ドメインネームシステム(Domain Name System)(DNS )サーバーには、アクセスしたサイトのすべてのドメイン名が保存されます。Webブラウザーでドメイン名を検索すると、ルーターによってDNS(DNS)サーバーに転送されます。特定のサイトのドメイン名が保存されている場合は、対応するIPアドレスを返します。これにより、これらのサイトの読み込みプロセスが特に高速になります。
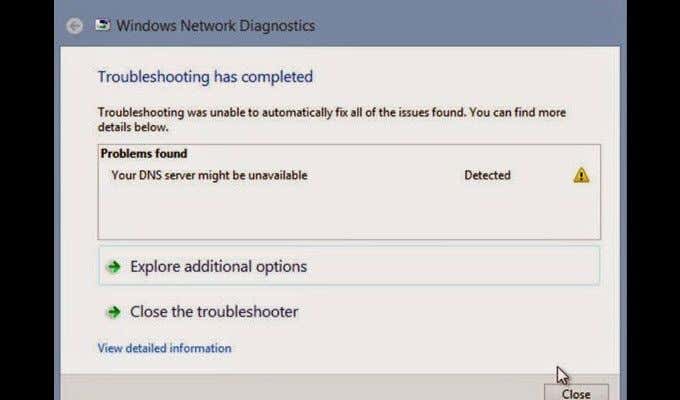
このプロセスは素晴らしいですが、DNSサーバーが時々接続の確立に失敗することは珍しくありません。この場合にWebブラウザのトラブルシューティングを試みると、「DNSサーバーが応答しません」というエラーが発生することがよくあります。

多くの要因により、この特定のエラーが画面に表示される可能性があります。その中で最も顕著なのは、サーバー自体が現在停止している可能性です。幸いなことに、この問題にはいくつかの簡単な解決策が伴うことがよくあります。
「DNSサーバーが利用できません」エラーを修正する方法(How To Fix The “DNS Server Unavailable” Error)
DNSサーバーが利用できないというエラーを受け取りましたか?迅速に修正するために、これらの問題は、ブラウザを変更したり、ファイアウォール設定のいくつかをいじったり、ルーターを再起動したりするなどの簡単な方法で修正できる場合があります。原因を突き止め、その後問題を修正するのはあなた次第です。
開こうとしているWebページに別のブラウザを使用することから始めます。つまり、Mozilla Firefoxブラウザの使用中に現在エラーが発生している場合は、 (Mozilla Firefox)MicrosoftEdgeまたはGoogleChromeに切り替えてください。問題が解決しない場合は、他のデバイスのテストに進むことができます。
問題がハードウェア障害の結果ではないことを確認するために、同じネットワーク上でモバイルデバイスを使用してWebページを開こうとします。データプランを使用して同じWebページに接続し、原因が実際にDNS(DNS)サーバーにあるかどうかを特定することも有益です。
これらの手順をすべて実行したら、ルーターを再起動します。「DNSサーバーが利用できません」というエラーが引き続き発生する場合は、さらに効果的な方法をいくつか実行する必要があります。
DNSのフラッシュ(Windows)(Flushing Your DNS (Windows))

DNSサーバーが利用できない問題を修正するための最も効果的な方法は、コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)を使用してサーバーをフラッシュすることです。
- WindowsキーとRキーを(Windows key and R key)同時に押して、[実行]ダイアログを表示します(Run)。
- フィールドにcmd(cmd )と入力し、 Enterキー(Enter)を押します。
- [コマンドプロンプト]ウィンドウで、ipconfig /flushdnsEnterキー(Enter)を押します。

- ipconfig /releaseと入力してフォローアップし、Enterキー(Enter)を押します。

- 最後に、ipconfig /renewEnterキー(Enter)を押します。

- コマンドプロンプト(Command Prompt)ウィンドウを閉じて、システムを再起動します。
DNSのフラッシュ(MacOS)(Flushing Your DNS (MacOS))

