リモートの場所からWindowsPCに接続する場合は、いくつかの方法があります。たとえば、 SSHを介してVNCをトンネリング(tunnel VNC over SSH)し、暗号化されたSSH接続を介してオープンソースのVNCプロトコルを使用できるようにすることができます。(VNC)ただし、最善の方法は、Windowsリモートデスクトップ(Windows Remote Desktop)ツールを使用することです。
Windows PCにリモートで接続する準備が整う前に、いくつかの手順を実行する必要があります。ルーターを介してリモートデスクトップ(Remote Desktop)を構成し、必要なポートが開いていて、ポート転送がアクティブであることを確認する必要があります。これを実行してリモートデスクトップ(use Remote Desktop)をリモートで使用するには、次の手順に従う必要があります。

リモートデスクトップアクセスを許可するようにWindowsファイアウォールを構成する(Configuring Windows Firewall to Allow Remote Desktop Access)
ルーターを介してリモートデスクトップ(Remote Desktop)接続を構成する前に、 WindowsがPCへの送受信接続を許可していることを確認する必要があります。
- これを行うには、[スタート(Start)]メニューを右クリックし、[設定(Settings)]を選択します。

- [設定](Settings)メニューで、[更新とセキュリティ(Update & Security )] >[ Windowsセキュリティ(Windows Security )] >[ファイアウォールとネットワーク保護(Firewall & network protection)]を選択します。

- [ファイアウォールとネットワーク保護(Firewall & network protection)]メニューで、[ファイアウォールを介したアプリの許可](Allow an app through firewall )オプションを選択します。

- [許可されたアプリ(Allowed apps)]ウィンドウの[設定の変更(Change settings)]ボタンを選択して、メニューのロックを解除します。

- このメニューのロックを解除したら、表示されるリストからリモートデスクトップ(Remote Desktop)およびリモートデスクトップ(WebSocket)(Remote Desktop (WebSocket) )オプションを見つけます。これらのオプションの横にあるチェックボックスを選択して、ファイアウォールを介したRDP接続を許可します。[ OK ]ボタンを選択して、選択内容を保存します。

Windows10でのデフォルトのRDPポートの変更(Changing the Default RDP Port on Windows 10)
RDP(リモートデスクトッププロトコル(Remote Desktop Protocol))接続を許可するようにWindowsファイアウォール(Windows Firewall)を設定しました。ここで、 Windows(Windows)がRDP接続に使用するデフォルトのRDPポートを(RDP)ポート3389(port 3389)から代替ポート番号に変更する必要があります。
これは、リモートデスクトッププロトコル攻撃のリスク(risk of Remote Desktop Protocol attacks)が非常に高いためです。ポートを変更することはRDP(RDP)接続を保護する唯一の方法ではありませんが、ルーターで開いているRDPポートを検索するランダムなポートスキャンボットによるリスクを軽減し、制限するのに役立ちます。
- RDPポートを変更するには、[スタート(Start)]メニューを右クリックし、[ファイル名を指定して実行(Run)]オプションを選択します。Windows key + Rを選択します。
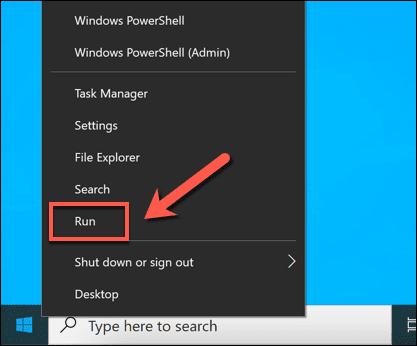
- [実行(Run)]ダイアログボックスで、[ OK ]を選択する前にregeditと入力します。これにより、 Windowsレジストリエディタ(Windows Registry Editor)が開きます。

- 新しいレジストリエディタ(Registry Editor)ウィンドウの左側にあるツリーメニューを使用して、 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\PortNumberキーを見つけます。右側のPortNumber(PortNumber )キーを右クリックし、 [変更(Modify )]オプションを選択します。

- [ DWORD(32ビット)値(Edit DWORD (32-bit) Value )の編集]ボックスで、[ベース(Base)]カテゴリから[ 10進数(Decimal)]を選択し、[値]データ(Value data)ボックスに新しいポート値を設定して、使用する値が他の既知のポートで一般的に使用されていないことを確認します。[ OK]を選択して、選択内容を保存します。

