リモートデスクトッププロトコル(RDP)は、 (Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP))Microsoftが開発した独自のプロトコル であり、ネットワーク接続を介して別のコンピューターに接続するためのグラフィカルインターフェイスをユーザーに提供します。ユーザーはこの目的でRDPクライアントソフトウェアを使用しますが、他のコンピューターはRDPサーバーソフトウェアを実行する必要があります。この投稿では、Windows11/10での一般的なリモートデスクトップ接続の問題をトラブルシューティングする方法について説明します。(troubleshoot general Remote Desktop connection issues)

リモートデスクトップ(Fix Remote Desktop)接続の問題を修正する
リモートデスクトップクライアントが(Remote Desktop client is not working)機能していないか、リモートデスクトップに接続できない(cannot connect to a remote desktop)が、原因の特定に役立つメッセージやその他の症状が表示されない場合は、以下に概説するトラブルシューティング手順を試してください。
1]ローカルコンピューターでRDPプロトコルのステータスを確認します(Check)
ローカルコンピューターのRDP(RDP)プロトコルのステータスを確認および変更するには、リモートデスクトップ(enable Remote Desktop)を有効にする必要があります。コマンドプロンプトまたはPowerShellを使用してリモートデスクトップを有効に(enable Remote Desktop using Command Prompt or PowerShell)することもできます。
2]リモートコンピューターでRDPプロトコルのステータスを確認します(Check)
リモートコンピューターのRDPプロトコルのステータスを確認および変更するには、ネットワークレジストリ接続を使用します。
これはレジストリ操作であるため、必要な予防措置として、レジストリをバックアップする(back up the registry) か 、システムの復元ポイントを作成する ことをお勧めします。完了したら、次のように進めることができます。
- Windowsキー+Rを押して、[実行(Run)]ダイアログを呼び出します。
- [ファイル名を指定して実行]ダイアログボックスで、
regeditEnterキーを押して入力し、レジストリエディタを開き(open Registry Editor)ます。 - レジストリエディタで、[ ファイル] 、[(File)ネットワークレジストリの接続](Connect Network Registry)の順に選択し ます。
- [コンピューターの 選択](Select Computer)ダイアログボックスで、リモートコンピューターの名前を入力します。
- [名前の確認]を(Check Names.)選択します。
- [ OK]を選択します。
- 次に、 以下のレジストリキーパスに移動またはジャンプします。
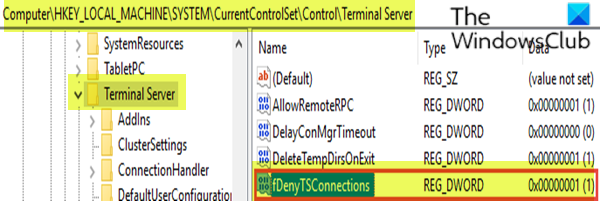
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server
- その場所の右側のペインで、fDenyTSConnectionsキーをダブルクリックして、そのプロパティを編集します。
- RDPを有効にするには、 fDenyTSConnectionsの(fDenyTSConnections)値(Value)データを1 から 0に設定 し ます。
値0はRDPが有効であることを示し、値1はRDPが無効であることを示します。
関連(Related):リモートデスクトップオプションは(Remote Desktop option is greyed out)、Windows10ではグレー表示されています
3]グループポリシーオブジェクト(Group Policy Object)(GPO )がローカルコンピューターでRDPをブロックしているかどうかを確認します(Check)
ユーザーインターフェイス でRDPをオンにできない場合、または 変更後にfDenyTSConnectionsの値が1に 戻る 場合は、 GPOがコンピューターレベルの設定を上書きしている可能性があります。(GPO)
ローカルコンピューターでグループポリシーの構成を確認するには、次の手順を実行します。
