます。
グーグルクローム(Google Chrome)
Chromeメニューを開き、 [設定](Settings) >[プライバシーとセキュリティ(Privacy and security )] > [閲覧データの消去(Clear browsing data)]を選択します。
次に表示される[閲覧履歴データの消去]ダイアログで、[時間範囲(Time range )]を[すべての時間]に設定し、 (All time)[キャッシュされた画像とファイル](Cached images and files)の横のチェックボックスをオンにします。最後に、[データのクリア(Clear data)]を選択します。

Mozilla Firefox
Firefoxメニューを開き、 [オプション(Options)] >[プライバシーとセキュリティ(Privacy and security)] >[データの消去(Clear Data)] ( [ Cookieとサイトデータ(Cookies and Site Data)]セクションの下)に移動します。次に、[キャッシュされたWebコンテンツ]の横のチェックボックスをオンにして、[(Cached Web Content)クリア(Clear)]を選択します。
マイクロソフトエッジ(Microsoft Edge)
[エッジ(Edge )]メニューを開き、[設定(Settings)]を選択します。次に、サイドバーの[プライバシー、検索、およびサービス(Privacy, search, and services )]タブに切り替え、 [閲覧履歴データ(Clear browsing data)のクリア]で[クリアする対象を選択]を選択し(Choose what to clear )ます。
次に、[時間範囲(Time range )]を[すべての時間]に設定し、 (All time)[キャッシュされた画像とファイル](Cached images and files)の横にあるチェックボックスをオンにして、[データを消去(Clear data)]を選択します。
10.WinDirStat(WinDirStat)を使用して大きなファイルを検索する
WinDirStatは無料のオープンソースアプリで、コンピューター上の大きなファイルやフォルダーを視覚的な形式で見つけることができます。プログラムをインストールして開いた後、スキャンするストレージドライブまたはパーティションを選択します。(storage drive or partition)次に、ドライブサイズに対するパーセンテージ形式(percentage form relative)を含め、最も多くのストレージを占有しているディレクトリのリストが表示されます。

WinDirStatがドライブのスキャンを終了すると、(WinDirStat)選択したドライブ(chosen drive)上のファイル(形式別)を示す多くの色付きのブロックも表示されます。サイズが大きいほど、より多くのスペースを消費します。アイテムを右クリックして[ここでエクスプローラー](Explorer Here)を選択すると、(item and select) ファイルエクスプローラー(File Explorer)でアイテムを表示(および削除)できます。
11.休止状態ファイルを削除します
Windows 10の休止状態モード(Hibernate mode)では、コンピューターの電源を切った後でもファイルやプログラムを復元できます。ただし、プログラムとオペレーティングシステムの状態を保存することで機能を促進するファイルは、多くのディスク領域(disk space)を占有する可能性があります。したがって、Hibernateの使用をスキップしてもかまわ(t mind)ない場合は、Hibernateを無効にして、ストレージを再利用することを選択できます。
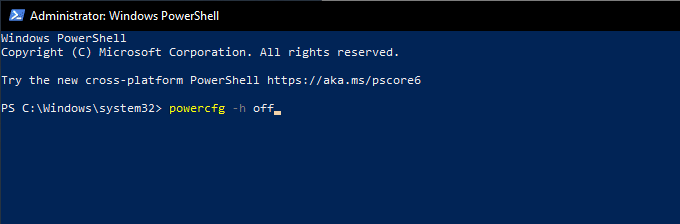
これを行うには、[スタート(Start )]ボタンを右クリックし、 [ Windows PowerShell(管理者)(Windows PowerShell (Admin)) ]を選択します。次に、以下のコマンドを実行します。
powercfg-hオフ(powercfg -h off)
その後、ファイルエクスプローラー(File Explorer)を開きます。次に、[ファイル(File )] >[フォルダと検索オプションの変更]を(Change folder and search options)選択します。
次に表示される[フォルダオプション]ダイアログボックスで、 (Folder Options dialog)[表示(View )]タブに切り替え、 [隠しファイル、フォルダ、およびドライブを(Show hidden files, folder, and drives)表示する]を選択します。最後に、Windows 10 インストールドライブ(installation drive—)(ローカルディスク(C :) )を開き、 (Local Disk (C:))hiberfil.sysというラベルの付いたファイルを削除します。
完全なステップバイステップの手順については、Windows10でハイバネーションを無効(disabling Hibernation in Windows 10)にするためのこのガイドを確認してください。
12.古いユーザーアカウントを削除します
コンピューターに複数のWindows10ユーザーアカウント(multiple Windows 10 user accounts)がある場合は、目的を果たさなくなったアカウントを削除することをお勧めします。削除したアカウントに関連するすべてのデータが完全に失われることに注意してください。(Just note)
コンピュータの[スタート(Start )]メニューを開くことから始めます。次に、[設定](Settings ) >[アカウント](Accounts ) >[家族と他のユーザー]に移動し、[(Family & other users)他のユーザー(Other users )]セクションからアカウントを選択して、[削除(Remove)]を選択します。