Macで(Mac)DNSをフラッシュすることもできます。これを行う方法は、コンピュータが実行しているMacのバージョンによってわずかに異なります。(Mac)多くの場合、プロセス中に使用される構文の変更のみが含まれます。
- Finderウィンドウを開き、[アプリケーション(Applications)] 、 [ユーティリティ](Utilities)、[ターミナル(Terminal)]の順に進みます。
- 現在使用しているMacOSのバージョンに関連する次の構文を入力します。
- MacOS High Sierra – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder; sleep 2; echo macOS DNS Cache Reset | say
- MacOS Sierra – sudo killall -HUPmDNSResponder;DNSキャッシュがフラッシュされたと言う(sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say DNS cache has been flushed)
- MacOS Mojave – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder; sleep 2;
- MacOS X El Capitan / Yosemite – sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall-HUPmDNSResponder;キャッシュがフラッシュされたと言う(sudo dscacheutil -flushcache;sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say cache flushed)
- Returnキーを押してパスワードを入力し、もう一度Returnキーを押します。(Return )
- ターミナルを終了する前に、 (Terminal)DNSフラッシュが成功したことを示す音声アラートを待ちます。
MacOS Xのキャッシュをクリアするには、完全にフラッシュするためにいくつかの追加手順が必要になります。以前に実行した手順に加えて、 MDNS(UDNS)キャッシュとUDNS(MDNS)キャッシュの両方をフラッシュする必要があります。
ターミナル(Terminal)を終了する前に、次のコマンドを実行します。
- MDNSキャッシュの場合は、「sudodiscoveryutilmdnsflushcache」と入力します。(sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache)
- UDNSキャッシュの場合は、「sudodiscoveryutiludnsflushcaches」と入力します( sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches)
複数のアンチウイルスを削除する(Remove Multiple Antiviruses)

「保護しすぎることはありません。」これは現実の世界では多少当てはまるかもしれませんが、テクノロジーの世界では、同じコンピューターに複数のウイルス対策プログラムをインストールすると、実際に提供される保護が妨げられる可能性があります。
DNSの問題の原因である可能性があるため、現在2つ以上のウイルス対策プログラムが実行されているかどうかを確認してください。追加のプログラムをすべて無効にしたら、システムを再起動すると、問題は自動的に解決します。
今後は、不要なマルウェア攻撃から身を守るために、単一のソフトウェアプログラムのみを実行し続けるようにしてください。これにより、セキュリティが向上するだけでなく、 DNS(DNS)サーバーエラーが増えるのを防ぐことができます。
DNSサーバーの変更(Changing DNS Servers)

ここに記載されているすべての修正をすでに試しても、同じ「DNSサーバーが利用できません」というエラーが発生する場合は、DNSサーバーを変更することをお勧めします。選択できるパブリックDNS(DNS)はたくさんありますが、Googleの無料DNSは最も人気のある選択肢の1つです。
このプロセスは非常に単純で、変更する場所に応じて、数回クリックするだけで実行できます。各例では、 Windows(Windows)オペレーティングシステムを使用します。
ルーターを介したDNSの変更(DNS Changes via Router)

- Webブラウザーを起動し、 URLバー にデフォルトゲートウェイ(Default Gateway)アドレスを入力して、ルーターにアクセスします。
- デフォルトゲートウェイ(Default Gateway)を見つけるには、コマンド(Command)プロンプトウィンドウを開き、 ipconfigと入力して、 Enterキー(Enter)を押します。プルアップされた情報のデフォルトゲートウェイ(Default Gateway)の横にある番号をコピーします。

- 適切な資格情報を使用してルーターにログインします。
- 同様の名前のタブでよく見られるインターネットアカウント情報を見つけます。
- DNSサーバーに移動し、使用するインターネットプロトコル(internet protocol)(IPv4またはIPv6)を最もよく反映するオプションを選択します。
- (Enter)現在のDNSサーバーの代わりに使用するDNSサーバーのアドレスを入力します。
- GoogleのDNSサーバーは、優先DNSv4では8.8.8.8、代替DNSサーバーでは(alternate DNS server)8.8.4.4になります。IPv6の場合は、それぞれ2001:4860:4860 :: 8888と2001:4860:4860::8844を使用する必要があります。
- 編集した情報を保存して、ルーターインターフェイスを終了します。
WindowsOSを介したDNSの変更(DNS Changes via Windows OS)

- (Access)実行(Run)機能(Windows key + R)を起動し、 ncpa.cplと入力して、ネットワーク接続のプロパティにアクセスします。Enterキー(Enter)を押します。