gpresult /H c:\gpresult.html
- コマンドが実行されたら、gpresult.htmlを開きます。
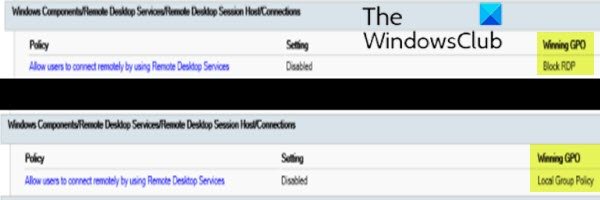
- Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Connectionsで、[ユーザーがリモートデスクトップサービス(Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services) ポリシーを使用してリモート接続できるようにする]を見つけます。
このポリシーの設定が 有効(Enabled)になっている場合、グループポリシーは(Group Policy)RDP接続をブロックしていません。このポリシーの設定が 無効(Disabled)に なっている場合は、[勝利のGPO](Winning GPO)をオンにします。これは、RDP接続をブロックしているGPOです。(GPO)
4] GPOがリモートコンピューターのRDPをブロックしているかどうかを確認します(Check)
リモートコンピューターでグループポリシー(Group Policy)の構成を確認するには、昇格したCMDプロンプトで次のコマンドを実行します。
gpresult /S <computer name> /H c:\gpresult-<computer name>.html
このコマンドが生成するファイル(gpresult-<computer name>.htmlgpresult.html )が使用するのと同じ情報形式を使用します。
5]ブロッキングGPOを変更します
これらの設定は、グループポリシーオブジェクトエディター(Group Policy Object Editor)(GPE)およびグループポリシー管理コンソール(GPMC)で変更できます。
ブロッキングポリシーを変更するには、次のいずれかの方法を使用します。
GPEを使用して、次の手順を実行します。
- Windows key + Rを押して、[実行]ダイアログを呼び出します。
- [ファイル名を指定して実行]ダイアログボックス
gpedit.mscで、Enterキーを押して入力し、グループポリシーエディターを開き(open Group Policy Editor)ます。 - ローカルグループポリシーエディター(Local Group Policy Editor)内で、左側のウィンドウを使用して以下のパスに移動します。
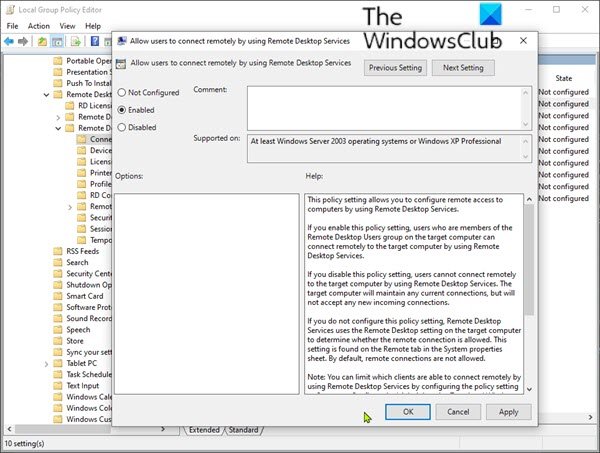
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections
- その場所の右側のウィンドウで、[ユーザーがリモートデスクトップサービスを使用してリモート接続できるようにする](Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services)をダブルクリックして、そのプロパティを編集します。
- ポリシーを[ 有効](Enabled) または [未構成(Not configured)]に設定します。
- [適用](Apply) >[ OK]をクリックして終了します。
- 影響を受けるコンピューターで、管理者としてコマンドプロンプトウィンドウを開き、次のコマンドを実行します。
gpupdate /force
GPMCを使用して、影響を受けるコンピューターにブロックポリシーが適用されている組織単位(OU)に移動し、OUからポリシーを削除します。
6] RDPサービスのステータスを確認します(Check)
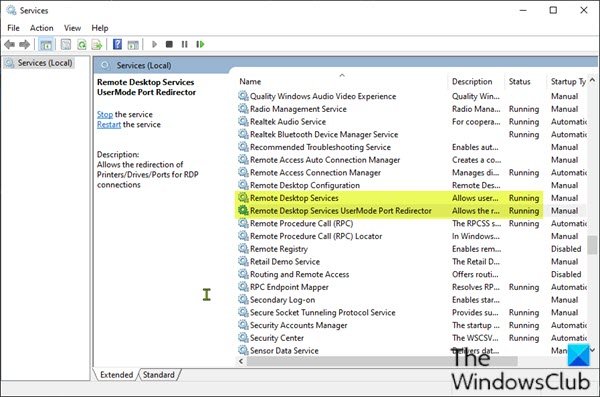
ローカル(クライアント)コンピューターとリモート(ターゲット)コンピューターの両方で、次のサービスが実行されている必要があります。
- リモートデスクトップサービス(Remote Desktop Services)(TermService)
- リモートデスクトップサービスUserModeポートリダイレク(Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector)ター(UmRdpService)
どちらのコンピューターでも、一方または両方のサービスが実行されていない場合は、それらを開始します。
以下をせよ:
- Windows key + Rを押して、[実行]ダイアログを呼び出します。
- [実行]ダイアログボックスで、