13.システムの復元を無効にする
システムの復元(System Restore)は、問題が発生した場合にコンピュータを以前の状態に復元するのに役立つ便利なバックアップ機能です。(backup function)ただし、大量のストレージも使用します。したがって、まだストレージが不足している場合は、最後のシステムの復元ポイント(System Restore point)を除くすべてを削除することを選択できます。
これを行うには、ディスククリーンアップ(Disk Cleanup)ユーティリティを開き、[システムファイルのクリーンアップ]を選択し、[(Clean up system files)その他のオプション(More Options)]タブに切り替えて、 [クリーンアップ(Clean up)] > [削除](Delete)を選択します。

システムの復元(disabling System Restore)を完全に無効にしてもかまわない場合は、[実行]ボックスを開き、 (Run box)sysdm.cplと入力して、[ OK ]を選択します。表示される[システムの(System) プロパティ(Properties)]ダイアログボックスで、[保護設定](Protection Settings )の下の[構成(Configure )]を選択し、[システム保護(Disable system protection)を無効にする]の横のラジオボタン(radio button)を選択します。

14.Windows10のサイズを縮小します
CompactOSと呼ばれる機能をアクティブにすることで、 (CompactOS)Windows10自体のサイズを縮小してディスク領域を解放できます。オペレーティングシステムを(operating system)わずかに圧縮し、ストレージスペースがほとんど残っていないコンピューターでアクティブ化する価値があります。
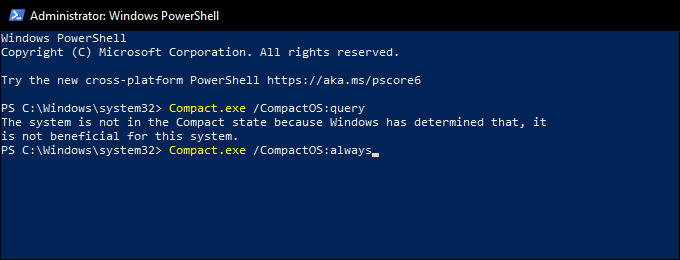
[スタート(Start )]ボタンを右クリックして開始します。次に、Windows PowerShell(管理者)(Windows PowerShell (Admin))を選択し、次のコマンドを実行します。
Compact.exe /CompactOS:query
CompactOSがシステムでまだアクティブになっていない場合は、次のコマンドを実行してアクティブにします。
Compact.exe /CompactOS:always
15.予約済みストレージを無効にする
Windows 10は、予約済みストレージ(Reserved Storage)と呼ばれる機能を使用して、将来のオペレーティングシステムの更新をダウンロードしてインストールするための十分なスペースを確保します。しかし、それは数ギガバイトのストレージの損失にもつながります。したがって、必要に応じて、システムレジストリ(system registry)を微調整して予約済みストレージ(disable Reserved Storage)を無効にすることを選択できます。
まず、 Windows(Windows ) + Rを押して、[実行]ボックスを開きます。次に、regeditと入力して、[ (regedit )OK ]を選択します。続いて表示される[レジストリエディタ]ウィンドウで、(Registry Editor window)アドレスバー(address bar and press) に次のパスを入力し、 Enterキー(Enter)を押します。
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ReserveManager

続いて、 ShippedWithReserves(ShippedWithReserves )キーをダブルクリックします。次に、[値のデータ(Value Data )を0 ]を選択し、[ OK]を選択して、(OK)レジストリエディタ(Registry Editor)を終了します。変更を有効にするには、コンピューターを再起動する必要があります。
たくさんのスペースが解放されました
上記のポインタは、Windows10のディスク領域を解放するのに間違いなく役立ちました。Storage Senseを単独でセットアップする時間をとることは、手動のクリーニングセッションを定期的に行わないようにするための優れた方法です。ただし、より多くのストレージが必要な場合は、リストをもう一度確認することで、PCの大量の使用済みスペースを再利用できます。
15 Ways to Free Up Disk Space in Windows 10
Whеn you use Windows 10, the internal storage on yoυr PC fills up gradually over time. That’s not a major problem on high capacity HDDs and SSDs. But you’ll run into space-related snags on drives that don’t offer much breathing room to start with.
You can rely on several methods to free up disk space in Windows 10. Some of them help you free up tens (if not hundreds) of gigabytes, while others net you only a few extra megabytes.

