PCでウイルスやマルウェアのスキャンを行っていて、検出された「脅威」の数が増えていることに驚いたことはありますか?あなたのラップトップには確かに220台のトロイの木馬が乗っているわけではありませんよね?
Webの閲覧やファイルのダウンロードの際に少しの裁量を使用すると仮定すると、これはほとんどあり得ません。ただし、何らかの方法でアクティビティを追跡しているWebサイトを閲覧している可能性があります。

トラッキングCookieを悪意のある、または危険なものと呼ぶのは難しいかもしれませんが、ユーザーは、Cookieを定期的にスキャンして削除する価値があるかどうかを判断する必要があります。Do Not Track(Track)の導入により、多くのブラウザでほとんどのトラッキングCookieをブロックできます。それでも、いくつかはすり抜けます。
この記事では、Cookieの追跡について詳しく説明し、Cookieとは何か、Cookieの使用方法、およびCookieを削除する方法について説明します。
トラッキングCookieとは何ですか?
トラッキングCookieを理解するために、最初にCookieとは何かについて説明しましょう。Cookieは、ユーザー固有のデータを保存するために使用される小さなテキストファイルです。(text file)たとえば、Webサイトにログインし、チェックボックスをオンにして今後のアクセスに備えてログインしたままにすると、ブラウザはハードドライブにCookieを保存し、後でWebサイトがユーザーの設定を知るために対話できるようにします。

訪問者の好みを保存する以外に、Cookieのもう1つの良性の用途(benign use)は、マーケティングデータを保存することです。これにより、ウェブサイトはターゲットを絞った広告をユーザーに表示できるようになり、コンバージョン率が上がる可能性があります。ただし、Cookieの追跡は、多くの場合、さらに一歩進んでいます。
一部のトラッキングCookieは、インターネット(Internet)全体で使用され、再訪問したときに個人情報とデータ(information and data)をWebサイトに中継します。これは通常、広告目的のリターゲティングに使用されます。
たとえば、ウェブサイトでGoogleが配信する広告を掲載している場合、そのウェブサイトでのアクティビティは、 (Google)Googleの広告も表示しているまったく別のウェブサイトに引き継がれる可能性があります。
トラッキングCookieは悪いですか?
これは主に、「悪い」の定義が何であるかに依存します。ウイルススキャン中にCookieを追跡することで警告を受けている場合は、これらのファイルは悪意のあるものではなく、コンピュータに損傷を与えることはないことに注意してください。
ただし、長期間にわたって、主要な広告ネットワークからのトラッキングCookieは非常に大きくなり、個人情報でいっぱいになる可能性があるため、侵入型と見なされる可能性があります。このようにトラッキングCookieを利用している企業には、AddThis、Facebook、Google、
Quantserve、Twitterなどがあります。
アグレッシブなトラッキングCookieを使用すると、これらの企業はあなたの場所、デバイス情報(device information)、購入履歴(purchase history)、検索クエリなどを知ることができます。場合によっては、この情報が収集されていることすら知らないことがあります。ただし、英国など一部の国では、Cookieを介して収集されたデータについてユーザーに通知することをWebサイトに要求する法律を採用しています。

要約すると、Cookieの追跡はPCに損害を与えますか?いいえ。Cookieの追跡は、非倫理的と見なされる可能性のある方法でプライバシーを侵害する可能性がありますか?はい。
どうすればCookieの追跡を回避できますか?
Do Not Track法(Track legislation)のおかげで、多くのトラッキングCookieが実現する前に停止することができます。すべての主要なブラウザは、プライバシー設定を介してこの機能をサポートしています。MicrosoftEdge(Microsoft Edge)で追跡禁止を有効にするためのガイドもあります。
Google Chromeユーザーは、[設定](Settings)ページに移動し、ページの下部にある[詳細(Advanced)設定]をクリックして、[閲覧トラフィックで[追跡しない]リクエストを送信する(Send a “Do Not
Track” request with your browsing traffic)]オプションを有効にすることができます([プライバシーとセキュリティ(Privacy and Security)]の下)。

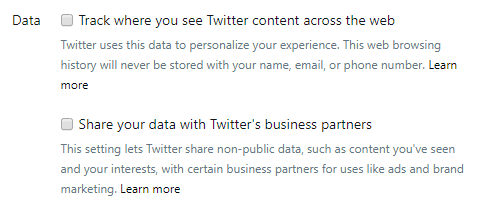
多くの個々の広告主やウェブサイトも追跡禁止機能(Track functionality)を提供しています。Twitterはその一例であり、パーソナライズとデータ(Personalization and Data)の設定に移動すると、さまざまな追跡ベースの設定が表示されます。
広告主に関する限り、NAI Consumer Opt-Outページは、ブラウザでトラッキングCookieを使用している広告主を特定してオプトアウトするのに役立ちます。大量のオプトアウト機能をサポートしているため、プロセスが大幅に簡素化されます。

