Superfetchは、何年にもわたって複数の名前が付けられてきたWindowsシステムプロセスです。(Windows)Windows XPでは(Windows XP)、プリフェッチと呼ばれていました(Prefetch)。スーパーフェッチは(Sysmain)WindowsVistaで導入され、最新バージョンのWindows10では(Windows 10)Sysmain(Superfetch)として知られています。
最終的に、Superfetchのすべての世代の目的は同じです。つまり、頻繁に使用するアプリを使用する前にRAMにプリロードすることで、 (RAM)Windowsのパフォーマンスを向上させることです。しかし、Superfetchとは何ですか?

Superfetch(Sysmain)はどのように機能しますか?(How Does Superfetch (Sysmain) Work?)
Windows 10の最新バージョンでは、SuperfetchサービスがSysMainという名前で表示されるようになりました。タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)では、サービスホスト:SysMain(Service Host: SysMain)として表示されます。
古いバージョンのWindows10または任意のバージョンのWindows7または8を実行している場合、これはタスクマネージャー(Task Manager)にサービスホスト:スーパーフェッチ(Service Host: Superfetch)として表示されます。

このサービスはバックグラウンドで実行され( CPU(CPU)パワーをほとんど使用しません)、使用しているRAMの量と、最も頻繁に実行しているアプリを分析します。サービスが「頻繁に使用する」と認識するアプリはすべて、アプリのRAMへのプリロードを開始します。このようにすると、次にアプリを実行したときに、はるかに速く起動します。
これは、 Superfetchが(Superfetch)RAMをすべて使い果たしていることを意味するのではないかと心配するかもしれませんが、そうではありません。このサービスは、未使用のRAM(RAM)へのアプリのプリロードに重点を置いています。これは消費メモリとして登録されません。タスクマネージャ(Task Manager)を開いて[プロセス(Processes)]タブを開き、メモリ(Memory)使用量を確認すると、これが表示されます。

Superfetchはプリロードされたアプリで未使用のRAMをすべて消費していますが、消費されたRAMの使用量は100%ではありません。これは、Superfetchがバックグラウンドで実行されており、他のアクティブなタスクにそのメモリを使用する必要があるときはいつでも、使用していた未使用のRAMを解放するためです。
Superfetch(Sysmain)を強制終了する必要がありますか?(Should You Kill Superfetch (Sysmain)?)
通常、 Superfetch(Superfetch)の実行を停止する必要はありません。非常に少量のCPUを使用し、未使用の(CPU)RAMのみを使用します。これらはすべて、一般ユーザーには気づかれません。
ただし、 Microsoft(Microsoft)ユーザーフォーラム全体で、Superfetch(Sysmain)プロセスが実際にパフォーマンスの問題を引き起こすことがあるという報告がいくつかあります。これらの報告された問題のいくつかは次のとおりです。
- 一定の100%のディスク使用率。
- 過熱(Overheating)してシステムがシャットダウンします。
- (Slow)コンピュータを起動するときの起動時間が遅い。
- 弱いハードウェアでは、Superfetchはあなたが望むよりも多くの(Superfetch)CPUとRAMを使用する可能性があります。
- ゲーム中にパフォーマンスの問題(performance issues while gaming)を引き起こすことが知られています。
人々が報告する最も一般的な問題は、100%のディスク使用率の問題です。これがあなたの場合、SuperfetchまたはSysmainを無効にすると問題が解決する場合があります。
Superfetchはシステム最適化機能にすぎないため、サービスを停止してもWindowsを傷つけることはありません。ただし、お気に入りのアプリの起動に通常より少し時間がかかる場合があります。
Windows 10でスーパーフェッチ(Sysmain)を無効にする方法(How To Disable Superfetch (Sysmain) In Windows 10)
スーパーフェッチを無効にしても安全ですか?
パフォーマンスの問題やその他の問題が発生していない場合は、Superfetch(Sysmain)を実行したままにしておくことをお勧めします。これは、頻繁に使用するプログラムの起動にかかる時間を大幅に短縮する便利なプロセスです。
ただし、ハードドライブの使用率が高い、メモリの問題が常に発生している、または全体的なパフォーマンスが低下している場合は、 Superfetchを無効にして、問題が解決するかどうかを確認できます。含まれている場合は、サービスを無効のままにします。それ以外(Otherwise)の場合は、オンに戻し、トラブルシューティングを続行します。
Windows 10でSuperfetch(Sysmain )を無効にするには:
- [スタート]メニューを選択し、servicesと入力して、(services)サービス(Services)アプリを選択します。Windows + Rを押し、services.mscと入力して、Enterキーを押すこともできます。
- サービス(Services)アプリで、 [ SysMain ]まで下にスクロールし、サービスを右クリックして[停止(Stop)]を選択します。古いバージョンのWindows(Windows)を実行している場合は、 SuperFetchサービスを右クリックして、 [停止(Stop)]を選択します。

- ここで、 Windows(Windows)の起動時にサービスが再起動しないようにする必要があります。サービスが停止したら、サービスをもう一度右クリックして、[プロパティ(Properties)]を選択します。
- [スタートアップ(Startup)の種類]ドロップダウンで、[無効(Disabled)]を選択します。