services.mscEnterキーを押して入力し、[サービス]を開きます(open Services)。 - [サービス](Services)ウィンドウで、前述の両方のサービスをスクロールして見つけます。
- (Double-click)エントリをダブルクリックして、プロパティを編集します。
- プロパティウィンドウで、[スタート(Start)]ボタンをクリックします。
- [ OK]をクリックします。
PowerShellを使用して、サービスをローカルまたはリモートで管理することもできます(リモートコンピューターがリモートPowerShellコマンドレットを受け入れるように構成されている場合)。
7] RDPリスナーのステータスを確認します(Check)
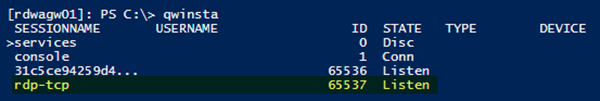
同じコマンドレットがローカルとリモートの両方で機能するため、この手順ではPowerShellを使用します。(PowerShell)ローカルコンピューターの場合は、管理者権限を持つコマンドプロンプトを使用することもできます。
リモートコンピューターに接続するには、次の手順を実行します。
- Windows key + Xを押して、パワーユーザーメニューを開きます(open Power User Menu)。
- キーボードのA(A)をタップして、 PowerShellを管理/昇格モードで起動します。
- PowerShellコンソールで、以下のコマンドを入力し、Enterキー(Enter)を押します。
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <computer name>
上の画像に示すように、リストに ステータスが Listenの(Listen)rdp-tcpが含まれている場合 、 RDPリスナーは機能しています。以下のトラブルシューティング手順10]に(Troubleshooting step 10])ジャンプ(Jump)します。それ以外の場合は、動作中のコンピューターから(Otherwise)RDPリスナー構成をエクスポートする必要があります。
以下をせよ:
- 影響を受けるコンピューターと同じオペレーティングシステムバージョンのコンピューターにサインインし、そのコンピューターのレジストリにアクセスします。
- (Navigate)次のレジストリエントリに移動またはジャンプします。
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
- エントリを.regファイルにエクスポートします(Export the entry to a .reg file)。
- エクスポートした.regファイルを影響を受けるコンピューターにコピーします。
- RDPリスナー構成をインポートするには、影響を受けるコンピューターの管理者権限を持つPowerShellウィンドウを開きます(または、 (PowerShell)PowerShellウィンドウを開いて、影響を受けるコンピューターにリモートで接続します)。
既存のレジストリエントリをバックアップする(To back up the existing registry entry)には、次のコマンドレットを入力します。
cmd /c 'reg export "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-tcp" C:\Rdp-tcp-backup.reg'
既存のレジストリエントリを削除する(To remove the existing registry entry)には、次のコマンドレットを入力します。
Remove-Item -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-tcp' -Recurse -Force
新しいレジストリエントリをインポートしてからサービスを再起動する(To import the new registry entry and then restart the service)には、以下のコマンドレットを実行します。<filename>プレースホルダーを、エクスポートされた.regファイルの名前に置き換えます。
cmd /c 'regedit /s c:\<filename>.reg'
Restart-Service TermService -Force
コマンドレットの実行が完了したら、リモートデスクトップ接続を再試行して構成をテストできます。それでも接続できない場合は、影響を受けるコンピューターを再起動してください。