デフォルトのRDPポート番号を変更したら、PCを再起動する必要があります。RDPを使用してPCに接続する場合は、選択したポート番号を使用して構成する必要があります(たとえば、 10.0.0.10(10.0.0.10:1337) :3389ではなく10.0.0.10:1337(10.0.0.10:3389))。
ネットワークルーターでのポートフォワーディングの有効化(Enabling Port Forwarding on Your Network Router)
これで、インターネットからローカルネットワーク上のPCへの接続を許可するようにルーターの構成を開始できます。このプロセスの最初のステップは、ハッカーを侵入させず(without letting hackers in)にルーターでポート転送を有効にすることです。
- まず、Webブラウザ(通常は192.168.1.1、192.168.1.254(192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.254)、または同様のバリエーション)を使用してルーターのWeb管理ページにアクセスし、サインインします。Webへのアクセスに使用しているデバイスを確認する必要があります。ポータルは同じネットワークに接続されています。よくわからない場合は、ネットワークルーターのユーザーマニュアルで詳細を確認してください。

- ルーターにサインインしたら、ポート転送設定を見つける必要があります(例:転送(Forwarding)> TP-Linkルーター上の仮想サーバー)。( Virtual Servers)これらの設定を見つけたら、 RDP(RDP)ポート(デフォルトでは3389、または設定したカスタムポート)をPCのローカルネットワークIPアドレス(パブリックIPアドレスではない)にマップするエントリを追加する必要があります。)。

RDPポートがマップされたら、ポートフォワーディングがアクティブになり、インターネット経由でリモートデスクトップ接続を許可できるようになります(Remote Desktop)。パブリックIPアドレスとRDP(RDP)ポート番号を使用してリモートでPCに接続し、ネットワークルーターが要求をPCに転送できるようにする必要があります。
ダイナミックDNSサービスを使用したIPアドレスのマッピング (Mapping Your IP Address Using a Dynamic DNS Service )
ポートフォワーディングがアクティブになると、ポートフォワーディングルールがアクティブで、PCの電源がオンになってルーターに接続され、インターネット接続がアクティブで、パブリックIPアドレス(public IP address)がアクティブである限り、インターネット経由でリモートデスクトップ(Remote Desktop)接続を確立できるはずです。同じまま。
ただし、ISPが動的IPアドレス(定期的に変更されるIPアドレス)を使用している場合、パブリックIPアドレスが変更された場合、または変更された場合は接続できません。この問題を回避するには、ダイナミックDNSサービスを使用し(using a Dynamic DNS service)てIPアドレスをマッピングし、IPアドレスが変更された場合でも、リモートで接続できるようにします。
ただし、ダイナミックDNS(Dynamic DNS)サービスを使用する前に、 No-IPなどの適切なプロバイダーでアカウントを設定する必要があります。
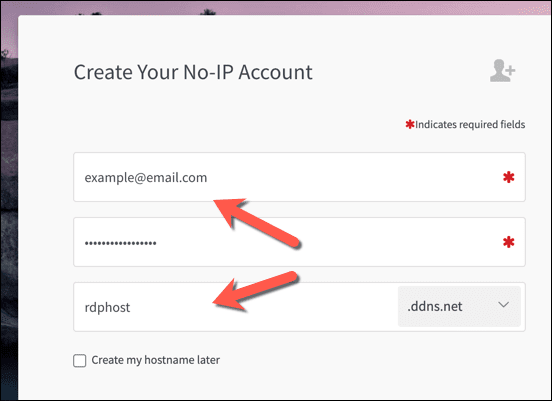
- ダイナミックDNS(Dynamic DNS)にNo-IPを使用する場合は、メールアドレスと適切なパスワードを入力してアカウントを作成してください。(create your account)また、IPアドレスを使用せずにRDP接続を確立するために使用できるホスト名(example.ddns.netなど)を提供する必要があります。
- アカウントを作成したら、アクティブ化する必要があります。メールの受信トレイを確認し、確認メールを受け取ったら、確認メールに含まれている[アカウント(Confirm account )の確認]ボタンを選択します。

- アカウントをアクティブにした状態で、次にPCにDynamicUpdateClientをインストールする必要があります。これにより、No IPアカウントに常に正しいパブリックIPアドレスが割り当てられ、接続が可能になります。Dynamic Update Client(Download the Dynamic Update Client)をPCにダウンロードし、インストールして続行します。

- Dynamic Update ClientがPCにインストールされると、アプリが自動的に開きます。この時点で、NoIPのユーザー名とパスワードを使用してサインインします。(Sign)