これで、SuperFetch(SysMain)サービスは完全に無効になり、次にコンピューターを起動したときに再起動しなくなります。
レジストリエディタでスーパーフェッチ(Sysmain)を無効にする(Disable Superfetch (Sysmain) With Registry Editor)
タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)を使用してWindows10で(Windows 10)スーパーフェッチ(Superfetch)を無効にする代わりに、レジストリエディター(Registry Editor)を使用することもできます。
レジストリ内で何かを始める前に、何か問題が発生した場合に備えて、まずレジストリの完全バックアップを作成してください。(take a full backup of the registry)
準備ができたら:
- [スタート]メニューを選択し、regeditと入力して、(regedit)レジストリエディタ(Registry Editor)アプリ を選択します。
- レジストリエディタ(Registry Editor)で、HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Control > Session Manager > MemoryManagement > PrefetchParametersに移動します。
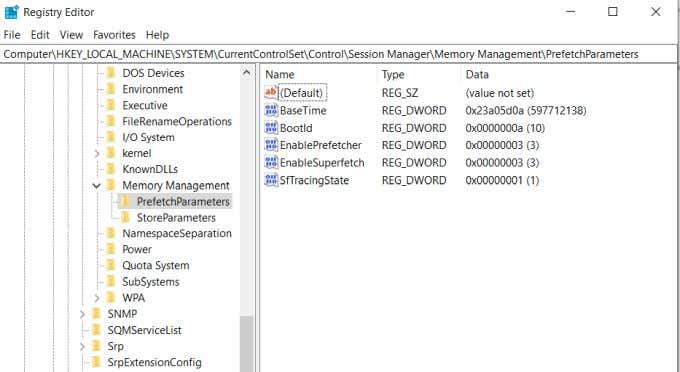
- このセクションでは、 EnableSuperfetch(EnableSuperfetch)というキーが表示されます。このキーを右クリックして、[変更]を選択します(Modify)。
- ポップアップ表示される[ DWORD(Edit DWORD)の編集]ウィンドウで、[値のデータ(Value data)]フィールドを0に変更し、[ (0)OK]を選択します。

終了したら、レジストリエディタ(Registry Editor)を閉じることができます。
このレジストリエントリは、システムのSuperFetch(SysMain)サービスを無効にします。ただし、このレジストリ設定を有効にする前に、 Windowsマシンを再起動する必要がある場合があります。
コマンドプロンプトでSuperFetch(SysMain)を有効または無効にする(Enable Or Disable SuperFetch (SysMain) With Command Prompt)
コマンドプロンプトを使用したい場合は、 SuperFetch(SuperFetch)サービスを有効または無効にするために使用できる簡単なコマンドがいくつかあります。
最初に管理者モードでコマンドプロンプトを(command prompt in administrator mode)開き、次に次のコマンドを使用します。
- 有効(Enable)化:sc config“ SysMain” start = auto&sc start“ SysMain”
- 無効(Disable)化:sc stop“ SysMain”&sc config“ SysMain” start = disable
注:古いバージョンのWindows(Windows)を使用している場合は、上記のコマンドで「SysMain」を「SuperFetch」に置き換えてください。
PowerShellを使用する場合は、管理者権限でPowerShell(prefer PowerShell)を開き、次のコマンドを使用します。
- 有効(Enable)化:Set-Service -Name“ SysMain” -StartupType Automatic -Status Running
- 無効(Disable)化:Stop-Service -Force -Name“ SysMain”; Set-Service -Name“ SysMain” -StartupType
このアプローチは、タスクマネージャー(Task Manager)またはWindowsレジストリをクリックするよりもはるかに高速で簡単です。
これで問題が解決しない場合はどうなりますか?(What If This Doesn’t Fix The Problem?)
SuperFetch(SysMain )を無効にしても問題が解決しない場合は、他の何かが問題の原因である可能性があります。
それでも100%のディスク使用率がある場合は、より大きなハードドライブにアップグレードするか、SSDドライブにアップグレードすることを選択する必要があります。SSDドライブ(SSD drives)は現在非常に手頃な価格であり、従来のハードドライブよりもはるかに高いデータ転送速度を備えています。
CPU使用率の問題が発生している場合は、他のCPUトラブルシューティングのヒント(other CPU troubleshooting tips)を調べて、すべてのCPUリソースをかみ砕いている原因を突き止めてください。
What Is Superfetch (Sysmain) On Windows 10 And How To Disable It
Superfetch is a Windows system process that has had multiplе names throughoυt the years. Оn Windows XP it was known as Prefetch. Superfetch was introduced in Windows Vista, and on the latest νersions of Windows 10 іt’s nоw known as Sysmain.
Ultimately, the purpose of every generation of Superfetch has been the same: to increase the performance of Windows by preloading apps you frequently use into RAM before you need to use them. But what is Superfetch?