それでも接続できない場合は、次のトラブルシューティング手順に進みます。これは、RDP自己署名証明書のステータスを確認すること(check the status of the RDP self-signed certificate)です。
8] RDP自己署名証明書のステータスを確認します(Check)
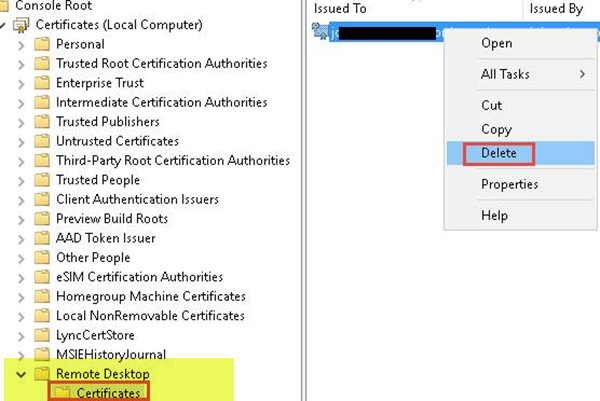
それでも接続できない場合は、次の手順を実行してください。
- Windows key + Rを押して、[実行]ダイアログを呼び出します。
- [ファイル名を指定して実行]ダイアログボックスで、
mmcEnterキーを押して入力し、 Microsoft管理コンソールを開きます(open Microsoft Management Console)。 - [ファイル(File)]メニューをクリックします。
- Add/Remove Snap-in選択します。
- (Certificates)(Select Certificates)スナップインのリストから[証明書]を選択 します。
- [追加]を(Add)クリックします。
- 管理する証明書ストアを選択するように求められたら、[ コンピューターアカウント]を選択します。(Computer account.)
- [次へ(Next)]をクリックします。
- 影響を受けるコンピューターを選択します。
- [完了(Finish)]ボタンをクリックします。
- [ OK]をクリックします。
- 次に、リモートデスクトップの下の[(Remote Desktop)証明書(Certificates) ]フォルダーで 、 RDP自己署名証明書を削除します。
- 影響を受けるコンピューターで、リモートデスクトップサービス(Remote Desktop Services)サービスを再起動します。
- 証明書スナップインを更新します。
- RDP自己署名証明書が再作成されていない場合は、 MachineKeysフォルダーのアクセス許可を確認してください。
9] MachineKeysフォルダの権限を確認してください(Check)
影響を受けるコンピューターで、次の手順を実行します。
- Windows key + Eを押して、ファイルエクスプローラーを開きます(open File Explorer)。
- 以下のディレクトリパスに移動します。
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\
- その場所で、[ MachineKeys ]を右クリックし、[(MachineKeys)プロパティ(Properties)] 、[ セキュリティ(Security)] 、 [詳細]の順に選択し ます(Advanced)。
(Make)次の権限が構成されていることを確認してください。
- BuiltinAdministrators:フルコントロール(Full control)
- みんな:読んで、書いて(Read, Write)
10]RDPリスナーポートを確認します
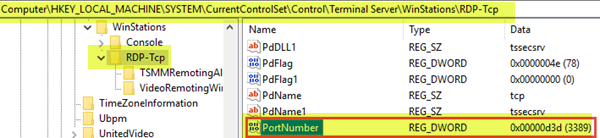
ローカル(クライアント)コンピューターとリモート(ターゲット)コンピューターの両方で、RDPリスナーはポート3389でリッスンしている必要があります。他のアプリケーションがこのポートを使用してはなりません。
RDPポートを確認または変更するには、レジストリエディタ(Registry Editor)を使用します。予防措置として、レジストリをバックアップするか、システムの復元ポイントを作成してから、次の手順を実行します。
- レジストリエディタを開き、[ファイル]、[(File)ネットワークレジストリの接続](Connect Network Registry)の順に選択し ます。
- [コンピューターの 選択](Select Computer)ダイアログボックスで、リモートコンピューターの名前を入力します。
- [名前の確認]を(Check Names.)選択します。
- [ OK]を選択します。
- 次に、 以下のレジストリキーパスに移動またはジャンプします。
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
- その場所の右側のペインで、PortNumberエントリをダブルクリックしてプロパティを編集します。
- プロパティウィンドウで、[値(Value)のデータ]フィールドの値が3389以外の場合は、3389に変更し ます。(3389.)