1. Free Up Recycle Bin
When you delete files on your computer, Windows 10 does not remove them outright. Instead, it stashes them away in the Recycle Bin. That allows you to restore deleted files if you change your mind later. But you end up trading disk space for convenience.
If you don’t plan on restoring any deleted files, you can choose to empty the Recycle Bin. To do that, right-click the Recycle Bin icon on the desktop and select Empty Recycle Bin. Alternatively, you can open the Recycle Bin and remove select files inside it.

It’s also possible to delete a file permanently without sending it to the Recycle Bin by pressing Shift + Delete after selecting it.
2. Clear the Downloads Folder
The Downloads folder on your Windows 10 PC is a hotspot for junk files and program installers that you’ll rarely ever re-use.
Open File Explorer and select This PC > Downloads on the sidebar. Then, delete any files that you don’t want. You can also switch the folder to List view and filter files by Size to locate and remove items that use up space the most.

3. Delete Unwanted Apps
Getting rid of unwanted apps and programs from your computer is another quick way to cut down the amount of used storage on your Windows 10 computer.
To do that, open the Start menu and go to Settings > Apps > Apps & Features. Then, scroll through the list, pick the apps you don’t use anymore, and select Uninstall to delete them.

4. Use Files On-Demand in OneDrive
OneDrive comes built into Windows 10 and allows you to back up documents and photos to the cloud easily. It also supports Files On-Demand functionality, allowing you to download backed-up files to local storage only when needed.
To enable Files On-Demand in OneDrive, select the OneDrive icon on the taskbar and choose Help & Settings > Settings. On the Microsoft OneDrive dialog box that then shows up, switch to the Settings tab. Follow that by checking the box next to Save space and download files as you use them.
With Files On-Demand active, you can directly offload backed-up files and folders whenever you want by right-clicking and selecting Free up space. You’ll continue to see placeholder icons of the items. Attempting to access an offloaded file shall prompt OneDrive to download it locally.

5. Use Storage Pane in Settings
Windows 10’s Settings app comes with a Storage pane to help you identify data types that use up the most amount of storage on your PC.
You can access it by going to Start > Settings > System > Storage. You’ll then see a list of categories such as Apps & Features, Temporary Files, Pictures, Music, etc., all of which you can dive into and remove space-consuming programs and files.
However, the most important of the lot is Temporary Files. Select it, and you’ll immediately come across a list of areas that hold temporary files, such as the Downloads folder, Recycle Bin, and Windows Update cache. Next, pick what you want to delete and select Remove files.

6. Run or Activate Storage Sense
The Storage pane above also comes with a feature called Storage Sense. Activate it, and you provide Windows 10 permissions to delete temporary files on your computer automatically.
Go to Start > Settings > System > Storage > Configure Storage Sense or run it now to access your Storage Sense settings.
Then, turn on the switch under Storage Sense to activate the feature. Follow that by tweaking the settings to determine how you want Storage Sense to run on your computer. For example, you can specify when it should run (while low on disk space, for example), how often it should delete the contents inside your Recycle Bin and Downloads folder, and so on.

You can also choose to run Storage Sense manually whenever you want. Just scroll to the bottom of the screen and select Clean now.
7. Use Disk Cleanup
If you prefer a more compact view than the Storage screen in the Settings app, you can opt for the legacy Disk Cleanup utility instead. It offers similar functionality and allows you to delete loads of temporary files quickly. You can bring it up by searching for Disk Cleanup on the Start menu.
Follow by checking the boxes next to the data types you want to delete—e.g., Windows Update Cleanup, Temporary Internet Files, System error memory dump files, etc. Then, select OK.
You can also select the Clean up system files option to view additional temporary file types.

8. Delete More Temporary Files
Windows 10 also contains large amounts of other temporary files that you can safely delete. For a complete step-by-step walkthrough, we recommend checking out this guide about removing temporary files in Windows 10. But here’s the process in brief.
Start by pressing Windows + R to open the Run box. Then, type %temp% and select OK.
Follow by deleting all files and folders within the directory that shows up. Next, type temp into another Run box, select OK, and remove all files inside that directory as well. Finally, wrap up by restarting your computer.