How Does Superfetch (Sysmain) Work?
In the latest versions of Windows 10, the Superfetch service now shows up under the name SysMain. In the Task Manager, it shows up as Service Host: SysMain.
If you’re running an older version of Windows 10 or any version of Windows 7 or 8, this will show up in the Task Manager as Service Host: Superfetch.

This service runs in the background (using very little CPU power) and analyzes how much RAM you’re using and what apps you run most frequently. Any apps the service recognizes as “frequently used”, it’ll start preloading the app into RAM. This way, the next time you run the app, it’ll launch much more quickly.
You may be concerned that this means Superfetch is using up all of your RAM, but it isn’t. The service focuses on pre-loading apps into unused RAM. This doesn’t register as consumed memory. You’ll see this if you open Task Manager to the Processes tab and look at your Memory usage.

Even though Superfetch is consuming all unused RAM with preloaded apps, consumed RAM usage still doesn’t show 100%. This is because Superfetch is running in the background, and it’ll release any unused RAM it’s using whenever you need to use that memory for other active tasks.
Should You Kill Superfetch (Sysmain)?
Generally, there’s no need to stop Superfetch from running. It uses a very miniscule amount of CPU, and only uses unused RAM. All of this is unnoticeable to the general user.
However, there have been some reports throughout Microsoft user forums that sometimes the Superfetch (Sysmain) process actually causes performance issues. Some of these reported issues include:
- Constant 100% disk utilization.
- Overheating leading to system shutdown.
- Slow bootup time when you start your computer.
- On weak hardware, Superfetch could use more CPU and RAM than you might like.
- Has been known to cause performance issues while gaming.
The most common problem people report is the 100% disk utilization issue. If this is you, then disabling Superfetch or Sysmain may resolve the problem.
Since Superfetch is only a system optimization feature, you won’t hurt Windows by stopping the service. However, you may notice that launching your favorite apps may take a little longer than usual.
How To Disable Superfetch (Sysmain) In Windows 10
Is it safe to disable Superfetch?
If you aren’t experiencing performance issues or other problems, it’s a good idea to leave Superfetch (Sysmain) running. It is a useful process that significantly cuts down on the time it takes you to launch programs that you use frequently.
However, if you are experiencing high hard drive utilization, constant memory issues, or overall poor performance, you can try disabling Superfetch to see if it resolves the problem. If it does, then leave the service disabled. Otherwise, turn it back on and continue troubleshooting.
To disable Superfetch (Sysmain) on Windows 10:
- Select the Start menu, type services, and select the Services app. You could also press Windows + R, type services.msc and press Enter.
- In the Services app, scroll down to SysMain, right-click on the service and select Stop. If you’re running an older version of Windows, right-click on the SuperFetch service and select Stop.

- Now you need to prevent the service from restarting when you start Windows. Once the service is stopped, right-click on the service again and select Properties.
- In the Startup type dropdown, select Disabled.

Now the SuperFetch (SysMain) service is permanently disabled and will not restart the next time you start your computer.
Disable Superfetch (Sysmain) With Registry Editor
An alternative to using Task Manager to disable Superfetch on Windows 10 is using the Registry Editor.
Before you start doing anything inside the registry, make sure you take a full backup of the registry first, just in case anything goes wrong.
When you’re ready:
- Select the Start menu, type regedit, and select the Registry Editor app.
- In the Registry Editor, navigate to HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE > SYSTEM > CurrentControlSet > Control > Session Manager > MemoryManagement > PrefetchParameters.

- In this section, you should see a key called EnableSuperfetch. Right-click this key and select Modify.
- In the Edit DWORD window that pops up, change the Value data field to 0 and select OK.

You can close the Registry Editor when you’re finished.
This registry entry will disable the SuperFetch (SysMain) service on your system. However, you may need to restart your Windows machine before this registry setting takes effect.
Enable Or Disable SuperFetch (SysMain) With Command Prompt
If you prefer working with the command prompt, there are some simple commands you can use to enable or disable the SuperFetch service.
Open the command prompt in administrator mode first, and then use the following commands:
- Enable: sc config “SysMain” start=auto & sc start “SysMain”
- Disable: sc stop “SysMain” & sc config “SysMain” start=disabled
Note: If you’re using an older version of Windows, replace “SysMain” with “SuperFetch” in the commands above.
If you prefer PowerShell, open it with administrator rights and use the following commands:
- Enable: Set-Service -Name “SysMain” -StartupType Automatic -Status Running
- Disable: Stop-Service -Force -Name “SysMain”; Set-Service -Name “SysMain” -StartupType
This approach can be much faster and simpler than clicking around in the Task Manager or the Windows registry.
What If This Doesn’t Fix The Problem?
If disabling SuperFetch (SysMain) doesn’t resolve your issue, then something else may be the source of the problem.
If you’re still having 100% disk utilization, you may need to upgrade to a larger hard drive, or opt to upgrade to an SSD drive. SSD drives are very affordable now, and have data-transfer rates far above that of traditional hard drives.
If you’re having CPU utilization issues, then explore other CPU troubleshooting tips to nail down the culprit that’s chewing up all of your CPU resources.