- [ OK]をクリックして変更を保存します。
- リモートデスクトップサービス(Remote Desktop Services)サービスを再起動します。
11]別のアプリケーションが同じポートを使用していないことを確認してください(Check)
以下をせよ:
- PowerShellを昇格モードで開きます。
- リモートコンピューターに接続するには、次のコマンドを実行します。
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <computer name>
次に、次のコマンドを実行します。
cmd /c 'netstat -ano | find "3389"'
- (Look)ステータスが リスニングの(Listening)TCPポート3389(または割り当てられたRDPポート)のエントリを探します。
注(Note):そのポートを使用するプロセスまたはサービスのプロセスID(PID )は、 (PID)PID列の下に表示されます。
- ポート3389(または割り当てられたRDPポート)を使用しているアプリケーションを判別するには、次のコマンドを入力します。
cmd /c 'tasklist /svc | find "<pid listening on 3389>"'
- (Look)(出力から)ポートに関連付けられて いるPID番号のエントリを探し
netstat ます。そのPIDに関連付けられているサービスまたはプロセスが右側の列に表示されます。 - リモートデスクトップサービス(Remote Desktop Services)(TermServ.exe )以外のアプリケーションまたはサービスがポートを使用している場合は、次のいずれかの方法を使用して競合を解決できます。
別のポートを使用するように他のアプリケーションまたはサービスを構成します(推奨)。
他のアプリケーションまたはサービスをアンインストールします。
別のポートを使用するようにRDPを構成してから、リモートデスクトップサービス(Remote Desktop Services)サービスを再起動します(非推奨)。
12]ファイアウォールがRDPポートをブロックしているかどうかを確認します(Check)
pspingツールを使用し て、ポート3389を使用して影響を受けるコンピューターに到達できるかどうかをテストできます。
以下をせよ:
- 影響を受けていない別のコンピューターに移動し、pspingを(psping)ダウンロードします(download) 。
- 管理者としてコマンドプロンプトウィンドウを開き、 pspingをインストールしたディレクトリに移動して、次のコマンドを入力します。
psping -accepteula <computer IP>:3389
- 次のような結果については、 psping(psping) コマンドの出力を確認してください 。
Connecting to <computer IP>の接続:リモートコンピューターにアクセスできます。
(0% loss):接続のすべての試行が成功しました。
リモートコンピューターがネットワーク接続を拒否しました(The remote computer refused the network connection):リモートコンピューターにアクセスできません。
(100% loss):接続のすべての試行が失敗しました。
- 複数のコンピューターでpsping(psping)を実行 して、影響を受けるコンピューターに接続する能力をテストします。
- 影響を受けるコンピューターが、他のすべてのコンピューター、他の一部のコンピューター、または他の1台のコンピューターからの接続をブロックしていないかどうかに注意してください。
実行できる追加の手順は次のとおりです。
- ネットワーク管理者に連絡して、影響を受けるコンピューターへのRDPトラフィックがネットワークで許可されていることを確認します。
- ソースコンピューターと影響を受けるコンピューター(影響を受けるコンピューターのWindowsファイアウォールを含む)の間のファイアウォールの構成を調べて、ファイアウォールが(Windows Firewall)RDPポートをブロックしているかどうかを確認します。
この投稿が、発生している可能性のあるRDP(RDP)接続の問題のトラブルシューティングに役立つことを願っています。
Fix Remote Desktop connection issues & errors on Windows 11/10
Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft which provides a user with a graphical interface to connect to another computer over a network connection. The user employs RDP client software for this purpose, while the other computer must run RDP server software. In this post, we will explore how to troubleshoot general Remote Desktop connection issues on Windows 11/10.

Fix Remote Desktop connection issues
Try the outlined troubleshooting steps below when a Remote Desktop client is not working or cannot connect to a remote desktop but doesn’t provide messages or other symptoms that would help identify the cause.
1] Check the status of the RDP protocol on a local computer
You’ll need to enable Remote Desktop to check and change the status of the RDP protocol on a local computer. You can also enable Remote Desktop using Command Prompt or PowerShell.
2] Check the status of the RDP protocol on a remote computer

To check and change the status of the RDP protocol on a remote computer, use a network registry connection.
Since this is a registry operation, it is recommended that you back up the registry or create a system restore point as necessary precautionary measures. Once done, you can proceed as follows:
- Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type
regedit and hit Enter to open Registry Editor. - In the Registry Editor, select File, then select Connect Network Registry.
- In the Select Computer dialog box, enter the name of the remote computer.