- サインインした後、パブリックIPアドレスにリンクするホスト名を選択する必要があります。リストから適切なホスト名を選択し、[保存](Save)を選択して確認します。

- この時点で、ダイナミックDNS(Dynamic DNS)ホスト名と使用中のRDPポート(例:example.ddns.net(example.ddns.net:3389) :3389)を使用してPCにリモート接続できるはずです。Dynamic Update Clientは、パブリックIPアドレスの変更を5分ごとにチェックしますが、これを自分で更新する場合は、DUC設定ウィンドウの[今すぐ更新]ボタンを選択します。(Refresh Now)

- 特定の(Certain)ネットワークルーター(TP-Linkなど)は(TP-Link)ダイナミックDNS(Dynamic DNS)をサポートしており、PCにダイナミックアップデートクライアント(Dynamic Update Client)をインストールしなくても、パブリックIPアドレスを自動的に更新できます。ただし、バックアップオプションとしてこれを行うことをお勧めします。たとえば、TP-Linkルーターを使用しているユーザーは、Web管理ページで[ダイナミックDNS ]メニューオプションを選択することにより、これらの設定にアクセスできます。(Dynamic DNS)その他のモデルについては、続行方法の詳細について、ネットワークルーターのユーザーマニュアルを参照してください。

- これらの手順を使用してルーターを構成すると、 RDP(RDP)を使用してリモートで接続できるようになります。正しく認証するには、リモートデスクトップ接続(Remote Desktop Connection)ツールに正しいダイナミック(Make)DNS(Dynamic DNS)ホスト名とポート番号(例:example.ddns.net(example.ddns.net:3387) :3387 )を入力してください。ルーターが適切に構成されていて、他に接続の問題がない場合は、接続を確立してリモートデスクトップ(Remote Desktop)接続を正常に確立できるはずです。

リモートデスクトップの代替手段(Alternatives to Remote Desktop)
上記の手順により、ルーターを介したリモートデスクトップ(Remote Desktop)接続を構成できるようになります。ただし、リモートデスクトップ(Remote Desktop)接続が機能しない場合、または品質に不満がある場合は、RDPの代替手段を(alternatives to RDP)利用できます。たとえば、TeamViewerなどのアプリを使用すると、PCに簡単に接続できます。
さまざまなリモートデスクトップ管理ツールを使用して接続を維持することもできます。または、代わりにリモートPCへの接続を確立するためにVPNを設定することを検討することもできます。(setting up a VPN)問題が発生した場合に、PCをリモートでシャットダウンまたは再起動してPC(how to remotely shutdown or restart your PC)をリセットする方法を検討することもできます。
How to Configure Remote Desktop Through Router
If you’re looking tо connect to your Windows PC from a remоte location, there are several ways to do it. For instance, you could tunnel VNC over SSH, allowing you to use the open-source VNC protocol over an encrypted SSH connection. The best method, however, is to use the Windows Remote Desktop tool.
There are some steps you’ll need to take before you’re ready to connect to a Windows PC remotely. You’ll need to configure Remote Desktop through your router, ensuring that the necessary ports are open and that port forwarding is active. To do this and use Remote Desktop remotely, you’ll need to follow these steps.

Configuring Windows Firewall to Allow Remote Desktop Access
Before you can configure Remote Desktop connections through your router, you’ll need to make sure that Windows will allow ingoing and outgoing connections to your PC.
- To do this, right-click the Start menu and select Settings.

- In the Settings menu, select Update & Security > Windows Security > Firewall & network protection.

- In the Firewall & network protection menu, select the Allow an app through firewall option.

- Select the Change settings button in the Allowed apps window to unlock the menu.

- Once you’ve unlocked this menu, find the Remote Desktop and Remote Desktop (WebSocket) options in the list provided. Select the checkboxes next to these options to allow RDP connections through the firewall. Select the OK button to save your choices.

Changing the Default RDP Port on Windows 10
You have set up Windows Firewall to allow RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) connections. Now, you should change the default RDP port used by Windows for RDP connections from port 3389 to an alternative port number.
This is because the risk of Remote Desktop Protocol attacks is extremely high. While changing ports isn’t the only way to secure your RDP connections, it will help to slow down and limit the risks from random, port scanning bots that search for open RDP ports on your router.
- To change the RDP port, right-click the Start menu and select the Run option. Alternatively, select the Windows key + R on your keyboard.

- In the Run dialog box, type regedit before selecting OK. This will open the Windows Registry Editor.