9. Clear Browser Cache
When you surf the internet, your browser ends up caching data to make subsequent website visits faster. But if you’re crunched for storage, you can quickly free up roughly 500 megabytes to one gigabyte of storage by clearing the browser cache.
Google Chrome
Open the Chrome menu and select Settings > Privacy and security > Clear browsing data.
On the Clear browsing data dialog that then shows up, set Time range to All time and check the box next to Cached images and files. Finally, select Clear data.

Mozilla Firefox
Open the Firefox menu and go to Options > Privacy and security > Clear Data (under the Cookies and Site Data section). Then, check the box next to Cached Web Content and select Clear.
Microsoft Edge
Open the Edge menu and select Settings. Then, switch to the Privacy, search, and services tab on the sidebar and select Choose what to clear under Clear browsing data.
Next, set the Time range to All time, check the box next to Cached images and files, and select Clear data.
10. Find Large Files With WinDirStat
WinDirStat is a free and open-source app that allows you to locate large files and folders on your computer in visual format. After installing and opening the program, pick the storage drive or partition you want to scan. You should then see a list of directories that occupy the most storage, including in percentage form relative to drive size.

Once WinDirStat finishes scanning the drive, you should also see many colored blocks denoting files (by format) on the chosen drive. The larger the size, the more space they consume. You can right-click an item and select Explorer Here to view (and delete) it in File Explorer.
11. Delete Hibernation File
Windows 10’s Hibernate mode allows you to restore files and programs even after you’ve powered down your computer. But the file that facilitates the functionality by saving the state of the programs and operating system can hog up a lot of disk space. So if you don’t mind skipping out on using Hibernate, you can choose to disable it and reclaim the storage.
To do that, right-click the Start button and select Windows PowerShell (Admin). Then, run the command below:
powercfg -h off

Follow that by opening File Explorer. Then, select File > Change folder and search options.
On the Folder Options dialog box that then shows up, switch to the View tab and select Show hidden files, folder, and drives. Finally, open the Windows 10 installation drive—Local Disk (C:)—and delete the file labeled hiberfil.sys.
For complete step-by-step instructions, check out this guide to disabling Hibernation in Windows 10.
12. Delete Old User Accounts
If your computer has multiple Windows 10 user accounts, you might want to delete any that don’t serve a purpose anymore. Just note that you’ll permanently lose all data related to the accounts you remove.
Start by opening the Start menu on your computer. Then, go to Settings > Accounts > Family & other users, select an account from the Other users section, and select Remove.

13. Disable System Restore
System Restore is a handy backup function that helps you restore your computer to an earlier state should something go wrong. But it also uses a hefty chunk of storage. So if you’re still running low on storage, you can choose to delete all but the last System Restore point.
To do that, open the Disk Cleanup utility, select Clean up system files, switch to the More Options tab, and select Clean up > Delete.

If you don’t mind disabling System Restore completely, open the Run box, type sysdm.cpl, and select OK. On the System Properties dialog box that shows up, select Configure under Protection Settings and select the radio button next to Disable system protection.

14. Reduce the Size of Windows 10
You can tone down the size of Windows 10 itself to free up disk space by activating a feature called CompactOS. It compresses the operating system slightly and is well worth activating on computers with very little storage space remaining.
Start by right-clicking the Start button. Then, select Windows PowerShell (Admin) and run the following command:
Compact.exe /CompactOS:query
If you see that CompactOS isn’t already active on your system, run the following command to activate it:
Compact.exe /CompactOS:always

15. Disable Reserved Storage
Windows 10 uses a feature called Reserved Storage to ensure it has sufficient space to download and install future operating system updates. But that also translates to multiple gigabytes of lost storage. So, you can choose to disable Reserved Storage with a tweak to the system registry should you want.
Start by pressing Windows + R to open the Run box. Then, type regedit and select OK. On the Registry Editor window that shows up subsequently, type the following path into the address bar and press Enter:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\ReserveManager

Follow that by double-clicking the ShippedWithReserves key. Then, select Value Data to 0, select OK, and exit the Registry Editor. You must restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
Lots of Space Freed Up
The pointers above should’ve definitely helped you free up disk space in Windows 10. Taking the time to set up Storage Sense alone is a great way to stop yourself from going on manual cleaning sessions regularly. But whenever you want more storage, working your way through the list again can help you reclaim large amounts of used-up space on your PC.

