- Select Check Names.
- Select OK.
- Next, navigate or jump to the registry key path below:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server
- At the location, on the right pane, double-click the fDenyTSConnections key to edit its properties.
- To enable RDP, set the Value data of fDenyTSConnections from 1 to 0.
The value of 0 indicates RDP is enabled, while the value of 1 indicates RDP is disabled.
Related: Remote Desktop option is greyed out on Windows 10,
3] Check whether a Group Policy Object (GPO) is blocking RDP on a local computer

A GPO may be overriding the computer-level settings, if you can’t turn on RDP in the user interface or the value of fDenyTSConnections reverts to 1 after you’ve changed it
To check the group policy configuration on a local computer, do the following:
- Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type
cmd and then press CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER to open Command Prompt in admin/elevated mode. - In the command prompt window, type the command below and hit Enter.
gpresult /H c:\gpresult.html
- Once the command executes, open gpresult.html.
- In Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Remote Desktop Services\Remote Desktop Session Host\Connections, find the Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services policy.
If the setting for this policy is Enabled, Group Policy is not blocking RDP connections. If the setting for this policy is Disabled, check Winning GPO. This is the GPO that is blocking RDP connections.
4] Check whether a GPO is blocking RDP on a remote computer
To check the Group Policy configuration on a remote computer, run the command below in elevated CMD prompt:
gpresult /S <computer name> /H c:\gpresult-<computer name>.html
The file that this command produces (gpresult-<computer name>.html) uses the same information format as the local computer version (gpresult.html) uses.
5] Modify a blocking GPO

You can modify these settings in the Group Policy Object Editor (GPE) and Group Policy Management Console (GPMC).
To modify the blocking policy, use one of the following methods:
Using GPE, do the following:
- Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box type
gpedit.msc and press Enter to open Group Policy Editor. - Inside the Local Group Policy Editor, use the left pane to navigate to the path below:
Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections
- At the location, on the right pane, double click the Allow users to connect remotely by using Remote Desktop Services.to edit its properties.
- Set the policy to either Enabled or Not configured.
- Click Apply > OK and exit.
- On the affected computers, open a command prompt window as an administrator, and run the command below:
gpupdate /force
Using GPMC, navigate to the organizational unit (OU) in which the blocking policy is applied to the affected computers and delete the policy from the OU.
6] Check the status of the RDP services

On both the local (client) computer and the remote (target) computer, the following services should be running:
- Remote Desktop Services (TermService)
- Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector (UmRdpService)
On either computer, if one or both services are not running, start them.
Do the following:
- Press Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type
services.msc and hit Enter to open Services. - In the Services window, scroll and locate both aforementioned service.
- Double-click on the entry to edit its properties.
- In the properties window, click the Start button.
- Click OK.
You can also use PowerShell to manage the services locally or remotely (if the remote computer is configured to accept remote PowerShell cmdlets).
7] Check the status of the RDP listener

This procedure uses PowerShell because the same cmdlets work both locally and remotely. For a local computer, you can also use a command prompt that has administrative permissions.
To connect to a remote computer, do the following:
- Press Windows key + X to open Power User Menu.
- Tap A on the keyboard to launch PowerShell in admin/elevated mode.
- In the PowerShell console, type in the command below and hit Enter:
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <computer name>
If the list includes rdp-tcp with a status of Listen, as shown in the image above, the RDP listener is working. Jump to the Troubleshooting step 10] below. Otherwise, you’ll need to export the RDP listener configuration from a working computer.
Do the following:
- Sign in to a computer that has the same operating system version as the affected computer has, and access that computer’s registry.
- Navigate or jump to the following registry entry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
- Export the entry to a .reg file.
- Copy the exported .reg file to the affected computer.
- To import the RDP listener configuration, open a PowerShell window that has administrative permissions on the affected computer (or open the PowerShell window and connect to the affected computer remotely).
To back up the existing registry entry, enter the following cmdlet:
cmd /c 'reg export "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-tcp" C:\Rdp-tcp-backup.reg'
To remove the existing registry entry, enter the following cmdlets:
Remove-Item -path 'HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-tcp' -Recurse -Force
To import the new registry entry and then restart the service, run the cmdlets below. Replace the <filename> placeholder with the name of the exported .reg file.
cmd /c 'regedit /s c:\<filename>.reg'
Restart-Service TermService -Force
Once done executing the cmdlets, you can test the configuration by trying the remote desktop connection again. If you still can’t connect, restart the affected computer.