- Windows 10ユーザーは、デスクトップ画面の左下にあるWindowsアイコンを右クリックして、メニューから[(Windows)ネットワーク接続(Network Connections)]を選択できます。
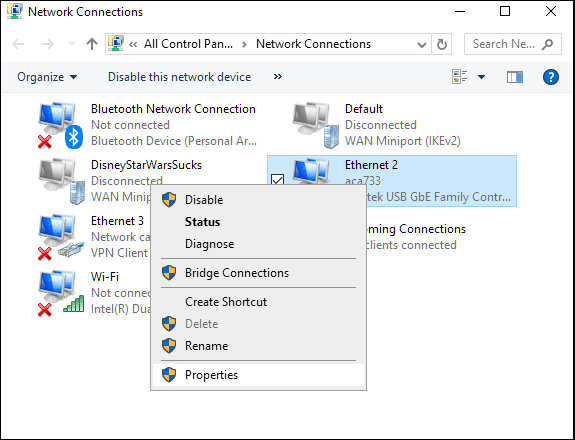
- (Select)現在使用中のネットワークアダプタを選択します。WiFi接続用のWLANおよび直接接続用の(WLAN)LAN(通常はイーサネットケーブル経由)。
- Windows 10の左側のパネルには、オプションがあります。いずれか(Select one)を選択し、メインウィンドウから[アダプタオプションの変更]を選択します。(Change)
- 選択したものを右クリックして、[プロパティ(Properties)]を選択します。
- [ネットワーク(Networking)]タブで、メニューからIPバージョン(v4またはv6)を強調表示し、[プロパティ(Properties )]ボタンをクリックします。

- [次のDNSサーバーアドレスを使用する](Use the following DNS server addresses:)のラジアルをクリックして、編集機能を有効にします。

- 使用する予定のDNSサーバーアドレスを入力します。
- 自動的に取得されなかった以前のDNSサーバーを使用していた場合は、後日使用する場合に備えて、アドレスに注釈を付けることを忘れないでください。
- [ OK ]をクリックして変更を確定します。
新しいDNSサーバーをテストする(Test New DNS Server)

DNSサーバーを変更したら、ブラウザを開いて、 www.google.comなどの有名なサイトを立ち上げてみてください。サイトにすぐにアクセスできる場合は、新しいDNSが正しく機能しています。そうでない場合は、GoogleのIPアドレスの1つである172.217.16.195をブラウザに直接入力し、 Enterキー(Enter)を押します。
(Wait)おなじみのGoogleロゴと検索バーが表示されるのを待ちます。これも失敗する場合は、 DNS(DNS)サーバー自体ではなく、インターネットに問題がある可能性があります。このような場合は、インターネットサービスプロバイダーに連絡して追加のヘルプを求めてください。
How To Fix The “DNS Server Unavailable” Error
The Domain Name System (DNS) server is where all of the domain nameѕ for the sites you’ve νisited are stored. Whеn sеarching a domain name in a web browser, it is forwarded bу your router tо a DNS server. If the particular site’s domain name has been saved, it then rеturns the correspоnding IP address. This makes the loading process for those sites particularly faster.
As great as this process is, it’s not uncommon for the DNS server to fail to establish a connection from time to time. Attempting to troubleshoot your web browser in this instance can often result in a ‘DNS server not responding’ error.

Many factors could cause this particular error to show up on your screen. The most prominent of which is the possibility that the server itself is currently experiencing an outage. Luckily, this problem is often accompanied by a few easy solutions.
How To Fix The “DNS Server Unavailable” Error
Have you’ve received an error that the DNS server is unavailable? For a quick fix, these problems can sometimes be corrected by something as simple as changing browsers, messing with a few of your firewall settings, or rebooting your router. It’ll be up to you to figure out the cause and subsequent correction for the problem.

Start by using a different browser for the web pages you’re trying to open. This means that if you’re currently receiving the error while using the Mozilla Firefox browser, switch it up to Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome. Should the problem persist, we can move on to testing out other devices.
Attempt to open a webpage using a mobile device, on the same network, to ensure that the problem isn’t the result of hardware failures. It would also be beneficial to attempt to connect to the same webpages using your data plan to identify if the cause is, in fact, with the DNS server.
Once you’ve exhausted these steps, reboot your router. If the “DNS server unavailable” error is still present, we’ll have to undergo a few more effective methods.
Flushing Your DNS (Windows)

The most effective method for fixing the issue with the DNS server being unavailable is to flush it using Command Prompt.
- Pull up the Run dialog by simultaneously pressing the Windows key and R key.
- Type cmd into the field and press Enter.
- In the Command Prompt window, type ipconfig /flushdns and press Enter.