- Using the tree menu on the left in the new Registry Editor window, locate the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp\PortNumber key. Right-click the PortNumber key on the right then select the Modify option.

- In the Edit DWORD (32-bit) Value box, select Decimal from the Base category, then set a new port value in the Value data box, making sure that the value you use isn’t commonly used by any other known ports. Select OK to save your choice.

Once you’ve made the changes to the default RDP port number, you’ll need to restart your PC. Any connections you make to your PC using RDP moving forward will need to be configured using the port number you selected (eg. 10.0.0.10:1337 rather than 10.0.0.10:3389).
Enabling Port Forwarding on Your Network Router
You can now begin to configure your router to allow connections from the internet to your PC on your local network. The first step in this process is to enable port forwarding on your router without letting hackers in.
- To begin, access your router’s web administration page using your web browser (typically 192.168.1.1, 192.168.1.254, or a similar variation) and sign in. You’ll need to make sure that the device you’re using to access the web portal is connected to the same network. If you’re unsure, consult with the user manual for your network router for additional information.

- Once you’ve signed into your router, you’ll need to locate the port forwarding settings (eg. Forwarding > Virtual Servers on a TP-Link router). Once you’ve located these settings, you’ll need to add an entry that maps the RDP port (3389 by default, or a custom port you’ve set) to the local network IP address of your PC (not your public IP address).

With the RDP port mapped, port forwarding should be active and ready to allow Remote Desktop connections over the internet. You should be able to connect to your PC remotely using your public IP address and RDP port number, with your network router forwarding the requests to your PC.
Mapping Your IP Address Using a Dynamic DNS Service
Once port forwarding is active, you should be able to make Remote Desktop connections over the internet as long as the port forwarding rule is active, your PC is switched on and connected to your router, your internet connection is active, and your public IP address remains the same.
However, if your ISP uses dynamic IP addresses (IP addresses that regularly change), you won’t be able to connect if or when your public IP address changes. To get around this problem, you can map your IP address using a Dynamic DNS service so that, when your IP address changes, you can still make connections remotely.
Before you can use a Dynamic DNS service, however, you’ll need to set up an account with an appropriate provider like No-IP.
- If you want to use No-IP for Dynamic DNS, create your account by providing your email address and a suitable password. You’ll also need to provide a hostname (eg. example.ddns.net) that you can use to establish RDP connections without using your IP address.

- Once you’ve created your account, you’ll need to activate it. Check your email inbox and select the Confirm account button included in the confirmation email once you receive it.

- With your account activated, you’ll need to install the Dynamic Update Client on your PC next. This ensures that your No IP account always has your correct public IP address, allowing you to make connections. Download the Dynamic Update Client to your PC and install it to proceed.

- Once the Dynamic Update Client is installed on your PC, the app should open automatically. Sign in using your No IP username and password at this point.

- After signing in, you’ll need to select which hostnames to link to your public IP address. Select the appropriate hostname from the list, then select Save to confirm.

- At this point, you should be able to connect to your PC remotely using your Dynamic DNS hostname and the RDP port in use (eg. example.ddns.net:3389). The Dynamic Update Client will check for changes to your public IP address every five minutes, but if you want to refresh this yourself, select the Refresh Now button in the DUC settings window.

- Certain network routers (such as TP-Link) support Dynamic DNS and allow you to automatically refresh your public IP address without installing the Dynamic Update Client on your PC. Though, it’s recommended that you still do so as a backup option. For example, users with a TP-Link router can access these settings by selecting the Dynamic DNS menu option on the web administration page. For other models, consult your network router’s user manual for more information on how to proceed.

- Once you’ve configured your router using these steps, you should be able to connect remotely using RDP. Make sure to type the correct Dynamic DNS hostname and port number (eg. example.ddns.net:3387) in the Remote Desktop Connection tool to authenticate correctly. If your router is configured properly and there are no other connection issues, you should be able to make the connection and establish the Remote Desktop connection successfully.

Alternatives to Remote Desktop
The steps above should allow you to configure Remote Desktop connections through your router. However, if your Remote Desktop connections aren’t working, or you’re unhappy with the quality, there are alternatives to RDP available. For instance, apps like TeamViewer will allow you to connect to your PC with ease.
You can also use various Remote Desktop management tools to maintain your connections, or you could think about setting up a VPN to establish connections to your remote PC instead. You may also want to consider how to remotely shutdown or restart your PC to reset your PC if you run into problems.




