If you still can’t connect, proceed with the next troubleshooting step which is to check the status of the RDP self-signed certificate.
8] Check the status of the RDP self-signed certificate

If you still can’t connect, do the following:
- Press the Windows key + R to invoke the Run dialog.
- In the Run dialog box, type
mmc and hit Enter to open Microsoft Management Console. - Click the File menu.
- Select Add/Remove Snap-in.
- Select Certificates from the list of snap-ins.
- Click Add.
- When you are prompted to select the certificate store to manage, select Computer account.
- Click Next.
- Select the affected computer.
- Click the Finish button.
- Click OK.
- Now, in the Certificates folder under Remote Desktop, delete the RDP self-signed certificate.
- On the affected computer, restart the Remote Desktop Services service.
- Refresh the Certificates snap-in.
- If the RDP self-signed certificate has not been recreated, check the permissions of the MachineKeys folder.
9] Check the permissions of the MachineKeys folder
On the affected computer, do the following:
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\
- At the location, right-click MachineKeys, select Properties, select Security, and then select Advanced.
Make sure that the following permissions are configured:
- Builtin\Administrators: Full control
- Everyone: Read, Write
10] Check the RDP listener port

On both the local (client) computer and the remote (target) computer, the RDP listener should be listening on port 3389. No other applications should be using this port.
To check or change the RDP port, use the Registry Editor. As a precautionary measure back up the registry or create a system restore point, then continue as follows:
- Open Registry Editor, select File, then select Connect Network Registry.
- In the Select Computer dialog box, enter the name of the remote computer.
- Select Check Names.
- Select OK.
- Next, navigate or jump to the registry key path below:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp
- At the location, on the right pane, double-click the PortNumber entry to edit its properties.
- In the properties window, if the Value data field has a value other than 3389, change it to 3389.
- Click OK to save changes.
- Restart the Remote Desktop Services service.
11] Check that another application isn’t using the same port
Do the following:
- Open a PowerShell in elevated mode.
- To connect to a remote computer, run the command below:
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName <computer name>
Next, run the following command:
cmd /c 'netstat -ano | find "3389"'
- Look for an entry for TCP port 3389 (or the assigned RDP port) with a status of Listening.
Note: The process identifier (PID) for the process or service using that port appears under the PID column.
- To determine which application is using port 3389 (or the assigned RDP port), enter the following command:
cmd /c 'tasklist /svc | find "<pid listening on 3389>"'
- Look for an entry for the PID number that is associated with the port (from the
netstat output). The services or processes that are associated with that PID appear on the right column. - If an application or service other than Remote Desktop Services (TermServ.exe) is using the port, you can resolve the conflict by using one of the following methods:
Configure the other application or service to use a different port (recommended).
Uninstall the other application or service.
Configure RDP to use a different port, and then restart the Remote Desktop Services service (not recommended).
12] Check whether a firewall is blocking the RDP port
You can use the psping tool to test whether you can reach the affected computer by using port 3389.
Do the following:
- Go to a different computer that isn’t affected and download psping.
- Open a command prompt window as an administrator, change to the directory in which you installed psping, and then enter the following command:
psping -accepteula <computer IP>:3389
- Check the output of the psping command for results such as the following:
Connecting to <computer IP>: The remote computer is reachable.
(0% loss): All attempts to connect succeeded.
The remote computer refused the network connection: The remote computer is not reachable.
(100% loss): All attempts to connect failed.
- Run psping on multiple computers to test their ability to connect to the affected computer.
- Note whether the affected computer blocks connections from all other computers, some other computers, or only one other computer.
Additional steps you can take includes;
- Engage your network administrators to verify that the network allows RDP traffic to the affected computer.
- Investigate the configurations of any firewalls between the source computers and the affected computer (including Windows Firewall on the affected computer) to determine whether a firewall is blocking the RDP port.
Hope this post can help you successfully troubleshoot RDP connection issues you might be having!