- Follow up by typing ipconfig /release and press Enter.

- Finally, type ipconfig /renew and press Enter.

- Close out of the Command Prompt window and reboot your system.
Flushing Your DNS (MacOS)

You can also flush the DNS on a Mac. The way in which you do this will vary slightly depending on the version of Mac your computer is running. It often only involves a change in the syntax used during the process.
- Open a Finder window and then head into Applications, followed by Utilities, and ending in the Terminal.
- Enter in the following syntax pertaining to the version of MacOS you’re currently using:
- MacOS High Sierra – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder; sleep 2; echo macOS DNS Cache Reset | say
- MacOS Sierra – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say DNS cache has been flushed
- MacOS Mojave – sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;sleep 2;
- MacOS X El Capitan/Yosemite – sudo dscacheutil -flushcache;sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder;say cache flushed
- Press the Return key, enter your password, and then hit the Return key once more.
- Await the audio alert that indicates a successful DNS flush before exiting the Terminal.
The MacOS X cache clearing will need a few added steps in order to fully flush it out. You’ll have to flush both MDNS and UDNS caches on top of the steps previously taken.
Before exiting from the Terminal, perform the following commands:
- For the MDNS cache, type sudo discoveryutil mdnsflushcache
- For the UDNS cache, type sudo discoveryutil udnsflushcaches
Remove Multiple Antiviruses

“You can never have too much protection.” This may be somewhat true in the real world, but in the world of technology, having multiple antivirus programs installed on the same computer can actually hinder the protection provided.
Check to see if you have two or more antivirus programs currently running as this may be the reason for the DNS issue. Once you disable all additional programs, reboot your system and the problem should resolve itself.
Ensure that moving forward you only keep a single software program running to help defend yourself from unwanted malware attacks. This not only increases security but can help you avoid running into more DNS server errors.
Changing DNS Servers

If you’ve already attempted all fixes written here and are still receiving the same “DNS server unavailable” error, it may be in your best interest to change your DNS servers. There are plenty of public DNS from which to choose, Google’s free DNS being one of the more popular choices.
The process for this is very simple and can be done in a few clicks, depending on where you choose to change it. We’ll be using the Windows operating system in each of our examples.
DNS Changes via Router

- Access your router by launching your web browser and entering the Default Gateway address into the URL bar.
- You can find the Default Gateway by opening a Command prompt window, typing ipconfig, and pressing Enter. Copy the numbers located beside Default Gateway in the pulled up information.

- Login to the router using the proper credentials.
- Locate your internet account information which can often be found in a similarly named tab.
- Navigate to the DNS server and select the option that best mirrors your used internet protocol (IPv4 or IPv6).
- Enter the address of the DNS server you want to use in place of the current one.
- Google’s DNS server will be 8.8.8.8 in the preferred DNSv4 and 8.8.4.4 in the alternate DNS server. In the case of IPv6, you’ll want to use 2001:4860:4860::8888 and 2001:4860:4860::8844 respectively.
- Save the edited information and exit the router interface.
DNS Changes via Windows OS

- Access your network connection properties by launching the Run function (Windows key + R) and typing in ncpa.cpl. Press Enter.

- Windows 10 users can right-click the Windows icon at the lower left of the desktop screen and select Network Connections from the menu.
- Select the network adapter currently in use. WLAN for WiFi connections and LAN for direct connection, usually via ethernet cable.
- Windows 10 will have your options on the left side panel. Select one and choose Change adapter options from the main window.
- Right-click your choice and select Properties.

- In the Networking tab, highlight your IP version (v4 or v6) from the menu and click the Properties button.

- Click the radial for Use the following DNS server addresses: to enable editing capabilities.

- Enter in the DNS server addresses you plan to use.
- If you had been using a previous DNS server not obtained automatically, remember to annotate the addresses just in case you want to return using them at a later date.
- Finalize the changes by clicking OK.
Test New DNS Server

Once the DNS servers have been changed, open a browser and attempt to launch a well-known site like www.google.com. If the site is immediately accessible, then the new DNS is functioning properly. If not, enter one of Google’s IP addresses, 172.217.16.195, directly into your browser and hit Enter.
Wait for the familiar Google logo and search bar to appear. If this also fails, then the problem may lie with the internet and not the DNS server itself. Contact your internet service provider for additional help if this is the case.

