OracleやAcxiomなどの組織に直接アクセスして、サードパーティのインタレストベース広告をオプトアウトすることもできます。
それ以外の場合は、定期的にブラウザのCookieをクリアするか、定期的なヘルススキャン中にトラッキングCookieを削除することができます。これは、Cookieが侵入的で危険であると見なされるほど大きくなるのを防ぐのに十分な注意を払っています。
最後に、Cookieの処理方法は、ユーザー自身の好みと裁量(preference and discretion)の問題です。Webサイトが個人データを追跡し、閲覧習慣に関連するコンテンツを表示することは無害であると思われる場合は、気にしないでください。それ以外の場合、上記の手順は、プライバシーが尊重されていることを確認するのに役立ちます。いずれにせよ、あなたのPCは安全です!
What Are Tracking Cookies and Are They Bad?
Have you ever been in the middle оf a νirus or
malware scan on уоυr PC and been surprised аt the climbing number of “threats”
detected? Υour laptop surely doesn’t have 220 trojans festering on it, right?
Assuming you use a bit of discretion while
browsing the Web and downloading files, this is highly unlikely. What is
likely, however, is that you’ve been browsing websites that have been tracking
your activity in some way.

To call tracking cookies malicious or
dangerous might be a stretch—however, it’s for the user to determine if they’re
something worth regularly scanning for and deleting. With the introduction of
Do Not Track, many browsers allow you to block most tracking cookies. Still,
some slip through.
In this article, let’s dive into tracking
cookies and discuss what they are, how they’re used, and how you can get rid of
them.
What are Tracking Cookies?
To understand tracking cookies, let’s first
discuss what cookies are. A cookie is a small text file that is used to save
user-specific data. For example, when you log in to a website and tick the
checkbox to keep yourself logged in for future visits, your browser will store
a cookie on your hard drive that the website can later interact with to know your
preferences.

Other than storing visitors’ preferences,
another benign use for cookies is to store marketing data. This allows websites
to show targeted ads to users which may increase their conversion rates.
However, tracking cookies often take it a step further.
Some tracking cookies will go with you all across the Internet and relay your personal information and data back to a website when you revisit it. This is commonly used for retargeting advertising purposes.
For example, if a website is running ads served by Google, your activity on that website may carry over with you to an entirely different one that is also displaying Google’s ads.
Are Tracking Cookies Bad?
This mostly depends on what your definition of
“bad” is. If you’re someone who is alerted by tracking cookies during a virus
scan, be advised that these files are not malicious and will not do damage to
your computer.
However, over a long period of time, tracking
cookies from major advertising networks can grow to be so large and full of
your personal information that they may be seen as invasive. A few companies
that utilize tracking cookies in this way include AddThis, Facebook, Google,
Quantserve, and Twitter.
With aggressive tracking cookies, these
companies can know your location, device information, purchase history, search
queries, and so much more. Sometimes, you never even know this information is
being collected. However, some countries, like the UK, have adopted laws that
require websites to notify users about their data being collected through
cookies.

In summary, will tracking cookies damage your
PC? No. Can tracking cookies infringe upon your privacy in ways that you may
consider to be unethical? Yes.
How Can I Avoid Tracking Cookies?
Thanks to Do Not Track legislation, you can put a stop to many tracking cookies before they even materialize. Every major browser supports this functionality via privacy settings—we even have a guide on enabling Do Not Track in Microsoft Edge.
Google Chrome users can head to the Settings page, click on Advanced, at the bottom of the page,
and enable the “Send a “Do Not
Track” request with your browsing traffic” option (under Privacy and Security).

Many individual advertisers and websites also
offer Do Not Track functionality. Twitter is one example, where going to the Personalization and Data settings will
show a variety of tracking-based preferences.

As far as advertisers go, the NAI Consumer Opt-Out page can assist you in identifying and opting out of advertisers who are using tracking cookies on your browser. It supports a mass opt-out feature that really simplifies the process.

You can also go directly to organizations like Oracle and Acxiom to opt out of their third-party, interest-based advertising.
Otherwise, you can clear your browser’s cookies at a regular interval or just get rid of tracking cookies during routine health scans. This is mindful enough to help prevent cookies from growing large enough to where they can be seen as invasive and dangerous.
In closing, the way you handle cookies is a
matter of your own preference and discretion. If you think it’s harmless for
websites to track your personal data and show you content related to your
browsing habits, pay no mind to them. Otherwise, the steps above can help in
making sure that your privacy is respected. Either way, your PC is safe!






